- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Culture and Nucleofection of Postnatal Day 7 Cortical and Cerebellar Mouse Astroglial Cells
Published: Vol 8, Iss 3, Feb 5, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2712 Views: 8719
Reviewed by: Ehsan KheradpezhouhAnna La TorreAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Identification and Sorting of Adipose Inflammatory and Metabolically Activated Macrophages in Diet-Induced Obesity
Dan Wu [...] Weidong Wang
Oct 20, 2025 2233 Views

Selective Enrichment and Identification of Cerebrospinal Fluid-Contacting Neurons In Vitro via PKD2L1 Promoter-Driven Lentiviral System
Wei Tan [...] Qing Li
Nov 20, 2025 1335 Views

Revisiting Primary Microglia Isolation Protocol: An Improved Method for Microglia Extraction
Jianwei Li [...] Guohui Lu
Dec 5, 2025 1460 Views
Abstract
Lineage reprogramming of astroglial cells isolated from different brain regions leads to the generation of different neuronal subtypes. This protocol describes the isolation and culture of neocortical and cerebellar astrocytes from postnatal mice. We also present a comprehensive description of the main steps towards successful gene delivery in these cells using nucleofection. Neocortex and cerebellum astrocyte cultures obtained with these methods are suitable for the study of molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in direct cell lineage reprogramming into induced neurons (iNs).
Keywords: Primary cell cultureBackground
Astrocyte culture has been extensively described in the literature (Saura, 2007; Schildge et al., 2013). Several protocols, mostly differing in the number of steps for cell isolation, yield astrocyte cultures with sufficient purity (up to 98%). However, most protocols described to date focus on the isolation of astrocytes from the neocortex and use chemical dissociation (Schildge et al., 2013). Here, we provide an alternative method to generate highly enriched astrocyte monolayers without the necessity of chemical tissue dissociation, what makes the protocol rather faster as compared to previous methods. Additionally, we also describe the isolation and culture of neocortical and cerebellum astrocytes, highlighting some important differences between these two cell populations. Finally, we describe an alternative, cost-effective approach for gene delivery in astrocytes using nucleofection (Chouchane et al., 2017). This technique consists of the direct delivery of DNA molecules following electroporation of the cells using a specific voltage and reagent. Nucleofection of proneural genes into astrocytes is a cheap, fast and relatively efficient method that leads to similar results as compared to retroviral-mediated transfection (Heins et al., 2002; Berninger et al., 2007; Heinrich et al., 2012; Chouchane et al., 2017). It also presents a great advantage as quiescent astrocytes are easily targeted, hence bypassing the precondition of having dividing cells.
Materials and Reagents
- Pipette tips and micropipettes (Gilson, catalog numbers: K31-1001B , K31-201Y , K31-11 )
- Petri dish (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5731 )
Manufacturer: Excel Scientific, catalog number: D-910 . - Micro scalpel
- T75 culture flasks
- 15 ml tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430791 )
- 24-well tissue plates (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030722019 )
- Mice
Note: Postnatal day 7 (P7) C57BL/6 mice were used from the animal facility of the Brain Institute (UFRN, Natal). All animal procedures were done in accordance with national and international laws and were approved by the local ethical committee (CEUA/UFRN, license # 008/2014). - Hank’s balanced salts solution (HBSS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14025092 )
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9625 )
- Tryple dissociation reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12604013 )
- Poly-D-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0899 )
- Nucleofection device and kit
- 4D nucleofector (LONZA) X unit
- 16 wells Nucleocuvettes strips (20 µl)
- Solution for primary cells P3 (Lonza, catalog number: V4XP-3032 )
- 4D nucleofector (LONZA) X unit
- Astromedium (see Recipes)
DMEM-F12 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12634010 )
Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10082147 )
Horse serum (HS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 16050122 )
Penicillin/streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140122 )
Glucose (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: A2494001 )
B27 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 17504044 )
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: P35375 )
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 68-8785-82 ) - Differentiation medium (see Recipes)
DMEM/F12 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12634010 )
Glucose (Sigma-Alrich, catalog number: G8270 )
Penicillin/streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15070063 )
B27 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 17504044 )
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B3795 )
Equipment
- Dissection microscope (ZEISS, model: Stemi DV4 )
- Incubator (Shell Lab CO2 Incubator)
- Refrigerated centrifuge (Hettich Lab Technology, model: Rotina 420 R )
- Nucleofection device (Lonza, 4D nucleofector controller and X unit) (Lonza, model: 4D-NucleofectorTM )
- 1,000 µl micropipette
Software
- GraphPad Prism version 5.00
Procedure
Note: The following protocol should be held in a sterile environment. Familiarity with basic cell culture is expected.
