- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
F-actin Bundle Sedimentation Assay
(*contributed equally to this work) Published: Vol 9, Iss 21, Nov 5, 2019 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3419 Views: 5676
Reviewed by: David PaulGuillaume BompardEsteban Paredes-Osses

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Protein Structural Characterization Using Electron Transfer Dissociation and Hydrogen Exchange-Mass Spectrometry
Rupam Bhattacharjee and Jayant B. Udgaonkar
Jun 20, 2025 1776 Views

A Step-by-Step Computational Protocol for Functional Annotation and Structural Modelling of Insect Chemosensory Proteins
Rajeswari Kalepu [...] Nor Azlan Nor Muhammad
Nov 20, 2025 1664 Views

On-Column Dual-Gradient Refolding for Efficient Recovery of Insoluble Affinity-Tagged Recombinant Proteins
Anna Vlaskina [...] Maxim Patrushev
Feb 5, 2026 42 Views
Abstract
Understanding the molecular mechanism governing the higher-order regulation of actin dynamics requires chemically-defined and quantitative assays. Recently, the membrane remodeling large GTPase, dynamin, has been identified as a new actin cross-linking molecule. Dynamin regulates actin cytoskeleton through binding to, self-assembling around, and aligning them into actin bundles. Here we utilize dynamin as an example and present a simple protocol to analyze the actin bundling activity in vitro. This protocol details the method for F-actin reconstitution as well as quantitative and qualitative analyses for actin bundling activity of dynamins. Measurement of the actin bundling activity of other actin-binding proteins may also be applied to this protocol with appropriate adjustments depending on the protein of interest.
Keywords: Actin crosslinkerBackground
Dynamin is a membrane remodeling GTPase best-known for catalyzing membrane fission during clathrin-mediated endocytosis to release vesicles from the plasma membrane (McMahon and Boucrot, 2011; Schmid and Frolov, 2011; Antonny et al., 2016). In addition to its indispensable role for membrane fission, dynamin is also localized to actin-rich structures, such as lamellilpodia, dorsal membrane ruffles, and invadosomes, where it regulates actin reorganization via interacting with other actin polymerization factors (Ferguson and De Camilli, 2012). It has been discovered that the neuronal isoform of dynamin, dynamin-1 (Dyn1), could directly interact with actin filaments and facilitate the rate of actin polymerization (Gu et al., 2010). Subsequently, the ubiquitously expressed dynamin isoform, dynamin-2 (Dyn2), was also proved to be equipped with actin bundling activity and to affect the structure and stiffness of the protrusive actin-based structure, invadosome (Chuang et al., 2019). Here we detail the simple method to quantitatively analyze the actin bundling activity of Dyn1 and Dyn2. Dynamin may be substituted with other actin-binding and crosslinking proteins with proper adjustments of protein concentration, incubation time, or buffer composition in order to test their actin bundling activity.
Materials and Reagents
- 1.5 ml clear microcentrifuge tubes (Gunster biotech, catalog number: MB-E17-A)
- Rabbit muscle G-actin (Cytoskeleton, catalog number: AKL99-C)
- Recombinant human Dyn1 and Dyn2 proteins were expressed and purified as described previously (Liu et al., 2011; Chin et al., 2015)
- Protein Ladder (ARROWTEC, catalog number: PM2500)
- Tris (AppliChem, catalog number: A1086)
- CaCl2 (AppliChem, catalog number: A1873)
- ATP (Jena Bioscience, catalog number: NU-1010)
- DTT (AppliChem, catalog number: A2948)
- KCl (AppliChem, catalog number: A1362)
- MgCl2 (AppliChem, catalog number: 131396)
- SDS, 20% (w/v) solution (Bio Basic Canada Inc., catalog number: SD8119)
- Glycine (AppliChem, catalog number: A1067)
- Methanol (J.T.Baker, catalog number: 9093-68)
- Coomassie Brilliant blue R-250 (AppliChem, catalog number: A1092)
- Acetic acid (AppliChem, catalog number: 131008)
- Alexa Fluor 488 phalloidin (optional, Invitrogen, catalog number: A12379)
