- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Quantification of Triphenyl-2H-tetrazoliumchloride Reduction Activity in Bacterial Cells
Published: Vol 7, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2115 Views: 10524
Reviewed by: Zhaohui LiuChijioke JoshuaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

H2 Production from Methyl Viologen–Dependent Hydrogenase Activity Monitored by Gas Chromatography
Nuttavut Kosem
Dec 5, 2023 1794 Views

Monitoring Protein Stability In Vivo Using an Intein-Based Biosensor
John S. Smetana [...] Christopher W. Lennon
Apr 20, 2025 1617 Views

Endo-1,4-β-D-xylanase Assay Using Azo-Xylan and Variants Thereof
Luca Bombardi [...] Salvatore Fusco
Apr 20, 2025 1961 Views
Abstract
This protocol describes the use of the 2,3,5-triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride (TTC) salt to evaluate the cell redox potential of rhizobia cells. The production of brightly colored and insoluble 1,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium formazan arising from TTC reduction is irreversible and can be easily quantified using a spectrophotometer. This protocol allows the production of reproducible results in a relatively short time for Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 cells grown both in exponential and stationary phases. The results here presented show that the S. meliloti cells deriving from exponential-phase cultures had increased cell redox potential as compared to the ones deriving from stationary-phase cultures. This means that under exponential growth conditions the S. meliloti cells generate higher amount of reducing equivalents needed for TTC reduction.
Keywords: Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021Background
The TTC salt is a water-soluble and colorless compound that can be reduced to formazan, a highly colored compound. The irreversible formation of formazan can be quantified using a spectrophotometer. Owing to its property and its low reduction potential, this tetrazolium salt is widely used in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes as an indicator of cell redox activity, viability, drug susceptibility and substrate utilization assays (Byth et al., 2001; Hayashi et al., 2003; Raut et al., 2008; Lin et al., 2008). The net positive charge on tetrazolium salts facilitates cellular uptake due to the membrane potential, allowing their intracellular reduction (Berridge et al., 2005). In prokaryotes, the main studies of TTC reduction have concerned the Gram-negative respiring bacterium Escherichia coli, while only a few studies have been reported for members of the Rhizobiacea family. In this protocol, one of the best genetically characterized members of this family, the S. meliloti 1021 rhizobium strain, was used. The respiratory activity, expression of cytochrome terminal oxidases, of this strain was analysed using TTC as an indicator of cell redox potential.
To enable the development of a measurable color intensity and, at the same time, to avoid any possible inhibition of bacterial growth, the bacteria were incubated in the presence of TTC for an appropriate period of time compared to those described by other authors (Tengerdy et al., 1967; Byth et al., 2001; Tachon et al., 2009).
Materials and Reagents
- Sterile inoculation loop with incorporated needle (NUOVA APTACA, catalog number: 6001/SG/CS )
- 14-ml polypropylene round-bottom tubes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352059 )
- 50-ml conical centrifuge tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 339652 )
- Safe-lock 2-ml tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030120094 )
- Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021
- 2,3,5-triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride (TTC) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8877 )
- 1,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium formazan (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93145 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5879 )
- Tryptone (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9410 )
- Yeast extract (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Y0375 )
- Calcium chloride (CaCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C3306 )
- Na2HPO4 (Acantor® Performance Materials, J.T. Baker, catalog number: 4062-01 )
- NaH2PO4 (Acantor® Performance Materials, J.T. Baker, catalog number: 3818-05 )
- TYR broth medium (5 g/L tryptone, 3 g/L yeast extract, 6 mM CaCl2) (see Recipes)
- Sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Incubator room (at 30 °C)
- Rotary shaker
- Spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: DU800 )
- Cuvettes for spectrophotometry application in the visible spectrum (Kartell, catalog number: 1938 )
- Micro-centrifuge (SCILOGEX D3024 High Speed Micro-Centrifuge) (Scilogex, catalog number: 912015139999 )
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: HeraeusTM MegafugeTM 16R )
- Oven (at 65 °C)
- Balance (Mettler Toledo, catalog number: B204-S )
Procedure
- Growth of bacterial cells
- Pure cultures of S. meliloti 1021 stored at -80 °C were taken by sterile loops, inoculated in 15-ml round-botton tubes containing 2.0 ml of TYR medium and incubated for 24 h at 30 °C on a rotary shaker (200 rpm).
- Aliquots of the cultures (0.15 ml) were transferred into 50-ml conical centrifuge tubes containing 15 ml of fresh TYR medium (OD600 = 0.2) and the optical density measured at 600 nm using a spectrophotometer and cuvettes for spectrophotometry application in the visible spectrum.
