- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Preparation of Primary Astrocyte Culture Derived from Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Specimen
Published: Vol 7, Iss 8, Apr 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2241 Views: 11887
Reviewed by: Oneil G. BhalalaSébastien GillotinEmmanuelle Berret

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay as a Hallmark of Carcinogenesis
Feng Du [...] Daiming Fan
Jun 20, 2017 30551 Views

Total RNA Isolation from Separately Established Monolayer and Hydrogel Cultures of Human Glioblastoma Cell Line
Manasi P Jogalekar and Elba E Serrano
Jul 20, 2019 6218 Views

A Fast and Reliable Method to Generate Pure, Single Cell-derived Clones of Mammalian Cells
Zhe Han [...] Varun Kumar
Aug 20, 2022 4099 Views
Abstract
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a grade 4 astrocytoma tumor in central nervous system. Astrocytes can be isolated from human GBM. Study of astrocytes can provide insights about the formation, progression and recurrence of glioblastoma. For using isolated astrocytes, new studies can be designed in the fields of pharmacology, neuroscience and neurosurgery for glioblastoma treatment. This protocol describes the details for preparing high purity primary astrocytes from human GBM. Tumor tissue is disrupted using mechanical dissociation and chemical digestion in this protocol. 2 weeks after plating the cell suspension in culture, primary astrocytes are available for further subculturing and immunocytochemistry of S100-beta antigen.
Keywords: Glioblastoma multiformeBackground
Astrocytes are glial cells that provide structural and nutritional support for brain neurons. The cell cycle of astrocytes seems to be disrupted in astrocytoma brain tumors. The World Health Organisation (WHO) has classified astrocytomas into four grades according to their malignancy. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM, grade IV) is the most malignant form of astrocytoma. Glioblastoma is characterized by the invasive cells with the rapid proliferation rate and angiogenesis. Prognosis is poor for patients with glioblastoma. Current therapeutic approaches including surgery, chemo-therapy and radiation don’t have good effects on the treatment of suffering patients. Median survival time for patients is about one year after treatment (Stuup et al., 2005; Wen and Kesari, 2008). So many researchers focus on the study of evaluating the physiological function and apoptosis of glioblastoma cells in order to detect more effective treatment methods. Here we present a method for isolation of high purity primary astrocyte from human glioblastoma specimen without fibroblast contamination (Hashemi et al., 2016).
Materials and Reagents
- 15 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352096 )
- Petri dish culture (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 704001 )
- No. 10 scalpel blade surgical tool (BD, catalog number: 371610 )
- Cell strainer sieve (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352340 )
- 50 ml centrifuge tubes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352070 )
- T25 flask culture (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 707003 )
- 1 ml microtube (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 613111 )
- 24-well plates of polystyrene with high clarity (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 702001 )
- 5 ml pipette (Nest Biotechnology, catalog number: 326001 )
- Glioblastoma multiforme sample (Human)
- Hanks’ balanced salt solution (HBSS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 24020117 )
- Antibiotic-antimycotic (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15240062 )
- 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 25200056 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10270106 )
- Trypan blue solution 0.4% (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8154 )
- Primary antibody of rabbit anti-S100-beta (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S2644 )
- Primary antibody of rabbit anti-fibronectin (Abcam, catalog number: ab23751 )
- FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit (Abcam, catalog number: ab6717 )
- Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium/F12 (DMEM/F12) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 31331028 )
- Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (tablet) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 18912014 )
- Paraformaldehyde (powder) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6148 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787 )
- Bovine serum albumin (powder) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2058 )
- Culture medium (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
- 4% paraformaldehyde (see Recipes)
- 0.2% Triton X-100 (see Recipes)
- 10% bovine serum albumin (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Ventilation hood (VISION SCIENTIFIC, model: VS-7120LV )
- 37 °C water bath (Memmert, model: WNB14 )
- Centrifuge machine (Hettich Lab Technology, model: Universal 320R )
- Hemocytometer (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z359629 )
- CO2 cell culture incubator (Memmert, model: INC108 T2T3 )
- Inverted fluorescence microscope (Optika, model: XDS-2FL )
- Small forceps surgical tools (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11050-10 )
Procedure
- Collection of primary glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) tissue
- A glioblastoma multiforme sample was obtained from a patient with glioblastoma who underwent surgical treatment.