- Sucrose (AppliChem, catalog number: 131621)
- Glycerol (AppliChem, catalog number: 141339)
- Bromophenol blue (AppliChem, catalog number: A3640)
- HEPES (AppliChem, catalog number: A1069)
- EDTA (AppliChem, catalog number: A1104)
- BSA (AppliChem, catalog number: A1391)
- Methylcellulose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M0387)
- Liquid nitrogen
- Dextran
- HCl
- Glucose
- 4x SDS-PAGE sample buffer (see Recipes)
- Coomassie Brilliant Blue solution (see Recipes)
- General actin buffer (see Recipes)
- 10x actin polymerization buffer (see Recipes)
- Imaging buffer (optional, see Recipes)
- SDS running buffer (see Recipes)
- Destain buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- P2 and P200 Micropipettes
- -80 °C freezer
- High Speed Micro Refrigerated Centrifuge (KUBOTA, model: 3700)
- Biohazard-proof Rotor (KUBOTA, model: AF-2724A)
- Fluorescence confocal microscope equipped with 63x, 1.4-NA oil-immersion objective (ZEISS, LSM 700)
- Electrophoresis power supply (Major Science MP-300V power supplies or similar)
- SDS-PAGE electrophoresis system
- Scanner (EPSON Perfection V600 Photo)
Software
- ImageJ image processing and analysis software (National Institutes of Health Image, https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/)
Procedure
- Preparation of actin stock
- Briefly centrifuge the lyophilized G-actin powder at 3,000 x g for 5 min, 4 °C to collect the powder at the bottom of the tube.
- For one vial of G-actin powder, reconstitute G-actin with 10 μl distilled water to 10 mg/ml, then the protein would be in the following buffer: 5 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 0.2 mM CaCl2, 0.2 mM ATP, 5% (w/v) sucrose, and 1% (w/v) dextran. After aliquoting into experimental size stocks (e.g., 5 μl), the actin should be snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C.
- F-actin reconstitution
Note: the following procedure is demonstrated for one 5 μl actin aliquot.- Rapidly defrost the aliquot of muscle actin and then place on ice.
- Prepare general actin buffer by supplying with 0.2 mM ATP and 0.5 mM DTT and followed by cool down on ice.
Note: ATP and DTT should be added freshly before use. - Dilute and resuspend muscle actin to 0.4 mg/ml in cold general actin buffer (e.g., 5 μl G-actin stock plus 120 μl general actin buffer).
Note: Mix the solution gently by slowly pipetting to avoid bubbles. Do not vortex. - Incubate on ice for 60 min to depolymerize actin oligomers.
- Pre-cool the centrifuge to 4 °C during incubation.
- Centrifuge the actin solution at 20,000 x g for 15 min at 4 °C.
- Aliquot and transfer 120 µl of the G-actin solution (supernatant) into a new, precooled microcentrifuge tubes and add 12 µl freshly prepared 10x polymerization buffer (1/10th the volume). Mix well by pipetting.
- Incubate at room temperature for 1 h to form F-actin.
- F-actin bundling (the following steps should be done at room temperature)
- Dilute 50 µl fresh prepared 10x actin polymerization buffer to 1x with distilled water. (e.g., 50 μl fresh prepared 10x actin polymerization buffer plus 450 μl distilled water).
- Dilute dynamin to 2 μM in 1x actin polymerization buffer (20 µl of 2 μM dynamin is used for each reaction).
- Aliquot 20 μl of the polymerized F-actin derived from Procedure B into new sets of microcentrifuge tubes.
- Add 20 μl of 2 μM dynamin from Step C2 into the F-actin tube and mix well by pipetting. The resulting concentrations of proteins in reaction is 1x polymerization buffer with 1 μM dynamin and 5 μM F-actin.
Note: For a control, remember to include one tube of F-actin alone (e.g., 20 µl actin + 20 µl 1X polymerization buffer). - Incubate reactions for 30 min at room temperature.
- Visualizing F-actin bundles (OPTIONAL)
- Prepare imaging buffer.
- Dilute 0.5 μl actin solution from Step C5 with 5 μl imaging buffer.
- Take 4 μl from the above mixture and put on a slide, and cover with a coverslip.
- Image immediately under confocal microscope to check the bundling status. Representative image is shown in Figure 1.