- When the cultures reach the exponential growth phase (OD600 = 0.7), which requires about 4 h of incubation, stop the growth and split the cultures in 10 ml for biomass evaluation and 1.5 ml for TTC reduction measurement.
- Pure cultures of S. meliloti 1021 stored at -80 °C were taken by sterile loops, inoculated in 15-ml round-botton tubes containing 2.0 ml of TYR medium and incubated for 24 h at 30 °C on a rotary shaker (200 rpm).
- TTC assay
- Centrifuge the 10 ml bacterial cultures in 15-ml polypropylene round-bottom at 5,000 x g for 20 min (at room temperature) and discard the supernatant.
- Incubate the cells at 65 °C in an oven for 4 h until dryness and weigh the cells with a balance.
- Centrifuge the 1.5 ml bacterial cultures in 2-ml Eppendorf tubes at 8,000 x g for 5 min (at room temperature) and discard the supernatant.
- Wash the bacteria with 1 ml of 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5), centrifuge at 8,000 x g for 5 min (at room temperature) and discard the supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells in 1 ml of 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 24 mM 2,3,5-triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride (TTC) and incubate at 30 °C for 1 h on a rotary shaker at 200 rpm (Figure 1).
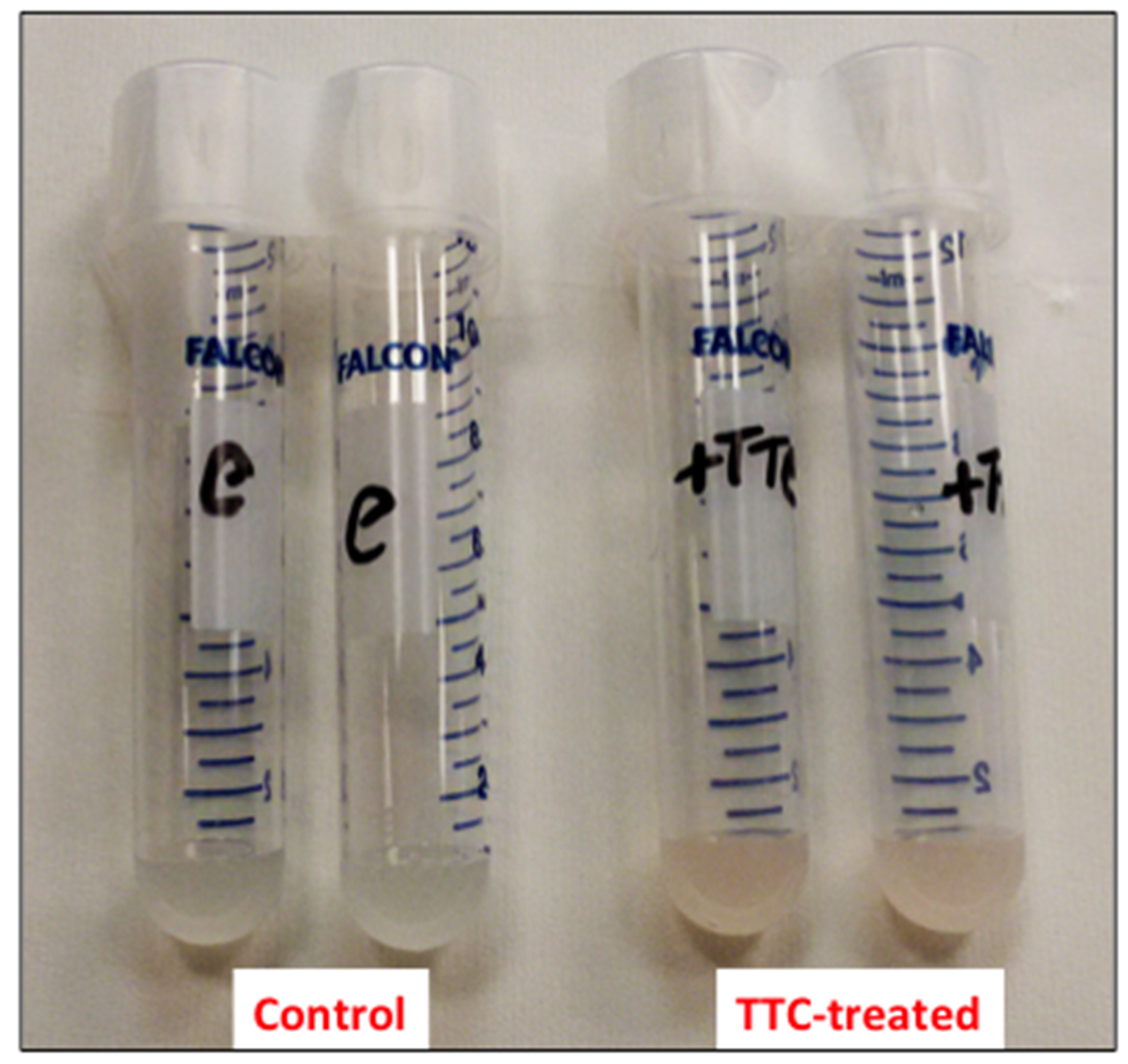
Figure 1. Picture of the cell suspensions after 1 h of incubation at 30 °C - Collect the cells by centrifugation at 8,000 x g for 5 min (at room temperature) and discard the supernatant (Figure 2).
