- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Preparation of Cell-free Synthesized Proteins Selectively Double Labeled for Single-molecule FRET Studies
Published: Vol 8, Iss 12, Jun 20, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2881 Views: 7220
Reviewed by: Elizabeth LibbyKate HannanAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Protocol for Spontaneous and Chaperonin-assisted in vitro Refolding of a Slow-folding Mutant of GFP, sGFP
Anwar Sadat [...] Koyeli Mapa
Jul 20, 2021 3498 Views

Fluorometric Measurement of Calmodulin-Dependent Peptide–Protein Interactions Using Dansylated Calmodulin
Eider Nuñez [...] Alvaro Villarroel
Apr 5, 2024 2095 Views

Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) as a Tool to Study Binding Interactions of Oxygen-Sensitive Biohybrids
Bhanu P. Jagilinki [...] John W. Peters
Aug 5, 2024 2952 Views
Abstract
Single-molecule FRET (smFRET) is a powerful tool to investigate molecular structures and conformational changes of biological molecules. The technique requires protein samples that are site-specifically equipped with a pair of donor and acceptor fluorophores. Here, we present a detailed protocol for preparing double-labeled proteins for smFRET studies. The protocol describes two cell-free approaches to achieve a selective label scheme that allows the highest possible accuracy in inter‐dye distance determination.
Keywords: Cell-free protein synthesisBackground
Single-molecule FRET (smFRET) is one of the most prominent tools in structural biology, in particular for analyzing structures and functional conformational changes of proteins (Michalet et al., 2006; Roy et al., 2008; Sustarsic and Kapanidis, 2015). However, an extensive application of smFRET is in many cases limited by the elaborative production of suitable protein samples. These proteins need to be equipped with two fluorophores, site-specifically attached at different positions within the protein structure.
The classical cell-based production of proteins requires a sequence of time-consuming steps that can be overcome by employing cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) systems, allowing a much faster and straightforward production and selection of proper double-labeled proteins. Moreover, another advantage of CFPS is given by the fact that several classes of proteins like proteases or membrane proteins, which are toxic to living cells or for other reasons are difficult to express in cells, can be synthesized successfully in CFPS systems. Finally, CFPS is an ideal tool for labs focusing on spectroscopic techniques like smFRET, since cell cultures are not necessary and safety regulations for recombinant organisms do not have to be considered.
Despite the inherently low sample amounts required for smFRET, CFPS was so far not standardly employed for the production of samples in smFRET studies. This was mostly due to the much lower protein yields as compared to cell-based systems and the lack of an appropriate cell-free approach that allows for a convenient synthesis of adequate amounts of double-labeled protein. However, as demonstrated by our group, thanks to either a much more efficient orthogonal label scheme (Sadoine et al., 2017) or a direct incorporation of dyes with superior photophysical properties (Sadoine et al., 2018), the obtained protein yield from our two cell-free approaches perfectly meets the requirement of related measurements. Combined with state-of-the-art procedures in smFRET studies, the obtained efficiency histograms allow for the highest possible accuracy in inter-dye distance determination the method can deliver today.
Here we present a general combined protocol to be used as a guide for preparing double-labeled proteins suitable for smFRET studies, using either one of the two cell-free methods or a combination of both. CFPS and smFRET represent a perfect combination to achieve the full potential of analyzing protein structures with fluorescence-based techniques and the two presented approaches have the potential to become the standard method to produce protein samples for smFRET studies.