- Day 1. Dissection and tissue plating
Note: Prior to dissection, prewarm astromedium and prepare ice cold HBSS.- Remove the brain from P7 pups brain.
- Transfer the brain to a Petri dish filled with ice cold HBSS.
- Keep the brain in a ventral side down position and use a blade to make two coronal cuts (Figure 1, step 1). Do the first cut near the optic chiasm and the second 2-4 mm further caudally to obtain a 2-4 mm thick coronal slice.
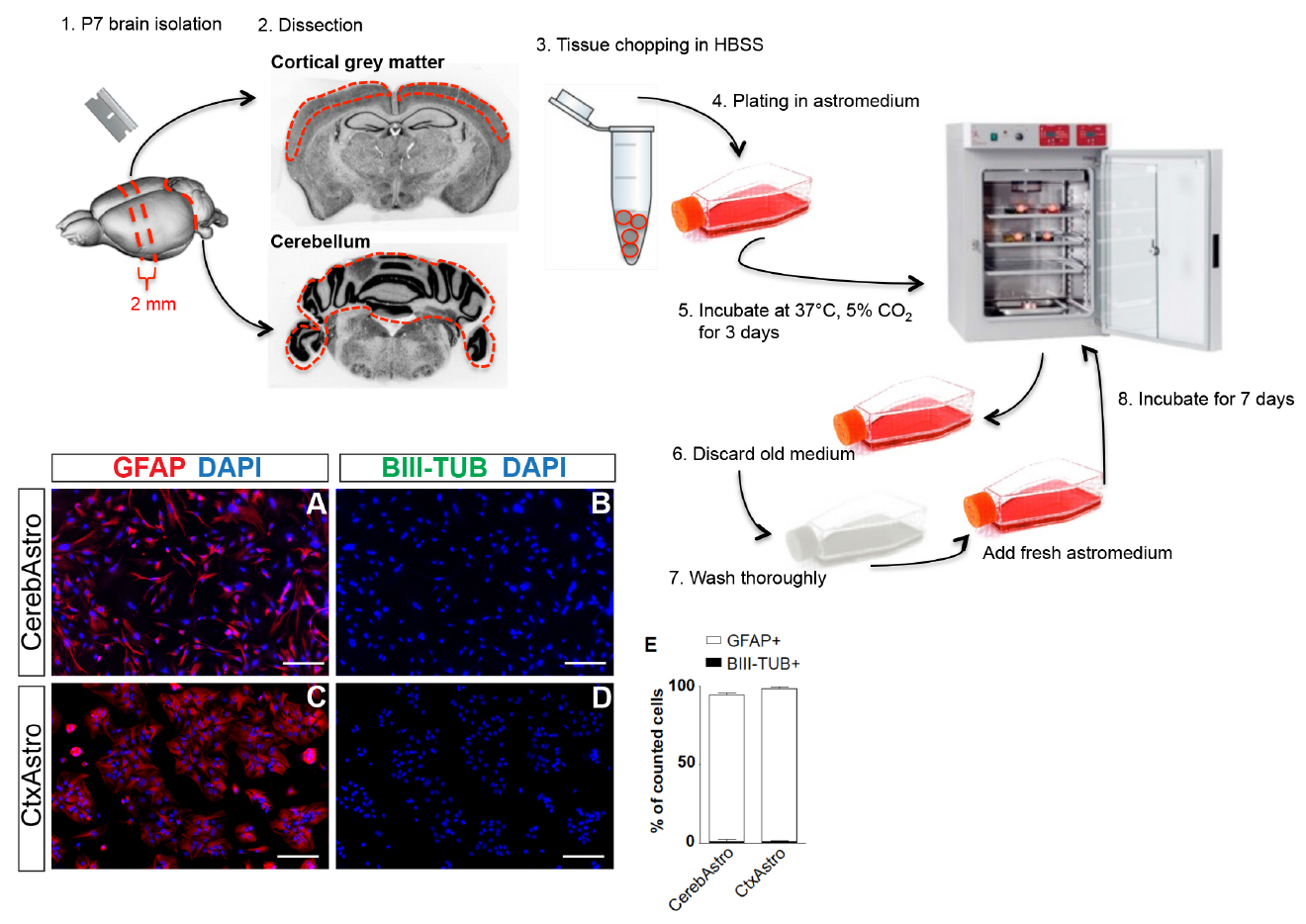
Figure 1. Postnatal astrocyte culture. Upper scheme illustrates the main steps for cortical and cerebellar astrocyte culture. Red dashed lines represent approximate regions of cuts. Lower left panels (A-D) show both cultures at 80% confluence and immunostained for the astrocytic marker GFAP (red) and neuronal marker BIII-tubulin (green). Quantifications show that > 97% of the cells in both cultures are GFAP+/BIII-tubulin- (E). Cereb = cerebellum, Ctx = cortex, Astro = astrocytes. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue), scale bars = 25 µm. - Separate the cerebellum from the rest of the brain (Figure 1, step 2).
- Remove meninges from the coronal slice and the cerebellum under a dissection microscope. Make sure to get rid of the meninges between the circumvolution of the cerebellum, as meninges could be a source of contaminating fibroblast and/or macrophages.
- Use a stereomicroscope to magnify the coronal slice obtained from the forebrain and separate the grey matter from the white matter using a micro scalpel (Figure 1, step 2).
- Transfer both tissues in different Eppendorf tubes filled with 1 ml of ice cold HBSS (Figure 1, step 3).
- Using a 1,000 µl micropipette, pipette up and down 6 to 8 times the tissues until obtaining small pieces of 1-2 mm.
- Wait 2 min for the tissues pieces to decant at the bottom of the tubes.
- Discard the HBSS and suspend the tissue pieces in 500 µl of prewarmed astromedium (see Recipes).
