- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase Assay for Hepatitis E Virus
Published: Vol 7, Iss 7, Apr 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2199 Views: 11133
Reviewed by: Yannick DebingVamseedhar RayaproluDavid Paul

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Mapping RNA Sequences that Contact Viral Capsid Proteins in Virions
C. Cheng Kao [...] Doug B. Rusch
Jul 20, 2017 8852 Views

Real-time Fluorescence Measurement of Enterovirus Uncoating
Visa Ruokolainen [...] Varpu Marjomäki
Apr 5, 2020 4632 Views

Viral Double-Stranded RNA Detection by DNase I and Nuclease S1 digestions in Leishmania parasites
Nathalie Isorce and Nicolas Fasel
May 5, 2020 5888 Views
Abstract
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is essential for the replication of viral RNA for RNA viruses. It synthesizes the complementary strand of viral genomic RNA, which is used subsequently as a template to generate more copies of viral genome. This assay measures activity of the hepatitis E virus (HEV) RdRp. In contrast to protocols available to assay the RdRp activity of many other viruses, this assay utilizes DIG-11-UTP as a nonradioactive alternative to 32P-UTP, thereby increasing the convenience of performing the assay.
Keywords: Hepatitis E virusBackground
No assay was available to measure the activity of HEV RdRp. RdRp activity has been measured in few other viruses such as hepatitis C virus using a radiolabeled nucleotide (Behrens et al., 1996). We have adapted the protocol described by Behrens et al. (1996) and modified it to establish a non-radioactive assay protocol, which is dependent on incorporation of DIG-11-UTP into the antisense RNA strand as a measure of the activity of HEV RdRp. This assay utilizes an in vitro synthesized viral RNA fragment as a template to measure the activity of HEV RdRp protein purified from human hepatoma cells using a chemiluminescence-based strategy.
Materials and Reagents
- 60 mm plates
- 1.6 ml RNase free microcentrifuge tube
- PVDF (Polyvinylidene fluoride) membrane (Pall, catalog number: BSP0149 )
- Nylon membrane (Pall, catalog number: 60207 )
- Whatman filter paper (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: WHA10426972 )
- Cling film wrap/plastic food wrap (available in general stores/supermarkets)
- Blotting paper (Praveen Scientific, catalog number: PSC 006 )
Note: It is general blotting paper, used in labs in routine application, similar to but cheaper than Whatman filter paper. - Mammalian expression plasmids (pUNO RdRp-flag [RdRp sequence with C-terminal flag tag was PCR amplified, digested with AgeI, NheI and ligated into pUNO vector digested with same], pUNO ORF2-flag [ORF2 with C-terminal flag tag was PCR amplified with primers: pUNO ORF2-flag FP, pUNO ORF2-flag RP; digested with BglII and ligated into pUNO vector digested with NheI [blunted] and BamHI); Nair et al. [2016])
- Huh7 (human hepatoma cells, obtained from Dr. C. M. Rice; Blight et al. [2000])
- pSKHEV2 RdRp template (pSK HRt) plasmid (Genbank No. AF444002.1, Emerson et al., 2004)
- Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11668019 )
- DMEM
- 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS)
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Bio Basic, catalog number: PD0100 )
- Flag M2 agarose resin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2220 )
- Flag peptide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F4799 )
- Octa-probe antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-807 )
- Skimmed milk powder (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 70166 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Anti-rabbit IgG Horseradish peroxidase(HRPO) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-2004 )
- Clarity Western ECL blotting substrate (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1705061 )
- Silver stain kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 24612 )
- Bradford assay reagent (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 5000002 )
- StuI, NheI and Tth111I restriction enzymes
- BglII (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0144L )
- PCR purification kit (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 400771 )
- mMessage mMachine T7 kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, AmbionTM, catalog number: AM1344 )
- RNAsin
- ATP
- CTP
- GTP
- UTP
- DIG-UTP
- Actinomycin D (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A1410 )
- DMSO
- RNase A
- Proteinase K (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P2308 )
- Glycogen (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G0885 )