Materials and Reagents
- Eppendorf epT.I.P.S. standard pipette tips (Eppendorf, catalog numbers: 022492004 , 022492047 , 022492055 )
- Eppendorf Safe-Lock tubes 1.5 ml (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022363204 )
- Eppendorf Protein LoBind tubes 1.5 ml (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022431081 )
- Zeba Spin Desalting Columns, 7K MWCO, 0.5 ml (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 89882 )
- Coplin staining jar (DWK Life Sciences, Wheaton, catalog number: 900470 )
- High precision coverslides thickness No. 1.5H (Paul Marienfeld GmbH, catalog number: 0107242 )
- RTS 100 Site-specific Label Kit (biotechrabbit, catalog number: BR1402601 )
- Customized Cell-free E. coli-based protein synthesis system (RF1-depleted, w/o Cys) (biotechrabbit)
- SUPERase•InTM RNase inhibitor (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AM2694 )
- cOmplete Mini EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11836170001 )
- Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads, 5% suspension (QIAGEN, catalog number: 36111 )
- Alexa Fluor 488 C5-maleimide (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A10254 )
- Click-IT Alexa Fluor 647 DIBO alkyne (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C10408 )
- Atto633-AF-tRNACUA, amber (ProteinExpress, catalog number: CLD03 )
- BODIPY FL-Cys-tRNACys, cysteine (biotechrabbit, custom made)
- 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 440140 )
- Uvasol acetone (Merck, catalog number: 100022 )
- Uvasol methanol (Merck, catalog number: 106002 )
- Optical glue Norland Optical Adhesive 81 (Norland Products, catalog number: NOA 81 )
- Nitrogen 5.0 gas bottle 99.999% purity, 50 Lt, 200 bar (Linde Gas)
- Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) for molecular biology (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S5761 )
- Methoxy-PolyEthyleneGlycol-Succinimidyl-active ester (PEG-NHS) (Rapp Polymere, catalog number: 125000-35 )
- Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS) 10x pH 7.4 for molecular biology (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AM9625 )
- Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP-HCl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, PierceTM, catalog number: 20490 )
- 3-(N-Morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS) buffer grade (AppliChem, catalog number: A1076,1000 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) for molecular biology (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S3014 )
- Imidazole buffer grade (AppliChem, catalog number: A1073,1000 )
- Vaprox Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) 35% (STERIS, catalog number: PB006 )
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) ACS reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 258105 )
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Wash buffer (see Recipes)
- Elution buffer (see Recipes)
- Final buffer (see Recipes)
- Labeling buffer azide (see Recipes)
- Labeling buffer maleimide (see Recipes)
- Piranha solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Reverse action tweezers (IDEAL-TEK, catalog number: 2AX.SA )
- Duran 250 ml beakers (DWK Life Sciences, Duran, catalog number: 21 106 36 )
- Tubing cutter (BOLA, catalog number: S1852-28 )
- pH-meter S20 SevenEasy with InLab Micro Electrode (Mettler-Toledo International, model: S20 , product discontinued, newer models can be used)
- Eppendorf Thermomixer Compact (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5384000020 )
- Eppendorf Refrigerated Microcentrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5417R )
- Stuart Rotator SB2 (Carl Roth, catalog number: Y549.1 )
- Vortex Genie 2 (Scientific Industries, model: Vortex-Genie 2, catalog number: SI-0256 )
- NanoDrop 2000c Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: NanoDropTM 2000c , catalog number: ND-2000C)
- Confocal microscope MicroTime 200 with an inverted Olympus IX-81 microscope, pulsed excitation, pinhole diameter 30-75 μm and simultaneous dual color detection (PicoQuant, model: MicroTime 200 ; Olympus, model: IX81 )
- HydraHarp 400 Time Correlated Single Photon Counting (TCSPC) Acquisition unit (PicoQuant, model: HydraHarp 400 )
- Spectrofluorometer QuantaMaster 7 (Photon Technology International now Horiba, product discontinued, newer models can be used)
- High Output Vacuum-Pressure Pump (Merck, catalog number: WP6222050 )
- UV light transilluminator (Biometra, product discontinued, newer models can be used)
Software
- MATLAB R2012a and later versions (The MathWorks Inc.)
- SymPhoTime 64 (PicoQuant GmbH)
- OriginPro 2018 (OriginLab Corporation)
Procedure
- Cell-free expression and incorporation of unnatural amino acids
- Thaw DNA on ice (plasmid containing the gene of interest, with an amber stop codon and a cysteine codon in its sequence) (see Note 1).
- Thaw the components of the cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) kit on ice.
A1. Incorporation of p-azido-phenylalanine (AzF)- Mix all reaction components in an Eppendorf protein low binding tube. Use the RTS 100 Site-specific Label Kit (Table 1) in batch mode (see Note 2).