- Plate tissue pieces from both regions in separate T75 culture flasks containing 10 ml of prewarmed astromedium (Figure 1, step 4).
- Incubate cultures at 37 °C, 5% CO2 (Figure 1, step 5).
- Remove the brain from P7 pups brain.
- Day 3. Oligodendrocyte elimination and medium replacement
Note: Check cell culture under a light microscope. At day 3, you should be able to see isolated groups of proliferating cells all over the flask (first appearing cell islets are generally composed of 30-50 cells). If not enough cells attach wait one more day. When cells are ready, prewarm PBS and freshly prepared astromedium.- Aspirate medium from culture flasks and discard it (Figure 1, step 6).
- Wash the culture flasks three times each with 10 ml prewarmed PBS thoroughly by shaking the flasks (Figure 1, step 7).
- Discard washing PBS and add 10 ml of prewarmed fresh astromedium.
- Incubate the cells at 37 °C, 5% CO2 (Figure 1, step 8).
- Aspirate medium from culture flasks and discard it (Figure 1, step 6).
- Day 10. Astrocyte nucleofection
Note: Seven days after replacing medium, astrocyte culture must reach 80-90% confluence. At this time cells are ready to be used for further experiments. Note that astrocytes isolated from the cerebellum may reach this rate of confluence one or two days earlier than astrocytes isolated from the cortex.- Aspirate all astromedium and discard it.
- Add 5 ml of Tryple dissociation reagent (Gibco) in each culture flask and incubate at room temperature for 10-15 min.
- Pipette up and down the cells for further dissociation (10 times).
- Collect all the cells in 15 ml tubes.
- Centrifuge at 300 x g, 10 min at 4 °C.
- Discard supernatant.
- Suspend the cells in 1 ml DMEM-F12 and count.
- Before nucleofection, incubate primary cell solution P3 at room temperature for 20 min.
- Suspend 106 cells in 20 µl of P3 solution by pipetting gently 3 times.
