- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolation of Lipid Rafts from Cultured Mammalian Cells and Their Lipidomics Analysis
(*contributed equally to this work) Published: Vol 10, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2020 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3670 Views: 5685
Reviewed by: Alka MehraAmit Kumar DeyZijian Zhang

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Analysis and Quantification of the Mitochondrial–ER Lipidome
Alexis Diaz-Vegas [...] James G. Burchfield
Jul 5, 2024 2580 Views

Leveraging Circular Polymerization and Extension Cloning (CPEC) Method for Construction of CRISPR Screening Libraries
Bengisu Dayanc [...] Serif Senturk
Feb 20, 2025 2775 Views

Cost-Effective and Reproducible Preparation of mRNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticles Using a Conventional Laboratory-Scale Microfluidic Assembly System
Yunqi Li [...] Ruoyang Zhao
Sep 20, 2025 1444 Views
Abstract
Lipid rafts are distinct liquid-ordered domains of plasma membranes of most eukaryotic cells providing platform for signaling pathways. Lipid composition of rafts is critical for their structural integrity and for regulation of signaling pathways originating from rafts. Here we provide a protocol to isolate lipid rafts from cultured human and animal cells and comprehensively analyse their lipid composition.
Keywords: Lipid raftsBackground
Lipid rafts are distinct cholesterol- and sphingomyelin-rich structures in cell membranes, immersed into liquid-disordered surrounding membrane (Lingwood and Simons, 2010). They provide a “solid” platform to spatially organize elements of various signaling pathways as well as exo- and endocytosis machineries. The functional properties of lipid rafts are determined by interaction between raft lipids and proteins. Changes in raft lipid composition, both physiological and pathological, have striking consequences for the activity of the pathways originating from rafts and represent an important and underappreciated layer of their regulation. Isolation of lipid rafts is complicated by their dynamic nature and heterogeneity. Methods of raft isolation based on their resistance to detergents have been consistently criticized (Gaus et al., 2005). Here we describe a detergent-free method for isolating lipid rafts and establishing their lipid composition using comprehensive lipidomics analysis. One example of using this protocol has been recently published (Mukhamedova et al., 2019).
Part I: Isolation of Lipid Rafts
The protocol described below was used to isolate rafts from RAW 264.7 murine macrophages, THP-1 human macrophages and SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells, but is applicable to most cultured mammalian cells.
Materials and Reagents
- 12 ml ultracentrifuge tubes (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 344059 )
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf Safe-Lock Tube
- Spinal needle (BD, catalog number: 405256 )
- 75 cm2 flask
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS)
- OptiPrepTM Density Gradient Medium (iodixanol solution, Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D1556-250ML )
- Complete Protease inhibitors cocktail tablets (Roche, catalog number: 0 4906837001 )
- Complete Phosphatase inhibitors cocktail tablets (Roche, catalog number: 0 4693124001 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
- Na2HPO4·2H2O
- KH2PO4
- Tris hydrochloride (Tris-HCl)
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)
- Triton X-100
- Sucrose
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS; pre-made or see Recipes)
- RPMI media
- PBS (ice cold) (see Recipes)
- Solution A (see Recipes)
- Solution B (diluent) (see Recipes)
- Solution C (working solution) (see Recipes)
- Solution D (resuspension medium 1) (see Recipes)
- Solution E (resuspension medium 2) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes
- Centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Allegra X-15R )
- Ultracentrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Optima MAX-TL )
- Ultracentrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Optima L-90K )
- Two-chamber gradient former (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z340391 )
- Misonix sonicator S-4000 with micro tip
- Swing bucket rotor (SW41 Ti or similar)
- CO2 incubator
- -80 °C freezer
Procedure
This protocol is based on technical manuals from Alere Technologies AS, Norway.
- Seed cells in 2 x 75 cm2 flask at density 2.5 x 106 cells per flask in 9.5 ml of RPMI media containing 10% FBS. Incubate in CO2 incubator for 48 h at 37 °C. The duration should be optimized depending on a specific cell line. We recommend seeding at 30% confluency.
Note: All following procedures are carried on ice.
- Wash cells twice with cold PBS (7ml).
- Scrape cells and spin for 5 min at 1,000 x g at 4 °C. Remove supernatant.
- Prepare a membrane fraction by a hypo-osmotic shock:
- Add 1 ml cold 5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) containing complete cocktail of protease and phosphatase inhibitors (1 tablet/7 ml). Leave on ice for 30 min. Vortex every 10 min.
- Place in freezer for 15-30 min (until it freezes), then thaw on ice.
- Spin down cellular debris at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C. Collect supernatant.
- Spin supernatant in ultracentrifuge using fixed angle rotor 350,000 x g for 90 min at 4 °C.
- Re-suspend the pellet (membrane fraction) in 1 ml of solution D in a suitable tube (e.g., 1.5 ml Eppendorf Safe-Lock Tube).
- Place the tube on ice and introduce the tip of a sonicator probe (approx. diameter 3 mm) to a point equidistant from the top and bottom of the suspension.
- Sonicate once for 4 s at a total power of 25 J/W per second. Spin down undissolved particles. Estimate protein concentration by Bradford method using buffer D as blank. Adjust sample volume to 2.16 ml with buffer D.
- Mix sample with 1.84 ml of solution C. The final iodixanol concentration is 23% (w/v).
- Produce two gradient solutions: 10% (w/v) iodixanol (ρ = 1.076 g/ml) and 20% (w/v) iodixanol (ρ = 1.125 g/ml) by diluting solution C with solution E (1:4 and 2:3 v/v respectively).
- Produce 8 ml continuous 10-20% iodixanol gradient in a 12 ml ultracentrifuge tube using a standard two chamber gradient former. Put gradient former on magnetic stirrer. Pour 4 ml of 20% iodixanol into reservoir chamber and 4 ml of 10% iodixanol into mixing chamber (put small magnetic stirrer bar into the latter). Place tubing from mixing chamber valve into ultracentrifuge tube, open interconnecting valve, start form linear gradient. We recommend to use this gradient solution the same day, but it can be kept overnight in a fridge.
Note: For processing multiple samples or if gradient former is not available, an alternative protocol for preparation of continuous gradient may be more suitable.- Produce two gradient solutions: 10% (w/v) iodixanol (ρ = 1.076 g/ml) and 20% (w/v) iodixanol (ρ = 1.125 g/ml) by diluting solution C with solution E (1:4 and 2:3 v/v respectively to a final volume of 5 ml each).
- Mix the 10% and 20% gradient solutions at ratio 2:1 (v/v) to produce a 13.3% gradient solution (final volume 2.5 ml).
- Mix the 10% and 20% gradient solutions at ratio 1:2 to produce a 16.7% gradient solution (final volume 2.5 ml).
- Gently add 2 ml of the 20% solution to a 12 ml ultracentrifuge tube, ensuring that there are no bubbles.
- Cover the tube with Parafilm and freeze the solution at -80 °C until solution is completely frozen (approximately 30 min). Ensure that tubes are kept vertical.
- Repeat Steps 4 and 5 by layering the 16.7% gradient solution above the frozen layer. This is followed by the 13.3% and finally the 10% solution.
