- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Flight and Climbing Assay for Assessing Motor Functions in Drosophila
Published: Vol 8, Iss 5, Mar 5, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2742 Views: 12752
Reviewed by: Serge BirmanAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
![Proboscis Extension Reflex in <em>Apis mellifera</em> [Honeybee] with Only One Antenna](https://en-cdn.bio-protocol.org/imageup/arcimg/20171129091737284.jpg?t=1773351284)
Proboscis Extension Reflex in Apis mellifera [Honeybee] with Only One Antenna
Yu Guo [...] Runsheng Chen
Dec 5, 2017 7325 Views

Drosophila Endurance Training and Assessment of Its Effects on Systemic Adaptations
Deena Damschroder [...] Robert Wessells
Oct 5, 2018 7717 Views

Testing for Assortative Mating by Diet in Drosophila melanogaster
Philip T Leftwich and Tracey Chapman
Oct 20, 2018 5684 Views
Abstract
Motor control requires the central nervous system to integrate different sensory inputs and convey this information to the relevant central pattern generator for execution of motor function through motor neurons and muscles. Proper motor control is essential for any mobile organism to survive and interact with the external environment. For flying insects, motor control is required for flying, walking, feeding and mating apart from other more advanced behaviours such as grooming and aggression. Any perturbation to the sensory input or malfunctioning of neural connections to the motor output can result in motor defects. Here, we describe simple protocols for assessing flight and climbing ability of fruit flies, which can be used as two general tests to assess their motor function.
Keywords: TethersBackground
Coordinated motor functions are important for every mobile organism for survival as the major needs of finding food, shelter, mates and escaping from predators involve motor activity. Here we describe protocols to assess the flight and climbing ability of both individual and groups of Drosophila melanogaster. Both these protocols have been used extensively in earlier studies (Agrawal and Hasan, 2015; Pathak et al., 2015; Richhariya et al., 2017).
Part I: Flight protocol
Materials and Reagents
- Plastic tray of approximately 22 x 18 x 5 cm
- Petri dish of ~9 cm diameter (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12033333; Manufacturer: Pyrex, catalog number: 1480/08D ) with its outer side covered with Whatman filter paper (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 1001-918 ) (Figure 1A)
- Tethers made of stainless steel rod (diameter 0.2 cm) attached to stainless steel wire (diameter 0.01 cm) (Figure1B)
- Polystyrene foam of approximately 10 x 6 x 5 cm
- One glass slide (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 3011-002 )
- Round synthetic hair brush, size 4 (Camlin, series 66, size 4)
- Fly strains to be tested of either sex, aged 3-4 days
- Ice
- Transparent nail polish
Equipment
- Wide field microscope (Olympus, model: SZX9 )
- Timer/stop watch (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S02272 )
- Empty glass vials for cold anaesthesia
- Behaviour room with controlled temperature (~25 °C) and humidity (~60%)
- JVC colour video camera–ModelTK-C1481BEG (JVCKENWOOD, model: TK-C1481BEG )
Software
- Origin 8.0 software (MicroCal, Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA)
- Streampix digital video recording software
Procedure
- Place the Petri dish in a plastic tray filled with ice. Make sure that the filter paper edges are not touching the ice (Figure 1F). Keep the Petri dish on ice for 10 min before anaesthetising the flies.
- Add 5-6 flies of either sex into an empty vial. Flies are transferred to the empty vial by tapping the vial with flies on a pounding pad so that flies are located away from the cotton plug and are at the bottom of the vial. Following the tapping, the plug is removed and the vial is inverted rapidly onto a fresh empty vial, tapped hard so as to transfer all the flies into the empty vial which is closed immediately with another cotton plug to prevent flies from escaping (Figure 1C). Anaesthetise the flies in the empty vial by keeping the vial in ice for 5 min (Figure 1D).
- Gently tap the empty vial with flies on ice after 1 min and make sure all flies are at the bottom of the vial. Once anaesthetized, all flies will be immobile and will remain at the bottom of the vial (Figure 1E).
