- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Analysis of RNA-protein Interactions Using Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (Gel Shift Assay)
Published: Vol 3, Iss 22, Nov 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.967 Views: 31394
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Plant ARGONAUTE Protein Immunopurification for Pathogen Cross Kingdom Small RNA Analysis
Florian Dunker [...] Arne Weiberg
Feb 5, 2021 6398 Views

Assessing Metabolite Interactions With Chloroplastic Proteins via the PISA Assay
Anna Karlsson [...] Elton P. Hudson
May 5, 2025 2031 Views

Turbo-RIP: A Protocol for TurboID-based RNA Immunopurification to Map RNA Landscapes in Plant Biomolecular Condensates
Zhi Zhang [...] Panagiotis Nikolaou Moschou
Feb 5, 2026 430 Views
Abstract
RNA binding proteins (RBPs) play a crucial role in regulating gene expression at the post-transcriptional level at multiple steps including pre-mRNA splicing, polyadenylation, mRNA stability, mRNA localization and translation. RBPs regulate these processes primarily by binding to specific sequence elements in nascent or mature transcripts. There are several hundreds of RBPs in plants, but the targets of most of them are unknown. A variety of experimental methods have been developed to identify targets of an RBP. These include RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), UV cross-linking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) and many variations of CLIP (e.g. PAR-CLIP, iCLIP). These approaches depend on immunoprecipitation of RNAs bound to a specific RBP using an antibody to that RBP. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA), also called gel shift assay, has been used to analyze protein-nucleic acid interactions. It is a simple and powerful method to analyze protein-RNA/DNA interactions. In RNA EMSA, RNA-protein complexes are visualized by comparing the migration of RNA in the presence of a protein. Generally, in RNA EMSA a specific RNA sequence is used to analyze its interaction with a protein. In vitro transcribed 32P labeled or chemically synthesized RNA with a fluorescent tag is incubated with or without the protein of interest and the reaction mixture is then run on native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. RNA-Protein complexes migrate slowly as compared to free RNA, which can be visualized using an imaging system. In addition to test binding of an RBP to RNA, EMSA is also used to map the region in RNA and/or protein that is involved in interaction. Furthermore, the binding affinity can also be quantified using EMSA.
Materials and Reagents
Note: All work should be done in an RNase free environment, using only sterile, RNase free solutions and materials.
- E. coli BL21 (DE3)-pLysS host cells harboring SR45 cDNA
- In vitro transcribed RNA
- Purified recombinant protein
- Cap analogue (New England Biolabs, catalog number: S1404S )
- SP6 polymerase (Fermentas, catalog number: EP0131 20 U/μl)
- rNTPs
ATP (Fermentas, catalog number: R0441 )
CTP (Fermentas, catalog number: R0451 )
GTP (Fermentas, catalog number: R0461 )
UTP (Fermentas, catalog number: R0471 )
- RNase Inhibitor (Life Technologies, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 10777019 )
- 32P-UTP- Uridine 5’ triphosphate (PerkinElmer, catalog number: BLU007C001 )
- HEPES (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: AC172571000 )
- KCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9541 )
- MgCl2 (Mallinckrodt, catalog number: 5958-04 )
- Glycerol (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: G331 )
- Triton X-100 (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: BP151 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Mallinckrodt Baker, catalog number: 4095-02 )
- NaCl (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: 7647-14-5 )
- Na2HPO4 (Mallinckrodt, catalog number: 7917-04 )
- KH2PO4 (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: 7778-77-0 )
- Spermidine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 52626 )
- Heparin sulfate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H4784 )
- Tris base (AMRESCO, catalog number: 77-86-1 )
- Acrylamide/bis-acrylamide (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 16105B )