- Store formed gradient solutions in a freezer at -80 °C until required.
- Retrieve the tubes 18 h prior to spin and keep them at 4 °C to thaw.
- Retrieve tubes at least 2 h prior to spin and keep them at room temperature.
- Underlay the gradient with 4 ml of the sample using long spinal needle and centrifuge at 52,000 x g for 90 min at 4 °C using swing bucket rotor (SW41 Ti or similar).
- Collect the top 5 ml of the gradient, transfer to a new centrifuge tube and mix with 4 ml of solution C.
- Produce two OptiPrep gradient solutions, 5% and 15% (dilute solution C with solution E (100 µl + 900 µl and 450 µl + 1,050 µl respectively).
- Place 1.0 ml of 15% and 0.5 ml of 5% OptiPrep solutions over the sample and centrifuge at 52,000 x g for 90 min at 4 °C.
- Collect approximately 20 aliquots (100 µl each) from the top.
- Analyse fractions by Western Blot for protein markers and/or proceed to lipidomics analysis.
Expected Results
The example of lipid raft isolation from SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells is shown in Figure 1. In this experiment cellular cholesterol was trace-labelled with [3H]cholesterol (see Low et al., 2012) for labeling methodology) and fractions with maximum concentration of labelled cholesterol were defined as raft fractions (fractions 5-9). An example of using flotillin-1 (membrane protein abundantly present in lipid rafts and considered a raft marker) to identify lipid raft fractions has been recently published and also showed maximum abundance of this marker in fractions 5-9 (Mukhamedova et al., 2019).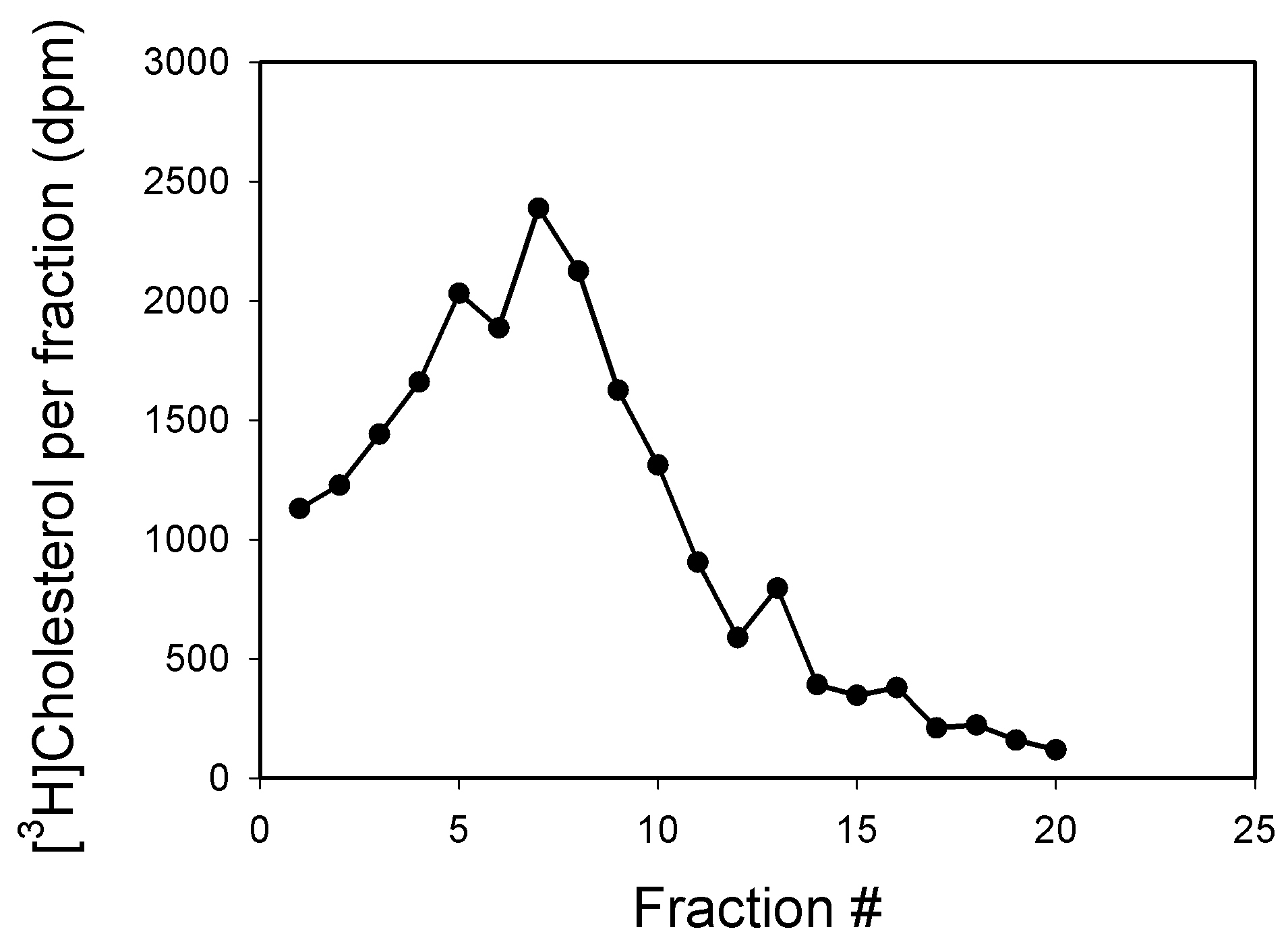
Figure 1. Representative profile of gradient centrifugation of plasma membranes from SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells
Recipes
- PBS (ice cold)
Purchase as a pre-made solution or tablets from multiple suppliers or prepare manually:
137 mM (8 g/L) NaCl
2.7 mM (0.2 g/L) KCl
10 mM (1.44 g/L) Na2HPO4·2H2O
1.8 mM (0.24 g/L) KH2PO4, pH to 7.4 - Solution A
OptiPrep (60% iodixanol, ρ = 1.32 g/ml) - Solution B (diluent)
0.25 M sucrose
6 mM EDTA
120 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6 - Solution C (working solution)
50% iodixanol (ρ = 1.282 g/ml)
Mix 5 vol. of solution A with 1 vol. of solution B - Solution D (resuspension medium 1)
0.25 M sucrose
1 mM EDTA
20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6 + complete protease and phosphatase inhibitors cocktails - Solution E (resuspension medium 2)
0.25 M sucrose
1 mM EDTA
20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6
Part II: Lipidomics Analysis of Lipid Rafts
This lipidomics protocol provides quantification of a large range of lipid species relative to appropriate internal standards. It is recognized that it is not possible to provide stable isotope internal standards for each lipid species and that differences between the response factors of the analytes and the corresponding internal standards are not adjusted for. Thus, the lipidomic measures should be considered as relative, rather than absolute, quantification.