- Once the flies are fully anaesthetised (within 5 min; it is important that flies are not kept on ice longer than 5 min), gently place the flies with a fine brush with their dorsal side up on the cold Petri dish (Figure 1G).
- Add a tiny drop of nail polish (~10 µl) onto a glass slide at room temperature, as the nail polish dries up faster on a pre-cooled glass slide. Take a very small drop of it (~1-2 μl) on the tip of the tether by gently dipping the tip of the tether (0.7-1 mm) on the drop of nail polish.
- Using a very fine brush in your left hand, gently hold the fly above its wings on the abdomen and hold the tether in your right hand. Gently place the tether on the neck in such a way that the drop of nail polish touches the posterior of the head segment and anterior of the thorax. This position of the tether is important to ensure that the body and head of the fly are not tilted. If tethered correctly a normal individual will fly between 5-15 min. It is important that the nail polish drop is of the optimum size, as bigger drops might cover the eyes or the sensory bristles on the thorax and thus affect flight durations. Tether only a maximum of 5-10 flies as a batch (Video 1). Once every fly is tethered, fix the tether to a polystyrene foam (Figures 1H and 1I).Video 1. Tethering a single fly for measuring flight durations
- Once all flies recover from anaesthesia (~5 min), touch the legs gently using a brush to stop them flying spontaneously. Keep a stop watch ready, give a gentle mouth blown or automated air puff to all the flies in a batch and immediately turn on the stop watch. Observe flight duration for all the flies in a batch (Figure 1J and Video 2). Video 2. Recording flight durations after an air-puff
- Note down the time at which each fly stops flying. This is the flight duration of a single fly. The flight duration can be monitored either manually or by recording a video using any smart phone camera. We use JVC colour video camera–Model TK-C1481BEG and StreamPix digital video recording software to record flight videos. In the latter case flight durations of each fly can be noted down later from the video.
