往期刊物2023
卷册: 13, 期号: 5
生物化学
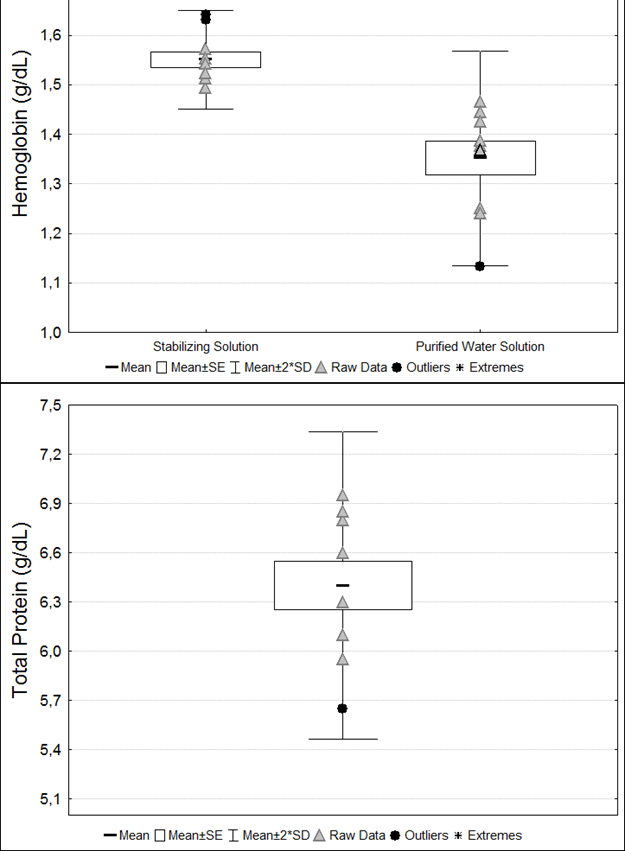
Assessment of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Rat Blood
大鼠血液中氧化应激生物标志物的评估
生物工程
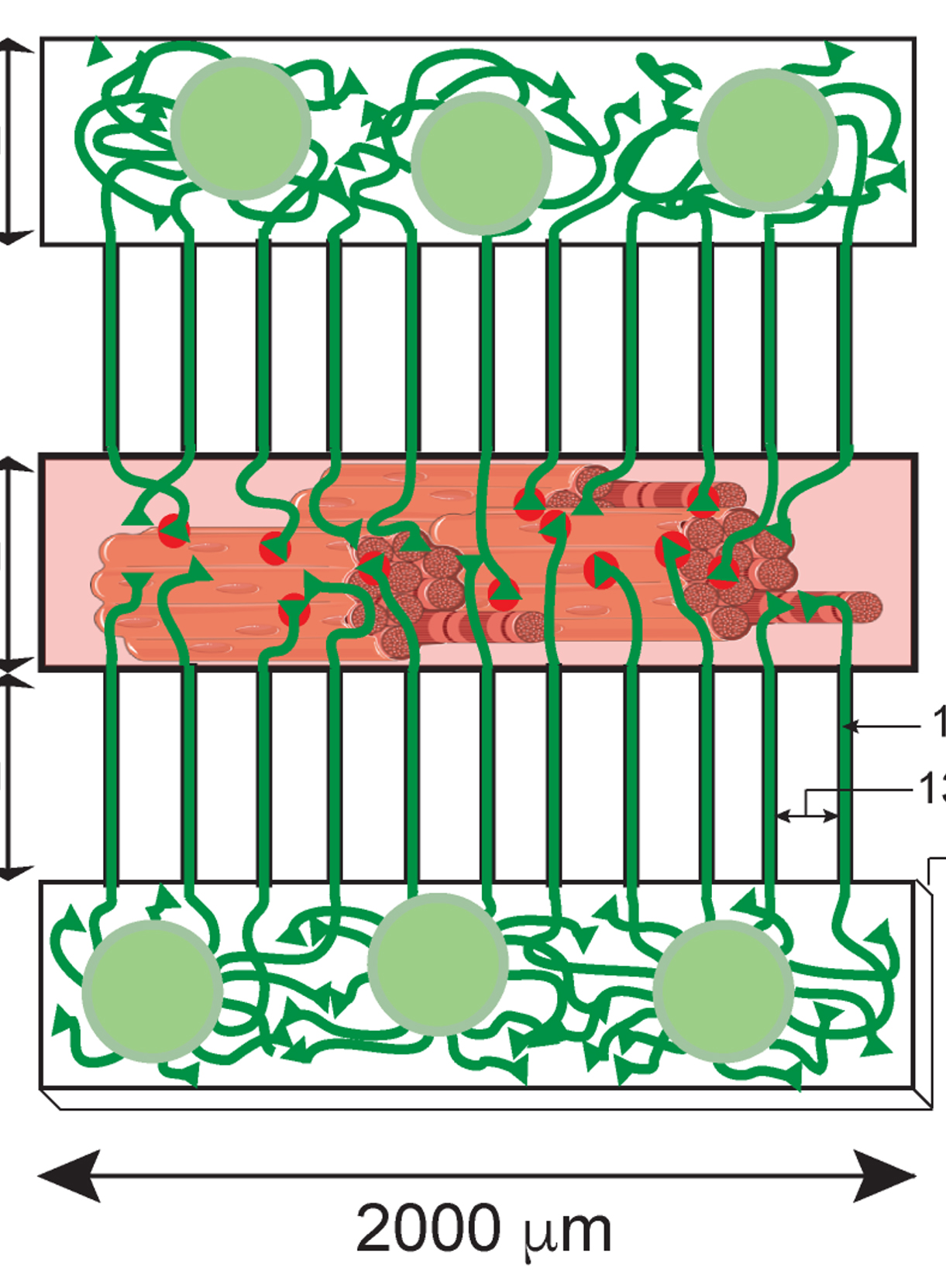