- Ethanol (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 100983 )
- Nuclease free water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, AmbionTM, catalog number: AM9937 )
- Agarose (Bio Basic, catalog number: AB0014 )
- DEPC-treated water (Thermo Fisher Scientific, AmbionTM, catalog number: AM9922 )
- 37% formaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F8775 )
- Formamide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F9037 )
- Gel loading dye
- Millennium marker (Thermo Fisher Scientific, AmbionTM, catalog number: AM7151 )
- Ethidium bromide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E1510 )
- DIG Northern Starter Kit (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 12039672910 )
- Tris (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6066 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E6758 )
- Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N’,N’,-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 03777 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93418 )
Note: This product has been discontinued. - Sodium pyrophosphate tetrabasic decahydrate (Na4P2O4·10H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6422 )
- β-glycerol phosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 50020 )
- Sodium orthovanadate (Na3VO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6508 )
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 04693132001 )
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8266 )
- DL-dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9333 )
- SDS
- MOPS (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5162 )
- Sodium acetate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S2889 )
- Maleic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M0375 )
- Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416 )
- Tri-sodium citrate dihydrate (Himedia, catalog number: RM1415 )
- IP (Immunoprecipitation) buffer (see Recipes)
- 5x assay buffer (see Recipes)
- 2x proteinase K buffer (see Recipes)
- 10x MOPS (pH 7.0) (see Recipes)
- 20x SSC buffer (see Recipes)
- Maleic acid buffer (pH 7.5) (see Recipes)
- 1x blocking solution (see Recipes)
- Washing buffer (pH 7.5) (see Recipes)
- Detection buffer (pH 9.5) (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffered saline with 0.1% Tween 20 (PBST, see Recipes)
Equipment
- 5% CO2 incubator
- Centrifuge
- Flip-flop rocker
- Gel documentation system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: ChemiDocTM MP )
- Chemical fume hood
- Conical flask
- Standard horizontal agarose gel electrophoresis apparatus
- Rectangular glass tray
- Glass plates
- Glass jar
- UV cross linker (UVP, model: CL-1000 )
Procedure
- Preparation of flag-affinity purified proteins
- Transfect 3 μg each of pUNO RdRp-flag and pUNO ORF2-flag plasmids into ten 60 mm plates (each plasmid transfected into 10 plates, not cotransfected), containing Huh7 human hepatoma cells, using Lipofectamine 2000 in 1:1 ratio, following manufacturer’s instructions. Incubate cells at 37 °C in 5% CO2 incubator. 24 h post-transfection, replace media with 2 ml DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum.
- 48 h post transfection, wash the cells with 1x PBS and resuspend each dish in 800 μl IP buffer.
- Generate a homogenous suspension by repeated pipetting and vortexing, and incubate overnight (16 h) on ice at 4 °C (cold room or fridge).
- Next day, clarify the lysate by centrifugation at 13,000 x g, 4 °C, 10 min and collect the supernatant into a fresh 1.6 ml RNase free microcentrifuge tube.
- Pool lysates of all ten plates and add 100 μl of flag agarose beads, incubate on rocker at 4 °C for 4 h, wash 3 x in 1 ml IP buffer each by centrifuging at 800 x g, 1 min, at 4 °C. Add 200 μl flag peptide (0.2 mg/ml in PBS) and incubate on a rocker for 15 min at 4 °C. Centrifuge at 800 x g, 1 min, at 4 °C and collect the supernatant, which contains the eluted protein.
- Check an aliquot of the purified protein by Western blotting using octa-probe antibody and silver staining, as mentioned below.
- Resolve the proteins by 10% SDS-PAGE and transfer onto a PVDF (Polyvinylidene fluoride) membrane.
- Block the membrane using 5% skimmed milk in 1x PBS for 45 min at room temperature, incubate overnight (16 h) with 1:1,000 octa-probe primary antibody diluted using 5% skimmed milk in 1x PBST at 4 °C, wash 3 x in PBST, incubate with 1:5,000 anti-rabbit IgG HRPO secondary antibody diluted using 5% skimmed milk in 1x PBST at room temperature, followed by detection of the signal by enhanced chemiluminescence using ‘clarity Western ECL blotting substrate’.
