往期刊物2025
卷册: 15, 期号: 6
生物工程
Dual-Modal Fast Photoacoustic/Ultrasound Localization Imaging with Sparsity-Constrained Optimization
基于稀疏约束优化的双模态快速光声/超声定位成像
细胞生物学
Generation of FECD Phenotypes in the Mouse Cornea by UVA Exposure and Surgical Removal of its Corneal Endothelial Layer
通过 UVA 照射和角膜内皮层手术去除在小鼠角膜中构建 FECD 表型
发育生物学
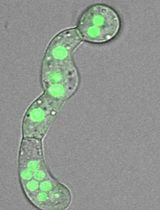
Visualization of mRNA Translation Within Germ Granule Biphasic Organization in Drosophila Early Embryo
果蝇早期胚胎生殖颗粒双相结构中 mRNA 翻译的可视化
微生物学
Improved Extraction Methods to Isolate High Molecular Weight DNA From Magnaporthaceae and Other Grass Root Fungi for Long-Read Whole Genome Sequencing
优化高分子量 DNA 提取方法以用于 Magnaporthaceae 及其他禾本科根部真菌的长读长全基因组测序
HS–GC–MS Method for the Diagnosis of IBD Dynamics in a Model of DSS-Induced Colitis
HS-GC-MS 方法用于 DSS 诱导性结肠炎模型中 IBD 动态变化的诊断
Evaluating In Vivo Translation Inhibition via Puromycin Labeling in Botrytis cinerea Germlings Treated With Antifungal Peptides
嘌呤霉素标记评估抗真菌肽对灰葡萄孢萌发菌丝的体内翻译抑制作用
Differentiation of Bacillus cereus Species Based on Detected Unamplified Bacterial 16S rRNA by DNA Nanomachine
基于 DNA 纳米机检测未扩增的细菌 16S rRNA 区分蜡状芽孢杆菌种群
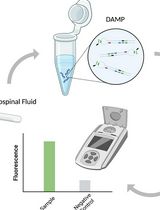
A Highly Sensitive and Selective DAMP Assay for the Detection of Bacterial Pathogens Associated With Brain Inflammation
高灵敏度、高选择性的 DAMP 检测法用于检测与脑部炎症相关的细菌病原体
分子生物学
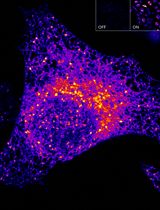
Sensitive and Adaptable Turn-On Maturation (ATOM) Fluorescent Biosensors for Detecting Subcellular Localization of Protein Targets in Cells
高灵敏且可调控的 ATOM 荧光生物传感器:用于检测细胞中蛋白质靶点的亚细胞定位
神经科学
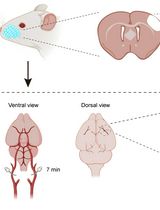
Developing a Ministroke Model in Mouse Barrel Cortex
小鼠桶状皮层微卒中模型的建立
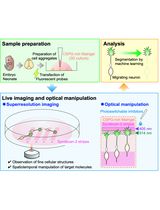
Time-Lapse Super-Resolution Imaging and Optical Manipulation of Growth Cones in Elongating Axons and Migrating Neurons
时间分辨超分辨成像与光学操控用于研究延伸轴突和迁移神经元的生长锥
植物科学
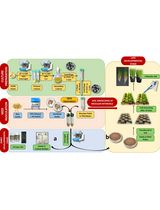
Protocol for Inoculation of PGPR Staphylococcus sciuri to Seeds and Seedlings of Rice and Tomato Plants for Increased Root and Shoot Growth
PGPR 金黄色葡萄球菌接种水稻和番茄种子及幼苗的方案以促进根系和茎叶生长
系统生物学
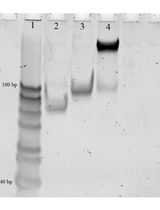
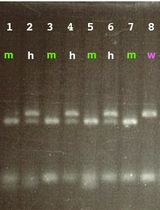
PCR-Based Genotyping of Zebrafish Genetic Mutants
基于 PCR 的斑马鱼基因突变体分型方法