- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Detection of DNA Methylation Changes Surrounding Transposable Elements
Published: Vol 3, Iss 11, Jun 5, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.784 Views: 11696
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Efficient Transient Gene Knock-down in Tobacco Plants Using Carbon Nanocarriers
Gozde S. Demirer and Markita P. Landry
Jan 5, 2021 6381 Views

Faster Bacterial Gene Cloning Using the Brick into the Gateway (BiG) Protocol
Flaviani G. Pierdoná [...] Fabio T. S. Nogueira
Dec 20, 2022 2353 Views
Abstract
Transposable elements (TEs) are a major component of all genomes, thus the epigenetic mechanisms controlling their activity is an important field of study. Cytosine methylation is one of the factors regulating the transcription and transposition of TEs, alongside Histone modifications and small RNAs. Adapter PCR-based methods [such as Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP)] have been successfully used as high-throughput methods to genotype un-sequenced genomes. Here we use methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes, in combination with PCR on adaptor-ligated restriction fragments, to evaluate epigenetic changes in TEs between genomic DNA samples.
Keywords: DNA methylationMaterials and Reagents
- Two oligonucleotides which form the double-stranded adapter, with an overhang complementary to the overhang of the restriction enzyme used. In the case of HpaII or MspI, the overhang is a 5' CG, and the adapter sequences are 5'-GATCATGAGTCCTGCT-3' and 5'-CGAGCAGGACTCATGA-3'. The two nucleotides at the 5' end of the latter oligonucleotide will constitute the 5' CG overhang, after hybridization of the two sequences (black rectangles in Figure 1, Shaked et al., 2001). These oligonucleotides should be designed such that they do not resemble know sequences in the examined species.
- Pre-selective primers, one complementary to the adapter with the addition of a G nucleotide at the 3' end (5'-ATCATGAGTCCTGCTCGG-3'; primer P2 in Figure 1), and the other complementary to the TE of interest (primer P1 in Figure 1). The TE-specific primer should be designed as a reverse-complement of the 5' end of the TE with a Tm=60 °C, between 30-50 bp into the TE (to allow for sequence validation in downstream assays). Restriction enzyme recognition sites (CCGG) between the primer and the 5' end of the TE should be avoided.
- Selective primers, one identical to the above TE-specific primer with the addition of a fluorescent tag (e.g. 6-FAM) or radioactive tag (end label with 32P), and one similar to the pre-selective primer complementary to the adapter with the addition of random nucleotides at the 3' end (e.g. 5'-CATGAGTCCTGCTCGGTCAG-3', includes an extra TCAG at the 3' end).
- NaCl
- T4 DNA ligase and buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0202 )
- Restriction enzymes HpaII and MspI (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0171 and R0106 )
- Taq DNA polymerase and Taq DNA polymerase buffer (EURx, catalog number: E2500 )
- MgCl2
- dNTP mix
- Polynucleotide Kinase (PNK) enzyme and PNK buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0201 )
- Gamma-phosphate (32P)-labeled ATP (or fluorescently-labeled primers)
- GS-500 ROX-labeled size standard (for fluorescently-labeled products only) (Applied Biosystems)
- Hi-Di Formamide (for fluorescently-labeled products only) (Applied Biosystems, catalog number: 4311320 )
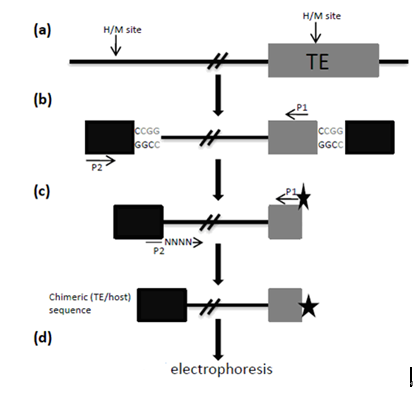
Figure 1. An overview of the TMD method, adapted from (Yaakov and Kashkush, 2011). The method steps include: (a) Restriction of genomic DNA with HpaII (H) or MspI (M); (b) The first round of PCR amplification, using a primer from within the TE (P1) and a primer from the adapter (P2); (c) The second round of PCR amplification, using primer P1 from within the TE, labeled with a radioactive or fluorescent tag, and primer P2 with the addition of random nucleotides at the 3' end; and (d) Electrophoresis of the resulting PCR amplicons on a polyacrylamide gel (in the case of a radioactive tag) or in a capillary fluorescence detection machine (in the case of a fluorescent tag).