Table 1. RTS 100 Site-specific Label Kit reaction mix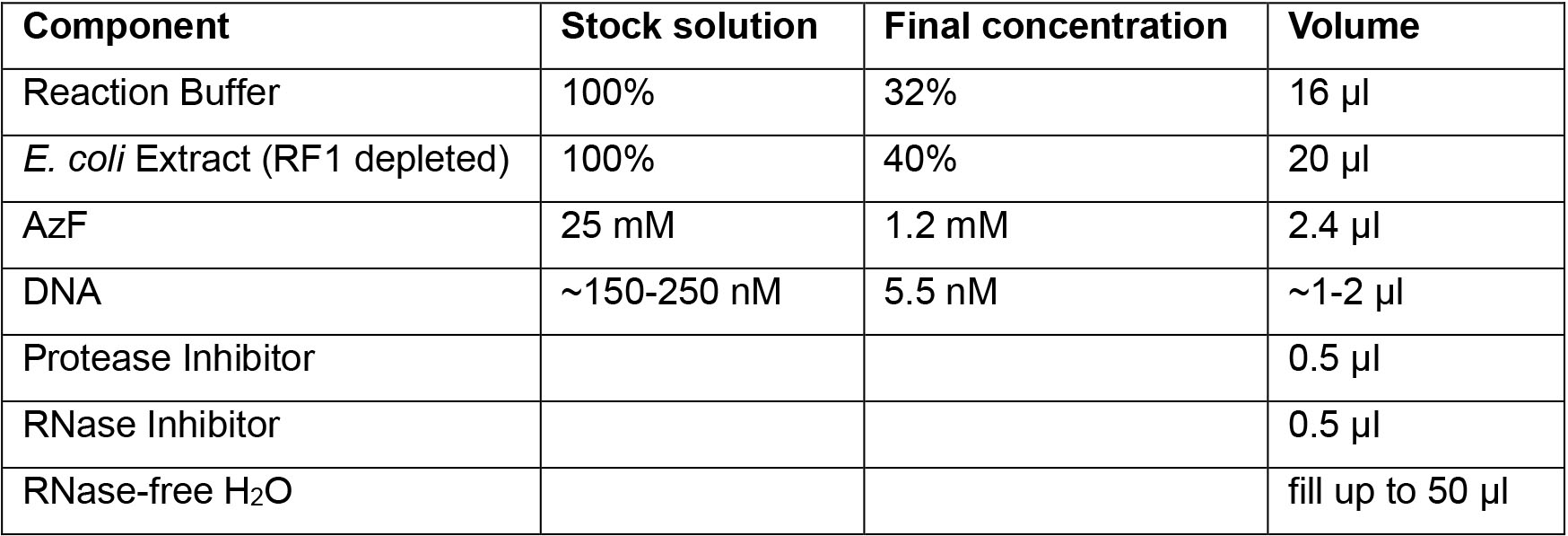
- Place the tube with the reaction mix into an Eppendorf thermomixer.
- Set the thermomixer at 32 °C and 900 rpm and let react for 2 h.
A2. Incorporation of fluorophores using precharged tRNAs- Mix all reaction components in an Eppendorf protein low binding tube. Use a customized cell-free system (Table 2) in batch mode (see Note 3).
Table 2. Customized cell-free system reaction mix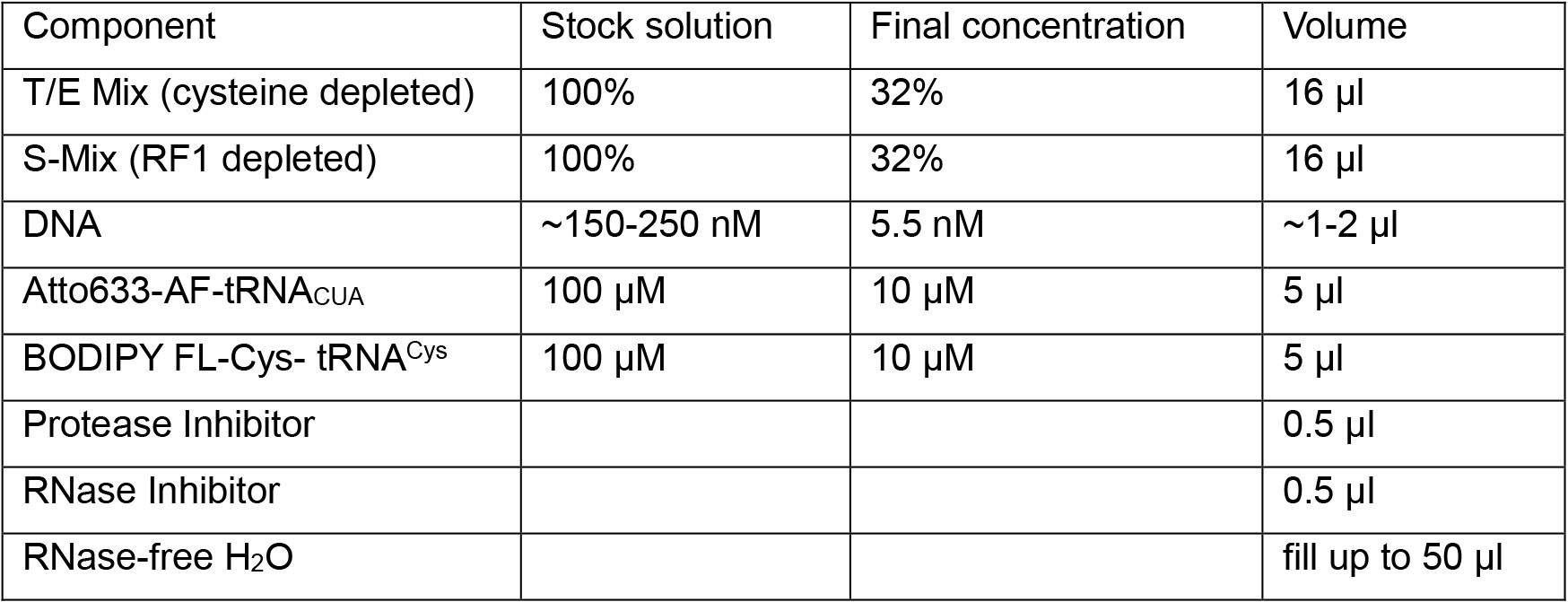
- Add a fluorophore-charged amber suppressor tRNACUA and a fluorophore-charged tRNACys. The two fluorophores should constitute a FRET pair. For example Atto633-AF-tRNACUA and BODIPY FL-Cys- tRNACys (see Note 4).
- Place the tube with the reaction mix into an Eppendorf thermomixer.
- Set the thermomixer at 32 °C and 900 rpm and let react for 2 h.
- Thaw DNA on ice (plasmid containing the gene of interest, with an amber stop codon and a cysteine codon in its sequence) (see Note 1).
- Purification of protein with Ni-NTA and buffer exchange (see Note 5)
- Add 50 μl magnetic Ni-NTA beads to a protein low binding tube.
- Equilibrate the Ni-NTA beads by adding 200 μl of lysis buffer (see Note 6 and Recipes).
- Use a magnet to hold the beads and remove the supernatant.
- Repeat 2 or 3 times.
