- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Homologous Recombination Assay
Published: Vol 3, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.914 Views: 19490
Reviewed by: Lin FangFanglian He

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Measurement of the Intracellular Calcium Concentration with Fura-2 AM Using a Fluorescence Plate Reader
Magdiel Martínez [...] Walter I. Silva
Jul 20, 2017 33952 Views

SMART (Single Molecule Analysis of Resection Tracks) Technique for Assessing DNA end-Resection in Response to DNA Damage
Angela Altieri [...] Alfano Luigi
Aug 5, 2020 6060 Views
Abstract
Repair of double strand break by homologous recombination was examined using U2OS cells or RG37 cells harbouring specific substrate developed by Puget et al. (2005) and Dumay et al. (2006), respectively, to measure the repair of DNA double strand breaks by homologous recombination. The substrate is composed of two inactive copies of the GFP gene. The upstream copy is inactive due to the absence of promoter, the downstream copy present a promoter but is inactivated by the insertion of the sequence coding for the recognition site of the I-SceI enzyme. The substrate is stably expressed in cells after its insertion in the genome and present as a unique copy. The unique DNA double strand break is then induced by the expression of the I-SceI enzyme after cell transfection with a plasmid coding for the I-SceI enzyme.
Keywords: DNA double strand break repairMaterials and Reagents
- U2OS or RG37 cell lines
Note: U2OS are osteosarcoma cells with active p53 pathway, RG37 are SV40-immortalized human fibroblasts with inactive p53 pathway. There are cells harbouring the substrate designed to measure Homology Directed repair. However, any cell line in which the HDR substrate has been inserted can be used.
- Culture medium (serum-free medium)
- siRNA for gene of interest (for example rad51, its depletion decreases the efficiency of repair of a DNA DSB by homologous recombination)
- Plasmid pcDNA3myc-NLS-I-SceI (coding for I-SceI created by Puget et al. (2005))
- INTERFERin Transfection Reagent (Ozyme, catalog number: POL409-10 )
- JetPEI Transfection Reagent (Ozyme, catalog number: POL101-10 )
- Trypsin
- Glycerol
- SDS
- Beta-mercaptoethanol
- Bromophenol blue
- Laemmli buffer (see Recipes)
- Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 35 mm tissue culture plate
- Tissue culture set up (e.g. 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator)
- Flow cytometer
- Western blotting apparatus
Procedure
- Plate 100,000 cells (U2OS or RG37) per 35 mm diameter plate at the end of the afternoon. Cells are cultured in humidified atmosphere in a cell incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
- Let attach overnight.
- Transfect with siRNA using INTERFERin according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use 10 nM of siRNA mixed in 200 μl of serum-free medium with 8 μl of INTERFERin.
- 24 h later, change the medium and transfect with the plasmid coding for I-SceI in order to induce DNA double strand breaks in the GFP copy harboring the I-SceI recognition site. Use 1 μg of plasmid per plate. Transfect using JetPEI according to the manufacturer’s instructions by mixing 1 μg of I-SceI plasmid in 200 μl of NaCl (150 mM) with 2 μl of JetPEI.
- In the following morning wash the cells with PBS and change the medium.
- Let incubate for 48 h after plasmid transfection.
- Harvest cells by trypsin treatment.
- Separate cells in two tubes. Use half of the cells to prepare cell extracts by adding Laemmli buffer in order to check siRNA effect and I-SceI expression by Western blotting.
- Wash the other half of the cells with PBS.
- Resuspend in PBS and analyze by flow cytometry to detect GFP positive cells. GFP positive cells represent the cell population in which the DNA double strand break induced at the I-SceI site has been repaired by homologous recombination. Quantify by examining at least 25,000 events per condition.
Note: First, as a negative control use cells not transfected with the I-SceI plasmid in order to define the window for the detection of negative cells for GFP expression. Then, use a sample of cells transfected with the I-SceI plasmid to obtain a sub population of GFP positive cells that are cells having repaired DNA breaks by homologous recombination (Figure 1).
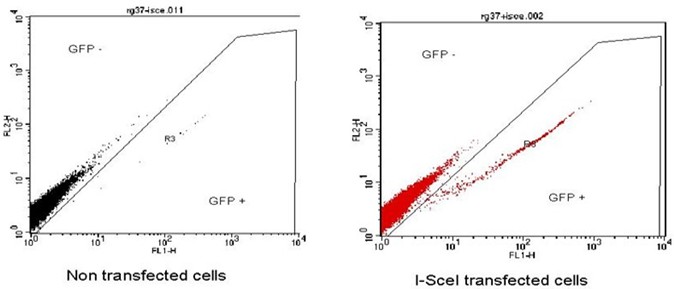
Figure 1. Example of FACS acquisition. Left panel, the majority of the cells are GFP negative only 0.06% are GFP positive. Right panel, cells transfected with the I-SceI plasmid, we observe the appearance of a population of GFP positive cells 1.8% present in the R3 region.
Recipes
- Laemmli buffer
Tris HCl pH 6.8 (60 mM)
10% glycerol
2% SDS
5% beta-mercaptoethanol
0.01% bromophenol blue
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
135 mM NaCl
2.5 mM KCl
10 mM Na2HPO4
1.75 mM KH2PO4
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from previous works by Dumay et al. (2006) and Puget et al. (2005). We acknowledge the use of the Toulouse Rio Imaging facilities for flow cytometry analysis. This work was supported by grants from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (D. Trouche; équipe labellisée), the Association de Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC) as a Programme ARC, the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (Projet 2011 blanc SVSE8 PinGs), and by an Electricité de France grant (Y. Canitrot).
References
- Courilleau, C., Chailleux, C., Jauneau, A., Grimal, F., Briois, S., Boutet-Robinet, E., Boudsocq, F., Trouche, D. and Canitrot, Y. (2012). The chromatin remodeler p400 ATPase facilitates Rad51-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks. J Cell Biol 199(7): 1067-1081.
- Dumay, A., Laulier, C., Bertrand, P., Saintigny, Y., Lebrun, F., Vayssiere, J. L. and Lopez, B. S. (2006). Bax and Bid, two proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members, inhibit homologous recombination, independently of apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 25(22): 3196-3205.
- Puget, N., Knowlton, M. and Scully, R. (2005). Molecular analysis of sister chromatid recombination in mammalian cells. DNA Repair (Amst) 4(2): 149-161.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Canitrot, Y. and Trouche, D. (2013). Homologous Recombination Assay . Bio-protocol 3(18): e914. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.914.
-
Courilleau, C., Chailleux, C., Jauneau, A., Grimal, F., Briois, S., Boutet-Robinet, E., Boudsocq, F., Trouche, D. and Canitrot, Y. (2012). The chromatin remodeler p400 ATPase facilitates Rad51-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks. J Cell Biol 199(7): 1067-1081.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Cell biology assays > Metabolism
Cancer Biology > Genome instability & mutation > Biochemical assays > DNA structure and alterations
Cell Biology > Cell-based analysis > Flow cytometry
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