- Acquire the Images and analyze using a gel documentation system. A single band of approximately 55 kDa should be obtained, as illustrated in Nair et al. (2016).
- For silver staining, resolve the proteins in 10% SDS-PAGE.
- Proceed for silver staining using silver stain kit, following the manufacturer’s protocol (Thermo Fisher Scientific). A single band of approximately 55 kDa should be obtained as illustrated in Nair et al. (2016).
- If expected bands are obtained in Western and silver staining, estimate the respective protein concentration by serial dilutions by Bradford assay and store the protein in single use aliquots at -80 °C.
- Transfect 3 μg each of pUNO RdRp-flag and pUNO ORF2-flag plasmids into ten 60 mm plates (each plasmid transfected into 10 plates, not cotransfected), containing Huh7 human hepatoma cells, using Lipofectamine 2000 in 1:1 ratio, following manufacturer’s instructions. Incubate cells at 37 °C in 5% CO2 incubator. 24 h post-transfection, replace media with 2 ml DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum.
- Preparation of template for RdRp assay
- Fuse HEV genomic regions 1-130 bases and 6,963-7,204 bases (from 5’-end) to each other by removing 131-6,962 bases from pSKHEV2 plasmid. Briefly, pSKHEV2 plasmid was digested with StuI, NheI and Tth111I restriction enzymes, followed by gel extraction of ~3.5 kb band. This fragment was treated with DNA polymerase I klenow fragment to generate blunt end, followed by self-ligation. Resulting plasmid is named as pSK HRt. Plasmid is available on request. This plasmid has been described in our earlier publication (Nair et al., 2016).
- Linearize 10 µg pSK HRt plasmid using 50 U BglII ( R0144L , NEB, buffer 3.1) in 50 µl reaction mix (5 µl 10x buffer, 20 µl DNA, 2.5 µl enzyme and 22.5 µl water). Purify the linearized DNA using PCR purification kit. Use 1 µg linearized DNA for in vitro transcription using mMessage mMachine T7 Kit, following manufacturer’s instruction, to generate a 340 nucleotide long capped RNA, which is to be used as template in RdRp assay to monitor antisense strand synthesis.
- Verify the size and integrity of the RNA by formaldehyde agarose gel electrophoresis.
- Quantify the RNA by spectrophotometry and store in single use aliquots in RNase free microcentrifuge tubes at -80 °C.
- Fuse HEV genomic regions 1-130 bases and 6,963-7,204 bases (from 5’-end) to each other by removing 131-6,962 bases from pSKHEV2 plasmid. Briefly, pSKHEV2 plasmid was digested with StuI, NheI and Tth111I restriction enzymes, followed by gel extraction of ~3.5 kb band. This fragment was treated with DNA polymerase I klenow fragment to generate blunt end, followed by self-ligation. Resulting plasmid is named as pSK HRt. Plasmid is available on request. This plasmid has been described in our earlier publication (Nair et al., 2016).
- RdRp assay
- Assemble the reaction as described below in RNase free tubes.
Nuclease free water: 16 µl 5x buffer 8 µl RNAsin 1 µl ATP (10 mM) 2 µl CTP (10 mM) 2 µl GTP (10 mM) 2 µl UTP (10 mM) 1.5 µl DIG-UTP (10 mM) 0.5 µl Actinomycin D (2 mg/ml stock in DMSO) 1 µl Protein (400 ng/µl) 5 µl RNA template (500 ng/µl) 1 µl Total volume 40 µl - Incubate at 22 °C for 2 h.
- Use appropriate negative controls such as RNA template without protein or RNA template with an unrelated protein (ORF2).
- Run one additional sample containing RNA template with RdRp and digest it with RNase A (add 1 μl of 10 mg/ml RNase A to the tube, incubate at 37 °C for 10 min).
- Add 50 µl 2x proteinase K buffer and 1 µl proteinase K (50 mg/ml stock solution in water) and incubate for 10 min at 37 °C.
- Add 1 µl glycogen (10 mg/ml stock solution in water) and 1 ml of ice-cold absolute ethanol to the samples; incubate at -80 °C for 45 min.