- Add the 50 μl of the reaction and 150 μl of lysis buffer to the equilibrated Ni-NTA beads.
- Leave for 2 h at 4 °C on a rotor (Stuart Rotator).
- Use a magnet to hold the beads and transfer the supernatant in an Eppendorf tube (Flow-through).
- Add 200 μl of wash buffer (see Note 6 and Recipes) to the Ni-NTA beads and vortex shortly (2-3 sec).
- Leave for 10 min at 4 °C on the rotor.
- Use a magnet to hold the beads and transfer the supernatant in an Eppendorf tube (Wash 1).
- Repeat 2 times (Washes 2 and 3).
- Add 70 μl of elution buffer (see Recipes) to the Ni-NTA beads and vortex shortly (2-3 sec).
- Leave for 10 min at 4 °C on the rotor.
- Use a magnet to hold the beads and transfer the supernatant to an Eppendorf protein low binding tube (Elution).
- Take a Zeba desalting column.
- Remove the column’s bottom and loosen the cap.
- Place the column into a collection tube.
- Centrifuge for 1 min at 1,500 x g in an Eppendorf microcentrifuge and discard the flow-through.
- Add 200 μl of the final buffer (see Recipes) or PBS (see Recipes) for further labeling of the sample.
- Centrifuge for 1 min at 1,500 x g in an Eppendorf microcentrifuge and discard the flow-through.
- Repeat 2 more times.
- Transfer the column to an Eppendorf protein low binding tube.
- Apply the 70 μl of sample eluted from the Ni-NTA beads.
