- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Streptavidin Bead Pulldown Assay to Determine Protein Homooligomerization
Published: Vol 7, Iss 22, Nov 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2901 Views: 22078
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

ZnCl2 Precipitation-Assisted Sample Preparation for Proteomic Analysis
Qiqing He [...] Fuchu He
Jul 20, 2025 2726 Views

Protocol for the Preparation of a Recombinant Treacle Fragment for Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) Assays
Nadezhda V. Petrova [...] Artem K. Velichko
Sep 20, 2025 1814 Views

Optimized Secretome Sample Preparation From High Volume Cell Culture Media for LC–MS/MS Proteomic Analysis
Basil Baby Mattamana [...] Peter Allen Faull
Dec 20, 2025 1229 Views
Abstract
Pulldown assay is a conventional method to determine protein-protein interactions in vitro. Expressing a protein of interest with two different tags allows testing whether both versions can be captured via one of the two tags as homooligomeric complex. This protocol is based on streptavidin bead capture of a biotinylated protein and co-associated Flag-tagged protein using Streptavidin MagBeads.
Keywords: Pulldown assayBackground
The amyloid precursor protein (APP) can form a homodimer through its large extracellular domain as well as its transmembrane domain, which plays an important role in biological function. The current protocol has been used in characterizing homo-dimerization of the APP transmembrane C-terminal 99 amino acid fragment (C99) (Yan et al., 2017). The basic principle of this assay is shown in Figure 1: The streptavidin-coated MagBeads can trap the biotinylated protein, which can pull down the interaction protein and detected by anti-FLAG antibody.
Figure 1. The principle of MagBeads-based pull-down assay. In this particular protocol, biotinylated Avi-tagged C99 proteins and associated C99-TEV site-rTA-Flag protein were used.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips (VWR)
- 6-well plate (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 3506 )
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube
- 96-well plate (Corning, catalog number: 3595 )
- Cell culture flask (Corning, catalog number: 430639 )
- 96-well OptiPlate (PerkinElmer, catalog number: 6005290 )
- Gel loading pipette tips
- InvitrolonTM PVDF/Filter Paper Sandwich (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: LC2005 )
- PS1/PS2-deleted HTL cells (PS1/PS2 gene were deleted by CRISPR/Cas9 from HTL cells [Xu et al., 2016])
- Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11965092 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 26140079 )
- Trypsin 0.25%-EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 25200056 )
- Opti-MEM (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 31985062 )
- Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11668019 )
- Streptavidin MagBeads (GenScript, catalog number: L00424 )
- CelLyticTM M (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C2978 )
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11836153001 )
- 2x SDS loading buffer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1610737 )
- β-Mercaptoethanol (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1610710 )
- BoltTM 4-12% Bis-Tris Plus Gels, 15-well (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: NW04125BOX )
- NovexTM Tris-Glycine Transfer Buffer (25x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: LC3675 )
- Precision plus Protein prestained standard (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1610374 )
- Methanol (EMD Millipore, catalog number: MX0485-5 )
- Seppro® stripping buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S4324 )
- Biotin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B4501 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SS255 )
- Sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S374-1 )
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: PX1565-1 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: SX0420-5 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP366-500 )
- Tris base (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP152-5 )
- Glycine (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP381-5 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L3771 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: HX0603-75 )
- Tween 20 (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 9480-OP )
- Milk powder (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1706404 )
- Anti-FLAG-peroxidase antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A8592 )
- Anti-beta actin antibody (Abcam, catalog number: ab6276 )
- Anti-mouse IgG, HRP-linked antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, catalog number: 7076S )
- SuperSignal West Pico substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 34080 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Highly pure water (ddH2O) (produced by PURELAB Ultra system)
- Biotin solution (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS buffer) 10x (see Recipes)
- Electrophoresis buffer (see Recipes)
- Tris-buffered saline (TBS buffer) 10x (see Recipes)
- TBST buffer (see Recipes)
- Blocking solution (see Recipes)
- Anti-FLAG antibody solution (see Recipes)
- Anti-beta actin primary antibody solution (see Recipes)
- Anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody solution (see Recipes)
- Substrate solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: FormaTM Series II 3110 Water-Jacketed)
- Cell culture microscope (Nikon Instruments, model: Eclipse TS100 )
- Biosafety cabinet (The Baker, model: SterilGARD® e3 )
- Standard tabletop centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5417 R )
- Invitrogen SDS-PAGE running cassette (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A25977 )
- Tank blot device (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: Mini Trans-Blot® Module, catalog number: 1658029FC )
- ChemiDocTM XRS+ Imager System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: ChemiDocTM XRS+ )
- Shaker (Fisher Scientific, model: Chemistry Mixer 346 )
- Rocking platform (ARMA LAB, model: Orbital Shaker 100 )
- Magnetic separation rack (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12321D )
Software
- Image Lab 5.2.1 software (http://www.bio-rad.com/en-ch/product/image-lab-software)
Procedure
- Cell culture
- The PS1/PS2-deleted HTL cells are routinely grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum at 37 °C under a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere.
