- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In silico Analysis and Site-directed Mutagenesis of Promoters
Published: Vol 7, Iss 6, Mar 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2181 Views: 10711
Reviewed by: HongLok LungRaghuveer KavarthapuAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Editing the Serratia proteamaculans Genome Using the Allelic Exchange Method
Ksenia Chukhontseva [...] Ilya Demidyuk
Sep 20, 2025 1390 Views

CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Targeted Mutagenesis of the Moss Physcomitrium patens by Particle Bombardment-Mediated Transformation
So Takenaka [...] Setsuyuki Aoki
Sep 20, 2025 1010 Views

Creating Loss-of-Function Mutants of Neurospora crassa Using a Novel CRISPR/Cas9 System
Stefanie Grüttner
Jan 5, 2026 203 Views
Abstract
In normal as in cancerous cells, gene expression is tightly regulated by transcription factors, which are responsible for up- or down-regulation of thousands of targets involved in different cell processes. Transcription factors can directly regulate the expression of genes by binding to specific DNA sequences known as response elements. Identification of these response elements is important to characterize targets of transcription factors in order to understand their contribution to gene regulation. Here, we describe In silico analysis coupled to selected mutagenesis and promoter gene reporter assay procedures to identify and analyze response elements in the proximal promoter sequence of genes.
Keywords: Site-directed mutagenesisBackground
The impact of a transcription factor on global gene expression can be studied through its knockdown using shRNA or CRISPR-Cas9 methods followed by microarray analysis which can provide significant data on hundreds of dysregulated genes. This analysis, although very useful, lacks information about the direct control of the dysregulated genes. To further investigate these genes, In silico analysis using bioinformatics provides additional information to identify direct targets of the transcription factor studied. Additionally, the functionality of these response elements can be analyzed using site-directed mutagenesis and promoter-gene-reporter assays. We have shown recently that the oncogenic transcription factor MYC (Cellular Myelocytomatosis Oncogene) controls the expression of the ITGA1 (integrin alpha 1 subunit) gene in colorectal cancer, and that their expression correlates in 72% of colorectal tumors. This protocol describes a procedure for the analysis of the ITGA1 promoter and the identification of response elements for the MYC oncogene. The latter is known to be a member of the MYC/MAX/MAD network. Interactions between these factors lead to gene activation or repression depending on upstream signalization and cell condition.
Materials and Reagents
- 1.5 ml tubes
- 10 cm dish
- 12-well plates (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 353043 )
- White 96-well assay plate (Corning, catalog number: 3912 )
- Ice
- HEK293T cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3216 ) at low passage
- DH5α competent cells
- Primers (Sequences of the oligonucleotide primers used for the site directed mutagenesis):
Forward 5’-CGACTTCACGGTGAATTTGGACAATCCGCAGGGGATGGAAGG-3’
Reverse 5’-CCTTCCATCCCCTGCGGATTGTCCAAATTCACCGTGAAGTCG-3’ - The promoter of interest, as for example here, the ITGA1 proximal promoter sequence inserted in the pLightSwitch_prom plasmid vector (SwitchGear Genomics, catalog number: S706788 )
- Plasmid constructs carrying the activator or repressor to be characterized, as for example here: pcDNA-Empty vector, pcDNA-MYC and pCMV-MAD, as described in Ni et al., 2005
- The pGL4.13 plasmid (luc2/SV40) as a control of transfection efficiency
- GeneArt Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: A13282 )
- DNase and RNase free water
- Distilled water
- 0.5 M EDTA, pH 8
- SOC medium
- LB agar plates
- Trypan blue
- Effectene transfection reagent (QIAGEN, catalog number: 301425 )
- PBS
- DMEM medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11995073 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (BOLLE COMMUNICATION, WISENT, catalog number: 080-150 )
- GlutaMAX (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 35050061 )
- HEPES (BOLLE COMMUNICATION, WISENT, catalog number: 330-050-EL )
- Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega, catalog number: E1980 )
Luciferase Assay substrate
Luciferase Assay buffer - DMEM culture medium for HEK293T cells (see Recipes)
- LAR II solution (see Recipes)
- 1x Stop & Glo (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Orion Microplate Luminometer (Berthold, Bad Wildbad, Germany)
- MyCycler Personal Thermal Cycler for PCR reactions (Bio-Rad Laboratories)
- Water bath
- Cell culture incubator
Software
- MatInspector web based software. Genomatix (Munich, Germany)
https://www.genomatix.de/online_help/help_matinspector/matinspector_help.html - Blast Global Align
https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&PROG_DEF=blastn&BLAST_PROG_DEF=blastn&BLAST_SPEC=GlobalAln&LINK_LOC=BlastHomeLink
Procedure
- Promoter analysis
- The proximal promoter sequence of the promoter of interest, the ITGA1 gene, can be downloaded from the reference human genome or from the switchdb website: http://switchdb.switchgeargenomics.com/productinfo/id_706788/
- Genomatix website: upload the promoter sequence and use the default parameters or use the promoter search.