- Centrifuge for 2 min at 1,500 x g in an Eppendorf microcentrifuge and keep the flow-through that contains the protein. The protein is either already double labeled (see Procedure A2), in which case can be used directly for smFRET measurements (see directly Procedure D) or it contains two orthogonal chemical groups, namely an azido- (from AzF) and a thiol-group (from Cys) (see Procedure A1), in which case they need to be labeled in a next step (see Procedure C).
- In the second case, measure protein concentration using a Nanodrop to calculate the concentration of dyes needed for the labeling.
- Add 50 μl magnetic Ni-NTA beads to a protein low binding tube.
- Labeling with fluorescent dyes
- Add to the protein sample (in PBS buffer) a 25x excess of the azido-reactive dye (e.g., Alexa647-DIBO).
- Place the tube with the reaction mix into an Eppendorf thermomixer.
- Set the thermomixer at 25 °C and 300 rpm and let react for 15 h in the dark.
- Prepare PBS-TCEP, pH 7.5 (see Recipes).
- Degas PBS-TCEP buffer for 2 h in a vacuum pump.
- Purify the single-labeled protein with magnetic Ni-NTA beads and size exclusion following the same procedure like before (see Procedure B). Use the degassed PBS buffer for the purification and elution of the protein.
- Add a 20x excess of the thiol-reactive dye (e.g., Alexa488-maleimide).
- Place the tube with the reaction mix at 4 °C for 15 h in the dark.
- Purify the double-labeled protein with magnetic Ni-NTA beads and size exclusion following the same procedure again (see Procedure B).
- Elute the double-labeled protein with the final buffer.
- Add to the protein sample (in PBS buffer) a 25x excess of the azido-reactive dye (e.g., Alexa647-DIBO).
- Preparation of passivated microscope slides for measurements in solution
- Place the microscope slides into a Coplin staining jar.
- Prepare a Piranha solution (see Recipes) (see Note 7).
- Carefully fill the Coplin staining jar with the Piranha solution.
- Leave it under the hood for at least 1 h (see Video 1).Video 1. Chemically clean microscope slides with Piranha solution
- Fill three beakers with MilliQ water.
- Hold the slides with tweezers and dip them from one beaker to the next to clean them.
- Keep them in the third beaker (see Figure 1).
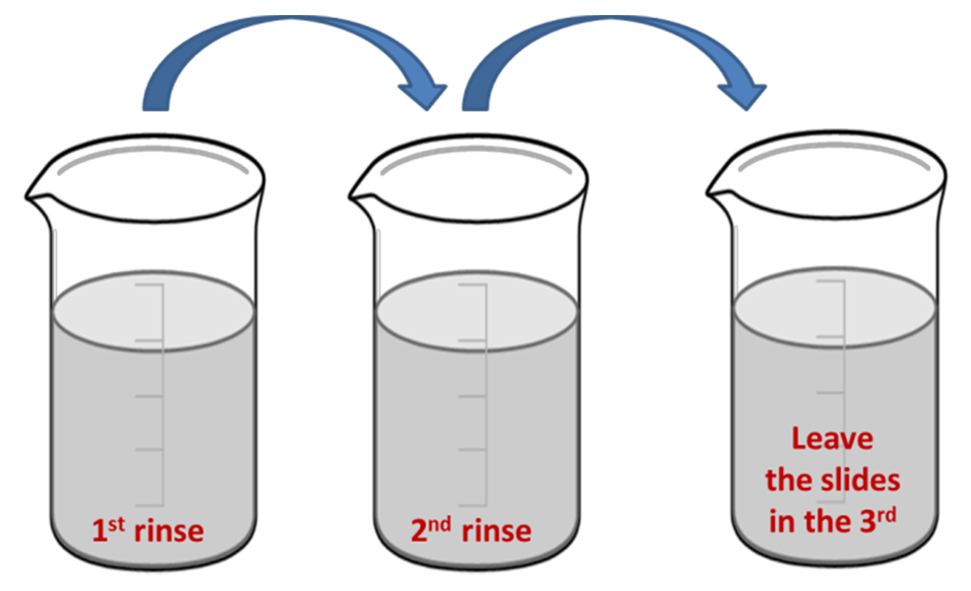
Figure 1. Cleaning microscope slides after Piranha treatment by dipping successively into three beakers with MilliQ water - Take the slides with tweezers, rinse them with methanol and dry with nitrogen flow.