- Treat the cells with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA at 37 °C for about 2 min. Dilute the cells to 0.4 x 106/ml with DMEM medium (supplemented with 10% [v/v] fetal bovine serum) and split at 0.8 x 106/well into a 6-well plate one day prior to transfection.
- The PS1/PS2-deleted HTL cells are routinely grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum at 37 °C under a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere.
- Transfection
- Prepare a master mix for one sample:
To a sterile 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube, add:
50 µl Opti-MEM medium
2.6 µl Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection Reagent.
Notes:- Avoid touching the side of the tube while adding reagent.
- Make a Master Mix for larger sample size: for example, for 10 samples, multiply by 11 to prepare some extra mix (50 x 11 = 550 µl medium; 2.6 x 11 = 28.6 µl Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection Reagent).
- Avoid touching the side of the tube while adding reagent.
- Add 1.3 µg total DNA to 50 µl Opti-MEM medium per well in a 96-well plate.
Note: 1.3 µg total DNA contains 300 ng BirA biotin ligase encoding DNA, 500 ng Avi-C99 encoding DNA, and 500 ng C99-TEV site-rTA-Flag encoding DNA. - Add 50 µl master mix to DNA mix per well of the 96-well plate and mix gently by pipetting.
- Incubate at room temperature for about 30 min.
- Transfer 100 µl mix into each well of cells cultured in a 6-well plate.
Note: Carefully add the 100 µl mix drop by drop with a pipette. - Add biotin solution (see Recipes) to a final concentration of 40 µM just after the transfection using a standard 0.1-2.5 µl pipettor.
Note: We usually culture 2 ml cells in a 6-well plate, so just add 2 µl biotin solution. Make sure you add the small amount of biotin. - Culture the cells in DMEM supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum at 37 °C under a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere.
- Prepare a master mix for one sample:
- Prewash the MagBeads
- Completely resuspend the beads by shaking.
- Add 20 µl 25% slurry of MagBeads (Beads with their storage buffer) into each sample in a new 1.5 ml tube.
Note: Prepare a total volume of MagBeads for all samples in one tube. - Place the tube on a magnetic separation rack to collect the beads. Remove and discard the supernatant by pipetting.
Note: Use gel loading pipette tips to avoid accidental pipetting of beads. - Add 0.1 ml/sample PBS buffer (see Recipes) to the tube and invert the tube several times to mix. Use the magnetic separation rack to collect the beads and discard the supernatant by pipetting with loading tips from the very bottom. Repeat this step twice
- Completely resuspend the beads by shaking.
- Cell lysis and protein purification
- One day after transfection, remove the medium from the cultured cells by vacuum pump using loading pipette tips and gently rinse with a sufficient volume of PBS (i.e., 500 µl/well).
- Dispense 150 µl CelLyticTM M lysis buffer supplemented with 1x protease inhibitor cocktail in each well.
- Lyse the cells on ice for about 30 min.
- Transfer the lysate to 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes with a pipette and spin at full speed (about 20,000 x g) in a microcentrifuge for 10 min at 4 °C to remove insoluble material.
- Take 10 µl supernatant and mix with 10 µl SDS loading buffer supplemented with 100 mM β-mercaptoethanol as input.
- The crude supernatant protein extracts are incubated with prewashed Streptavidin MagBeads for about 30 min at 4 °C on a shaker.
- Use the magnetic separation rack to collect the beads and discard the supernatant.