Note: This procedure is not suitable for time-lapse imaging analysis.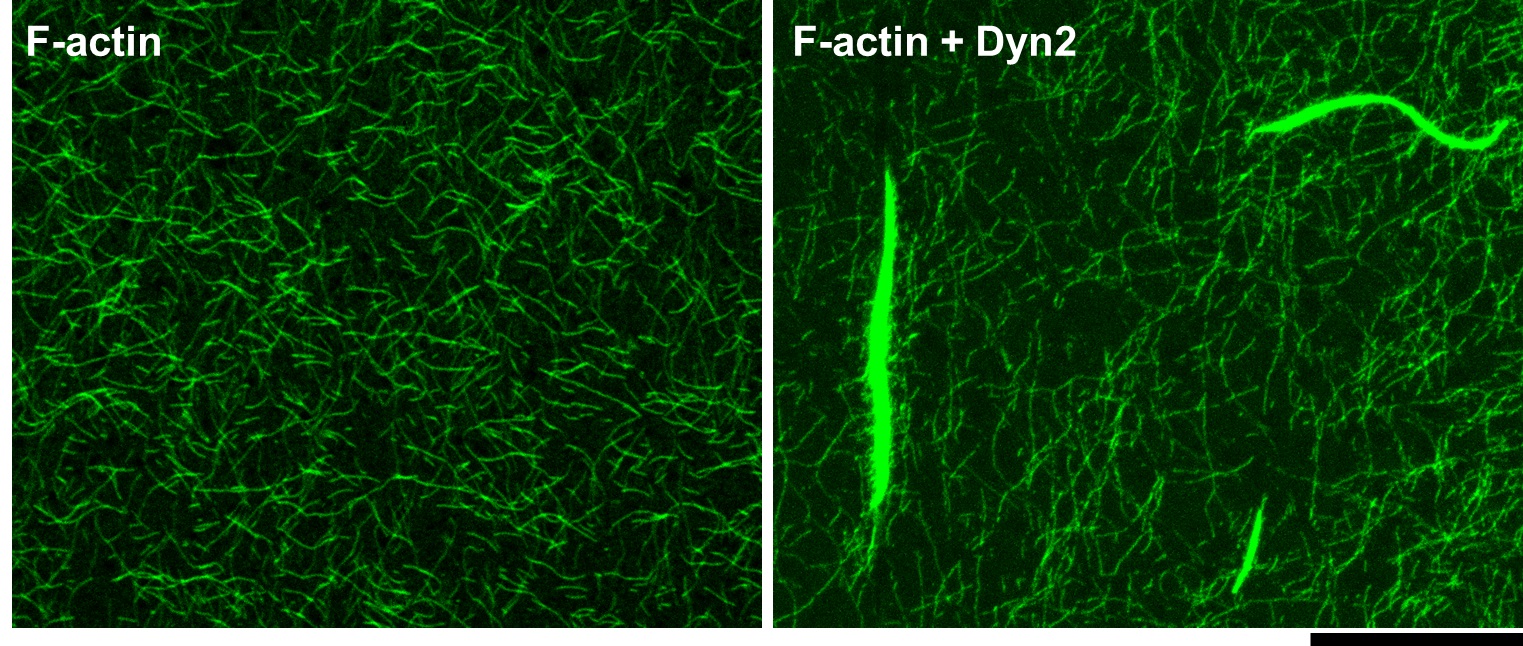
Figure 1. F-actin form bundles in the presence of Dyn2. Actin filaments were labelled by Alexa Fluor 488 phalloidin and imaged under confocal microscopy. Scale bar: 20 μm.
- Analyzing bundling activity (skip Procedure D)
- Sediment F-actin and its associated proteins by centrifugation at 14,000 x g for 20 min at room temperature.
- Carefully collect the supernatants to a new microcentrifuge tube and leave the pellets in the original one.
- Solubilize both supernatants and pellets in 1x SDS-PAGE sample buffer.
Note: The final volume in each fraction should be the same (e.g., resuspend 40 µl supernatant with 13 µl 4x sample buffer and resuspend pellet with 53 µl 1x sample buffer). - Equally subject the samples to SDS-PAGE and visualize proteins by 0.2% Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining.
- After destaining the background, carefully put the gel into two plastic sheets and capture digital images by scanning. A representative example is shown in Figure 2.