- Place the dried slides into a clean and dry Coplin staining jar.
- Prepare a 2% APTES solution in Uvasol acetone for silanization of the slides.
- Fill the Coplin staining jar with the APTES solution.
- Incubate for 10 min.
- Take the slides with tweezers and rinse them first with acetone and then with methanol.
- Dry the slides with nitrogen flow and place them on a clean surface.
- Cut Eppendorf protein low binding tubes just below the 1 ml line (see Note 8).
- Smooth the cut edge using sandpaper (see Figure 2 and Video 2).
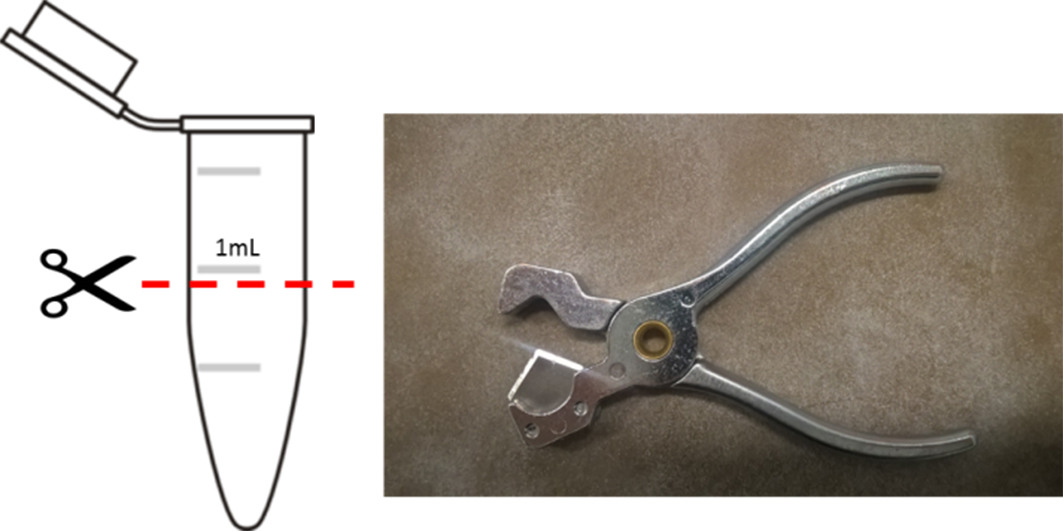
Figure 2. Use a tubing cutter to cut the tubes below the 1 ml lineVideo 2. Cut and smooth Eppendorf tubes - Apply optical glue on the rim of the cut tubes and place a single tube on one slide. Repeat with the other tubes on different slides.
- Place the slides with the tubes under UV light. The tube should touch the UV transilluminator, not the slide.
- Turn on UV light for 1-2 min to polymerize the glue (see Figure 3 and Video 3).
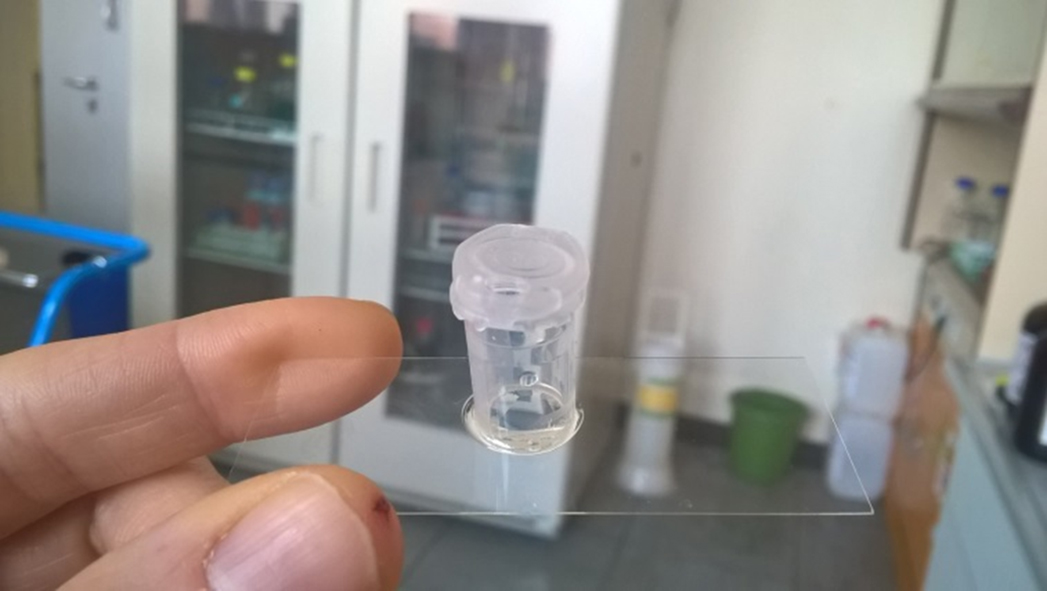

Figure 3. Slide with a tube glued onto itVideo 3. Gluing tubes onto microscope slides using UV light - Prepare 100 mM NaHCO3 solution, pH 8.3.
