- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Coculture between hMADS and Mouse Adult CM
人多能脂肪源干细胞(hMADS)与小鼠成熟心肌细胞(CM)的共培养
发布: 2014年07月20日第4卷第14期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1178 浏览次数: 10801
评审: Anonymous reviewer(s)
Abstract
Heart failure occurring after acute myocardial infarction (MI) is among the main causes of death in western countries. Cell therapies, particularly those based on mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), represent one of the most promising approaches to repair damaged heart tissues. Several reports have provided evidences that injection of mesenchymal stem cells improved heart function following myocardial infarction (Shake et al., 2002; Zimmet and Hare, 2005; Zeng et al., 2007). Nevertheless, the mechanism(s) by which MSC exert their therapeutic action is far from being understood, and further knowledges in this field are required especially to optimize efficiency of current cardiac cell therapies. To assess the regenerative mechanisms developed by MSC in vitro, we developed the method described above which is expected to mimic the micro-environment typical of an infarcted heart. This method consists in a species mismatch coculture between mouse terminally differentiated cardiomyocytes in a distressed state and human Multipotent Adipose Derived Stem cells (hMADS cells) used herein as an MSC model.
Materials and Reagents
- hMADS cells were isolated as described previously (Rodriguez et al., 2005)
- Perfusion Buffer stock solution (sPB)
- Liberase blendzyme TM (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 05401119001 )
- Trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4549 )
- Calcium chloride
- Annexin V/7AAD staining (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 559763 )
- 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid (18α-GA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G-8503 )
- M Latrunculin A (Life Technologies, catalog number: L12370 )
- Nocodazole (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M-1404 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S9625 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4504 )
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5379 )
- Sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0876 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4.7H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9397 )
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S5761 )
- Potassium bicarbonate (KHCO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9144 )
- 1 M HEPES buffer solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M3375 )
- Taurine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0625 )
- Phenol Red (last) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5530 )
- 5.5 mM glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7528 )
- 0.25 mg/ml liberase blendzyme (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 1988417 )
- Trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4549)
- 10% newborn calf serum (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 16010167 )
- 5% bovine calf serum (BCS) (HyClone, catalog number: SH30073 )
- Pentobarbital sodium (CEVA, CIP number: 6742145 )
- Heparin choay (sanofi-aventis, CIP number: 3048450 )
- 1x perfusion buffer stock solution (see Recipes)
- 2,3-Butanedione monoxime (BDM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B0753 ) (see Recipes)
- Perfusion buffer (pH 7.46) (PB) (see Recipes)
- Digestion buffer (see Recipes)
- Stopping buffer 1 (see Recipes)
- Stopping buffer 2 (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Langendorff apparatus (see below)
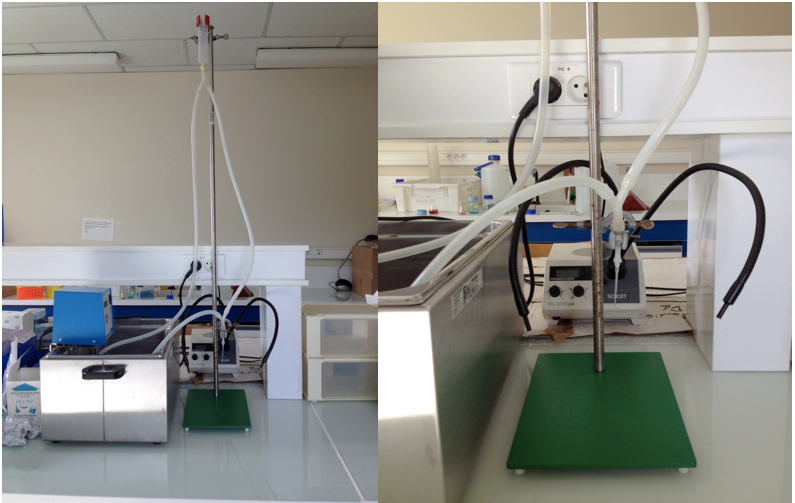
Figure 1. Langendorff apparatus - Water bath at 37 °C
- Surgical silk 4.0
- Petri dishes (Dutscher Scientific, catalog number: 628103 )
- Surgical instruments
- Disposable transfer pipets (VWR International, catalog number: 612-1681 )
- Falcon 15 ml propylene conical tubes (Dutscher Scientific, catalog number: 352095 )
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Figeac, F., Acquistapace, A., Coz, O. L., Lesault, P. F. and Rodriguez, A. (2014). Coculture between hMADS and Mouse Adult CM. Bio-protocol 4(14): e1178. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1178.
分类
干细胞 > 成体干细胞 > 间充质干细胞
干细胞 > 成体干细胞 > 维持和分化
细胞生物学 > 细胞分离和培养 > 细胞分化
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
