- A minimum of 30 flies should be tested per genotype in batches of 5-10.
Notes:
- In this protocol, both short and prolonged flight durations can be recorded by varying the duration of recording. For measuring short flight durations, flight time is recorded for 30 sec whereas to measure prolonged flight durations, the recording time is extended to 15 min/900 sec or longer as required. A majority of wild type (CS) flies fly for more than 5 min. In instances where the flies (experimental genotypes) are severely flight defective, they will fly for only a few seconds. In such instances flight times can be measured for 30 sec.
- The flies used for flight assays should not be exposed to CO2 for anaesthesia once they eclose as adults from pupal cases.
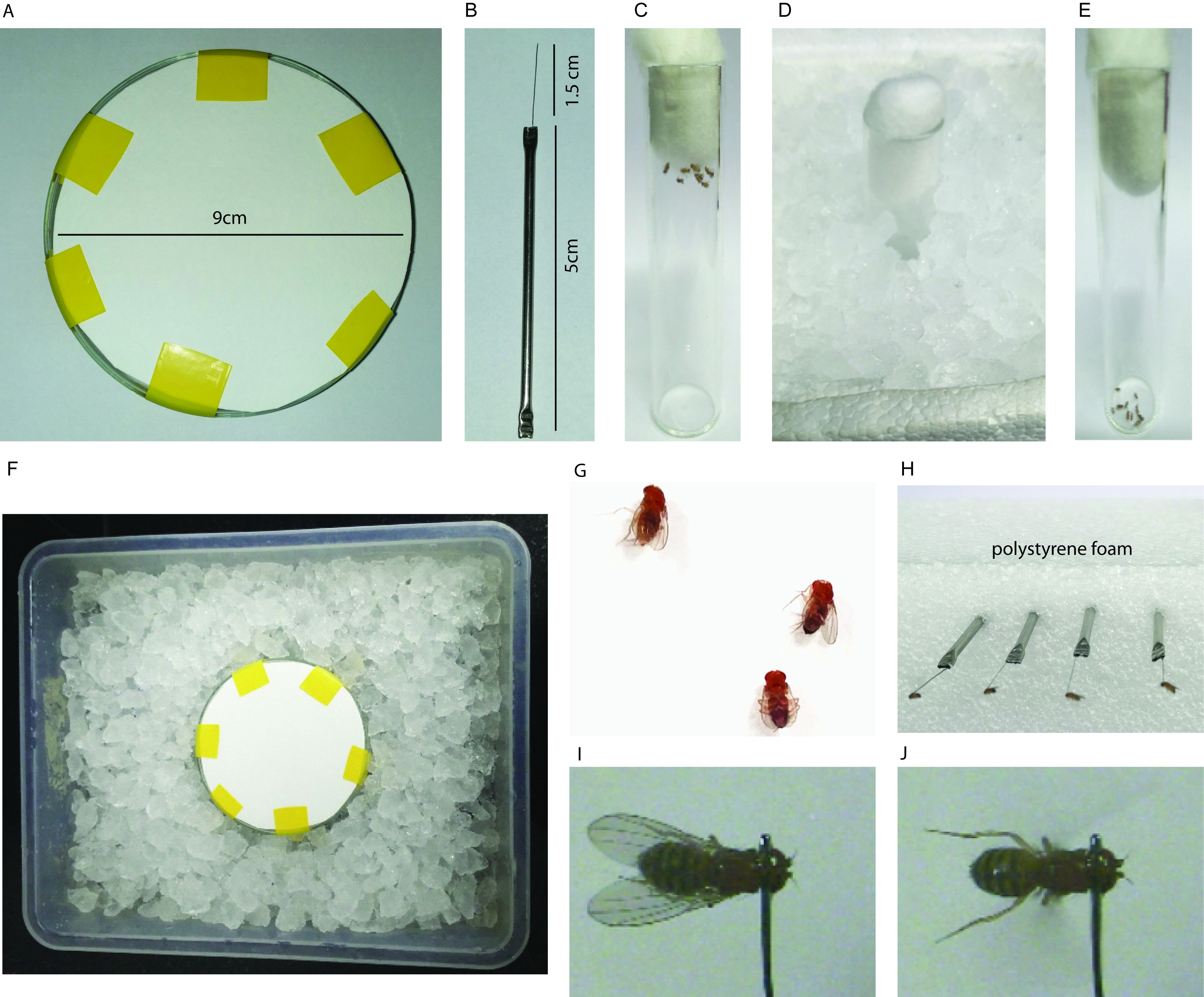
Figure 1. Tethering. A. Petri dish covered with filter paper; B. Tether with dimensions; C. Flies transferred to empty vial for cold anaesthesia; D. Empty vial with flies in ice; E. Anaesthetised flies in an empty vial; F. Tray filled with ice to keep the Petri dish cold for tethering; G. Orientation of anaesthetised flies for tethering on the Petri dish; H. Tethered flies fixed to polystyrene foam before assessing the flight durations; I. Tethered fly before air puff stimulated flight; J. Tethered fly after an air puff.
Data analysis
- Mean, median and SEM are calculated for a minimum of 30 flies per genotype. We did not find any significant difference between the flight and climbing ability of males and females. Flight durations are depicted as box plots with mean, median and the flight duration of individual flies are overlaid on the box using Origin 8.0 software (MicroCal, Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA)
- Mann Whitney U-test is applied to evaluate differences between samples as the data do not follow a normal distribution.
Flight durations for 30 Canton S (wild type) flies monitored for 15 min (900 sec) are given in Table 1 and a representative box plot of these data is depicted in Figure 2.