- Dissolve 50 mg PEG-NHS ester in 400 μl of NaHCO3 solution.
- Apply 80 μl in each tube to cover the surface.
- Close the tube carefully and keep the slides at 4 °C until use.
- Before use rinse the slides with MilliQ water, then methanol and dry with nitrogen flow.
- Place the microscope slides into a Coplin staining jar.
- smFRET measurements on a confocal microscope
- Place 100 μl of double-labeled protein sample at a concentration ~2 nM inside the half-cut tube that is glued onto the slide.
- Mount the slide on the confocal microscope.
- Perform a Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy (FCS) analysis for each fluorophore separately by exciting it using a 485 nm (for the blue dye) or a 640 nm laser (for the red dye).
- Determine the number of molecules N present in the confocal volume for the donor and the acceptor dyes, validate monomeric/non-aggregated protein, determine quantum yields (Kempe et al., 2015).
- Dilute the sample respectively for the single molecule measurement to N = 0.03, to make sure that at any given time at the most one molecule is present in the confocal volume.
- Perform an smFRET measurement by exciting the two fluorophores alternatingly (Müller et al., 2005) using both lasers (485 nm and 640 nm lasers).
- Place 100 μl of double-labeled protein sample at a concentration ~2 nM inside the half-cut tube that is glued onto the slide.
Data analysis
- Analysis of the FCS data was performed using the SymPhoTime 64 software.
- Analysis of smFRET data was performed by using self-written Matlab routines. For more details refer to Gabba et al. (2014).
Notes
- The positions at which the protein of interest is going to be labeled are mutated in the gene using site-directed mutagenesis, so that an amber stop codon (TAG) and a cysteine codon (TGC) are inserted instead of the existing codons.
IMPORTANT: No other cysteine codon should be present in the gene. - The RTS 100 Site-specific Label Kit is an E. coli derived cell-free transcription/translation system depleted from release factor 1 (RF1) and supplemented with enriched fractions of orthogonal amber suppressor tRNATyrCUA and AzF-tRNA synthetase specific for p-azido-phenylalanine (Gerrits et al., 2007; Serwa et al., 2009). This way the competition between the amber suppressor tRNA carrying the AzF and the RF1 is reduced, allowing more efficient incorporation of the unnatural amino acid. The kit consists of two solutions: the Reaction Buffer that contains low molecular weight compounds (e.g., buffer, energy, amino acids including AzF, etc.) and the E. coli extract that contains the translation machinery (ribosomes, translation factors, etc.) with overexpressed amber suppressor tRNATyrCUA and purified AzF-tRNA synthetase. The kit is stored at -80 °C.
- The customized cell-free E. coli-based protein synthesis system should be RF1-depleted for more efficient incorporation of the amber suppressor tRNA and also without cysteine for more efficient incorporation of the cys RNA. Our kit consists of two solutions: the T/E Mix that contains low molecular weight compounds (e.g., buffer, energy, amino acids except cysteine, etc.) and the S-Mix that contains the translation machinery (ribosomes, translation factors, etc.). The kit is stored at -80 °C.
- The choice of fluorophores that can be directly incorporated into proteins is limited. Large or charged fluorophores cannot fit or interact strongly with the ribosomal tunnel.
- Buffer solutions need to be adapted to the requirements of the protein of interest.