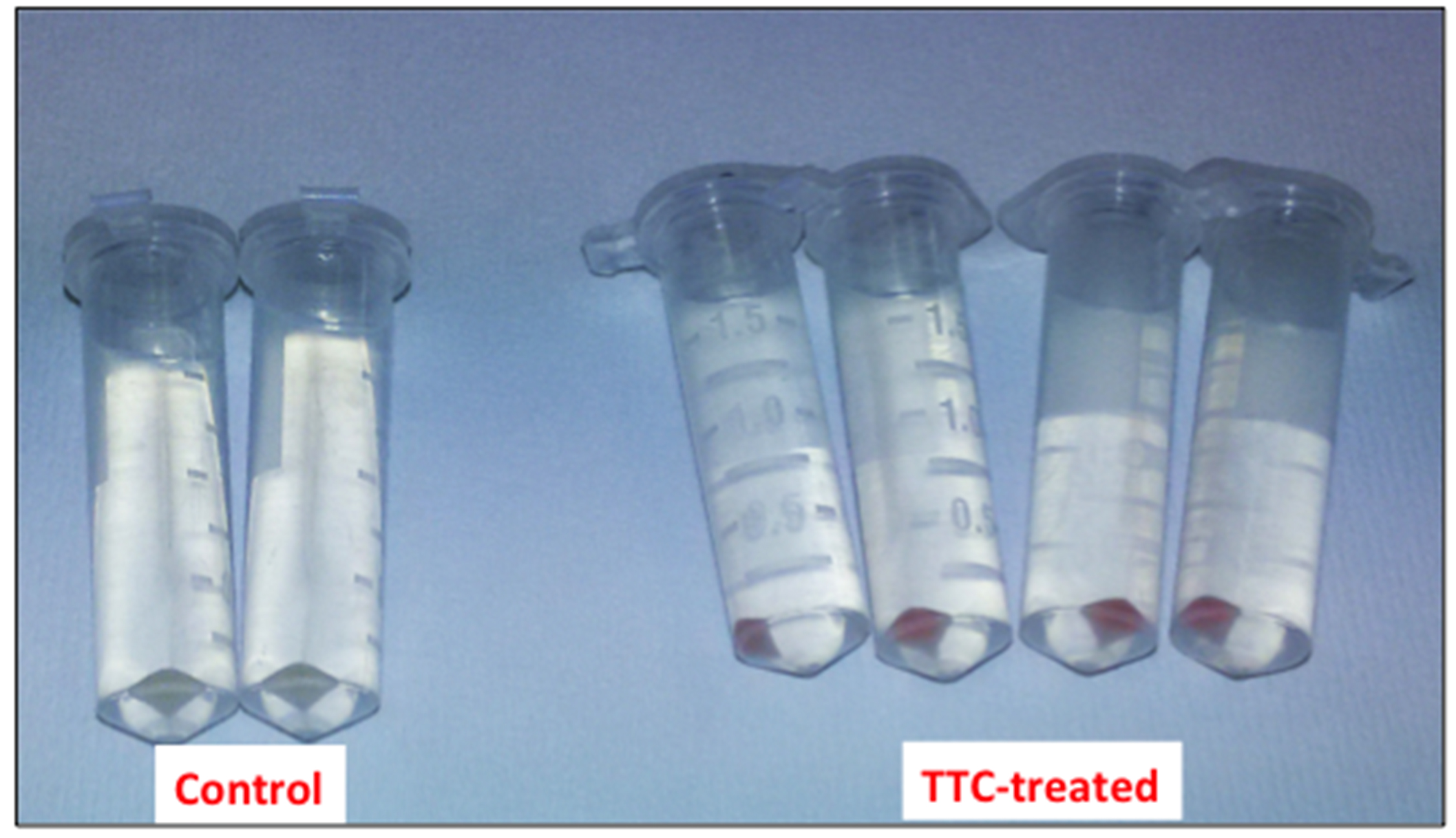
Figure 2. Picture of the bacterial cells after the centrifugation step - Resuspend the cells thoroughly in 1 ml 99.5 % DMSO (at room temperature) to dissolve the produced formazan.