Note: If necessary, keep the supernatant for analysis. - Add 0.5 ml CelLyticTM M lysis buffer to the tube and gently vortex to mix. Use the magnetic separation rack to collect the beads and discard the supernatant. Repeat this step twice.
- Elute the sample with 20 µl SDS loading buffer containing 100 mM β-mercaptoethanol at 54 °C for 10 min.
- One day after transfection, remove the medium from the cultured cells by vacuum pump using loading pipette tips and gently rinse with a sufficient volume of PBS (i.e., 500 µl/well).
- SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis
- Place a premade 4-20% SDS PAGE gel in Invitrogen SDS-PAGE cassette.
- Load 10 µl prestained protein standard and 25 µl samples with beads into the wells of the gel and run the gel in electrophoresis buffer (see Recipes) at 200 V for 1 h.
- Soak the PVDF membrane with methanol and transfer to transfer buffer.
- Soak the sponge and filter paper in transfer buffer.
- Prepare the blot sandwich in the following order: anode (-, black), sponge, filter paper, SDS gel, PVDF membrane, filter paper, sponge, anode (+, white).
- Perform protein transfer in a tank blot device at constant 90 V and 4 °C for about 90 min.
- Disassemble the blot-sandwich and immediately transfer membrane to 1x TBST (see Recipes) for a brief rinse.
Note: Check the protein standard to see the transfer efficiency. - Incubate the membrane with 20 ml blocking solution (see Recipes) at room temperature for 1 h on a shaker.
- Wash the membrane 3 x with 10 ml TBST at room temperature, 10 min each time.
- Incubate with 10 ml/membrane anti-Flag antibody solution (see Recipes) for 1 h at room temperature or overnight at 4 °C.
- Wash the membrane 3 x with 10 ml TBST at room temperature, 10 min each time.
- Incubate the membrane with enough freshly prepared substrate solution (2 ml for each membrane, see Recipes) at room temperature.
- Transfer the membrane between 2 layers of transparent sheets of plastic wrap and apply to Bio-Rad Imager system using the blots-chemi application from 1 sec to 120 sec to get 20 pictures.
- Strip the primary antibody with stripping buffer at room temperature for about 15 min.
- Repeat the Western blot starting from the blocking step, using anti-beta Actin primary antibody solution (see Recipes) for 1 h.
- After 3 x washing with 10 ml TBST (at room temperature, 10 min each time), incubate with 10 ml/membrane anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody solution (see Recipes) for about 45 min.
- After 3 x washing with 10 ml TBST (at room temperature, 10 min each time), record images using Bio-Rad Imager system.
Note: Image Lab 5.2.1 software setting for Western blot: choose Blots Chemi application; signal accumulation with the first image starts 1 sec, the last image ends 120 sec, total number of images is 20; select Position Gel and use ‘+’ or ‘-’ button to adjust the image area; run protocol to get images. Choose the best one for data analysis
- Place a premade 4-20% SDS PAGE gel in Invitrogen SDS-PAGE cassette.