- This study was approved by the Ethical Commission of the Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Before operation, a signed written consent was given by the patient.
- After coordination with the neurosurgery team, the neurosurgeon placed the resected glioblastoma sample in a 15 ml Falcon tube containing 5 ml cold HBSS with 10% antibiotics (antibiotic-antimycotic).
- The glioblastoma sample was delivered to the lab on dry ice.
- A glioblastoma multiforme sample was obtained from a patient with glioblastoma who underwent surgical treatment.
- Dissociation of GBM sample into single primary astrocytes
- Under biology’s hood, remove excess of the HBSS in the Falcon tube containing glioblastoma tissue. Wash the tissue 3 times with 5 ml cold PBS to remove the blood.
- Place the glioblastoma tissue in a Petri dish filled with 1 ml cold PBS.
- Shred and mince the tissue with a scalpel blade for 5 min until the sample is converted to a milky suspension. Mincing can help to speed up the trypsinization process through increasing the efficacy of tissue dissociation.
- Add 3 ml of warm (37 °C) 0.05% trypsin-EDTA to minced tissue. Then, transfer the suspension with trypsin into a new 15 ml Falcon tube.
- Incubate the produced suspension for 10 min at a 37 °C water bath for digestion of the minced tissue.
- Add 3 ml of DMEM/F12 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic to inhibit the activity of trypsin.
- Pipette the suspension 10 times with a 5 ml pipette and centrifuge at 180 x g for 10 min at room temperature.
- Remove the upper liquid and resuspend the resulting pellet slowly into 5 ml DMEM/F12 containing 2% FBS and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic by pipetting 10 times with a 5 ml pipette.
- Filter the cell suspension through a 40 micron cell strainer into a 50 ml tube to remove un-dissociated pieces and debris.
- Centrifuge the filtered suspension at 180 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Resuspend the pelleted cells into 1 ml DMEM/F12 containing 2% FBS and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (Figure 1).