- Guideline detailed in:
https://www.genomatix.de/online_help/help_matinspector/matinspector_help.html#eldo_promoters - The identified response elements are compared to the consensus sequence (which binds the transcription factor). For instance, for MYC, possible response elements are compared to the E-box element CACGTG. In addition to the results obtained with the software, visual analysis of the promoter sequence is highly recommended.
- Site directed mutagenesis
Design primers manually and change nucleotides in order to completely modify the sequence of the identified response elements (avoid creating a response element for another transcription factor). The mutations should be centrally located in both the forward and reverse primers. The primers should be complementary and 35 to 45 nucleotides in length to insure proper annealing. - Prepare the PCR mix (excepting primers, all reagents are included in the GeneArt Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit)

- PCR reaction
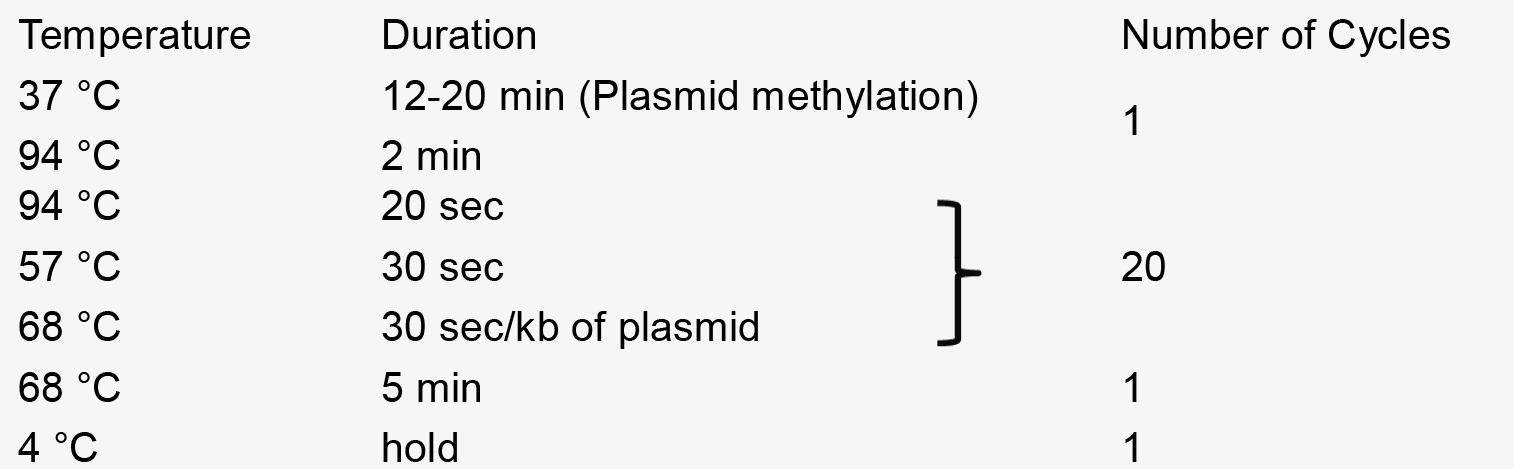
- Recombination reaction
This step allows the conversion of the plasmid from a linear to a circular form.
In a 1.5 ml tube add: 4 µl of reaction buffer (5x), 2 µl of enzyme mix (10x), 4 µl of PCR sample and complete to 20 µl with RNase-free water. Incubate 10 min at room temperature (RT). Stop the reaction with 1 µl of 0.5 M EDTA. The next step should be started immediately after recombination. Prepare for the transformation step before beginning the recombination reaction. - Transformation
- Thaw vials of DH5α cells on ice for 5 to 7 min.
- Transfer 2 μl of the recombination reaction directly to the vial of DH5α cells and mix by tapping gently (Reaction A).
- Incubate the tubes on ice for 12 min.