3D Compartmentalised Human Pluripotent Stem Cell–derived Neuromuscular Co-cultures
3D 区室化人类多能干细胞衍生的神经肌肉共培养物
生物物理学
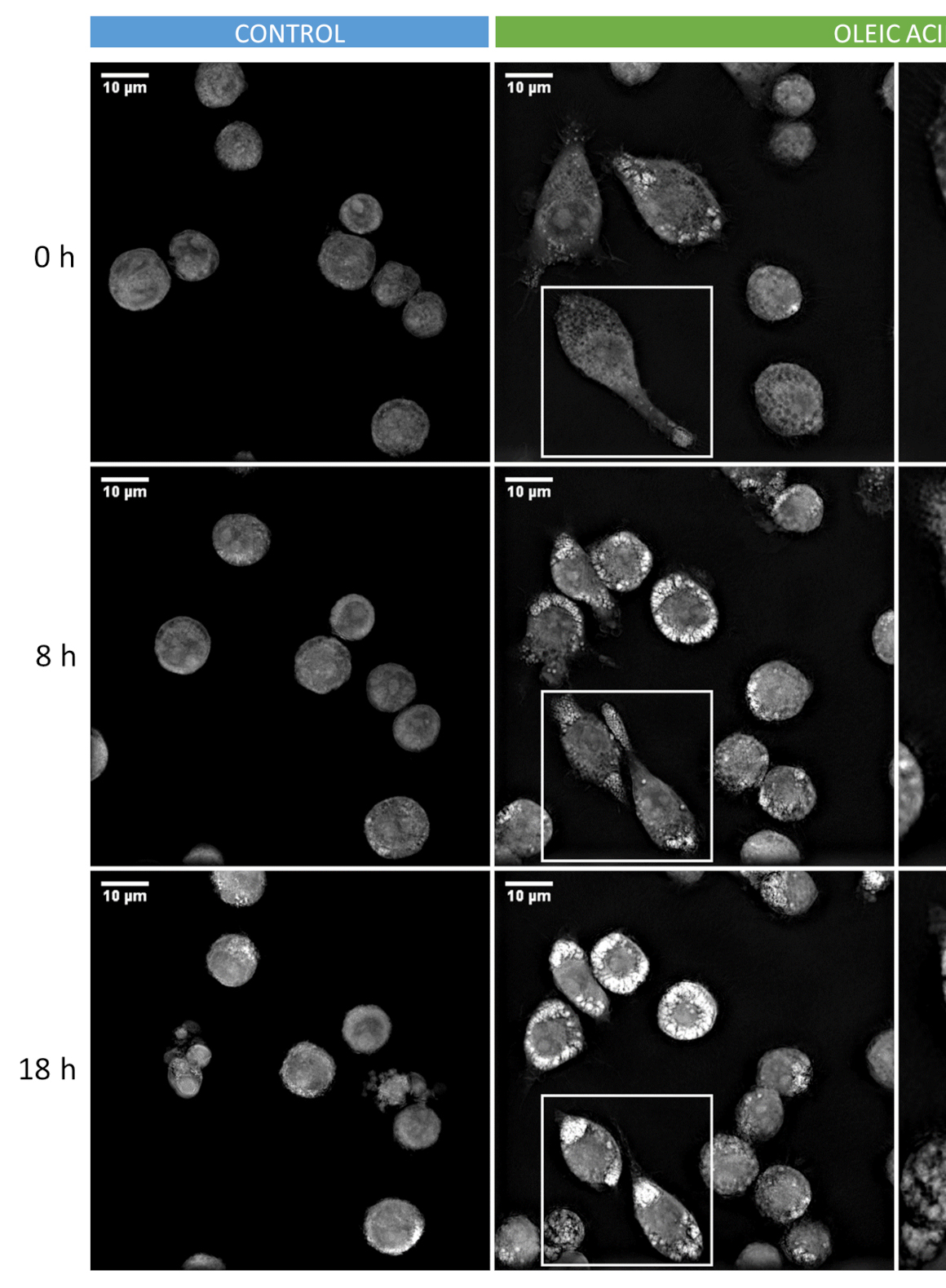
Visualization of Lipid Droplets in the Alveolar Macrophage Cell Line MH-S with Live-cell