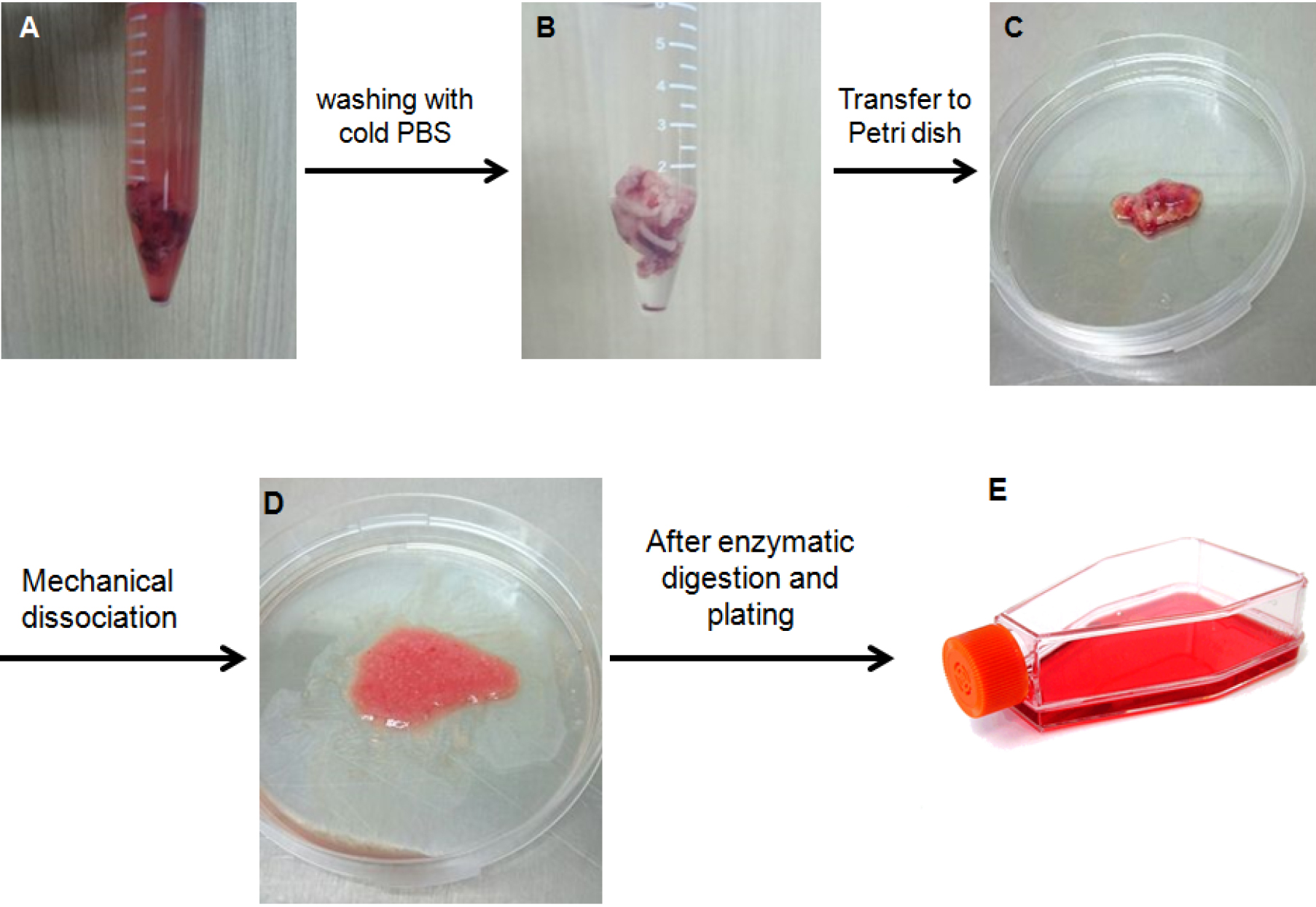
Figure 1. Procedure to isolate primary astrocyte for culture from human glioblastoma sample. A. A human glioblastoma sample after surgery; B. Glioblastoma sample was washed using cold PBS; C. Glioblastoma sample was transferred to Petri dish; D. Glioblastoma sample was shred and minced with scalpel blade; E. After enzymatic digestion, cell suspension was plated in a T25 flask.
- Under biology’s hood, remove excess of the HBSS in the Falcon tube containing glioblastoma tissue. Wash the tissue 3 times with 5 ml cold PBS to remove the blood.
- Cell counting and plating
- Add 10 μl of the cell suspension to a 1 ml tube containing 10 μl of 0.4% trypan blue in PBS.
- Transfer 10 μl of the cell-trypan blue mixture to a hemocytometer chamber. Count the number of the cells in each individual square (total, 4 squares) under an inverted microscope. Determine the average number of the cells per square and calculate the total cell number by multiplying the cell quantity per square by 2 x 104.
- Seed 1 x 105 cells in 5 ml DMEM/F12 containing 2% FBS and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic into T25 flasks.
- Place the flasks into an incubator at 37 °C, 5% CO2 and 95% humidity.
- Astrocytes usually attach to the bottom of flask after the first 24 h. Astrocytes neurites extend gradually after 3-4 days. Astrocytes start to grow and proliferate after the complete extension of their neurites at day 7 of culture.
- Replace half of the cell medium with fresh medium every 2 days. FBS concentration is gradually increased after each change of the culture medium, from 2% to 10% in 2 weeks (Table 1). 10% FBS amount in culture medium is preserved in the following primary astrocyte culture.
Table 1. FBS concentration in culture medium at different days after seedingDays after seeding to change medium FBS concentration Seeding (0) 2% 4 3% 6 4% 8 5% 10 6.5% 12 8% 14 10% - Gradual increase of FBS amount might avoid fibroblast contamination of the cell culture (Figure 2).