Table 1. Flight durations of 30 Canton S–4 days old (wild type) flies of either sex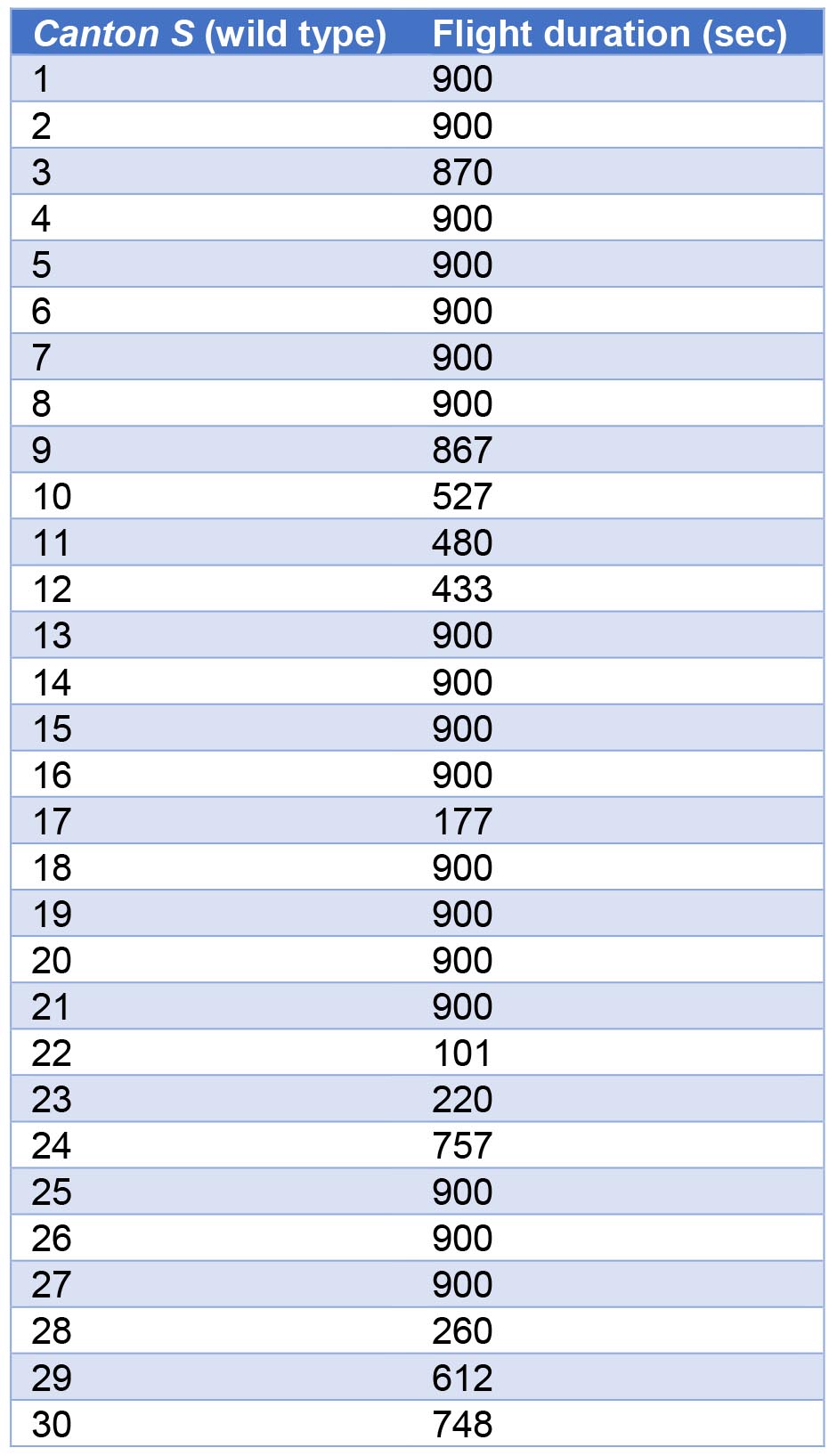
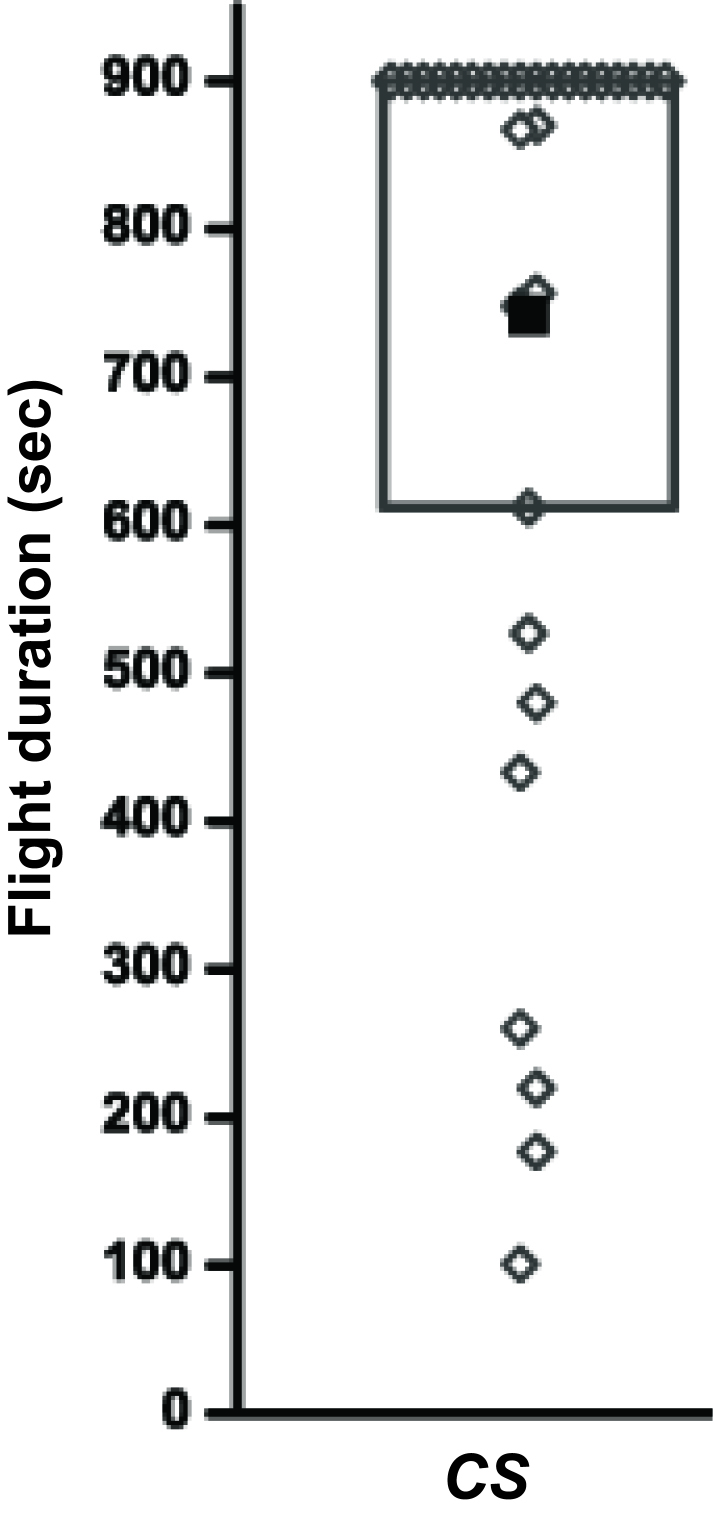
Figure 2. Flight durations of Canton S (wild type) flies depicted as a box plot. The filled square represents mean of the distribution, the box represents 25-75% of the distribution and open diamonds represent flight durations of individual flies.
Part II: Climbing protocol
Materials and Reagents
- Glass cylinder of diameter 2.5 cm (borosilicate glass measuring cylinder 50 ml with a diameter of 2.5 cm) with a mark at the height of 8 cm from the bottom
- Flies to be tested of appropriate genotypes and either sex aged 3-4 days
Equipment
- Timer/stop watch (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S02272 )
- Behaviour room with controlled temperature (~25 °C) and humidity (~60%)
Procedure
- Freshly eclosed flies of either sex should be collected in vials with standard corn meal media in batches of 10 and aged for 3-4 days.
- Transfer a batch of 10 flies (non anaesthetised) to the glass cylinder by tapping the vial with the flies on the pounding pad, immediately removing the cotton plug, inverting the flies into the glass cylinder, tapping hard and closing the cylinder with a fresh cotton plug.
- Allow the flies to get accustomed to the new environment for 3-4 min.
- Keep the stop watch ready, tap the measuring cylinder with 10 flies 3 times gently making sure all the flies reach the bottom of the cylinder and immediately turn on the stop watch (Video 3).
Video 3. Climbing assay with a batch of 10 flies - Count the number of flies that cross the 8 cm mark within 12 sec.
