- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Olfactory Habituation in Fasted Mice
禁食小鼠的嗅觉习惯化
发布: 2014年10月20日第4卷第20期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1267 浏览次数: 9771
评审: Soyun KimAnonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Sensory perception is tightly modulated by the individual’s internal states. In particular, it has been shown that olfactory processes are constantly influenced by metabolic signals reflecting the energy status of the body. Thus, it is important to implement novel approaches to evaluate the impact of body energy changes on olfactory performance. Here, we describe a behavioral protocol to accurately evaluate olfactory habituation in fasted mice (Soria-Gomez et al., 2014) using basic equipment that mice are familiar with. Briefly, the mouse is placed in a test cage where it is presented first, an odorless solvent (the control), then an odor A (twice) and finally an odor B. This test relies on the fact that animals present an attenuation of the behavioral response after several presentations of the same olfactory stimulus.
Keywords: Food intake (食物的摄入量)Materials and Reagents
- Animals: C57/BL6N male mice (Janvier Labs)
- Mineral oil (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M-5904 )
- Isoamyl acetate (banana odor) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: W205508 )
- Benzaldehyde (almond odor) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 418099 )
- 20% ethanol
Note: Mineral oil was used as a solvent, because of its odorless property as reported in the literature (Linster et al., 2009; Qiu et al., 2014; Slotnick and Restrepo, 2005; Tan et al., 2010). Almond and banana odors were used as novel, yet neutral odors(Yang et al., 2013; Yang and Crawley, 2009). However, other odors are also suitable to test in our conditions, such as hexanal.
Equipment
- Standard individual plexiglass cage for mice (see Figure 1A)
- Water bottle cap with sipper tube made in stainless steel (from now called Odor holder, see Figure 1B) (Tecniplast)
- Filter paper (Thermo Fisher Scientific, see Figure 1C and Figure 2)
- Opaque eppendorfs (1 ml volume) (Eppendorf, see Figure 1C)
- Scissors
- 10 µl pipet
- 10 µl pipet tips
- Tissue paper
- Standard table to place the test cage
- CCTV camera for an aerial view of the test
- Standard computer (PC or Mac)
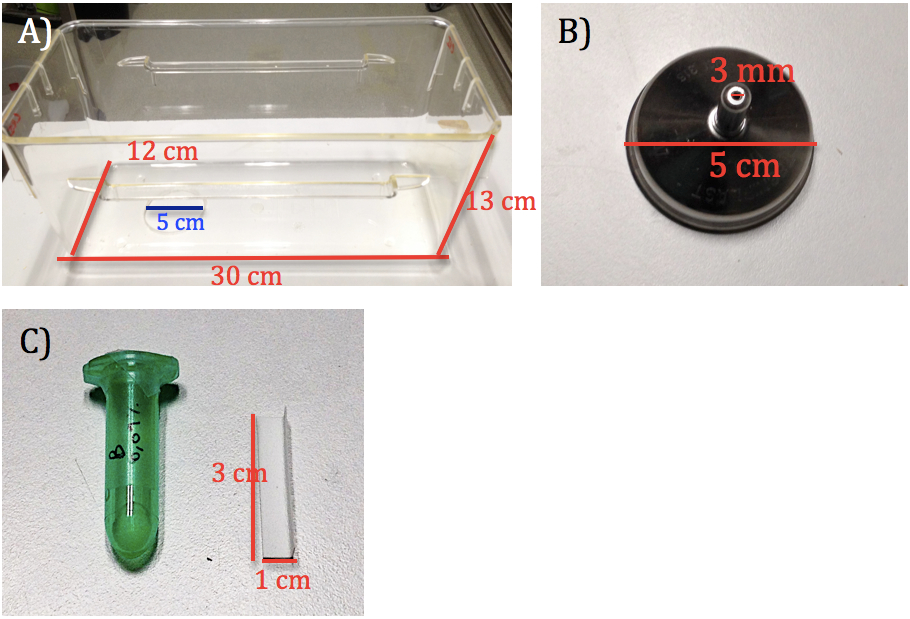
Figure 1. Basic material to perform the olfactory habituation test. A) Test cage made in plexiglass (12 cm width x 30 cm length x 13 cm height), with a circular perforation (5 cm diameter) in one of the extremes. B) Odor holder made in stainless steel (5 cm height from the base to the top of the sipper tube; base of 5 cm diameter; the hole of the sipper tube of 3 mm diameter). C) Standard opaque Eppendorf (left) containing the odor solution and the filter paper (3 cm height x 1 cm width) used to administer the odor. This filter paper is introduced in the sipper tube of B).
Software
- Video recording software (GrabBee, grabbee.software.informer.com)
- Software to analyze exploratory behavior (Behav_Scor_v3.0_beta)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Desprez, T., Marsicano, G. and Soria-Gómez, E. (2014). Olfactory Habituation in Fasted Mice. Bio-protocol 4(20): e1267. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1267.
分类
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 认知
神经科学 > 行为神经科学 > 学习和记忆
神经科学 > 感觉和运动系统
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link