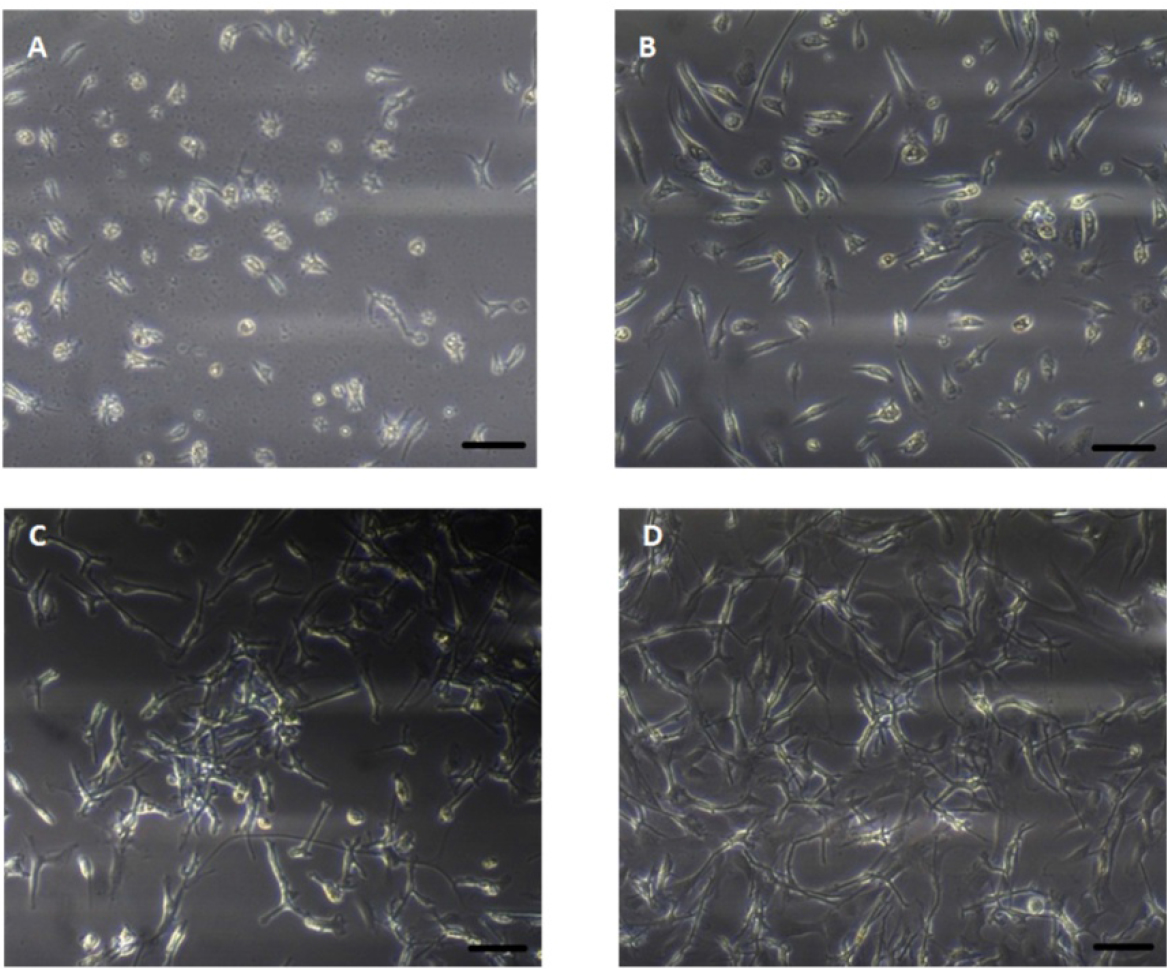
Figure 2. Phase contrast images of primary astrocytes of glioblastoma multiforme in the different days of cell culture. A. 2 days after cell culture; B. 4 days after cell culture; C. 9 days after cell culture; D. 14 days after cell culture. Scale bars = 100 µm.
- Add 10 μl of the cell suspension to a 1 ml tube containing 10 μl of 0.4% trypan blue in PBS.
- Sub-culture of primary astrocytes of GBM
- Check the level of cell confluency using an inverted microscope. Subculture the cells when they reach 80% of confluence 3 weeks after seeding.
- Remove the medium from each T25 flask under a biological hood with a 5 ml sterile pipette.
- Wash the cells with 3 ml of warm (37 °C) PBS and then remove PBS.
- Detach the cells with 1 ml of warm (37 °C) 0.05% trypsin-EDTA for 1 min in an incubator.
- Inhibit trypsin-EDTA reaction by adding 4 ml of DMEM/F12 containing 10% FBS and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic into each T25 flask and then transfer the cell suspension from each flask to a 15 ml Falcon tube.