- Repeat the experiment twice more with the same set of flies with an interval of 3-4 min in between trials and calculate the average climbing ability for the single batch of flies. Wipe the cylinder with dry tissue paper once the assay is done for one genotype. Wash the cylinder with water once the entire set of experiments are done for a day and let it dry. Make sure not to use soap, any other detergent or ethanol for cleaning.
- A minimum of 3 batches of 10 flies should be tested per genotype, each batch tested 3 times in total.
Data analysis
- The average number of flies that crossed the 8 cm mark in 12 sec of time can be plotted as a bar graph with SEM calculated from a minimum of 3 independent batches of 10 flies using Origin 8.0 software (MicroCal, Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA). A majority of wild type/control flies reach the 8 cm mark within 12 sec. Bar graphs allow for easier visualization and comparison between various genotypes. Box plots with individual batch values overlaid on the box can also be used for representing these data.
- Statistical significance between different genotypes was calculated using One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for P < 0.05 using Origin 8.0 software (MicroCal, Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA).
- Climbing data for Canton S flies are given in Table 2 and the same data are depicted as a bar graph in Figure 3.
Table 2. Data for climbing assay of wild type (Canton S) flies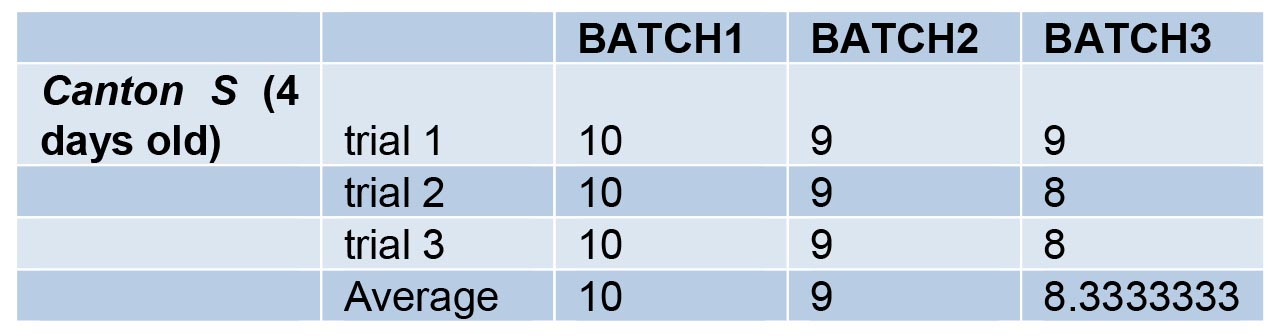
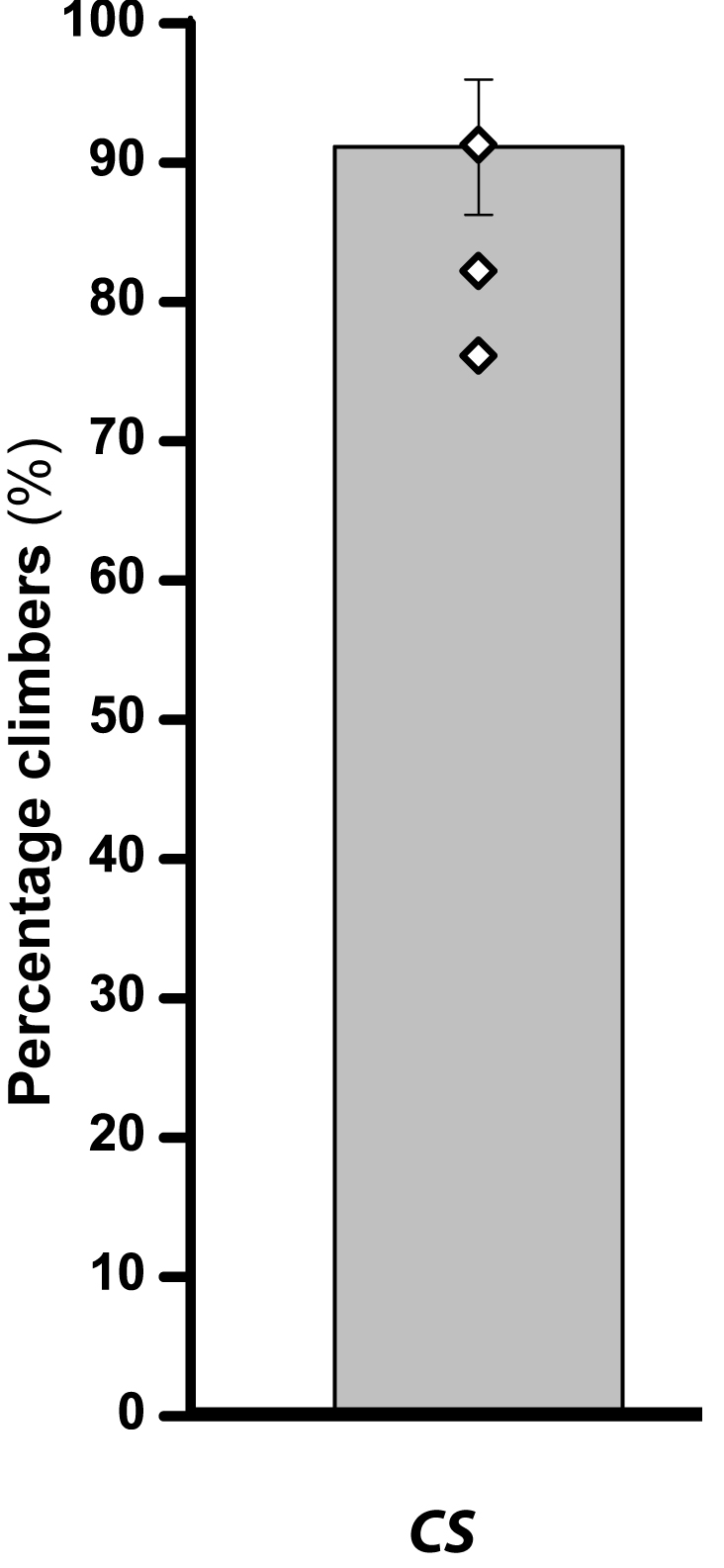
Figure 3. Climbing ability of flies (Canton S) depicted as percentage climbers. Bar graph represents the percentage of flies that crossed the 8 cm mark within 12 sec with error bar representing SEM and open diamonds on the bar representing the average of percentage climbers per batch.