Materials and Reagents
- Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030125.150)
- ZORBAX eclipse plus C18 column (2.1 x 100 mm 1.8 μm) (Agilent, catalog number: 959758-902)
- Chloroform (Merck, catalog number: 1.02445.2500)
- Methanol (Merck, catalog number: 1.06018.2500)
- Butanol (Merck, catalog number: 1.01988.2500)
- Ammonium formate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 516961-100G)
- Internal Standards (varies depending on requirements)
- Isopropanol (Merck, catalog number: 1010404000)
- Acetonitrile (Merck, catalog number: 1000292500)
- SPLASH® LIPIDOMIX® Mass Spec Standard, methanol solution (Avanti, catalog number: 330707, also refer to Recipes section)
- Deionized (MilliQ) H2O
- Liquid chromatography Solvent A (see Recipes)
- Liquid chromatography Solvent B (see Recipes)
- Extraction solvent (see Recipes)
- Water saturated butanol (see Recipes)
- Methanol with ammonium formate (see Recipes)
- Internal standard mix (see Recipes)
Equipment
- SpeedVac (Thermo Scientific Savan RVT5105 refrigerated vapour trap)
- Sonicator bath (Soniclean 500TD sonicator)
- Positive displacement pipettes (Gilson)
- Vortex mixer (Ratek VM1)
- Benchtop centrifuge (Beckman Coulter Microfuge 22R ccentrifuge)
- Rotary Mixer (Ratek)
- Agilent 6490 Triple Quadrapole Mass Spectrometer
- Agilent 1290 HPLC (Binary pump, autosampler, column compartment, divert valve)
Software
- Skyline (MacCoss Lab Software)
Procedure
- Quality control samples
- Ensure that appropriate controls are in place prior to extracting the samples. Required controls include:
- Blank solution without internal standards.
- Blank solution with internal standards (see “Recipes” for internal standards).
- Pooled quality control samples (replicates) that can be monitored for variation across the analytic run. This can be a preparation of a whole cell lysate.
- Isolation of lipids
This procedure was adapted from Weir et al. (2013). Prior to extraction, thaw internal standards to room temperature for an hour, sonicate in a sonicator bath for 15 min, then vortex.- Dry samples down in Eppendorf tubes in a SpeedVac. This will take approximately 1 h per 100 µl of sample.
- Reconstitute samples with 10 μl of MilliQ H2O. Depending on the relative concentration of each fraction, these can be pooled. In general, between 5 µg to 50 µg of protein is desirable for good lipidomic signal.
- Add 10 μl of the premixed standards using a positive displacement pipette (prewet tips in standard mix prior to use). Do not add premixed standards to the blanks.
- Add to each sample 200 μl of chloroform and methanol extraction solvent using a positive displacement pipette. For extractions where volume is below 10 μl, adjust appropriately by adding 20x volume of 2:1 chloroform methanol mixture.
- Vortex samples and mix them on a rotary mixer for 15 min.
- Sonicate samples in a sonicator bath on high (100% power) setting for 30 min. Ensure temperature of bath stays below 28 °C. The samples should be submerged partially in the water bath to ensure proper contact.
- Rest samples at room temperature for 20 min. For logistical reasons, this can be extended up to 2 h without affecting the extraction efficiency.
- Centrifuge samples at 13,000 x g for 10 min at 20 °C, ensure protein has been pelleted.