- Add gently 1-2 µg of plasmid DNA to the cell suspension.
- Drop cell/DNA suspension in the nucleofection wells (20 µl/well).
- Enter the cuvette inside the nucleofector 4D X-unit and select the program EM110 for mammalian glial cells.
- After nucleofection, take out the strip and let it wait at room temperature for 5 min before recollecting the cells.
- Aspirate cells from wells and suspend in preheated astromedium.
- Plate cells at a density of 70,000 to 100,000 cells/well in poly-D-lysine coated 24-well tissue plates containing astromedium (500 µl/well) (see Figure 2).
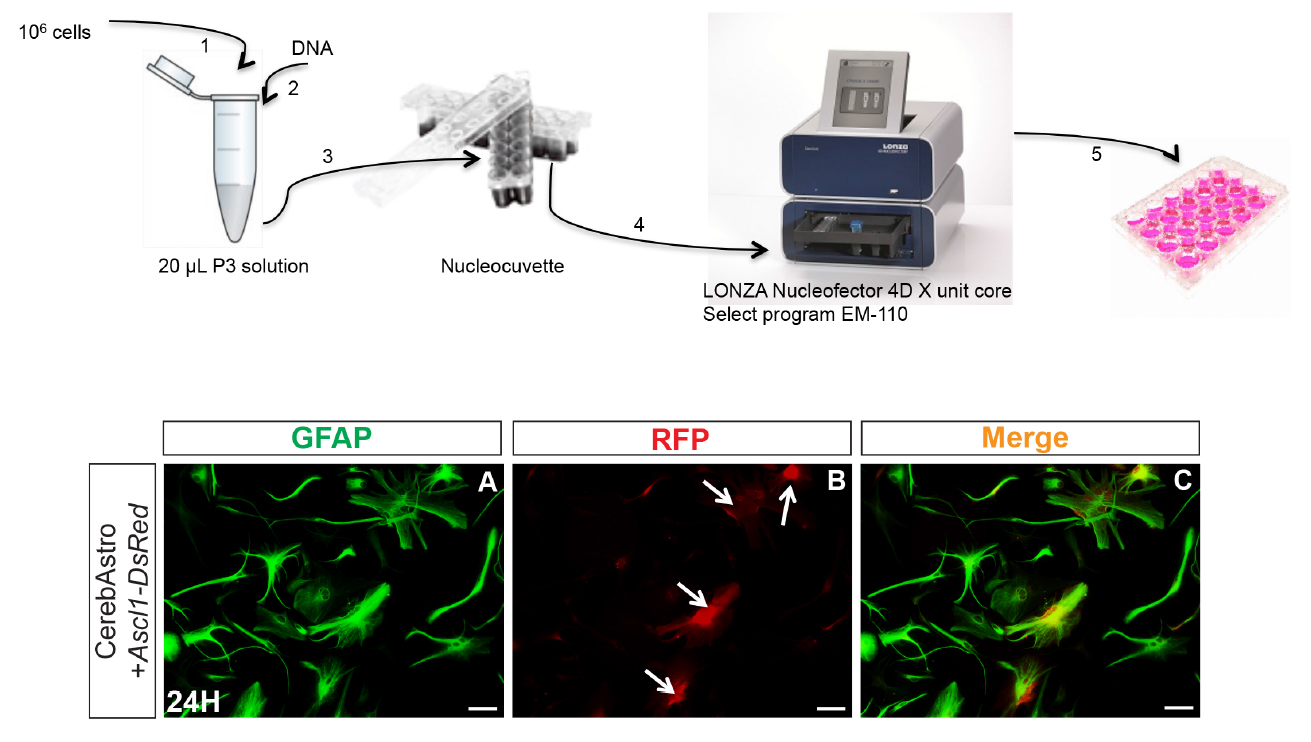
Figure 2. Astrocyte nucleofection. Upper scheme illustrates the principal steps of astroglial nucleofection using the 4D nucleofector (LONZA). Lower panels show an example of cerebellum astrocytes (GFAP+) 24 h after nucleofection with pCAG-Ascl1-IRES-DsRed (A). Astrocytes express reporter fluorescence (RFP+) (white arrows) (B, C). Scale bars = 25 µm.