Equipment
- Thermal cycler
- Agarose gel electrophoresis machine
- 43 cm PAGE machine (Thermo Scientific Owl Aluminum-Backed Sequencer S3S, for radiolabeled products only)
- Capillary electrophoresis machine (such as the Applied Biosystems 3730xl DNA analyzer; for fluorescently-labeled products only)
Procedure
- Adapter pair preparation
- Mix the two adapter oligonucleotides to a final concentration of 250 ng/μl.
- Incubate them at 95 °C for 5 min and then at room temperature for 10 min.
- Mix the two adapter oligonucleotides to a final concentration of 250 ng/μl.
- Restriction/Ligation
- Add to a 0.2 ml tube: 1 μl of 10x ligase buffer, 1 μl of 0.5 M NaCl, 1 μl of the adapter pair 120 units of T4 ligase, 2 units of HpaII or MspI, 300-500 ng of genomic DNA and ddH2O to a final volume of 10 μl.
- Mix well and incubate at 37 °C for 2-3 h.
- Dilute reaction 1: 10 by adding 90 μl of ddH2O.
- This reaction can be stored at -20 °C.
- Add to a 0.2 ml tube: 1 μl of 10x ligase buffer, 1 μl of 0.5 M NaCl, 1 μl of the adapter pair 120 units of T4 ligase, 2 units of HpaII or MspI, 300-500 ng of genomic DNA and ddH2O to a final volume of 10 μl.
- Pre-selective amplification
- Add to a 0.2 ml tube: 2 μl of 10x Taq DNA polymerase buffer, 2 μl of 25 mM MgCl2, 0.8 μl of dNTP mix, 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase, 1 μl of 50 ng μl-1 adapter-specific pre-selective primer, 1 μl of 50 ng/μl transposon-specific primer, 4 μl of Restriction/Ligation reaction products (cut with HpaII or MspI) and ddH2O to a final volume of 20 μl.
- Use the thermal cycler to PCR with the following program:
- 94 °C for 3 min
- 94 °C for 30 s
- 60 °C for 30 s
- 72 °C for 1 min
Return to step b 29 times
- 94 °C for 3 min
- Run 10 μl of the resulting products on a 1.5% agarose gel to validate amplification.
- Dilute the remaining 10 μl with 190 μl of ddH2O.
- This reaction can be stored at -20 °C.
- Add to a 0.2 ml tube: 2 μl of 10x Taq DNA polymerase buffer, 2 μl of 25 mM MgCl2, 0.8 μl of dNTP mix, 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase, 1 μl of 50 ng μl-1 adapter-specific pre-selective primer, 1 μl of 50 ng/μl transposon-specific primer, 4 μl of Restriction/Ligation reaction products (cut with HpaII or MspI) and ddH2O to a final volume of 20 μl.
- Radiolabeling
- For 20 reactions, add to a 0.2 ml tube: 6 μl of ddH2O, 6 μl of transposon-specific primer, 2 μl of 10x PNK buffer, 1 μl of PNK and 5 μl of radiolabeled ATP.
- Mix well and incubate at 37 °C for 1 h and then at 70 °C for 10 min.
- For 20 reactions, add to a 0.2 ml tube: 6 μl of ddH2O, 6 μl of transposon-specific primer, 2 μl of 10x PNK buffer, 1 μl of PNK and 5 μl of radiolabeled ATP.
- Selective amplification
- Add to a 0.2 ml tube: 2 μl of 10x Taq DNA polymerase buffer, 2 μl of 25 mM MgCl2, 0.8 μl of dNTP mix, 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase, 1 μl of 50 ng μl-1 adapter-specific selective primer, 1 μl of radiolabeled (or fluorescently labeled) transposon-specific primer, 3 μl of pre-selective amplification PCR products and ddH2O to a final volume of 20 μl.