Note: If protein does not pellet, it’s likely that the water/chloroform/methanol ratio is incorrect. Salvage samples by aspiring as much of the sample as possible while avoiding any precipitated protein. - Transfer supernatant to fresh Eppendorf tubes and dry under vacuum (SpeedVac).
- Reconstitute samples in 50 µl of water saturated butanol.
- Sonicate tubes in sonicator bath for 10 min.
- Add 50 µl of methanol containing 10 mM ammonium formate.
- Centrifuge tubes for 10 min at 13,000 x g at 20 °C.
- Transfer to 0.2 ml micro-inserts in 32 x 11.6 mm glass vials with Teflon insert caps and store at -80 °C until required.
Note: It is very important to use caps that have a Teflon underlay as silica based caps leech and increase background signal.
- Settings for targeted comprehensive lipidomic analysis
Lipidomics is an advanced technique that requires a basic understanding of liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Several online resources by vendors are available as a introductory guide to the concepts and techniques (view here).
In lipidomics, liquid chromatography in conjunction with mass spectrometry is commonly used to screen hundreds of compounds in a single run. In particular, a technique using multiple reaction monitoring is widely used owing to their benefits to selectivity and sensitivity. However, the mass spectrometer can only perform a finite number of scans per given moment. Our lipidomics methodology uses liquid chorography to separate and elute lipids over a 15 min timeframe. By combining the known elution times of each lipid we can assign specific regions where a particular multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) scan would take place. Together this would reduce the amount of time spent scanning unnecessary transitions and maximize the breadth of our methodology. A figure describing this is shown in Figure 2. A brief schematic of the described approach (Liquid chromatography mass spectrometry) is presented in Figures 3 and 4.
The protocol in Section D describes an approach that identifies the specific elution time of lipids without prior knowledge.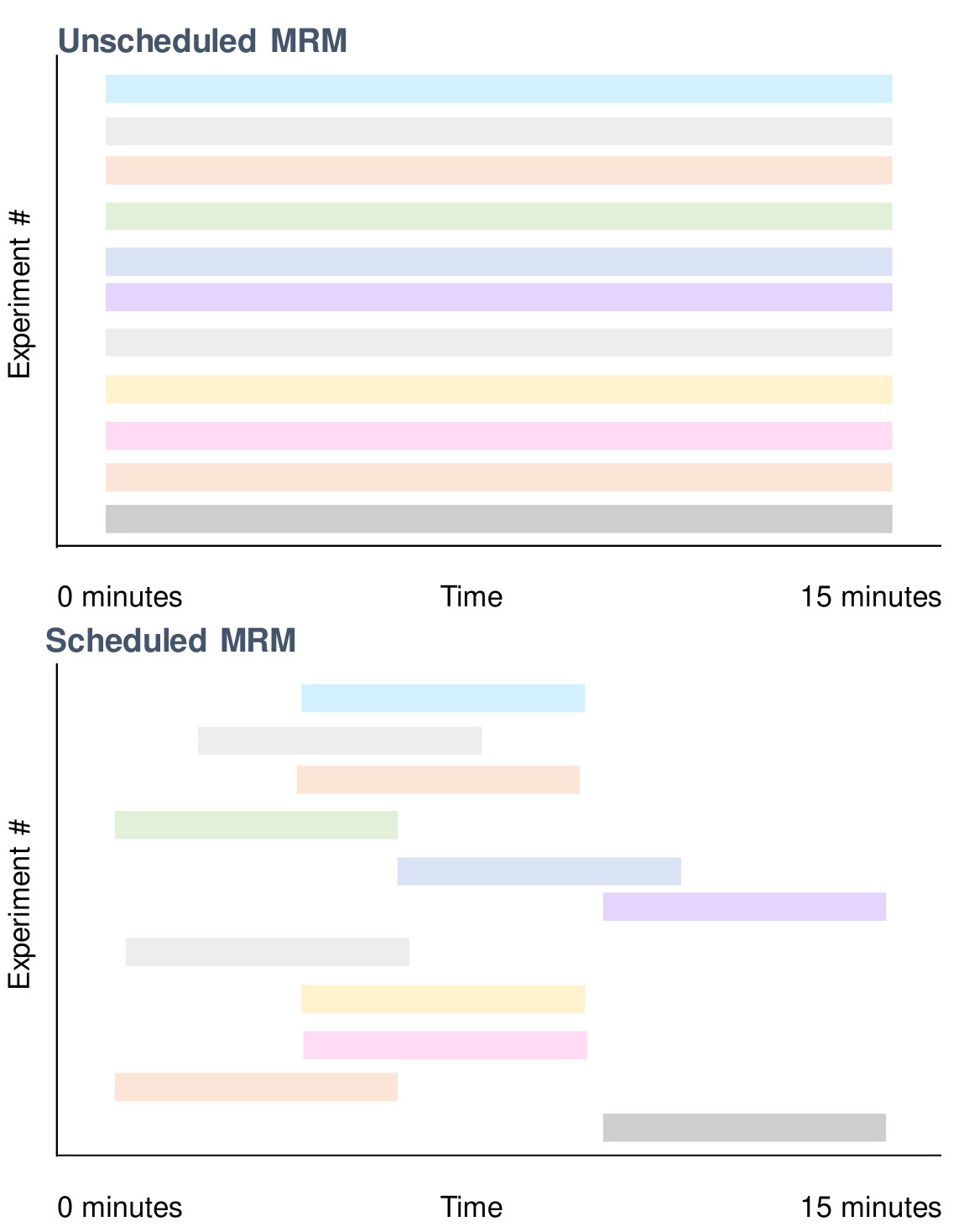
Figure 2. Utilizing scheduled MRMs to improve dwell time and reduce cycle time with reverse phase chromatography. Lipids elute at certain periods of the gradient prior to its ionization on the mass spectrometer (Figure 3). By capitalizing on this, certain scans only need to be carried out in particular time points when using schedule multiple reactions (Figure 4). This allows minimization of wasted scans where the lipid of interest does not elute. An example here is that at 15 min, only 2 scans are required (bottom) vs. 11 that is normally performed if unscheduled (top).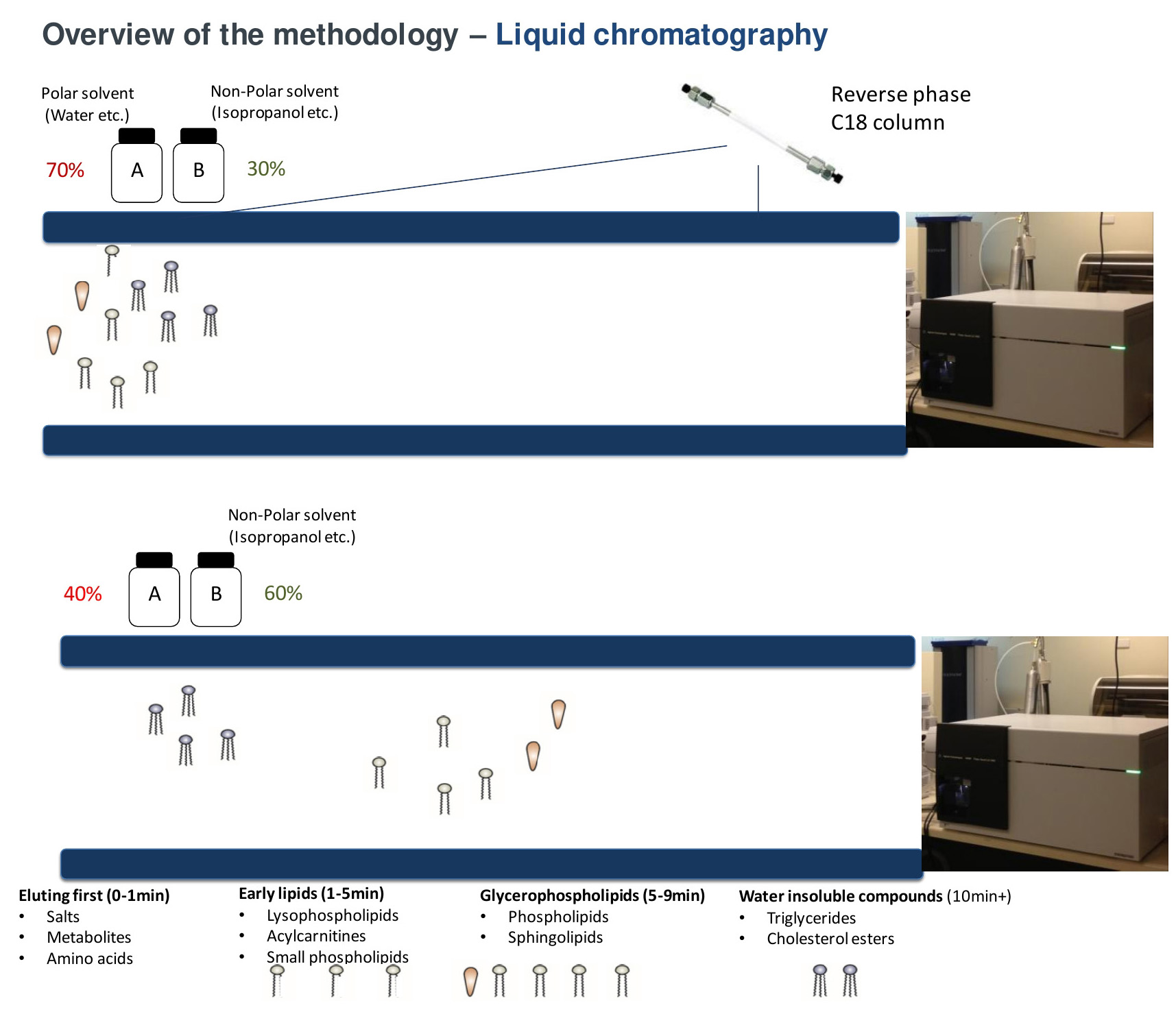
Figure 3. Separation of lipid species by reverse phase chromatography. Under reverse phase conditions, lipids are separated predominately based on its polarity. More polar compounds such as acylcarnitines elute into the mass spectrometer first with the more water insoluble compounds (cholesteryl esters, triacylglycerols) eluting last as the proportion of solvent B increases (up to 100%).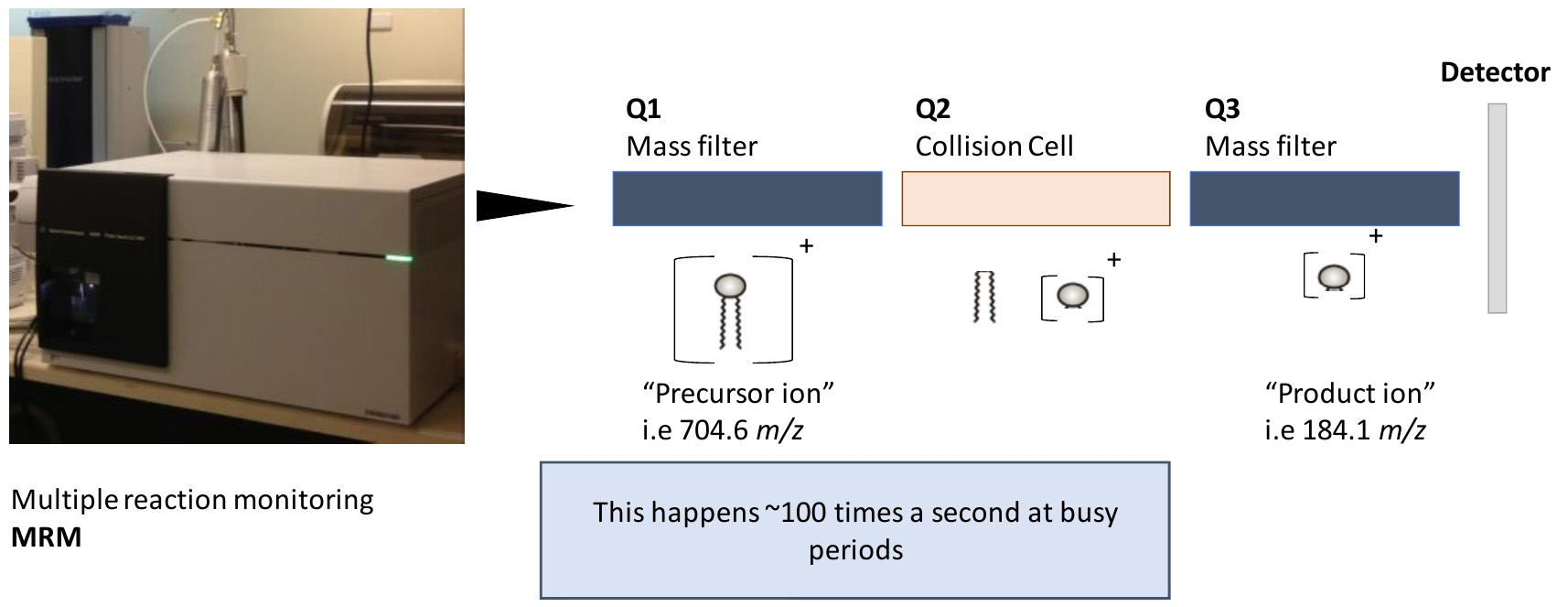