Imaging by 3D Holotomographic Microscopy (Nanolive)
通过 3D 全息显微术 (Nanolive)的活细胞成像实现肺泡巨噬细胞系 MH-S 中脂滴的可视化
癌症生物学
Amplification and Quantitation of Telomeric Extrachromosomal Circles
端粒染色体外环的扩增和定量
细胞生物学
Laser Capture Microdissection (LCM) of Human Skin Sample for Spatial Proteomics Research
用于空间蛋白质组学研究的人体皮肤样本激光捕获显微切割(LCM)
免疫学
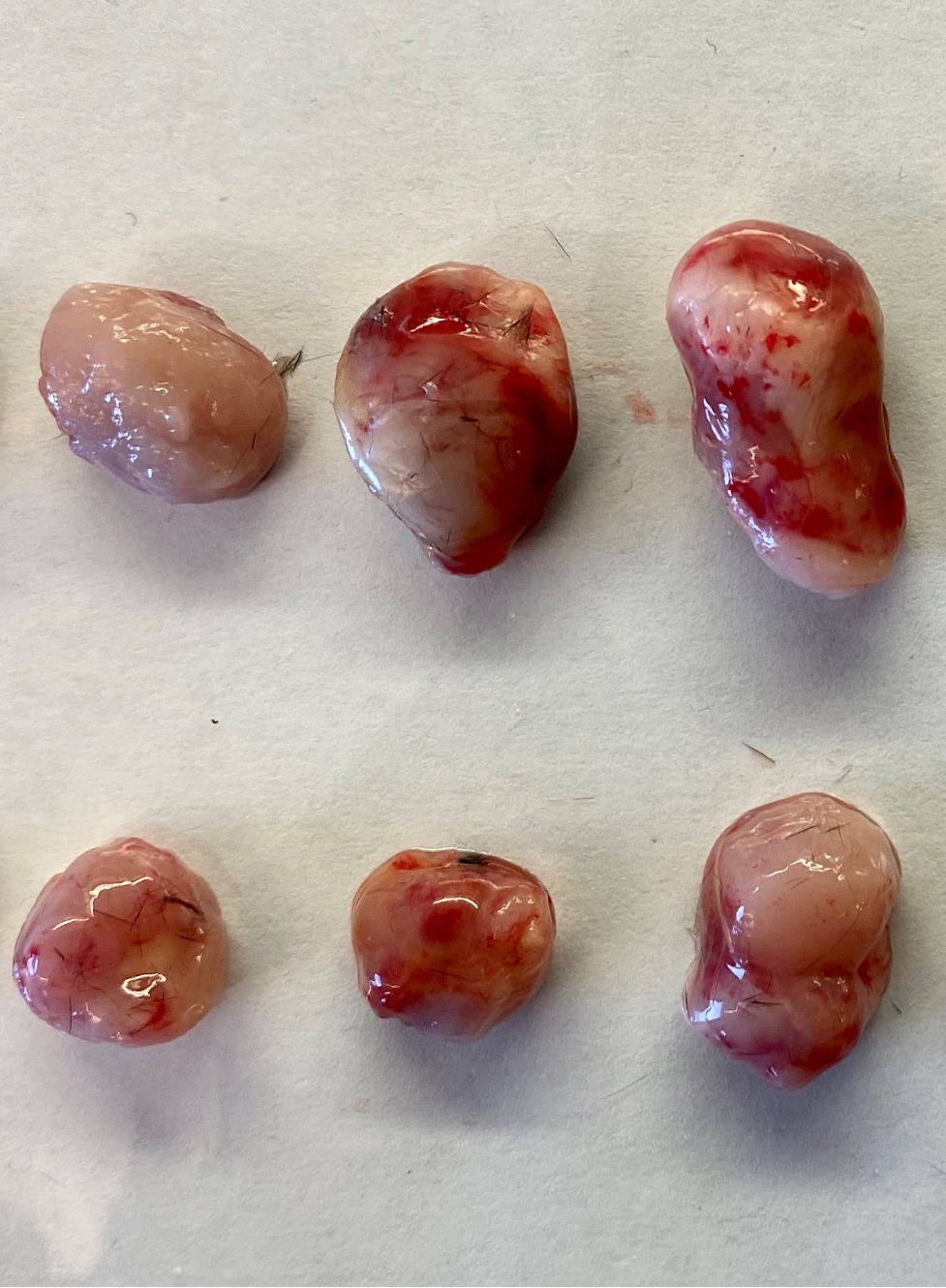
A Tumor-admixture Model to Interrogate Immune Cell–dependent Tumorigenesis
研究免疫细胞依赖性肿瘤发生的肿瘤混合模型