- Immediately incubate the vials at 42 °C for 30 sec (do not exceed 30 sec) and then re-incubate on ice for 2 min.
- Add 250 μl of SOC medium to each vial (Reaction A) and then incubate at 37 °C for 1 h with 225 rpm shaking (Reaction B).
- Add 10 μl from Reaction B to 90 μl of SOC medium, then spread 100 μl onto LB plates and incubate overnight.
- Select 5 to 10 colonies and isolate DNA from the bacteria.
- Analyze and confirm, by DNA sequencing, the presence of the induced mutations in the promoter.
- Store DNA at -20 °C.
- Transient transfection
- Culture HEK293T cells in DMEM media supplemented with 10% FBS (without antibiotics).
- Use trypsin to dissociate HEK293T cells (1 ml per 10 cm dish) and incubate at 37 °C for 2 min. Add DMEM and count live cells (using trypan blue) in suspension and then plate 50,000 cells per well in 12-well plates. Add a total of 1 ml of DMEM 10% FBS media to each well.
- Begin the transient transfection the following day.
- For transfection, prepare plasmids in 1.5 ml tubes as for the following example:
Table 1. Plasmid preparation for transient transfection into HEK293T cells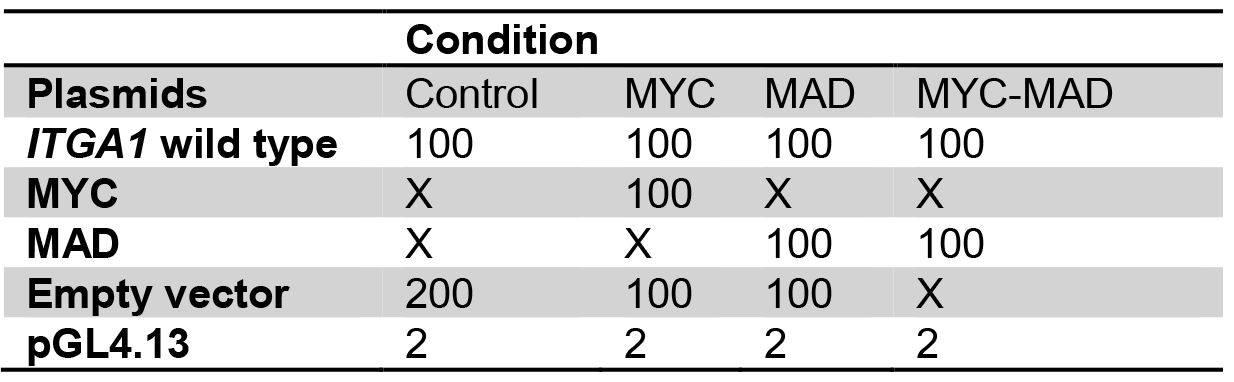
Table 2. Plasmid mix for the comparison between wild type and mutated ITGA1 promoter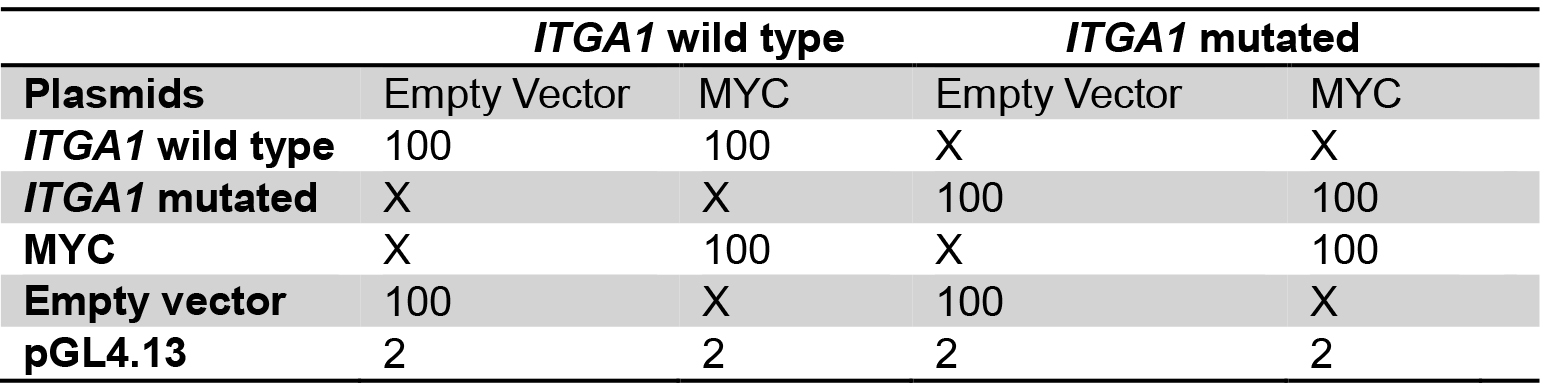
Plasmid quantities are in ng
X: no plasmid transfection
Transfect with the same total quantity of plasmid for every well.