Figure 4. Examining lipids using a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. This particular workflow utilizes a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with MRM’s. MRM’s enable several experiments to take place at a given time. Each experiment has conditions that enable isolation of a particular mass at the first stage (precursor ion), followed by fragmentation (at a defined collision energy) and isolation and measurement of the fragment (product ion). Together, this enables some level of specificity when examining lipids of various sizes and classes and is the core of this particular protocol.
Principle of Scheduled multiple reaction monitoring:- Scheduled multiple reaction monitoring
Multiple reaction monitoring settings:- Precursor (Q1) and product ions (Q3) are systematically generated based on the lipid classes. A summary of the conditions used is provided in Table 1.
- The precursor transition for each lipid is developed by adding the mass of each lipid with its adduct mass, i.e., PC (34:1) is generated by adding its exact mass (759.5778) with its adduct (+H, so 1.0073).
- Targeted lipidomics analysis requires multiple reaction monitoring to maximize dwell time (the time allowed for the instrument to examine the precursor/product combination) while minimizing cycle time (the time it takes to perform all scans at a given time).
- A high dwell time is necessary for good signal reproducibility and sensitivity. In general, a minimum of 2 milliseconds is required per transition on the Agilent 6490. To achieve this, relatively small scan windows (20-60 s) are provided for each transition depending on peak shape (narrow peaks require smaller windows). However, with small scan windows, there is a risk of not scanning the compound of interest due to retention time shift (usually from column ageing or solvent composition changes with evaporation etc.) thus it is essential that accurate and appropriate scan windows are set for each lipid of interest.
- After column and solvent changeovers, a retention time-check is conducted, where the analysis is run with larger scan windows (thus reducing dwelling time but allowing visual alignment of each peak) and each transition is centered towards the MS peak of interest.
- Setting up correction factors
- In instances where an appropriate internal standard is not available for a lipid or lipid class, an estimation of lipid concentration can be determined by generating an appropriate response factor. Response factors are required as equal amount of two lipid species from different classes (and sometimes within classes) does not give equal signal on the mass spectrometer.
- This is done by running equal concentrations (i.e., 1 µM) of a standard of the lipid of interest alongside the most appropriate internal standard. The relative difference in signal is used as the response factor.
Table 1. Conditions for tandem mass spectrometry analysis of lipid species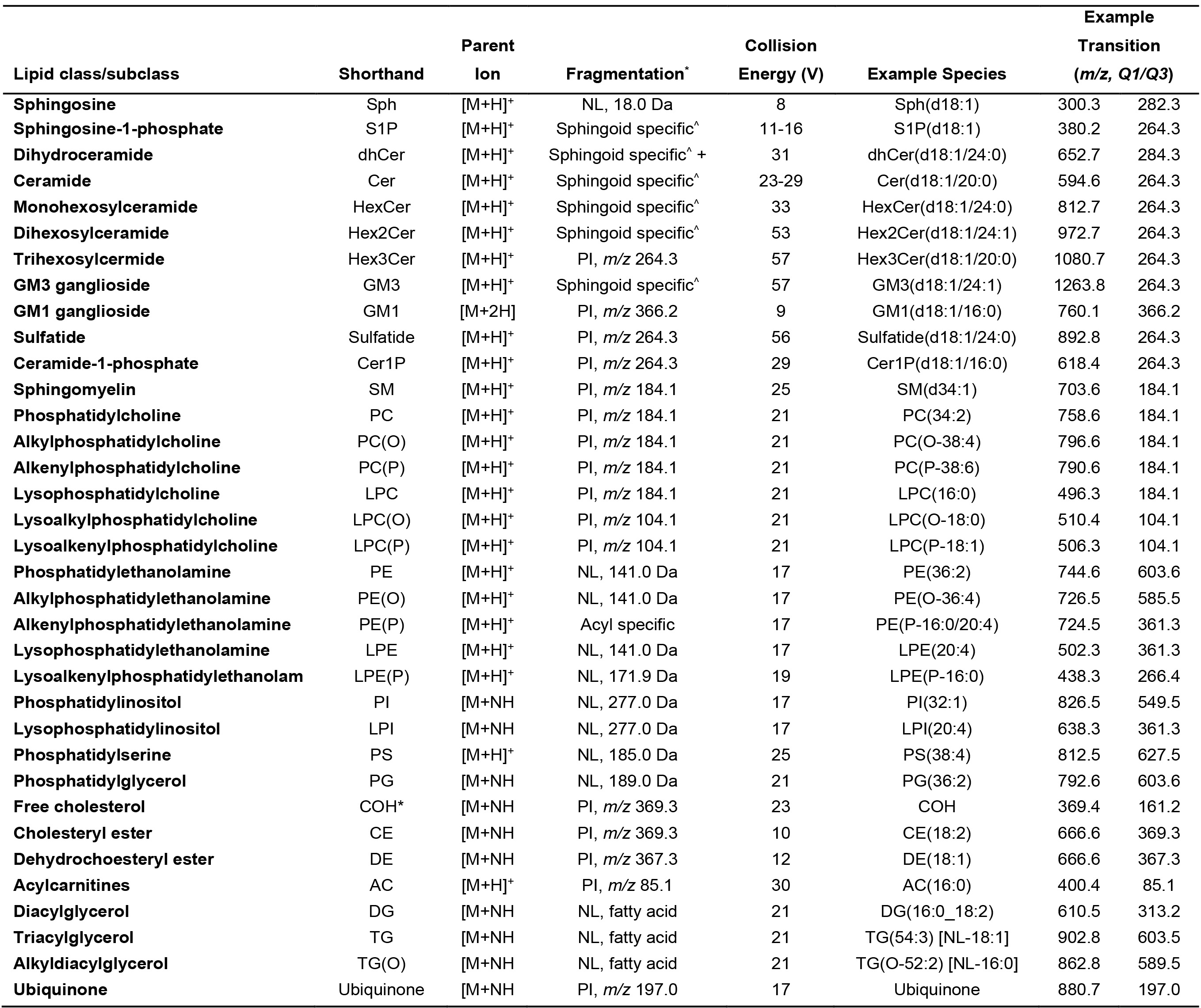
PI, product ion; NL, neutral loss, ^Sphingoid specific PI are: d18:1, 264.3, d18:0, 266.3, d16:1, 236.3, d18:2, 262.3, d17:1, 250.3, d19:1, 278.3. * COH is an insource fragment
- Scheduled multiple reaction monitoring
- Preparing the liquid chromatographer and mass spectrometer to run the samples
Current adaptation for the lipidomics methodology is from Huynh et al. (2019). Settings and conditions are reported for the Agilent 6490 QQQ mass spectrometer utilising MRM with scheduling, in conjunction with a 1290 Agilent HPLC system.