- Centrifuge the samples at 14,000 x g, 15 min, 4 °C.
- Wash the pellet with 1 ml 75% ethanol and resuspend in 10 µl nuclease free water.
Note: Be careful while removing the 75% ethanol, pellet may be lost. Although not necessarily a better alternative, it may be possible to minimize pellet loss by gently pipetting out 75% ethanol instead of directly decanting. Irrespective of whatever handling technique preferred, attention should be given not to disturb the pellet. - Resolve the samples by 1.5% formaldehyde agarose gel electrophoresis in a chemical fume hood.
- Assemble the reaction as described below in RNase free tubes.
- Formaldehyde agarose gel electrophoresis of RNA samples
- For 100 ml, add 0.75 g agarose in 72 ml DEPC-treated water in a conical flask and boil. When the solution has cooled to 55 °C, add 18 ml of 37% formaldehyde and 10 ml 10x MOPS. Cast the gel in gel running apparatus and allow to solidify.
Note: Do not add formaldehyde and MOPS to very hot agarose solution. Perform the entire procedure in a chemical fume hood. - Run the gel for 30 min prior to loading the samples.
- Mix 5 µl RNA, 3 µl 10x MOPS, 6 µl formaldehyde, 15 µl formamide and incubate at 85 °C for 10 min, followed by cooling on ice for 2 min. Add 2.5 µl of freshly prepared gel loading dye and load samples into the gel and run at 3-4 V/cm in 1x MOPS until the lower dye has migrated two third of the distance from the top.
- Run RNA molecular weight marker (Millennium marker, Ambion, USA) in parallel to monitor the size of the RdRp assay products. Excise the lane corresponding to the marker and stain with ethidium bromide (2 μl of 10 mg/ml stock in 50 ml running buffer) for 15 min to visualize the markers. Proceed with rest of the gel for transfer to nylon membrane.
- For 100 ml, add 0.75 g agarose in 72 ml DEPC-treated water in a conical flask and boil. When the solution has cooled to 55 °C, add 18 ml of 37% formaldehyde and 10 ml 10x MOPS. Cast the gel in gel running apparatus and allow to solidify.
- Transfer of RNA and detection of signal
- Rinse the gel twice in 20x SSC buffer for 15 min each.
- Incubate the positively charged nylon membrane in DEPC-treated water until it is completely wet from beneath.
- Immerse the membrane in 10x SSC buffer for 5 min.
- In a glass tray, add 20x SSC buffer and put a glass plate on a glass jar. Spread a Whatman filter paper wick over the glass plate so that the tips are completely immersed in the buffer.
- Place the gel in inverted position. Make a notch on left side of the gel.
- Place the membrane on the gel without trapping air bubbles.
- Cover the sides of the gel with plastic wrap and remove air bubbles.
- Place a Whatman paper cut in the same size of the gel on top of the membrane.
- Place a stack of blotting paper cut in the same size of the gel on top of the Whatman paper.
- Put a glass plate on the stack and keep a 500 g weight support on top of it.
- Allow transfer overnight without disturbance.
- Next day, dismantle the transfer assembly and keep the membrane on a filter paper.
- Fix the RNA to the membrane by UV crosslinking (120 millijoules/cm2) for 1 min.
- Rinse the membrane briefly in DEPC-treated water.
- Rinse the membrane in washing buffer for 5 min at room temperature.
- Incubate the membrane in 20 ml of 1x blocking solution (see Recipes) for 30 min at room temperature.
Note: Be careful not to allow the membrane to dry at any point from this step onwards. - Incubate in 10 ml of anti-DIG antibody solution (1:10,000 in 1x blocking solution) for 30 min at room temperature. Antibody comes in the DIG Northern Starter Kit.
- Equilibrate in 100 ml detection buffer for 5 min at room temperature.
- Place the membrane on a development folder and apply CDP star (part of DIG Northern Starter Kit) and incubate for 5 min in the dark at room temperature.
Note: Remove all air bubbles. - Acquire chemiluminescent images using a gel documentation system or using an X ray film.
- Rinse the gel twice in 20x SSC buffer for 15 min each.