Amounts are for one well, calculate quantities for triplicates. - Add 50 µl of buffer EC and 1.5 µl of enhancer, mix gently and incubate for exactly 5 min.
- Add Effectene reagent (2 µl/well), mix gently and then incubate for 10 min.
- Change the media in the 12-well plates and then add the plasmid mix to each well. Incubate for 48 h.
- Add one volume of passive lysis buffer to four volumes of distilled water.
- Remove the media from the wells and rinse once gently with cold 1x PBS.
- Add 250 µl of 1x passive lysis buffer for each well of the 12-well plates and then shake gently for 15 min.
- Luminometer settings: set injectors 1 and 2 to dispense 50 µl of LARII and Stop & Glo solutions.
- For measurement, use 10 sec for reading time and 2 sec as a delay.
- Transfer 10 µl from each PLB lysate and put in 96 well-plate (avoid pipetting the cell debris).
- Run the measurement of luciferase activity.
Data analysis
- Response elements identified using MatInspector© software should be analyzed and selected according to their similarity to the consensus sequence. Response elements with the same sequence as the consensus response element (for the transcription factor studied) as incomplete sequences should be taken into account for the mutagenesis analysis (Boudjadi et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2011; Teye et al., 2008).
- After plasmid mutation, the sequence of the new plasmid should be aligned to the original sequence to confirm that the introduced mutations are the only differences between the wild type promoter sequence and the mutated sequence (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Alignment of the promoter sequences. Comparison of the mutated ITGA1 promoter sequence to the wild type promoter. When present, the vertical bars indicate identical nucleotides between the two sequences. The sequence of the forward primer is underlined in blue. The red square points out the mutated response element (mutation of the first response element for MYC), as reported in Boudjadi et al., 2016. - After transient transfection and cell lysis, the enzymatic activity of luciferase (which reflects the promoter activity) will be quantified using a luminometer. The data obtained will be used to analyze the promoter activity under each condition. Two values are obtained: the first one indicates the activity of the promoter of interest and the second indicates the activity of the control promoter (reflecting the transfection efficiency). For each well, the final value is the ratio between the first and the second values.
Data may be presented as fold change as indicated in Figure 2.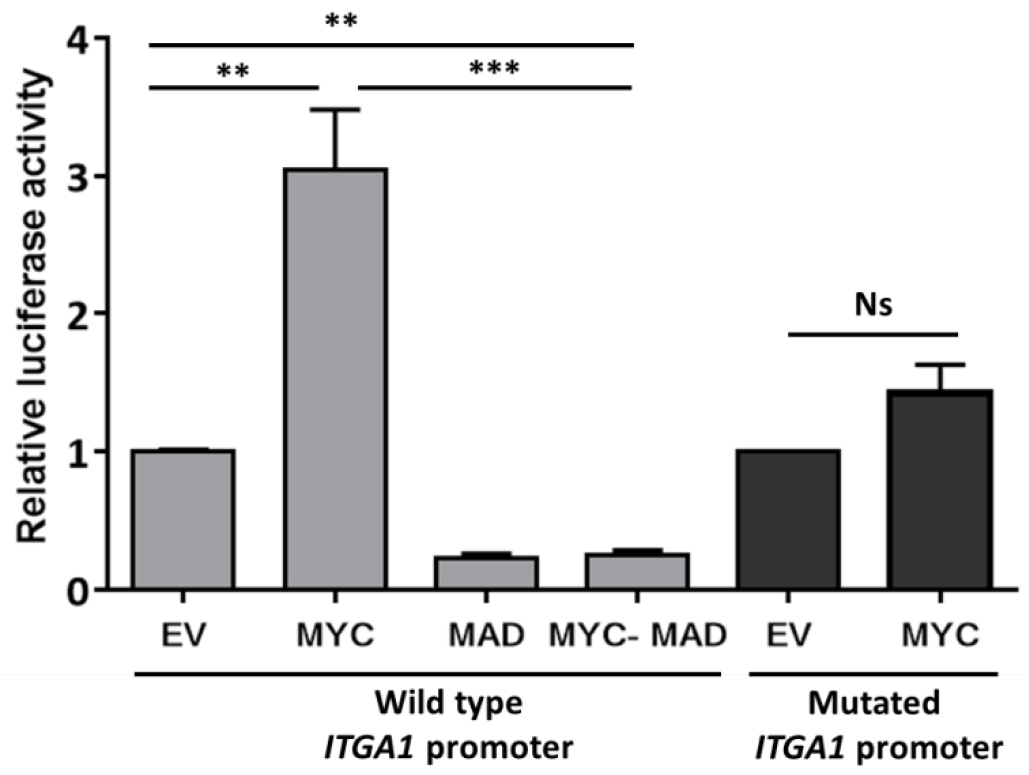
Figure2. Analysis of ITGA1 promoter activity. Results of the promoter gene reporter assay showing the relative luciferase activity presented as fold change compared to the empty vector (EV). The wild type ITGA1 promoter vector was transfected into HEK293T cells, together with the empty vector, a MYC expressing vector (MYC), the dominant negative MAD (MAD) or both (MYC-MAD). The dark gray columns indicate the activity of the mutated ITGA1 promoter (mutation of the first response element for MYC) after transfection with the empty vector or the MYC expressing vector. Experiments were repeated three times and performed in triplicate. t-test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Ns: non-significant.