Method can be adapted to other QQQ instruments but will need to be re-optimised. Additional background / more in depth description of key concepts and parameters behind triple quadrupole mass spectrometers can be found in vendor manuals (i.e., Agilent 6400 series).- Set up Solvent A and B into the appropriate lines of the HPLC.
- Purge lines to ensure no air bubbles are present.
- Set column compartment to 60 °C and run at a flow rate of 0.4 ml/min using starting conditions (90% Solvent A, 10% Solvent B) to ensure that there are no leaks.
Note: The retention time index has to be generated in an instrument dependent manner. Due to differences in dead volume, accuracy of solvent make up and variances in the columns (even from the same manufacturer), the retention time for a single compound can vary by several seconds. - Prepare a disposable quality control sample (i.e., pooled control cells) and extract lipids.
- The chromatographic solvent gradient used is presented in Table 2. As a general rule for lipids under reverse phase conditions. Increasing acyl chain length, i.e., PC(28:0) vs. PC(30:0), will increase retention resulting in a later elution time (i.e., 5.2 to 6.2 min), while increasing the level of unsaturation, i.e., PC(30:0) vs. PC(30:1), would reduce retention resulting in an earlier elution time (i.e., 6.2 to 5.3 min). An example of this is depicted in Figure 5.
Table 2. HPLC gradient used in the lipidomic analysis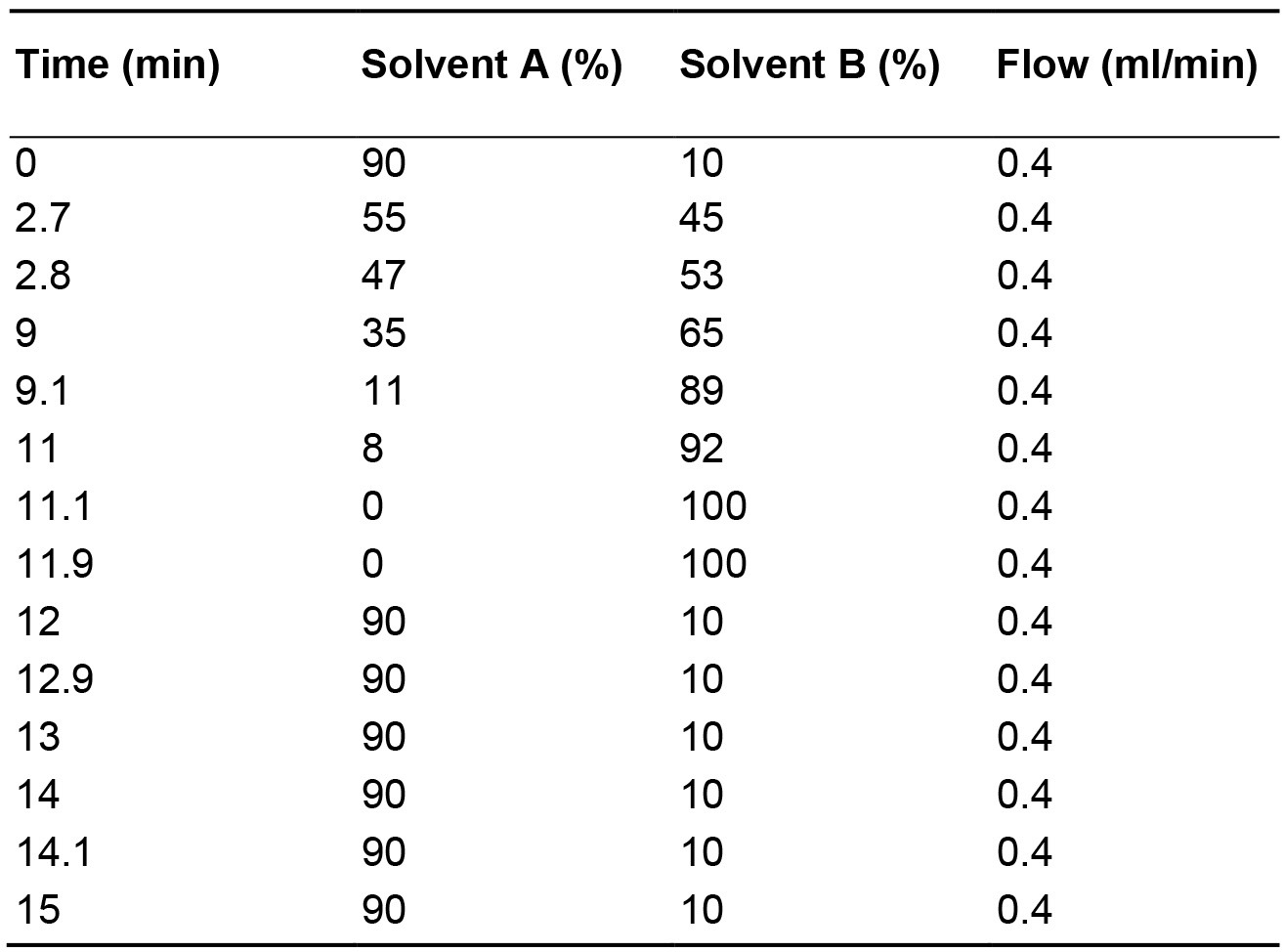
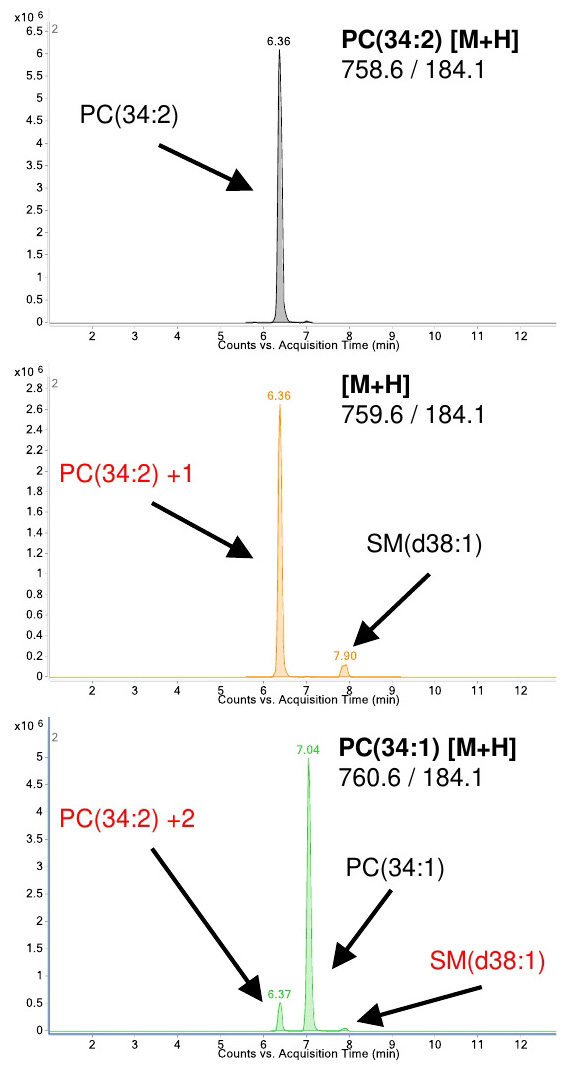
Figure 5. Identification of compounds to determine retention time for method generation. Example of the retention differences between PC(34:1) and PC(34:2). Due the prevalence of 13C in nature, approximately 1% of the signal will carry over to higher masses (i.e., 758.6 into 759.6) and eventually overlap with the monoisotopic transition of other species. Isotopes need to be accounted for and avoided (names in red) when integrating and assigning retention times for each compound. PC–Phosphatidylcholine, SM–Sphingomyelin. - Run the eluents of quality control sample as unscheduled (no retention time windows) on the mass spectrometer under the described chromatographic conditions. This will be used to determine the retention time (the time where a particular lipid elutes) for each lipid species. This retention time is used to assign a period where the mass spec performs a MRM experiment for the lipid of interest in conjunction with the known individual transitions (set of conditions with precursor ion mass, product ion mass and collision energy which are given in Table 1). The procedure is illustrated in Figures 3 and 4. This will help in scheduling lipid-specific transitions in the mass spec in the final method for the sample run (Section E of the procedure).
- Combine retention time data from the unscheduled runs of control quality sample for different lipid classes of interest into a single method. Assign retention windows dependent on peak width (as a rough guide, a 0.2 min chromatogram peak should have a window of about 0.7 min). This converts the unscheduled (time unrestricted) scans into scheduled (time dependent) scans. Figure 3 depicts an example of this.