Data analysis
While setting up the RdRp assay, appropriate controls should be included in order to interpret the data and rule out non-specific signal. Must have negative controls such as omission of nucleotides from the reaction mixture and inclusion of RNase A in the reaction mixture. No bands should be obtained in both the cases. A titration experiment using increasing quantities of RdRp protein in the assay should also be performed to rule out non-specific signals. Assay using an unrelated protein instead of RdRp will also rule out the possible non-specific signal. A sample assay with all controls has been illustrated in Figure 1. The effect of other factors or compounds on RdRp activity may be evaluated by adding them to the reaction mixture. In our experience, template itself does not give any false signal, as the assay is dependent on detection of DIG, which is incorporated into the RNA only as DIG-UTP. Free DIG-UTP is removed from the reaction during migration of the sample in agarose gel. Moreover, the labeled RNA migrates at ~800 base pairs size whereas template RNA size is 380 base pairs. Monitoring the size of the band also allows one to be confident of the output of the assay.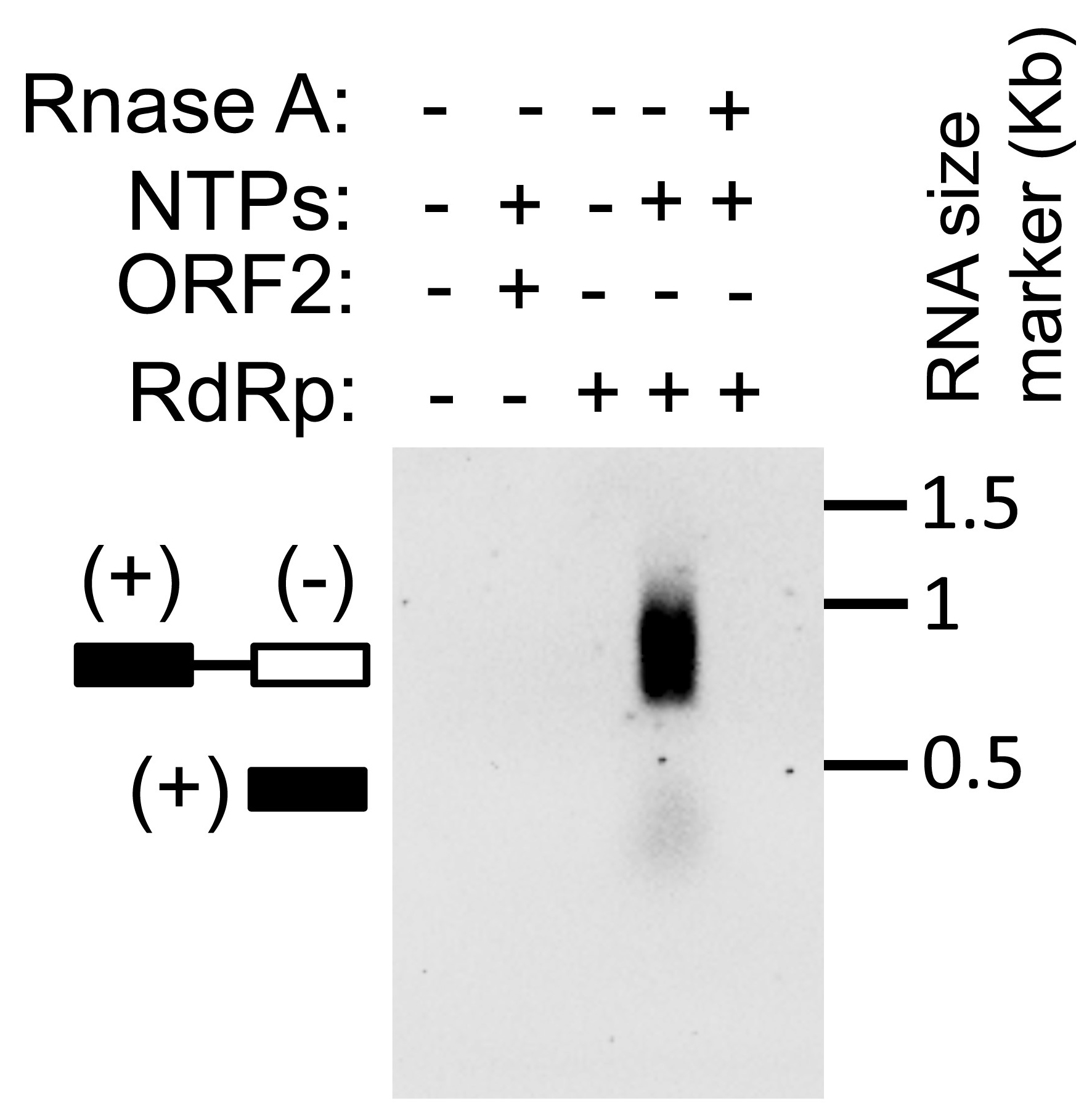
Figure 1. Assay of HEV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity. NTPs: nucleotide triphosphates.