Notes
- The methylation of the template plasmid is performed in order to allow its digestion by endonucleases in the host cells after transformation. Therefore, the template will be eliminated and only the mutated plasmid will be present in the transformed cells.
- HEK293T cells should not be allowed to reach confluency during the transfection.
- HEK293T cells form a fragile monolayer, therefore the media change should be done in a gentle manner.
- The MAD/MAX heterodimer recognizes the same response elements as MYC/MAX. The fact that the transfection of MAD alone or together with MYC reduced the activity of the ITGA1 promoter is an indication that this activity was enhanced when MYC was introduced alone.
- Store DMEM at 4 °C; heat to 37 °C before use, avoid keeping warm for a prolonged time.
- Do not mix the bacterial vials by pipetting up and down.
- Invert LB plate during incubation to avoid condensation and contamination.
- Prepare plasmids at 100 ng/μl to facilitate the transfection procedure.
Recipes
- DMEM culture medium for HEK293T cells
DMEM
10% FBS
2 mM GlutaMAX
10 mM HEPES - LAR II solution
Resuspend lyophilized Luciferase Assay substrate in Luciferase Assay buffer II (105 ml)
Aliquot and store at -20 °C - 1x Stop & Glo
Dilute the appropriate amount of Stop & Glo substrate (stock 50x) in Stop & Glo reagent (Always prepare a fresh solution)
Acknowledgments
We thank Elizabeth Herring for reviewing the manuscript. This work was supported by the Canadian Institute of Health Research Grant MOP-123415 (JFB is a member of the Centre de Recherche of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke funded by the Fonds de la Recherche du Québec-Santé. This protocol was adapted from Boudjadi et al. (2016), originally published in Oncogene.
References
- Boudjadi, S., Carrier, J. C., Groulx, J. F. and Beaulieu, J. F. (2016). Integrin α1β1 expression is controlled by c-MYC in colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene 35(13): 1671-1678.
- Chen, Y., Xu, J., Borowicz, S., Collins, C., Huo, D. and Olopade, O. I. (2011). c-Myc activates BRCA1 gene expression through distal promoter elements in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 11: 246.
- Ni, H., Dydensborg, A. B., Herring, F. E., Basora, N., Gagne, D., Vachon, P. H. and Beaulieu, J. F. (2005). Upregulation of a functional form of the β4 integrin subunit in colorectal cancers correlates with c-Myc expression. Oncogene 24(45): 6820-6829.
- Teye, K., Okamoto, K., Tanaka, Y., Umata, T., Ohnuma, M., Moroi, M., Kimura, H. and Tsuneoka, M. (2008). Expression of the TAF4b gene is induced by MYC through a non-canonical, but not canonical, E-box which contributes to its specific response to MYC. Int J Oncol 33(6): 1271-1280.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Boudjadi, S. and Beaulieu, J. (2017). In silico Analysis and Site-directed Mutagenesis of Promoters. Bio-protocol 7(6): e2181. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2181.
Category
Molecular Biology > DNA > Mutagenesis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