- Run each unscheduled method using the same gradient conditions. This is then used to assign a scan window for every given lipid of interest. For example, in Figure 5, PC(34:2) (top panel) would be assigned the retention time of 6.36. The final method would then have the transitions for PC(34:2) and a retention time specified. This is a separate run for each lipid class of interest. If everything was performed in into a single unscheduled run, we would be limited to 200 measurements. We opt here to run each class unscheduled, assign retention times and scan windows, and then merge them into a single method in the end for the true samples. This requires multiple injections of a single sample in the first instance.
Note: Ensure that isotopic peaks are avoided. Isotopic peaks arise due to the existence of carbon-13 in nature at approximately 1.1% abundance. Lipids comprise of mostly carbon-12 with different species differing in masses of 1 to 2 Da. In certain situations, an extremely abundant lipid can appear over several mass ranges that overlap with the monoisotopic mass of other species. An example of PC(34:2) overlapping with PC(34:1) is shown in Figure 5. Chromatography allows for the separation of overlapping isotopic compounds. - In the method, ensure divert valve is diverting the solvent front (typically the first 1.2 min, dependent on dead volume). Due to the large amount of iodixanol and non-volatile compounds in the final extract, failure to divert will lead to large signal variation over periods where multiple samples are run due to accumulation of these molecules on the mass spectrometer source.
- Agilent 1290 HPLC settings
Autosampler set at 25 °C
Column compartment set to 60 °C
HPLC column used ZORBAX eclipse plus C18 column (2.1 x 100 mm 1.8 μm, Agilent)
Flow rate set to 0.4 ml/min - Mass spectrometry settings
Gas temperature, 150 °C
Gas flow rate 17 L/min
Nebulizer 20 psi
Sheath gas temperature 200 °C
Capillary voltage 3,500 V
Sheath gas flow 10 L/min
Cycle time of 600 ms
Q1 and Q3 isolation width is set to 0.7 amu (Unit resolution)
- Running the samples
- Thaw out glass vials containing extracted samples and let them sit at room temperature for 1 h.
- Sonicate on the sonicator bath for 15 min and vortex.
- Allow to rest at room temperature for 3 h.
- Insert samples into the autosampler.
- Insert a wash vial containing 50% butanol and 50% methanol, use this vial to wash the needle in between injections.
- Proceed with running the samples with the developed method. Typically a 5 µl injection is done on each sample, which maximizes sensitivity while not affecting chromatographic peak shape.
- Data integration and analysis
- Data can be integrated (calculating the area of the peak) using any vendor (MassHunter) or open source (Skyline) software. This provides a value for each compound and is the end point of the lipidomics work.
- Each peak area is integrated, ensuring no isotopic peak is accidently integrated.
- To determine the concentration of each lipid, the area of each lipid of interest is divided by the area of the relevant internal standard. Any appropriate correction factor is then applied (see Step C2 “Setting up correction factors”).
- Data can be further normalized to measures of raft abundance (e.g., abundance of flotillin-1 or cholesterol), protein or total phosphatidylcholine.
- An example extracted ion chromatogram (all results overlayed) and a pull out of 1 lipid species is provided in Figure 6.