- When purifying samples with co-translationally incorporated fluorophores (see Procedure A2), the concentration of imidazole in the lysis and wash buffers could be reduced to avoid competition with the lowly concentrated protein. In that case, an increased number of wash steps is recommended.
- BE CAREFUL: Piranha solution is highly corrosive and causes severe burns. Work under the hood and wear full protection (i.e., lab coat, safety goggles, and appropriate chemically resistant gloves). ALWAYS put the oxygen peroxide first and add the sulfuric acid slowly.
- We construct a closed chamber by gluing a half-cut Eppendorf protein low binding tube onto the slide, in order to avoid sample evaporation during the measurements on the microscope.
Recipes
- Lysis buffer, pH 7.5
50 mM MOPS
300 mM NaCl
5 mM imidazole - Wash buffer, pH 7.5
50 mM MOPS
300 mM NaCl
10 mM imidazole - Elution buffer, pH 7.5
50 mM MOPS
300 mM NaCl
500 mM imidazole - Final buffer, pH 7.5
50 mM MOPS
100 mM NaCl - Labeling buffer azide, pH 7.5
1x PBS - Labeling buffer maleimide, pH 7.5
1x PBS
TCEP (10x the concentration of cysteines in the protein) - Piranha solution
1/3 (v/v) 30% H2O2
2/3 (v/v) H2SO4
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Forschungszentrum Jülich resources. The protocol was adapted from procedures published in Sadoine et al. (2017) and Sadoine et al. (2018).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Gabba, M., Poblete, S., Rosenkranz, T., Katranidis, A., Kempe, D., Zuchner, T., Winkler, R. G., Gompper, G. and Fitter, J. (2014). Conformational state distributions and catalytically relevant dynamics of a hinge-bending enzyme studied by single-molecule FRET and a coarse-grained simulation. Biophys J 107(8): 1913-1923.
- Gerrits, M., Strey, J., Claußnitzer, I., von Groll, U., Schäfer, F., Rimmele, M., and Stiege, W. (2007). Cell-free synthesis of defined protein conjugates by site-directed cotranslational labeling. In: Kudlicki, W. A., Katzen, F., and Bennett, R. P. (Eds.). Cell-free protein expression. 166-180, Landes Bioscience, Austin, Tex.
- Kempe, D., Schone, A., Fitter, J. and Gabba, M. (2015). Accurate fluorescence quantum yield determination by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 119(13): 4668-4672.
- Michalet, X., Weiss, S. and Jager, M. (2006). Single-molecule fluorescence studies of protein folding and conformational dynamics. Chem Rev 106(5): 1785-1813.
- Müller, B. K., Zaychikov, E., Brauchle, C. and Lamb, D. C. (2005). Pulsed interleaved excitation. Biophys J 89(5): 3508-3522.
- Roy, R., Hohng, S. and Ha, T. (2008). A practical guide to single-molecule FRET. Nat Methods 5(6): 507-516.
- Sadoine, M., Cerminara, M., Gerrits, M., Fitter, J. and Katranidis, A. (2018). Cotranslational incorporation into proteins of a fluorophore suitable for smFRET studies. ACS Synth Biol 7(2): 405-411.
- Sadoine, M., Cerminara, M., Kempf, N., Gerrits, M., Fitter, J. and Katranidis, A. (2017). Selective double-labeling of cell-free synthesized proteins for more accurate smFRET studies. Anal Chem 89(21): 11278-11285.
- Serwa, R., Wilkening, I., Del Signore, G., Muhlberg, M., Claussnitzer, I., Weise, C., Gerrits, M. and Hackenberger, C. P. (2009). Chemoselective Staudinger-phosphite reaction of azides for the phosphorylation of proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48(44): 8234-8239.
- Sustarsic, M. and Kapanidis, A. N. (2015). Taking the ruler to the jungle: single-molecule FRET for understanding biomolecular structure and dynamics in live cells. Curr Opin Struct Biol 34: 52-59.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sadoine, M., Cerminara, M., Fitter, J. and Katranidis, A. (2018). Preparation of Cell-free Synthesized Proteins Selectively Double Labeled for Single-molecule FRET Studies. Bio-protocol 8(12): e2881. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2881.
Category
Biochemistry > Protein > Single-molecule Activity
Biochemistry > Protein > Fluorescence
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