- Phenol: chloroform (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0883 )
- Ammonium persulfate (APS) (Gibco BRL®, catalog number: 5523UA )
- TEMED (VWR International, catalog number: 97064-684 )
- Bromophenol blue (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 161-0404 )
- Xylene cyanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X4126 )
- pGEM vector (Promega, catalog number: P2161 )
- Isopropyl-β-D thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (Gold Bio, catalog number: I2481C5 )
- Ampicillin (VWR International, catalog number: IB02040 )
- S-Protein agarose beads (Merck KGaA, Novagen®, catalog number: 80031-014 )
- Lysozyme (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L6876 )
- pET32c vector (Merck KGaA, Novagen®, catalog number: 69017-3 )
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9599 )
- Boric acid (Mallinckrodt, catalog number: 2549-04 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: S311-500 )
- Ammonium acetate (Thermo Fischer Scientific, catalog number: A637-500 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA)
- LB medium
- 5x Gel shift buffer (see Recipes)
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- 10x TBE (see Recipes)
- Gel Mix (see Recipes)
- 5% Denature Gel (see Recipes)
- 5% Non-Denaturing Gel (see Recipes)
- TNS Solution (see Recipes)
- RNA loading dye for Urea gel (see Recipes)
- 6x loading buffer for Non-Urea gel (see Recipes)
- Binding/wash buffers (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffer (see Recipes)
- Citrate buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube (BioExpress, catalog number: C-3262 )
- Saran wrap
- Whatman filter paper
- Water bath (VWR International, model: 1225 PC )
- Electrophoresis equipment with power supply (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: B2 easy cost )
- Gel drying apparatus (Savant System LLC, model: SGD 2000 )
- Phosphorimager (Molecular Dynamics, model: Storm 840 )
- Phosphorimager screen (Molecular Dynamics, model: 1000004864 )
- Sonicator (SP Scientific, model: 274480 )
- 0.45 micron syringe filter (Life Science Products, catalog number: 25CSO80AS )
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 022620401 )
- Vertical gel apparatus (Gibco BRL®, model: V15.17 )
- Liquid scintillation counter
- Orbital shaker
Procedure
Note: We routinely produce RNA probes by in vitro transcription using a linearized pGEM clone that contains the DNA corresponding to RNA of interest. pGEM vector has T7 and SP6 promoters. Depending on the orientation of insert DNA either T7 polymerase or SP6 polymerase is used in in vitro transcription to generate RNA probe.
- Preparation of RNA using in vitro transcription system
- Prepare the following reaction in a 1.5 ml of microcentrifuge tube. 1 μl DNA template (~ 1 μg of linearized plasmid DNA), 1 μl 10x RNA polymerase buffer, 1 μl rNTPs (5 mM ATP, CTP, 0.5 mM GTP, UTP), 1 μl cap analog (5 mM), 4.5 μl (45 μCi): a-32P-UTP (800 Ci/mmol; 10 mCi/ml), 0.5 μl RNase Inhibitor, and 1 μl SP6 polymerase a total of 10 μl of reaction.
- Incubate 37 °C, for 3 to 6 hours (Note 1).
- Add 90 μl dH2O to 10 μl total 100 μl.
- Add equal volume of (100 μl) of phenol/chloroform, mix by vortexing.
- Spin at 16,000 x g for 5 min.
- Transfer upper layer into a new Eppendorf (~100 μl).
- Add 33 μl 10 M ammonium acetate and 250 μl 100% ethanol to the 100 μl.
- Incubate at -80 °C for 10 min.
- Spin at 16,000 x g for 10 min.
- Wash the pellet with 500 μl of 80% ethanol.
- Air dry the pellet; resuspend in 10 μl RNA loading dye.
- Heat 1 min at 90 °C.
- Load on 5% denaturing acrylamide gel and run for one to two hours depending on the size of RNA (Note 2).
- Disassemble the gel chamber and dismantle the gel, leaving it mounted on one plate. To facilitate the alignment of the gel to the X-ray film in stepA16 below, cut one corner of the gel.
- Wrap the gel with Saran wrap to avoid contamination.
- Expose the gel to an X-ray film for 2-5 min and develop the film to visualize radioactive bands.
- Align the gel on top of the X-ray film and locate the region in the gel corresponding to the radioactive band on the film.
- Excise the gel corresponding to the band on the X-ray film (see Figure 1 and Notes 3 & 4).
