往期刊物2018
卷册: 8, 期号: 24
生物化学
Preparation of Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles and Enzyme-Entrapped Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles
制备丝素蛋白纳米颗粒和酶包裹丝素蛋白纳米颗粒
细胞生物学
Quantitative Analysis of Cargo Density in Single-extracellular Vesicles by Imaging
成像技术定量分析单细胞外囊泡中内容物的密度
Microirradiation for Precise, Double-strand Break Induction in vivo in Caenorhabditis elegans
显微照射用于秀丽隐杆线虫中双链断裂的精确体外诱导
免疫学
Method for Studying the Effect of Gene Silencing on Bacterial Infection-induced ERK1/2 Signaling in Bone-marrow Derived Macrophages
基因沉默对于细菌感染诱导骨髓巨噬细胞中ERK1/2信号通路的影响研究方法
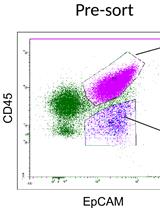
Monitoring Natural Killer Cell Function in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells of Ascitic Fluid
在人卵巢腹水癌细胞中监测自然杀手细胞功能
Eimeria vermiformis Infection Model of Murine Small Intestine
蠕形艾美耳球虫对小鼠小肠的感染模型
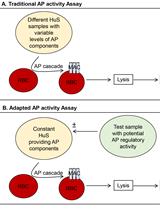
Quantitation of Regulatory Activity for the Complement Alternative Pathway Using an Adaptation of the AP50 in vitro Assay
应用改编过的AP50体外分析法定量测定补体旁路途径的调节活性
微生物学
Production, Titration and Imaging of Zika Virus in Mammalian Cells
哺乳动物细胞中寨卡病毒的制备、滴度测定和成像
Systematic Quantification of GFP-tagged Protein Foci in Schizosaccharomyces pombe Nuclei
粟酒裂殖酵母细胞核中GFP标记蛋白聚集点的系统量化
Analysis of DNA Exchange Using Thymidine Analogs (ADExTA) in Trypanosoma cruzi
克氏锥虫中利用胸苷类似物进行DNA交换分析
分子生物学
Variable Dose Analysis: A Novel High-throughput RNAi Screening Method for Drosophila Cells
可变剂量分析:一种果蝇细胞高通量RNAi筛选的新方法
神经科学
Three-chamber Social Approach Task with Optogenetic Stimulation (Mice)
配有光遗传学刺激的三间隔社交途径测试(小鼠)
Partial Transection of Adult Rat Optic Nerve as a Model of Secondary Degeneration in the Central Nervous System
成年大鼠视神经不完全横切作为中枢神经系统继发性损害模型
植物科学
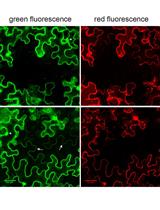
Visualization and Quantification of Cell-to-cell Movement of Proteins in Nicotiana benthamiana
本氏烟中蛋白的细胞间运动的可视化定量检测