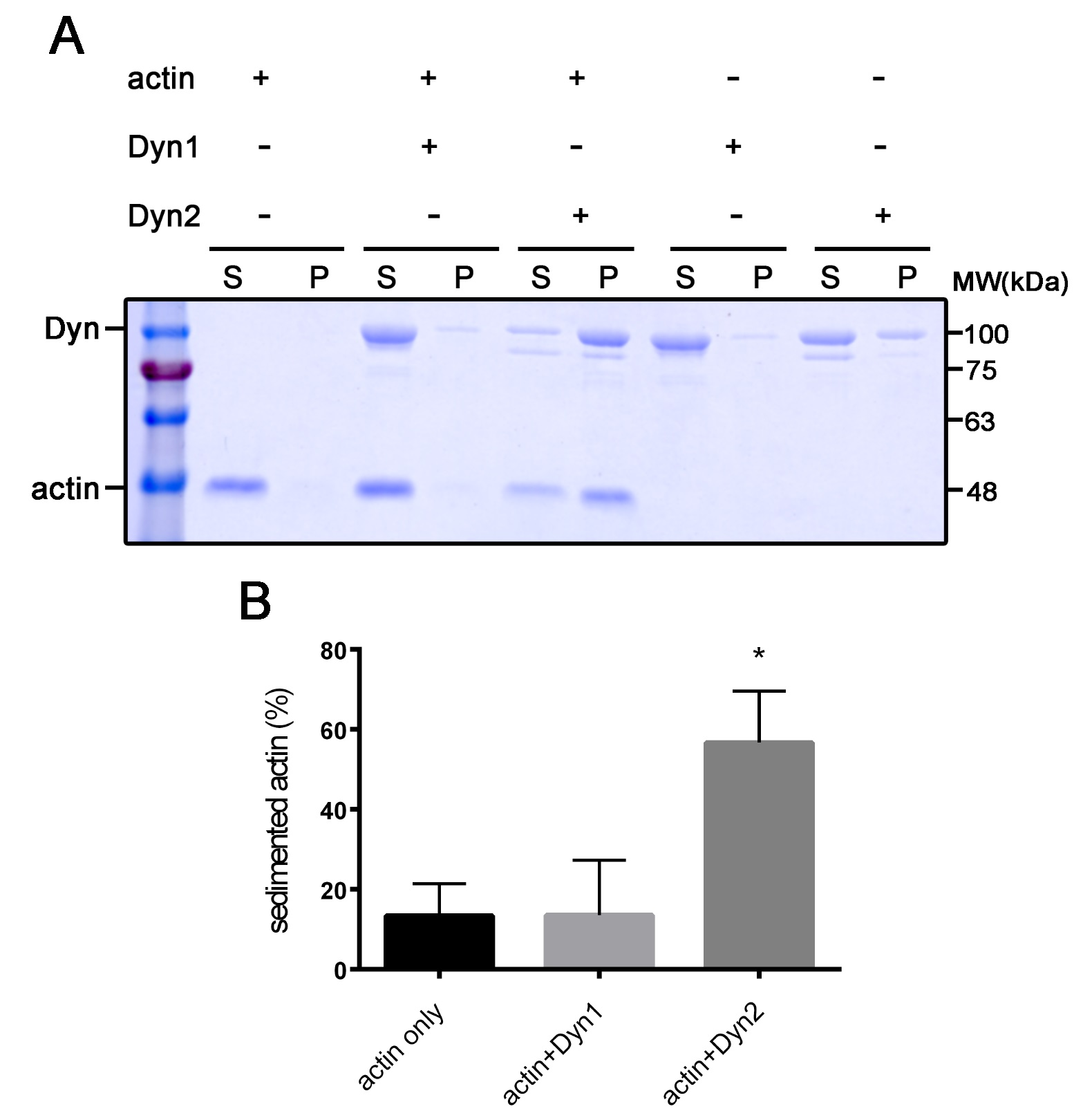
Figure 2. Dyn2 has prominent actin bundling activity. A. Actin was pelleted down after incubating with dynamin 1 and 2. S: supernatant; P: pellet. B. Quantitative result of actin bundling activity of dynamin. Data from three independent experiments were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet's post-hoc test. *P < 0.05.
Data analysis
Measure band intensity by ImageJ and subtract the background intensity. The proportion of sedimented actin is interpreted as the F-actin bundling activity in the presence of dynamin and is quantified as pellet fraction intensity in total actin intensity [pellet/(pellet + supernatant)]. Each reaction should be performed at least three times independently for the statistical quantification.