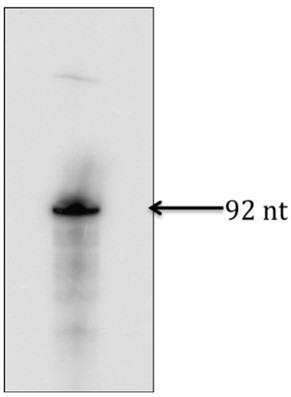
Figure 1. In vitro transcribed RNA used in Figure 2a and 2b. After exposing the gel to an X-ray film, identified the right size of RNA product, excised the gel corresponding to the band and used to extract RNA.
- Transfer the excised band to 400 μl of TNS solution in an Eppendorf tube and incubate overnight at room temperature.
- Next day, take out TNS solution, which contains radiolabelled RNA and add equal volume of phenol/chloroform, mix by vortexing.
- Spin at 16,000 x g for 10 min.
- Wash the pellet with 500 μl of 80% ethanol.
- Dry the pellet; resuspend the RNA pellet in 20 μl H2O.
- Measure radioactivity in1 μl of RNA using liquid scintillation counter and use this number to calculate concentration of labeled “U” residues in RNA probe (Note 5).
- Dilute RNA probe with RNase free water to 50 to100 K cpm/μl for use in EMSA assays.
- Prepare the following reaction in a 1.5 ml of microcentrifuge tube. 1 μl DNA template (~ 1 μg of linearized plasmid DNA), 1 μl 10x RNA polymerase buffer, 1 μl rNTPs (5 mM ATP, CTP, 0.5 mM GTP, UTP), 1 μl cap analog (5 mM), 4.5 μl (45 μCi): a-32P-UTP (800 Ci/mmol; 10 mCi/ml), 0.5 μl RNase Inhibitor, and 1 μl SP6 polymerase a total of 10 μl of reaction.
- Preparation and purification of recombinant protein
For EMSA analysis apart from RNA a purified protein of interest is needed. One can generate this protein by cloning the cDNA into a bacterial expression vector. Here we expressed SR45 in E.coli as an S.tag fusion and purified it using S-protein agarose beads.- Grow E. coli BL21 (DE3)-pLysS host cells harboring SR45 cDNA in LB medium containing ampicillin at 37 °C for overnight. Next day inoculate 1 ml of overnight culture into 100 ml of LB medium containing appropriate antibiotic, then grow culture until OD600 reaches ~0.6 (it will take approximately 2 h).
- Induce expression of recombinant protein by adding IPTG to a final concentration of 0.5 mM and allow the bacterial culture to grow for an additional 4 h at 30 °C.
- Harvest bacterial cells by centrifugation at 2,350 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the cell pellet in 1/10 culture volume (5 ml) of 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 2 mM EDTA.
- Add lysozyme to a concentration of 100 μg/ml; use a 10 mg/ml stock freshly prepared in 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 2 mM EDTA. Then add 1/10 volume (0.5 ml) of 1% Triton X-100. Incubate at 30 °C for 15 min.
- Place the tube in an ice bath and sonicate 4 times (at 3.5 setting) for 15 sec/each time.
- Centrifuge at 12,000 x g for 15 min at 4 °C. The supernatant contains soluble proteins.
- Filter the supernatant through a 0.45 micron membrane.
- Add 100 μl of binding/wash buffer to 100 μl of S-protein Agarose slurry in an Eppendorf tube and mix it gently, then add 1 ml of soluble proteins from step 8 (Note 6).
- Mix and incubate at room temperature on an orbital shaker for 30 min. (Do not shake vigorously as this may denature protein).
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 10 min at 4 °C and carefully decant supernatant and wash the beads with five times, 1 ml each time, with binding/wash buffer.
- Resuspend the washed beads containing the bound protein in 150 μl of the 0.2 M citrate buffer, pH 2.
- Incubate for 10 min at room temperature, mix gently every few minutes.
- Neutralized by adding 8 μl 2 M Tris-base (pH 10.4).
- The eluted proteins were dialyzed against phosphate buffer (Note 7).
- Grow E. coli BL21 (DE3)-pLysS host cells harboring SR45 cDNA in LB medium containing ampicillin at 37 °C for overnight. Next day inoculate 1 ml of overnight culture into 100 ml of LB medium containing appropriate antibiotic, then grow culture until OD600 reaches ~0.6 (it will take approximately 2 h).
- Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
Before setting up the reaction, prepare 5% non-denaturing (native) gel, and pre-run the gel at 200 V using 1x TBE buffer for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Prepare the following reaction mixture (final volume 14 μl) in a 1.5 ml of microcentrifuge tube. 1.5 μl of 1 mM spermidine (100 mM), 3 μl of 5x gel shift buffer, 0.5 μl of RNase Inhibitor, 1 μl of radiolabel RNA (50-100 K cpm), x μl lysis buffer (depending on protein volume) and x μl of protein of interest (Note 8).
- Incubate at 30 °C for 5 min.
- Add 1 μl of Heparin Sulfate (50 mg/ml) (Note 9).
- Transfer the reactions to ice for 5 min.
- Add 3 μl 6x urea free loading buffer.
- Load the reaction products on 5% non-denaturing gel and run at 200 V for 2 to 3 h or as long as necessary for good separation (normally we will run 2 h for RNA probe that is about 200 nt) (Note 10).
- Transfer the gel to Whatman filter paper, cover with Saran wrap, and dry with a gel-drying apparatus.
- The dried gel should be exposed to the phosphorimaging screen for 2 h to overnight.
- Free RNA and RNA – Protein complex(es) are visualized by using phosphorimager (see Figure 2a and 2b).
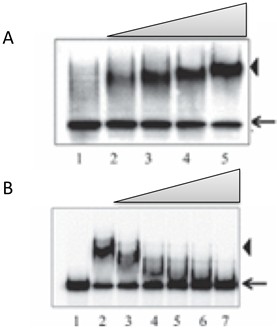
Figure 2. RNA EMSA. A. EMSA with an RNA probe using a purified recombinant protein. Lane 1, free probe; lanes 2-5, increasing concentration of recombinant protein. B. Binding of recombinant protein to RNA probe is competed by cold RNA. Lane 1, free probe; lane 2, probe + recombinant protein; lanes 3-7, as lane 2, with increasing concentration of cold RNA. Arrows indicate free probe, and the RNA-protein complex is indicated by arrowheads.
- Prepare the following reaction mixture (final volume 14 μl) in a 1.5 ml of microcentrifuge tube. 1.5 μl of 1 mM spermidine (100 mM), 3 μl of 5x gel shift buffer, 0.5 μl of RNase Inhibitor, 1 μl of radiolabel RNA (50-100 K cpm), x μl lysis buffer (depending on protein volume) and x μl of protein of interest (Note 8).
- Competition with unlabeled RNA
After confirming the binding of a protein with a specific RNA target using EMSA, the specificity of interaction can be tested by competition studies in the presence of excess amount of same RNA that is not labeled. Increasing amount of competitor RNA (up to 100x of labeled RNA) is added to the binding reaction mixture and the ability of the cold competitor RNA to disrupt the complex is determined as above using native gel electrophoresis (see Figure 2b). Unlabeled competitor RNAs is generated in the same manner as above (see A section), except that the amount of cold UTP is increased to 5 mM and the amount of radioactive UTP is reduced to 0.045 μCi.
Notes
- Three hours of incubation yields good amount of RNA.
- For ~100 base long RNA probe run the gel for 1 h; for 200 to 300 nts long probe run the gel for two to three hours.
- It is important to run in vitro transcribed RNA on a denaturing gel to confirm that the right size product is generated. The correct size band should then be excised and purified.
- Sometimes RNA templates yield two or more RNA products due to its secondary structure. If this happens, excise only the correct size band for purification.
- Concentration of labeled “U” in RNA is calculated using the specific activity of radiolabeled UTP, final concentration of UTP (radiolabeled UTP plus cold UTP) in the reaction and the number of “U” residues in the template. (fmoles of RNA = fmoles of UTP in the RNA probe/number of "U" residues in the labeled RNA).
- Since the amount of protein in soluble fraction varies depending on the clone and expression level, it is necessary to optimize the ratio between agarose beads and the protein.
- The recombinant protein should be purified to near homogeneity and protein concentration should be determined. It is not advisable to use crude extract from bacteria expressing recombinant protein.
- Always use a known concentration of RNA probe and increasing concentration of protein.
- Heparin sulfate reduces non-specific binding of RNA probe to proteins and eliminates background.
