- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Targeted Gene Mutation in Rice Using a CRISPR-Cas9 System
采用CRISPR-Cas9 系统进行水稻基因定点突变
发布: 2014年09月05日第4卷第17期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1225 浏览次数: 36429
评审: Arsalan DaudiFang XuVinay Panwar
Abstract
RNA-guided genome editing (RGE) using bacterial type II cluster regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)–associated nuclease (Cas) has emerged as a simple and versatile tool for genome editing in many organisms including plant and crop species. In RGE based on the Streptococcus pyogenes CRISPR-Cas9 system, the Cas9 nuclease is directed by a short single guide RNA (gRNA or sgRNA) to generate double-strand breaks (DSB) at the specific sites of chromosomal DNA, thereby introducing mutations at the DSB by error-prone non-homologous end joining repairing. Cas9-gRNA recognizes targeted DNA based on complementarity between a gRNA spacer (~ 20 nt long leading sequence of gRNA) and its targeted DNA which precedes a protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM, Figure 1). In this protocol, we describe the general procedures for plant RGE using CRISPR-Cas9 system and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The protocol includes gRNA design, Cas9-gRNA plasmid construction and mutation detection (genotyping) for rice RGE and could be adapted for other plant species.
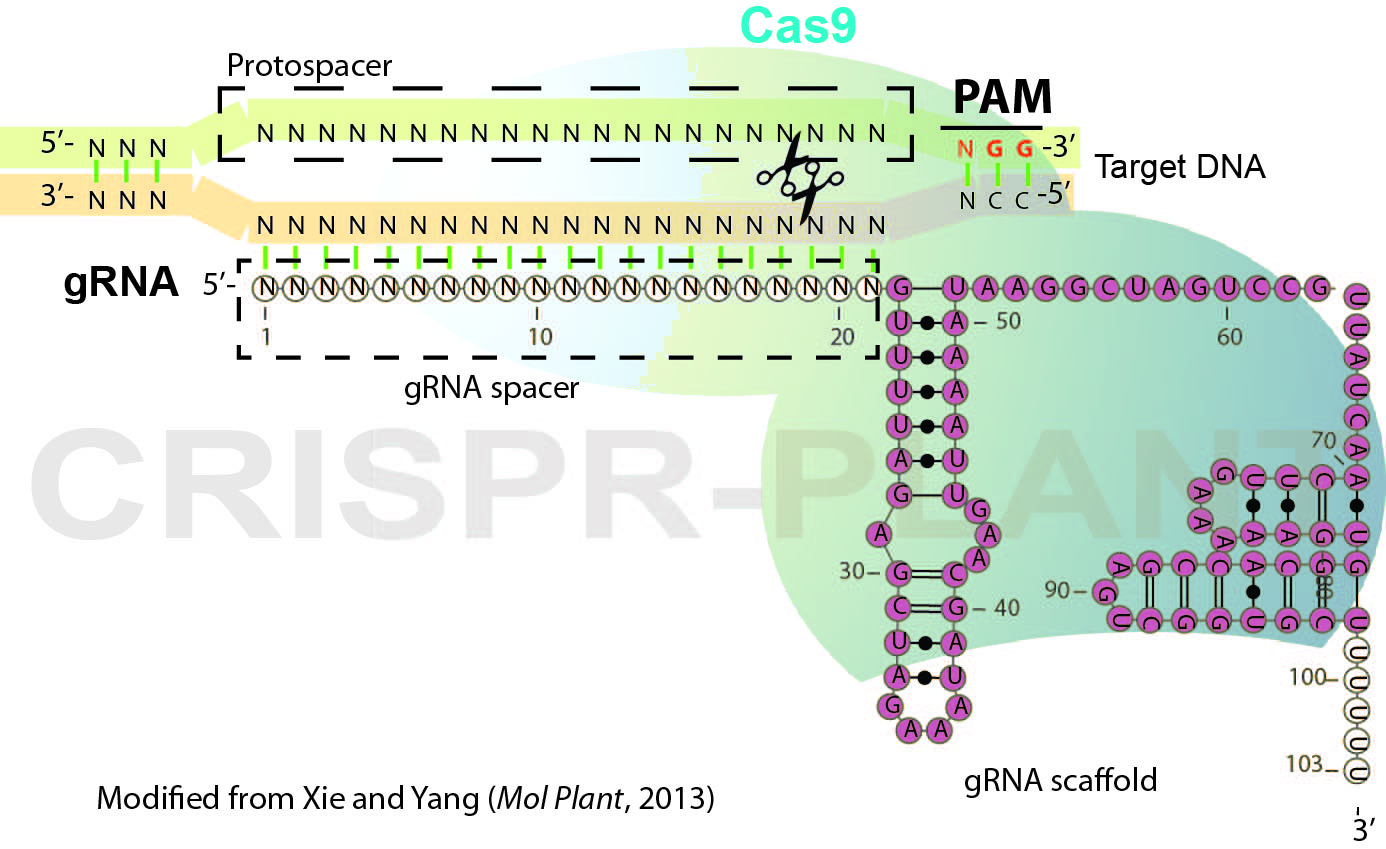
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of CRISPR-Cas9 system
Materials and Reagents
- Oryza sativa L. ssp japonica, Kitaake, Nipponbare, or other cultivars
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105
- pRGEB31 (Xie and Yang, 2013) (Addgene plasmid 51295 , plasmid map is shown in Figure 2)