Recipes
Note: For all recipes, use molecular biology grade reagents. Solutions should be prepared with distilled water.
- General actin buffer
5 mM Tris (pH 7.4)
0.2 mM CaCl2
0.2 mM ATP (add just before use)
0.5 mM DTT (add just before use) - 10x actin polymerization buffer
500 mM KCl
20 mM MgCl2
10 mM ATP (add just before use) - Imaging buffer
10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
50 mM KCl
1 mM MgCl2
0.1 mM EDTA
1 mM DTT
3 mg/ml glucose
2mg/ml BSA
0.2% methylcellulose
50 μl/ml Alexa Fluor 488 phalloidin - 4x SDS-PAGE sample buffer
200 mM Tris (pH 6.8)
8% SDS
40% glycerol
0.1% bromophenol blue - SDS running buffer
25 mM Tris
250 mM glycine
0.1% SDS - Coomassie Brilliant Blue Solution (100 ml)
45 ml methanol
45 ml distilled H2O
20 ml glacial acetate
0.2 g Coomassie Brilliant blue - Destain buffer (1 L)
500 ml distilled water
400 ml methanol
100 ml acetic acid
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology grant 107-3017-F-002-002 and National Taiwan University grant NTU-CDP-106R7808 to Y. W. Liu. This protocol was derived from our previous work (Chuang et al., 2019).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Antonny, B., Burd, C., De Camilli, P., Chen, E., Daumke, O., Faelber, K., Ford, M., Frolov, V. A., Frost, A., Hinshaw, J. E., Kirchhausen, T., Kozlov, M. M., Lenz, M., Low, H. H., McMahon, H., Merrifield, C., Pollard, T. D., Robinson, P. J., Roux, A. and Schmid, S. (2016). Membrane fission by dynamin: what we know and what we need to know. Embo J 35(21): 2270-2284.
- Chin, Y. H., Lee, A., Kan, H. W., Laiman, J., Chuang, M. C., Hsieh, S. T. and Liu, Y. W. (2015). Dynamin-2 mutations associated with centronuclear myopathy are hypermorphic and lead to T-tubule fragmentation. Hum Mol Genet 24(19): 5542-5554.
- Chuang, M. C., Lin, S. S., Ohniwa, R. L., Lee, G. H., Su, Y. A., Chang, Y. C., Tang, M. J. and Liu, Y. W. (2019). Tks5 and Dynamin-2 enhance actin bundle rigidity in invadosomes to promote myoblast fusion. J Cell Biol 218(5): 1670-1685.
- Ferguson, S. M. and De Camilli, P. (2012). Dynamin, a membrane-remodelling GTPase. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(2): 75-88.
- Gu, C., Yaddanapudi, S., Weins, A., Osborn, T., Reiser, J., Pollak, M., Hartwig, J. and Sever, S. (2010). Direct dynamin-actin interactions regulate the actin cytoskeleton. Embo J 29(21): 3593-3606.
- Liu, Y. W., Neumann, S., Ramachandran, R., Ferguson, S. M., Pucadyil, T. J. and Schmid, S. L. (2011). Differential curvature sensing and generating activities of dynamin isoforms provide opportunities for tissue-specific regulation. P Natl Acad Sci USA 108(26): E234-242.
- McMahon, H. T. and Boucrot, E. (2011). Molecular mechanism and physiological functions of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12(8): 517-533.
- Schmid, S. L. and Frolov, V. A. (2011). Dynamin: functional design of a membrane fission catalyst. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27: 79-105.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Lin, S., Chuang, M. and Liu, Y. (2019). F-actin Bundle Sedimentation Assay. Bio-protocol 9(21): e3419. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3419.
- Chuang, M. C., Lin, S. S., Ohniwa, R. L., Lee, G. H., Su, Y. A., Chang, Y. C., Tang, M. J. and Liu, Y. W. (2019). Tks5 and Dynamin-2 enhance actin bundle rigidity in invadosomes to promote myoblast fusion. J Cell Biol 218(5): 1670-1685.
Category
Cancer Biology > Invasion & metastasis
Biochemistry > Protein > Structure
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