- Running time of native gels is dependent on the RNA and protein complex, it must be optimized for each RNA and protein. For longer run times, gels must be run at 4 °C temperature.
- Smaller size RNA probes (from 50 to 200 nts) work well in RNA EMSA.
- If some RNA/protein complex stays in the well, add BSA to minimize this effect.
- The concentration of RNA and protein should be optimized for each RNA-protein complex. Approximately 100,000 cpm of RNA and 500 ng of protein is a good starting point for binding studies.
Recipes
Note: All buffers should be prepared with RNase free water.
- 5x Gel shift buffer
70 mM HEPES pH 7.9
450 mM KCl
11 mM MgCl2
28% Glycerol
- Lysis buffer
50 mM HEPES pH 7.9
150 mM KCl
1 mM MgCl2
1% Triton X–100
10% Glycerol
- 10x TBE
108 grams of Tris base
55 grams of boric acid
9.3 grams of EDTA dissolved in water
Made up to one liter and autoclaved
Use 1x as running buffer in running both denaturing and non-denaturing (Native) gels
- Gel Mix (500 ml)
240 grams of Urea
50 ml of 10x TBE
200 ml H2O
Gel mix is stable for at least two to three months at room temperature
- 5% Denature Gel (30 ml)
5 ml of 30% Acrylamide/bisacrylamide
25 ml gel mix
300 μl 10% APS
30 μl TEMED
- 5% Non-Denaturing Gel
6.75 ml of 40% Acrylamide/bisacrylamide (38:2)
4.5 ml of 10x TBE
300 μl of 10% APS
30 μl of TEMED
33.6 ml of H2O
- TNS Solution
25 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5
400 mM NaCl
0.1% SDS
- RNA loading dye for Urea gel
20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.6
8 M Urea
1 mM EDTA
0.05% Xylene cyanol
0.05% Bromophenolo blue
- 6x loading buffer for Non-Urea gel
30% Glycerol
0.3% Bromophenol Blue
0.3% Xylene Cyanol
- Binding/wash buffers
20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5
150 mM NaCl
0.1% Triton X-100
1x protease inhibitors
- Phosphate buffer
10 mM Na2HPO4
2 mM KH2PO4
2.7 mM KCl
137 NaCl pH 7.4
- Citrate Buffer
2 M citric acid
Adjust pH to 2 with 10 M KOH and dilute to 0.2 M
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Thomas et al. (2012). This work was supported by a grant from the US National Science Foundation.
References
- Day, I. S., Golovkin, M., Palusa, S. G., Link, A., Ali, G. S., Thomas, J., Richardson, D. N. and Reddy, A. S. (2012). Interactions of SR45, an SR-like protein, with spliceosomal proteins and an intronic sequence: insights into regulated splicing. Plant J 71(6): 936-947.
- Golovkin, M. and Reddy, A. S. (1999). An SC35-like protein and a novel serine/arginine-rich protein interact with Arabidopsis U1-70K protein. J Biol Chem 274(51): 36428-36438.
- Palusa, S. G. and Wilusz, J. (2013). Approaches for the Identification and Characterization of RNA-Protein Interactions. Biophysical approaches to translational control of gene expression, Biophysics for the Life Sciences, J. D. Dinman (eds). Springer: 199-212.
- Ryder, S. P., Recht, M. I. and Williamson, J. R. (2008). Quantitative analysis of protein-RNA interactions by gel mobility shift. Methods Mol Biol 488: 99-115.
- Thomas, J., Palusa, S. G., Prasad, K. V., Ali, G. S., Surabhi, G. K., Ben-Hur, A., Abdel-Ghany, S. E. and Reddy, A. S. (2012). Identification of an intronic splicing regulatory element involved in auto-regulation of alternative splicing of SCL33 pre-mRNA. Plant J 72(6):935-946.
- Wilusz, J. and Shenk, T. (1988). A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell 52(2): 221-228.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Palusa, S. G. and Reddy, A. S. N. (2013). Analysis of RNA-protein Interactions Using Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (Gel Shift Assay). Bio-protocol 3(22): e967. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.967.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Interaction
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Molecular Biology > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