- Centrifuge the cell suspensions at 250 x g for 5 min at room temperature.
- Remove the medium from each tube with a 5 ml sterile pipette.
- Resuspend the pellet in each tube with 1 ml of fresh medium containing DMEM/F12, 10% FBS and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic.
- After re-suspend and counting, plate the cells in 24-well dishes (at a density of 5 x 103 cells per well) for immunocytochemistry analysis and also T25 flasks for sub-culture.
- Check the level of cell confluency using an inverted microscope. Subculture the cells when they reach 80% of confluence 3 weeks after seeding.
- S100-beta staining
- Seed 5 x 103 cells into each well of a 24-well culture dish.
- Wash each well three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) after 24 h at room temperature.
- Fix cells with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 20 min.
- Wash cells three times in PBS at room temperature for 5 min each.
- Permeate cell membranes with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 15 min.
- Wash cells three times in PBS at room temperature for 5 min each.
- Block cells with 10% bovine serum albumin for 1 h.
- Dilute the primary antibody of rabbit anti-S100-beta 1:100 with PBS containing 1% BSA.
- Incubate cells with primary antibody of rabbit anti-S100-beta or primary antibody of rabbit anti-fibronectin overnight at 4 °C.
- Wash cells three times in PBS at room temperature for 5 min each.
- Dilute the secondary antibody of FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit 1:500 with PBS containing 1% BSA.
- Incubate cells with secondary antibody of FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit for 2 h at room temperature in the dark.
- Wash cells three times in PBS at room temperature for 5 min each.
- Image cells by an inverted fluorescence microscopy (Figures 3 and 4).
Note: Only the secondary antibody was added as a negative control.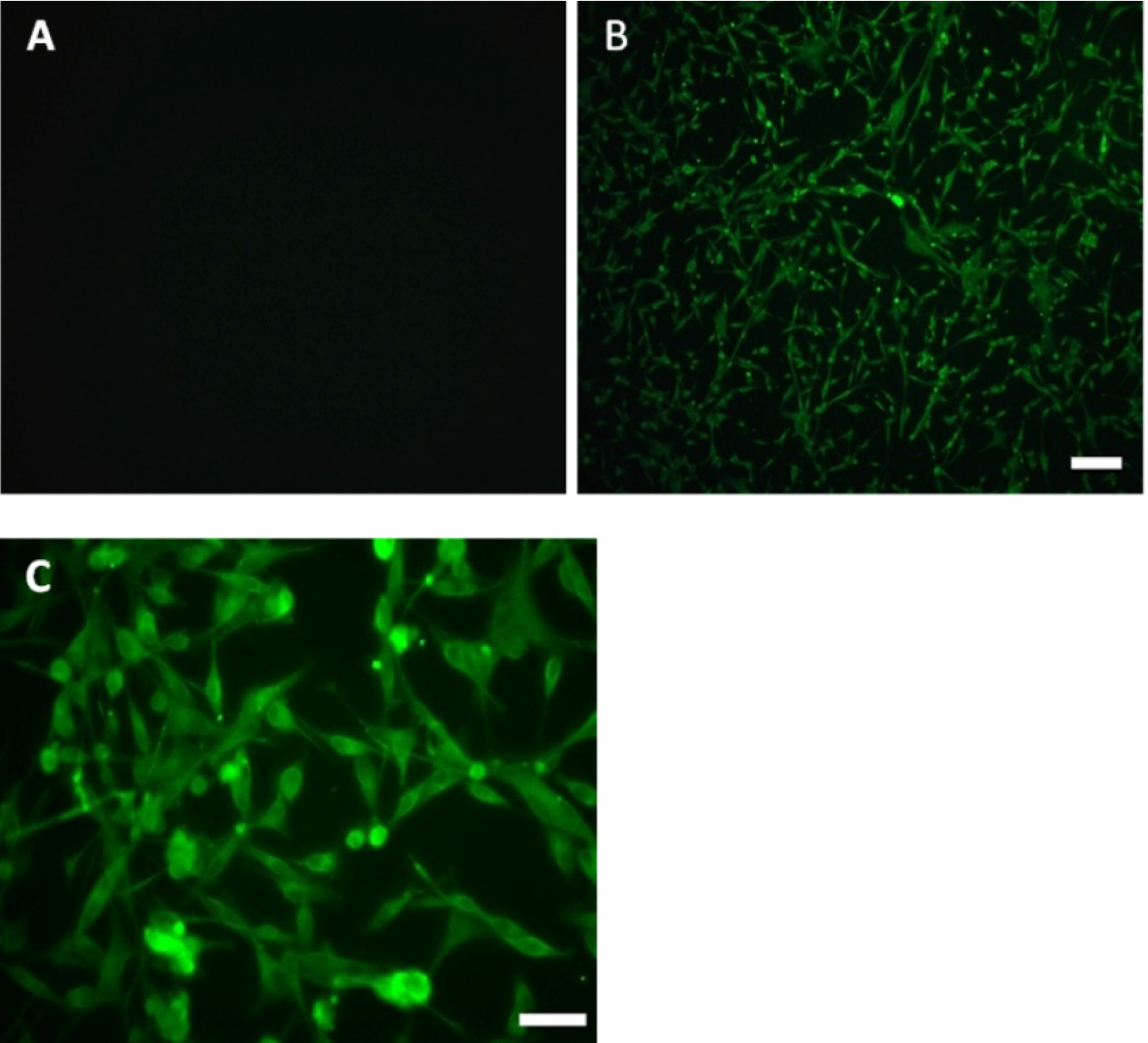
Figure 3. Expression of S100-beta antigen in purified primary astrocytes after 3 weeks of culture. A. Primary astrocytes were expressed astrocytic antigen of S100-beta (negative control); Primary astrocytes were expressed astrocytic antigen of S100-beta observed under an inverted fluorescence microscope with 10x objective lens (B) and 40x objective lens (C), scale bars = 50 µm (B), 100 µm (C).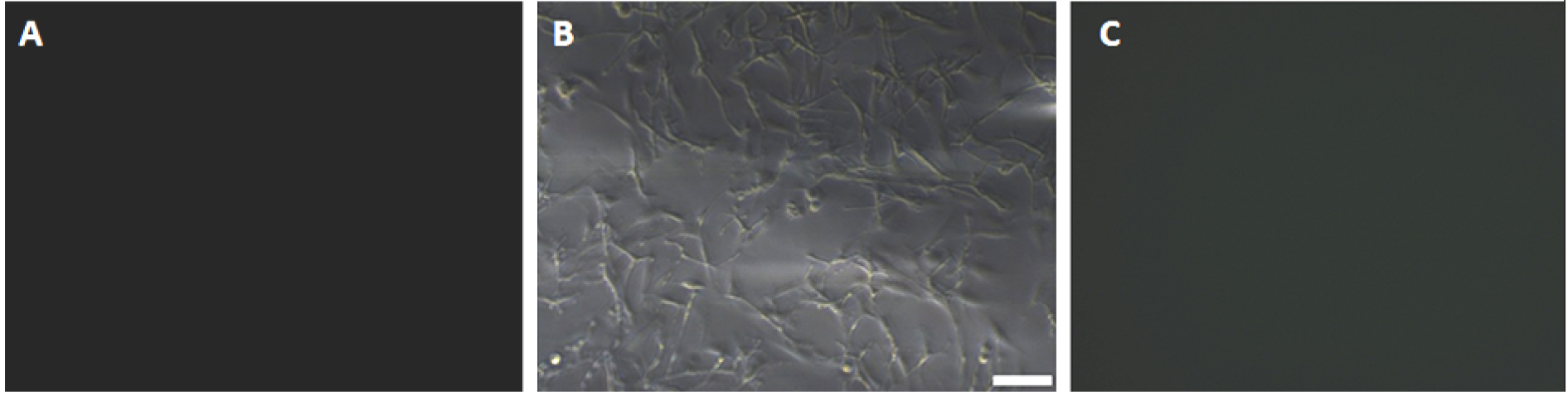
Figure 4. Assessment of fibronectin antigen in purified primary astrocyte culture in order to observe fibroblast cell contamination after 3 weeks of culture. A. Fibroblastic antigen of fibronectin was not observed in the negative control. B. Primary astrocytes were observed with phase contrast microscopy, scale bar = 100 µm. C. Fibroblastic antigen of fibronectin was not observed in primary astrocyte culture.