Notes
The diameter of the cylinder used for climbing assay should not be more than 2.5 cm as higher diameter columns also allow the flies to fly and jump during the assay.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Santanu Banerjee, Sufia Sadaf and Tarjani Agrawal for setting up and improvising the flight protocol to the current format. We would also like to thank NCBS, TIFR for funding. This is a modified version of protocol explained in Agrawal and Hasan, 2015, Pathak et al., 2015 and Richhariya et al., 2017. The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Agrawal, T. and Hasan, G. (2015). Maturation of a central brain flight circuit in Drosophila requires Fz2/Ca2+ signaling. Elife 4.
- Pathak, T., Agrawal, T., Richhariya, S., Sadaf, S. and Hasan, G. (2015). Store-operated Calcium entry through orai is required for transcriptional maturation of the flight circuit in Drosophila. J Neurosci 35(40): 13784-13799.
- Richhariya, S., Jayakumar, S., Abruzzi, K., Rosbash, M. and Hasan, G. (2017). A pupal transcriptomic screen identifies Ral as a target of store-operated calcium entry in Drosophila neurons. Sci Rep 7: 42586.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Manjila, S. B. and Hasan, G. (2018). Flight and Climbing Assay for Assessing Motor Functions in Drosophila. Bio-protocol 8(5): e2742. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2742.
- Pathak, T., Agrawal, T., Richhariya, S., Sadaf, S. and Hasan, G. (2015). Store-operated Calcium entry through orai is required for transcriptional maturation of the flight circuit in Drosophila. J Neurosci 35(40): 13784-13799.
Category
Neuroscience > Behavioral neuroscience > Animal model > Other
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link