微生物学
Optimized Expression and Isolation of Recombinant Active Secreted Proteases Using Pichia pastoris
毕赤酵母优化表达和分离重组活性分泌蛋白酶
分子生物学
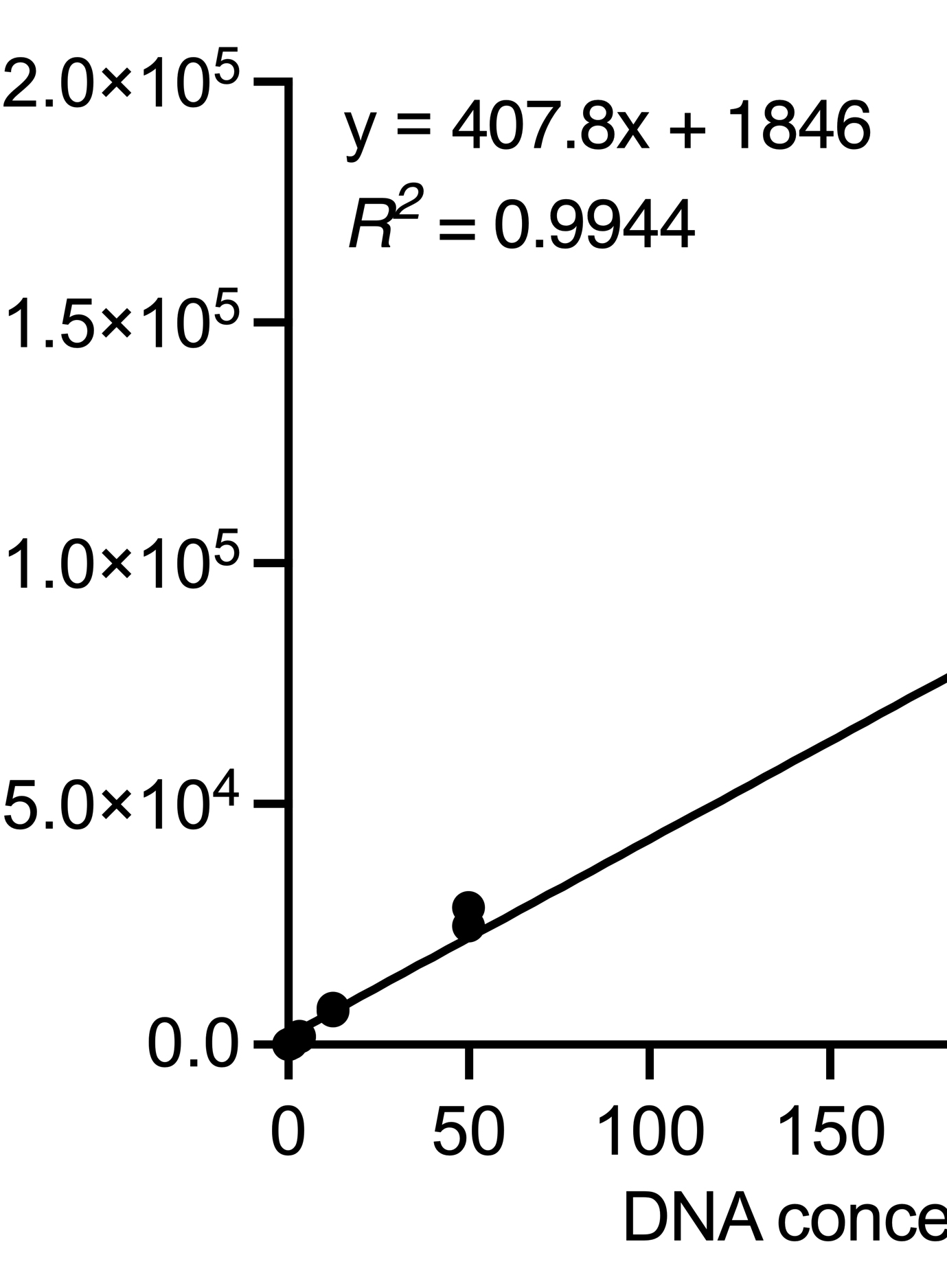
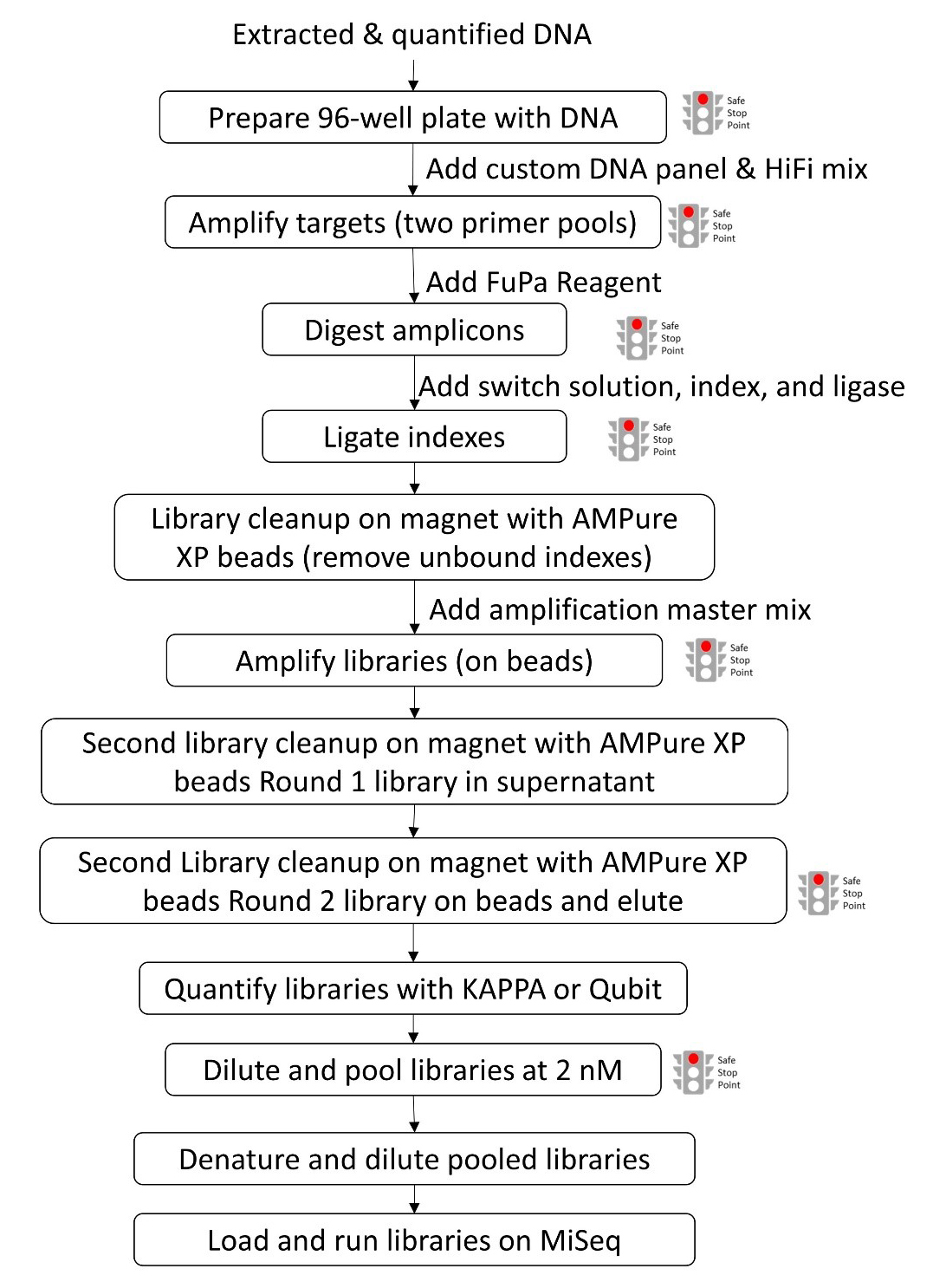