- Seed 5 x 103 cells into each well of a 24-well culture dish.
Data analysis
Confirmation of cultured primary astrocytes was done by detection of marker S100-beta via fluorescence immunocytochemical analysis. This analysis demonstrated that isolated cells from glioblastoma expressed S100-beta antigen. As a result, this protocol is efficient to isolate a purified population of astrocytes. Test results are obtained from three independent experiments.
Notes
- Pathological result should confirm that patient tumor specimen is glioblastoma multiforme.
- 15 ml Falcon tube containing 5 ml cold HBSS and 10% antibiotic-antimycotic was preserved in refrigerator and glioblastoma sample was transferred into the tube after surgery. Then, the tube containing HBSS, 10% antibiotic-antimycotic and glioblastoma sample was transferred to lab on dry ice.
- Freezed glioblastoma sample can’t be used to isolate primary cell culture. We have examined several freezed samples and we could not derive primary astrocyte from these freezed samples. So, sample must be fresh. Whereas, primary astrocytes derived from fresh sample have freeze-thaw tolerance.
- Most steps should be performed in a sterile ventilation hood.
- All reagents used in Procedures B-E should be pre-warmed at 37 °C before use. Exception is for washing and mincing tissue with cold PBS.
- The amount of trypsin directly depends on the sample size of glioblastoma. Increase the Trypsin volume for large tumor sample according to Table 2.
Table 2. Relation between sample diameter and trypsin volumeDiameter (millimeter) Trypsin volume (milliliter) 5 1 10 2 15 3 20 4 - Long time and vigorous mechanical dissociation decrease cell viability (survival rate and growth). Primary cells are sensitive.
- We don’t use any growth factor in this method and FBS is nutrition substance in culture medium.
- Glioblastoma tumors have abundant blood vessels. Blood vessels can transfer fibroblast cells to culture. According to this protocol, if add fetal bovine serum gradually to culture, fibroblast cells can’t attach to the bottom of culture flask. Finally, the purity of isolated astrocytes from glioblastoma can be increased.
Recipes
- Culture medium (200 ml)
178 ml DMEM/F12
20 ml FBS
2 ml Pen/Strep
Store at 4 °C - Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (500 ml)
Dissolve1 tablet PBS in 500 ml MiliQ water
Filter-sterilize and store at 4 °C - 4% paraformaldehyde
Dissolve 4 g paraformaldehyde in 100 ml PBS - 0.2% Triton X-100
Add 10 µl Triton X-100 in 5 ml PBS - 10% bovine serum albumin
Dissolve 0.5 g bovine serum albumin in 5 ml PBS
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant 20035 from School of Advanced Technologies in Medicine and grant 19925 from Brain and Spinal Cord Injury Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences. The protocol was adopted from Hashemi et al. (2016).
References
- Hashemi, M., Fallah, A., Aghayan, H. R., Arjmand, B., Yazdani, N., Verdi, J., Ghodsi, S. M., Miri, S. M. and Hadjighassem, M. R. (2016). A new approach in gene therapy of glioblastoma multiforme: human olfactory ensheathing cells as a novel carrier for suicide gene delivery. Mol Neurobiol 53(8): 5118-5128.
- Stupp, R., Mason, W. P., van den Bent, M. J., Weller, M., Fisher, B., Taphoorn, M. J., Belanger, K., Brandes, A. A., Marosi, C., Bogdahn, U., Curschmann, J., Janzer, R. C., Ludwin, S. K., Gorlia, T., Allgeier, A., Lacombe, D., Cairncross, J. G., Eisenhauer, E., Mirimanoff, R. O., European Organisation for, R., Treatment of Cancer Brain, T., Radiotherapy, G. and National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials, G. (2005). Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10): 987-996.
- Wen, P. Y. and Kesari, S. (2008). Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5): 492-507.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Hashemi, M. and Hadjighassem, M. (2017). Preparation of Primary Astrocyte Culture Derived from Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Specimen. Bio-protocol 7(8): e2241. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2241.
Category
Neuroscience > Nervous system disorders > Brain tumor > Glioblastoma multiforme
Cancer Biology > General technique > Cell biology assays > Cell isolation and culture
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link