- EN - English
- CN - 中文
Generation and Screening of a Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Tn-seq Mutant Library
非分型流感嗜血杆菌Tn序列突变体库的构建和筛选
发布: 2014年03月05日第4卷第5期 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1065 浏览次数: 11961
评审: Fanglian He
Abstract
The genome-wide screen Tn-seq (van Opijnen et al., 2009) is very valuable tools to identify bacterial genes with a conditionally essential function, for instance genes involved in bacterial virulence. These techniques are based on the generation of a random mutant library, which is grown in a control of challenge situation (Figure 1). The advantage of using a mariner transposon for the generation of a random transposon mutant library is its insertion into TA sites, which makes the insertion in the genome highly random. In addition, an MmeI restriction site can be introduced in the inverted repeat of the transposon, without affecting the recognition by HimarC9 transposase.
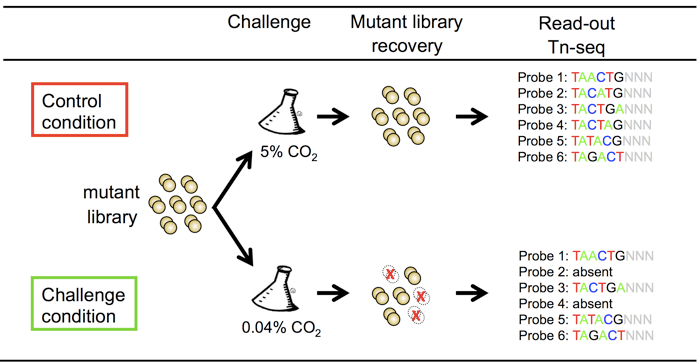
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae tn-seq mutant library screen for survival and growth in environmental air
Materials and Reagents
- 1 U/μl Calf Intestinal Alkaline Phoshatase (CIAP) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0290S )
- Chloroform: isoamyl alcohol
- Phenol: chloroform: isoamayl alcohol
- Milli-Q water
- 10 mM dNTP mix (New England Biolabs, catalog number: N0447S )
- 1 mM dNTP mix
- Absolute ethanol
- 70 % Ethanol
- 10 mg/ml Glycogen
- 2 U/μl MmeI restriction enzyme (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0637S )
- 10x NEBuffer 4
- 32 mM S-denosylmethionine
- 3 M NaAc (pH 5.3)
- 5 M NaCl
- 2 U/μl Phusion DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0530S )
- 5x Phusion HF buffer
- 10 U/μl T4 DNA ligase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0202S )
- 20 U/μl T4 DNA ligase
- 10x T4 DNA ligase buffer
- 2.5 U/μl T4 DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0203S )
- 10x T4 DNA polymerase buffer
- T4 polynucleotide kinase (3' phosphatase minus) (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0236S )
- 100x TE buffer
- 1 M NaOH
- 50 % Glycerol
- 1 mM DTT
- 5 M NaCl
- 1 M MgCl2
- 10 mg/ml BSA
- 5 U/ml E.coli DNA ligase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0205S )
- 10x E.coli DNA ligase buffer
- 1 M Hepes (pH 7.9)
- HimarC9 transposase
- M-IV medium (Herriott et al., 1970)
- 1 mg/ml Hemin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9039 )
- 10 mg/ml Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N7004 )
- Brain heart infusion medium (BHI) (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 237500 )
- Supplemented BHI, BHI medium containing 10 μg/ml Hemin and 2 μg/ml NAD
- Bacto-agar (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 212030 )
- Supplemented BHI plates, sBHI containing 1.5% bacto agar
- PBS
- 100 mg/ml RNase A (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10109142001 )
- Qiagen Genomic-tip 20/G columns (QIAGEN, catalog number: 10223 )
- Qiagen Genomic DNA buffer set (QIAGEN, catalog number: 19060 )
- Minelute Reaction Cleanup Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 28204 )
- Qubit dsDNA BR assay (Life technologies, catalog number: Q32850 )
- Acceptor DNA
Any type of DNA can serve as acceptor for in vitro mariner transposition. The most common types of acceptor DNA are: Chromosomal DNA of the target strain (High quality DNA is required, preferably isolated with Qiagen Genomic Tip columns) or PCR products of target genes or regions. - Donor DNA
Any type of DNA that carries a mariner transposon with MmeI restriction site in the inverted repeat can serve as donor for transposon in the in vitro mariner transposition reaction. Used pGSF8 plasmid, carrying transposon with spectinomycin resistance cassette, suitable for GAF and TnSeq (Langereis et al., 2013). - Primers used for sequence adapters ligation and PCR amplification (see Appendixes)
Equipment
- Pipet tips: 0.5-10 μl, 2-20 μl, 20-200 μl 100-1000 μl
- 15 cm dishes
- Heating block for incubations ranging from 16 °C and 75 °C (Grant QBD2)
- Microcentrifuge for 1.5 ml tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5417R )
- Centrifuge for 50 ml tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5810 )
- T100 thermal cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Nanodrop, model: ND1000 )
- Incubator with 5% CO2 (BINDER GmbH, model: CB 150 )
- Qubit Fluorometer (Life Technologies)
- Bioanalyser (Agilent Technologies)
Procedure
文章信息
版权信息
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
如何引用
Langereis, J. D. (2014). Generation and Screening of a Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Tn-seq Mutant Library . Bio-protocol 4(5): e1065. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1065.
分类
微生物学 > 微生物遗传学 > 诱/突变
分子生物学 > DNA > 诱/突变
系统生物学 > 基因组学 > 转座子
您对这篇实验方法有问题吗?
在此处发布您的问题,我们将邀请本文作者来回答。同时,我们会将您的问题发布到Bio-protocol Exchange,以便寻求社区成员的帮助。
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link