Molecular Surveillance of Malaria Using the PF AmpliSeq Custom Assay for Plasmodium falciparum Parasites from Dried Blood Spot DNA Isolates from Peru
使用 PF AmpliSeq定制检测法对秘鲁干血斑 DNA 中的恶性疟原虫寄生虫分子进行疟疾监测
神经科学
Establishment of an in vitro Differentiation and Dedifferentiation System of Rat Schwann Cells
大鼠雪旺细胞体外分化和去分化体系的建立
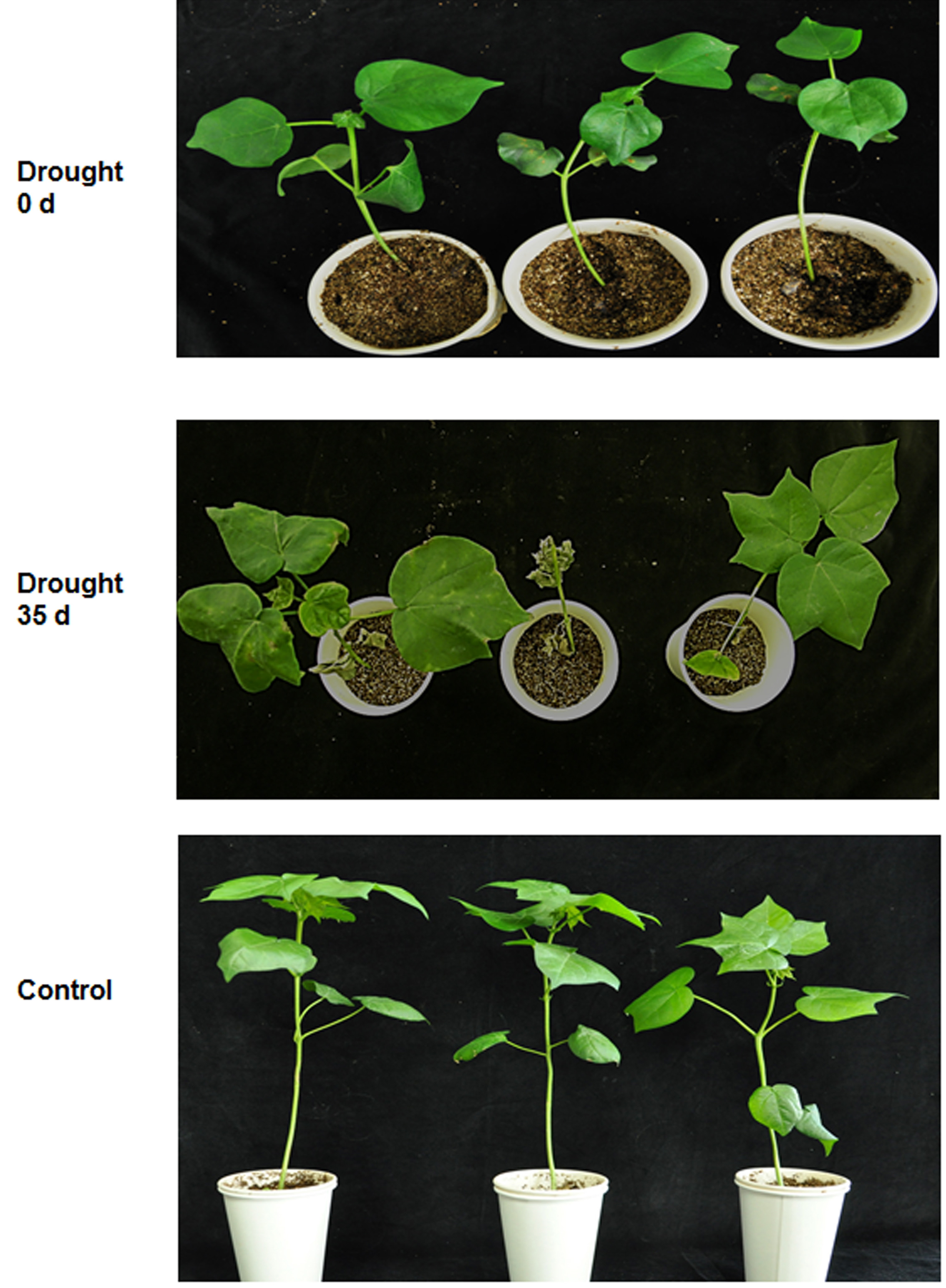
植物科学
Isolation of Intact Vacuoles from Arabidopsis Root Protoplasts and Elemental Analysis
拟南芥根原生质体完整液泡的分离及元素分析
更正