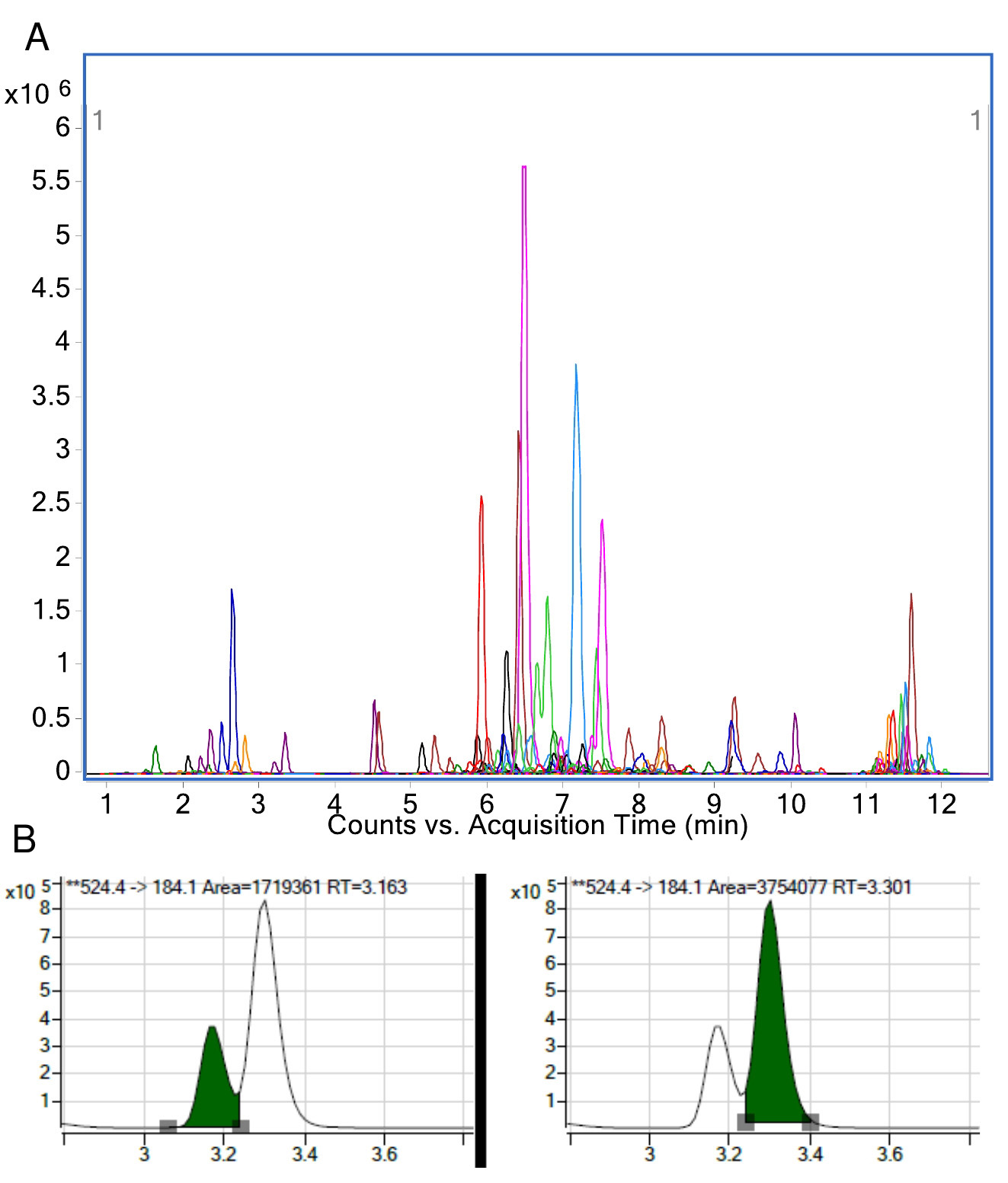
Figure 6. Example result of a plasma sample run on the targeted platform. A. Extracted ion chromatogram of all transitions measured. This represents counts (y-axis) and time (x-axis). B. An example of LPC(18:0) where each peak area is integrated separately. The resulting area is used for quantitation when calculated relative to its internal standard.
Recipes
- Liquid chromatography Solvent A
50% H2O
30% acetonitrile
20% isopropanol (v/v/v)
10 mM ammonium formate (630.6 mg per 1 L) - Liquid chromatography Solvent B
1% H2O
9% acetonitrile
90% isopropanol (v/v/v)
10 mM ammonium formate (630.6 mg per 1 L) - Extraction solvent
Chloroform:methanol mixture, 2:1 (v/v) - Water saturated butanol
- Combine equal parts of water and butanol and mix thoroughly
- Allow to rest for approx. 4 h prior to use
- Once settled, use top layer that contains butanol
- Methanol with ammonium formate
Methanol
10 mM ammonium formate (630.6 mg per 1 L) - Internal standard mix
- In-house standards can be used (with appropriate concentrations) but a pre-made standard is recommended (SPLASH® LIPIDOMIX® Mass Spec Standard)
SPLASH® LIPIDOMIX® Mass Spec Standards (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc.) comprises of:
15:0-18:1(d7) PC [160 µg/L]
15:0-18:1(d7) PE [5 µg/L]
15:0-18:1(d7) PS [5 µg/L]
15:0-18:1(d7) PG [30 µg/L]
15:0-18:1(d7) PI [10 µg/L]
15:0-18:1(d7) PA [7 µg/L]
18:1(d7) LPC [25 µg/L]
18:1(d7) LPE [5 µg/L]
18:1(d7) Chol Ester [350 µg/L]
18:1(d7) MG [2 µg/L]
15:0-18:1(d7) DG [10 µg/L]
15:0-18:1(d7)-15:0 TG [55 µg/L]
18:1(d9) SM [30 µg/L]
Cholesterol (d7) [100 µg/L] - Standards are dried down and reconstituted into the appropriate volume with the extraction solvent
- Ensure thorough mixing
- In-house standards can be used (with appropriate concentrations) but a pre-made standard is recommended (SPLASH® LIPIDOMIX® Mass Spec Standard)
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests related to this work.
Acknowledgments
The authors were supported by the grant from the National Institutes of Health (HL131473 to DS).
This protocol was modified from previous work: Mukhamedova et al. (2019) and Huynh et al. (2019).
References
- Gaus, K., Rodriguez, M., Ruberu, K. R., Gelissen, I., Sloane, T. M., Kritharides, L. and Jessup, W. (2005). Domain-specific lipid distribution in macrophage plasma membranes. J Lipid Res 46(7): 1526-1538.
- Huynh, K., Barlow, C. K., Jayawardana, K. S., Weir, J. M., Mellett, N. A., Cinel, M., Magliano, D. J., Shaw, J. E., Drew, B. G. and Meikle, P. J. (2019). High-throughput plasma lipidomics: detailed mapping of the associations with cardiometabolic risk factors. Cell Chem Biol 26(1): 71-84 e74.
- Lingwood, D. and Simons, K. (2010). Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327: 46-50
- Low, H., Hoang, A. and Sviridov, D. (2012). Cholesterol efflux assay. J Vis Exp(61): e3810.
- Mukhamedova, N., Hoang, A., Dragoljevic, D., Dubrovsky, L., Pushkarsky, T., Low, H., Ditiatkovski, M., Fu, Y., Ohkawa, R., Meikle, P. J., Horvath, A., Brichacek, B., Miller, Y. I., Murphy, A., Bukrinsky, M. and Sviridov, D. (2019). Exosomes containing HIV protein Nef reorganize lipid rafts potentiating inflammatory response in bystander cells. PLoS Pathog 15(7): e1007907.
- Weir, J. M., Wong, G., Barlow, C. K., Greeve, M. A., Kowalczyk, A., Almasy, L., Comuzzie, A. G., Mahaney, M. C., Jowett, J. B., Shaw, J., Curran, J. E., Blangero, J. and Meikle, P. J. (2013). Plasma lipid profiling in a large population-based cohort. J Lipid Res 54(10): 2898-2908.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2020 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Mukhamedova, N., Huynh, K., Low, H., Meikle, P. J. and Sviridov, D. (2020). Isolation of Lipid Rafts from Cultured Mammalian Cells and Their Lipidomics Analysis. Bio-protocol 10(13): e3670. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3670.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Molecular biology technique
Biochemistry > Lipid > Lipid isolation
Cell Biology > Cell metabolism > Lipid
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link