- Use the thermal cycler to PCR with the following program:
- 94 °C for 2 min.
- 63 °C for 30 sec (decrease temperature by 1 °C every cycle until 56 °C).
- 72 °C for 1 min.
Return to step b 32 times.
- 94 °C for 2 min.
- Run the resulting products on a denaturing 5% polyacrylamide gel (for radio-labeled products, see Figure 2 for an example); or add 0.5 μl of GS-500 ROX-labeled size standard, 1-2.5 μl of PCR product (add less PCR product if fluorescence intensity is too high) and complete to 13 μl with formamide (for fluorescently-labeled products only).
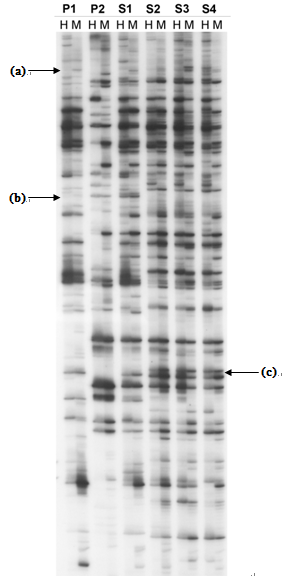
Figure 2. An example (Yaakov and Kashkush, 2011) of an autoradiogram showing TMD products for 6 DNA samples representing two parental plants (P1 and P2) and their allopolyploid offspring (S1-S4). The TE analyzed is a Stowaway-like miniature inverted repeat transposable element (MITE), called Thalos. Arrow (a) shows a change in methylation between S1 and S2, as only the MspI band is present in P1 and S1-S2, but both HpaII and MspI bands are present in S3-S4. The disappearence (b) or appearance (c) of bands can also be seen, which may arise as a result of complete methylation of the restriction site, or a mutation in the restriction or primer binding sites. The total percent methylation of all sites for a given sample analyzed can be calculated by dividing the number of polymorphic sites (those resenting bands for only one restriction enzyme) by the total number of sites (presenting bands for one and both restriction enzymes).
- Add to a 0.2 ml tube: 2 μl of 10x Taq DNA polymerase buffer, 2 μl of 25 mM MgCl2, 0.8 μl of dNTP mix, 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase, 1 μl of 50 ng μl-1 adapter-specific selective primer, 1 μl of radiolabeled (or fluorescently labeled) transposon-specific primer, 3 μl of pre-selective amplification PCR products and ddH2O to a final volume of 20 μl.
Acknowledgments
The transposon methylation display method (TMD) was adapted from the amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) (Vos et al. 1995), and used first by Shaked et al. (2001). This work was supported by a grant from the Israel Science Foundation (grant # 142/08) to Khalil Kashkush.
References
- Kashkush, K. and Khasdan, V. (2007). Large-scale survey of cytosine methylation of retrotransposons and the impact of readout transcription from long terminal repeats on expression of adjacent rice genes. Genetics 177(4): 1975-1985.
- Shaked, H., Kashkush, K., Ozkan, H., Feldman, M. and Levy, A. A. (2001). Sequence elimination and cytosine methylation are rapid and reproducible responses of the genome to wide hybridization and allopolyploidy in wheat. Plant Cell 13(8): 1749-1759.
- Vos, P., Hogers, R., Bleeker, M., Reijans, M., van de Lee, T., Hornes, M., Frijters, A., Pot, J., Peleman, J., Kuiper, M. and et al. (1995). AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23(21): 4407-4414.
- Yaakov, B. and Kashkush, K. (2011) Massive alterations of the methylation patterns around DNA transposons in the first four generations of a newly formed wheat allohexaploid. Genome 54: 42-49.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Yaakov, B. and Kashkush, K. (2013). Detection of DNA Methylation Changes Surrounding Transposable Elements. Bio-protocol 3(11): e784. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.784.
Category
Systems Biology > Epigenomics > DNA methylation
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > DNA > DNA modification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