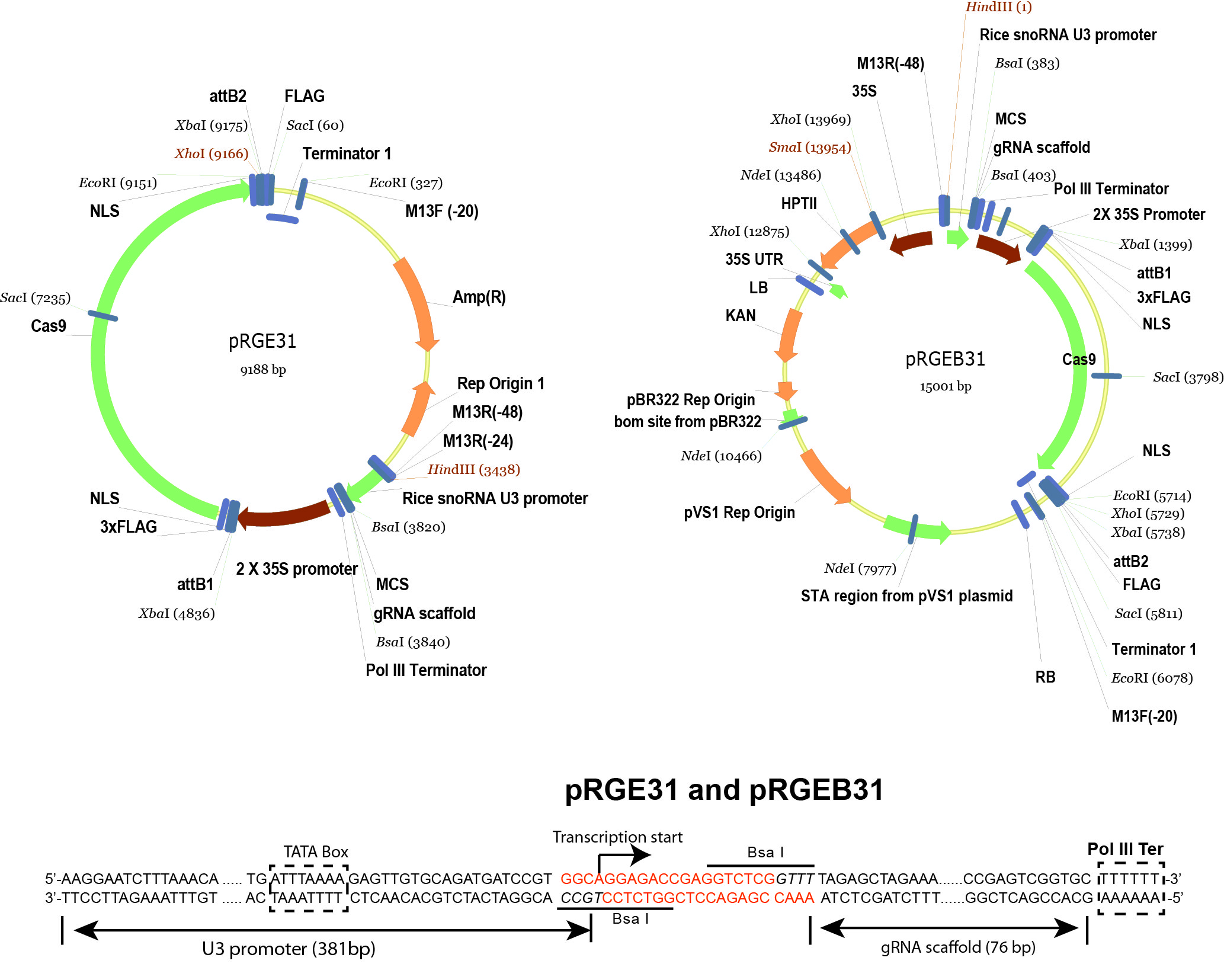
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of pRGE31 and pRGEB31 vectors. The pRGEB31 vector was used in this protocol. - Bsa I (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0535S )
- 70%, 100% ethanol
- Alkaline phosphatase, calf intestinal (CIP) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0290S )
- T4 DNA ligase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0202S )
- T4 polynucleotide kinase (T4 PNK) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0201S )
- T7 endonuclease I (T7EI) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0302S )
- GoTaq DNA polymerase (Promega Corporation, catalog number: M3001 )
- Phusion high-fidelity polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: F530S )
- 5x green GoTaq® reaction buffer (Promega Corporation, catalog number: M7911 )
- QIAGEN plasmid mini kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 12123 )
- QIAquick PCR purification kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 28104 )
- Hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9151 )
- Sodium lauroyl sarcosinate (sarkosyl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP235-500 )
- CTAB buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 37 °C water bath
- Thermal cycler
- DNA electrophoresis apparatus
- Microcentrifuge
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Xie, K., Minkenberg, B. and Yang, Y. (2014). Targeted Gene Mutation in Rice Using a CRISPR-Cas9 System. Bio-protocol 4(17): e1225. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1225.
分类
植物科学 > 植物分子生物学 > RNA > RNA 干扰
分子生物学 > RNA > mRNA 转译
分子生物学 > DNA > 诱/突变
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link