Data analysis
Anti-FLAG Western blot analysis reveals the presence of C99-TEV site-FLAG in the input lysate and in the Streptavidin Bead pulldown material (Figure 2), suggesting C99 homooligomerization. A practical example for Streptavidin Bead Pulldown Assay was previously shown in Yan et al., 2017.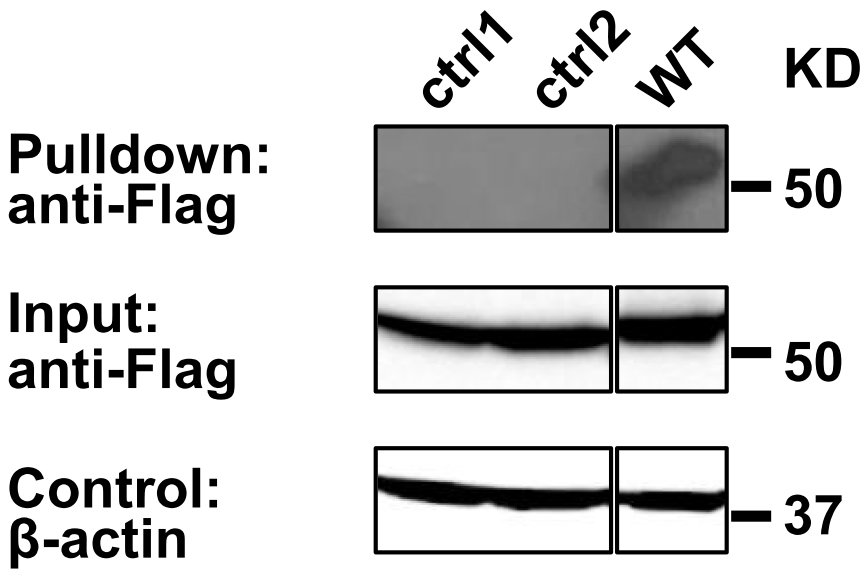
Figure 2. Pull down assay validation of C99 oligomerization. Biotinylated Avi-tagged C99 proteins and associated C99(WT)-TEV site-rTA-Flag were recovered on Streptavidin MagBeads (GenScript) and eluted with SDS sample buffer, while the dimer interface mutants (T43P/V45P: ctrl1 and I45P/V46P: ctrl2) (Yan et al., 2017) were not. Co-purified C99-TEV site-rTA-Flag proteins were detected by anti-FLAG immunoblotting. β-actin input levels serve as loading controls.
Recipes
- Biotin solution
Add 0.486 g biotin powder to 50 ml ddH2O and slowly add 10 N sodium hydroxide solution drop by drop until biotin is dissolved to make 40 mM biotin solution - Phosphate buffered saline (PBS buffer) 10x (1 L)
11.5 g Na2HPO4
2 g KH2PO4
80 g NaCl
2 g KCl
Dissolve in 1 L of ddH2O
The pH of 1x PBS should be 7.4 - Electrophoresis buffer (1 L)
3.03 g Tris
14.4 g glycine
1 g SDS
Add ddH2O to 1 L - Tris-buffered saline (TBS buffer) 10x (1 L)
24.228 g Tris-base
87.66 g NaCl
Dissolve in 1 L of sterile, deionized water and adjust pH to 7.4 with HCl - TBST buffer
Add 1 ml Tween 20 to 1 L TBS buffer - Blocking solution
1x TBST supplemented with 5% (w/v) milk powder - Anti-FLAG antibody solution
15 ml TBST with 3 μl primary anti-FLAG-peroxidase antibody - Anti-beta Actin primary antibody solution
15 ml TBST with 7.5 μl primary anti-beta Actin antibody - Anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody solution
15 ml TBST with 15 μl anti-mouse IgG, HRP-linked antibody - Substrate solution
1 volume of SuperSignal West Pico A and 1 volume of SuperSignal West Pico B, mix well
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Van Andel Research Institute, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31300607, 31300245 and 91217311), Ministry of Science and Technology grants 2012ZX09301001, 2012CB910403, and 2013CB910600, XDB08020303, 2013ZX09507001, Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (13ZR1447600), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (14QA1404300), and the National Institute of Health grants DK071662 (H.E.X.), GM102545 and GM104212 (K. M.). The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xu, T. H., Yan, Y., Kang, Y., Jiang, Y., Melcher, K. and Xu, H. E. (2016). Alzheimer's disease-associated mutations increase amyloid precursor protein resistance to γ-secretase cleavage and the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio. Cell Discov 2: 16026.
- Yan, Y., Xu, T. H., Harikumar, K. G., Miller, L. J., Melcher, K. and Xu, H. E. (2017). Dimerization of the transmembrane domain of amyloid precursor protein is determined by residues around the gamma-secretase cleavage sites. J Biol Chem.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Xu, T., Yan, Y., Harikumar, K. G., Miller, L. J., Melcher, K. and Xu, H. E. (2017). Streptavidin Bead Pulldown Assay to Determine Protein Homooligomerization. Bio-protocol 7(22): e2901. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2901.
- Yan, Y., Xu, T. H., Harikumar, K. G., Miller, L. J., Melcher, K. and Xu, H. E. (2017a). Dimerization of the transmembrane domain of amyloid precursor protein is determined by residues around the gamma-secretase cleavage sites. J Biol Chem, 292: 15826-15837.
Category
Biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Molecular Biology > Protein > Protein-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