Note: It is important to prevent bubble formation while loading the cell/DNA suspension in the wells. This will prevent more cell death. We also observed that cell clusters are more resistant to nucleofection than totally dissociated cells. It is preferable to plate cells in an already heated and equilibrated medium. Although using the same protocol, cell nucleofection efficiency and cell death vary a lot from one experiment to the other. In this protocol astroglial cells were nucleofected with pCAG-Neurog2-IRES-DsRed, pCAG-Ascl1-IRES-DsRed or the control plasmid pCAG-IRES-DsRed. However, other plasmids carrying other genes can be used following the same protocol. Optimal DNA concentration may vary. Therefore, different DNA concentrations should be tested in a pilot experiment. The same is applicable for the nucleofection program given that survival and nucleofection efficiency may vary depending on the chosen program. An optimal compromise should be found by testing all the following variables: cell number, DNA concentration and selected program. Using this protocol, we could observe reporter fluorescence expression as soon as 4 h after nucleofection and transfection efficiency was higher than 60% for both astrocyte populations. - Aspirate all astromedium and discard it.
Data analysis
Quantification of neuronal reprogramming and iNs phenotype in vitro must be performed in at least three independent batches of cell culture. However, the exact sampling size must be determined for each experiment considering the effect size, variation and statistical power. Statistical tests can be performed using GraphPad Prism version 5.00 for Windows or other statistic programs. The choice of the statistical test must be determined according to the experimental design. For examples of possible analyses using the astrocyte culture described herein, please refer to Chouchane and coworkers (2017) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/articles/28602612/).
Recipes
- Astromedium
DMEM-F12 containing:
10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)
5% horse serum (HS)
1% penicillin/streptomycin
3.5 mM glucose
Supplemented with 2% B27, epidermal growth factors (EGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2), each at 10 ng/ml
Note: Astromedium can be prepared and kept at 4 °C for 1 week. However, growth factors should be freshly added before using. - Differentiation medium
DMEM/F12 containing:
3.5 mM glucose
1% penicillin/streptomycin
2% B27
Note: This medium can be supplemented with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF, Sigma-Aldrich) at 20 ng/ml every fifth day of the differentiation process to improve survival of induced neurons.
Acknowledgments
The National council for scientific and technological development (CNPq) supported this work. The current protocol was adapted from Heins et al., 2002 and Berninger et al., 2007. The authors declare no conflicts of interest or competing interests.
References
- Berninger, B., Costa, M. R., Koch, U., Schroeder, T., Sutor, B., Grothe, B. and Gotz, M. (2007). Functional properties of neurons derived from in vitro reprogrammed postnatal astroglia. J Neurosci 27(32): 8654-8664.
- Chouchane, M., Melo de Farias, A. R., Moura, D. M. S., Hilscher, M. M., Schroeder, T., Leao, R. N. and Costa, M. R. (2017). Lineage reprogramming of astroglial cells from different origins into distinct neuronal subtypes. Stem Cell Reports 9(1): 162-176.
- Heinrich, C., Gotz, M. and Berninger, B. (2012). Reprogramming of postnatal astroglia of the mouse neocortex into functional, synapse-forming neurons. Methods Mol Biol 814: 485-498.
- Heins, N., Malatesta, P., Cecconi, F., Nakafuku, M., Tucker, K. L., Hack, M. A., Chapouton, P., Barde, Y. A. and Gotz, M. (2002). Glial cells generate neurons: the role of the transcription factor Pax6. Nat Neurosci 5(4): 308-315.
- Saura, J. (2007). Microglial cells in astroglial cultures: a cautionary note. J Neuroinflammation 4: 26.
- Schildge, S., Bohrer, C., Beck, K. and Schachtrup, C. (2013). Isolation and culture of mouse cortical astrocytes. J Vis Exp (71).
Article Information
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Chouchane, M. and Costa, M. R. (2018). Culture and Nucleofection of Postnatal Day 7 Cortical and Cerebellar Mouse Astroglial Cells. Bio-protocol 8(3): e2712. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2712.
Category
Neuroscience > Cellular mechanisms > Cell isolation and culture
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link