Recipes
- IP buffer (store at 4 °C)
20 mM Tris (pH 7.4)
150 mM NaCl
1 mM EDTA (pH 8.0)
1 mM EGTA (pH 8.0)
1% Triton X-100
2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate
1 mM β-glycerol phosphate
1 mM sodium orthovanadate
1x protease inhibitor cocktail (25x stock prepared by dissolving one tablet in 2 ml 1x PBS) - 5x assay buffer (store at -20 °C)
200 mM Tris (pH 7.5)
100 mM MgCl2
200 mM DTT
200 mM KCl
100 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) - 2x proteinase K buffer
300 mM NaCl
100 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5)
1% SDS - 10x MOPS (pH 7.0)
200 mM MOPS
50 mM NaAc
20 mM EDTA (pH 7) - 20x SSC
3 M NaCl
300 mM sodium citrate (pH 7) - Maleic acid buffer (pH 7.5)
100 mM maleic acid
150 mM NaCl (pH 7.5) - 1x blocking solution
Dilute the 10x blocking solution available in the DIG Northern Starter Kit with maleic acid buffer to 1x
Note: Prepare fresh. - Wash buffer (pH 7.5)
100 mM maleic acid
150 mM NaCl
0.3% Tween 20 (pH 7.5) - Detection buffer (pH 9.5)
100 mM Tris-Cl
100 mM NaCl (pH 9.5) - Phosphate buffered saline with 0.1% Tween 20 (PBST)
1x phosphate-buffered saline
0.1% Tween 20
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by Ramalingaswamy fellowship and THSTI core grant to MS. VN is supported by a grant from the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India. The protocol has been adapted from Behrens et al. (1996).
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest or competing interest.
References
- Behrens, S. E., Tomei, L. and De Francesco, R. (1996). Identification and properties of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus. EMBO J 15(1): 12-22.
- Blight, K. J., Kolykhalov, A. A. and Rice, C. M. (2000). Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290(5498): 1972-1974.
- Emerson, S. U., Nguyen, H., Graff, J., Stephany, D. A., Brockington, A. and Purcell, R. H. (2004). In vitro replication of hepatitis E virus (HEV) genomes and of an HEV replicon expressing green fluorescent protein. J Virol 78(9): 4838-4846.
- Nair, V. P., Anang, S., Subramani, C., Madhvi, A., Bakshi, K., Srivastava, A., Shalimar, Nayak, B., Ct, R. K. and Surjit, M. (2016). Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced synthesis of a novel viral factor mediates efficient replication of genotype-1 hepatitis E virus. PLoS Pathog 12(4): e1005521.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Nair, V. P., Anang, S., Srivastava, A. and Surjit, M. (2017). RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase Assay for Hepatitis E Virus. Bio-protocol 7(7): e2199. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2199.
- Nair, V. P., Anang, S., Subramani, C., Madhvi, A., Bakshi, K., Srivastava, A., Shalimar, Nayak, B., Ct, R. K. and Surjit, M. (2016). Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced synthesis of a novel viral factor mediates efficient replication of genotype-1 hepatitis E virus. PLoS Pathog 12(4): e1005521.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > RNA
Biochemistry > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