- Spin down the bacterial cells by one-minute centrifugation at 13,000 x g (at room temperature) and collect the supernatants.
- Prepare formazan standard solutions at different known concentrations dissolving the powder in 99.5 % DMSO.
- Read the absorbance of the samples (supernatants) and formazan standards at 510 nm using a spectrophotometer. Use the 99.5 % DMSO as blank control.
- Plot the calibration curve of the formazan standards (mg/ml) against the absorbance of the solutions at 510 nm.
- Determinate the amount of formazan produced from reactions with the bacterial cells directly from the formazan calibration curve.
- Normalize the data to cell biomass (g) corresponding to 1.5 ml bacterial cells and determine the amount of formazan produced per g cells.
- Centrifuge the 10 ml bacterial cultures in 15-ml polypropylene round-bottom at 5,000 x g for 20 min (at room temperature) and discard the supernatant.
Data analysis
- Perform at least five biological replicates, each conducted at different times.
- An example of the excel Formazan standard curve is described in Table 1.
- The readings of some experimental samples and the amount of formazan they produced are reported in Table 2 and Table 3.
Table 1. Formazan standards and their relative absorbance at 510 nmv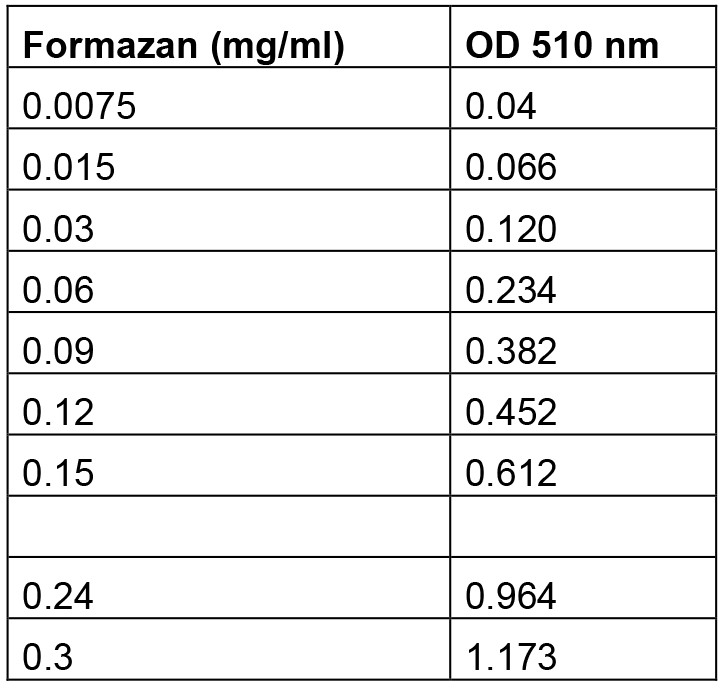
Optical densities were determined using a spectrophotometer and data were plotted as shown in Figure 3.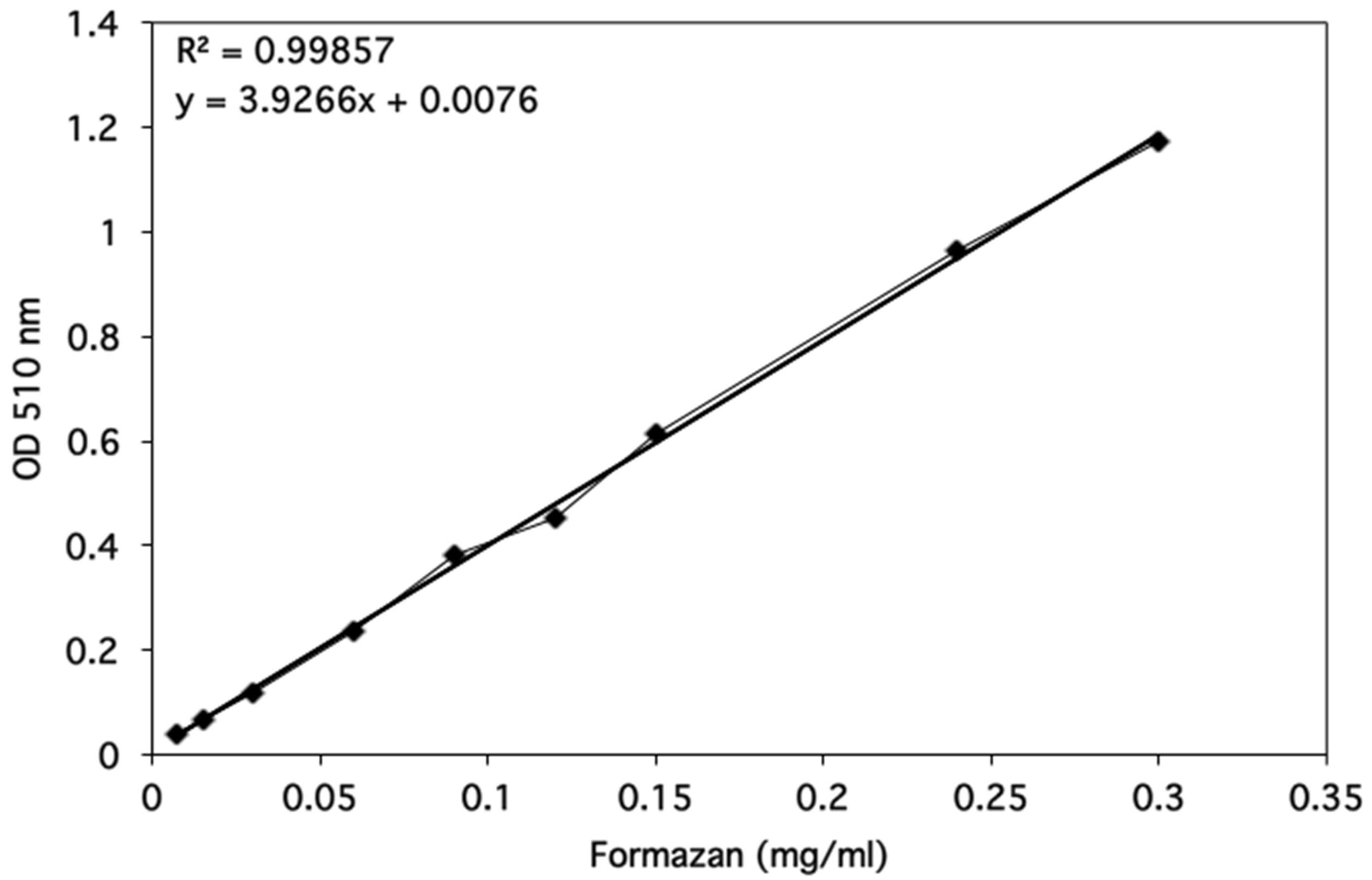
Figure 3. Formazan standard curve. The optical density at 510 nm was determined for a range of Formazan standards from 0.0075-0.3 mg/ml. The linear regression line was added by using the Excel 2011 for Mac (14.1.0 version). The equation for the regression line and the correlation coefficient are shown on the graph.
Table 2. Amount of formazan produced by S. meliloti 1021 cells grown up to exponential phase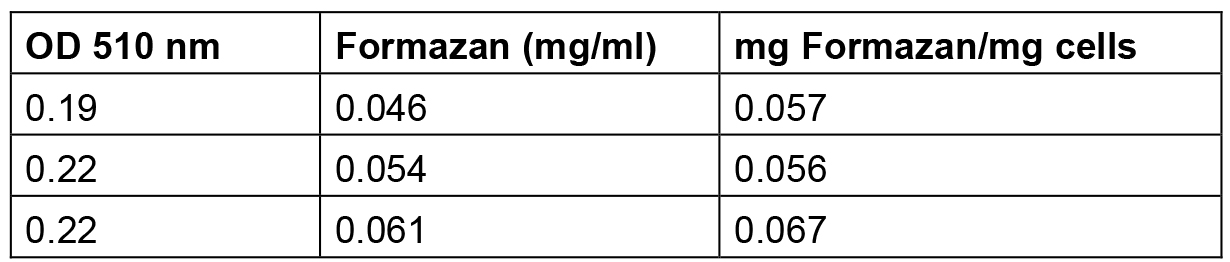
The amount of formazan reported in this table was calculated by interpolating the standard solution points reported in Table 1 and elaborated in Figure 1.
Table 3. Amount of formazan produced by S. meliloti 1021 cells grown up to stationary phase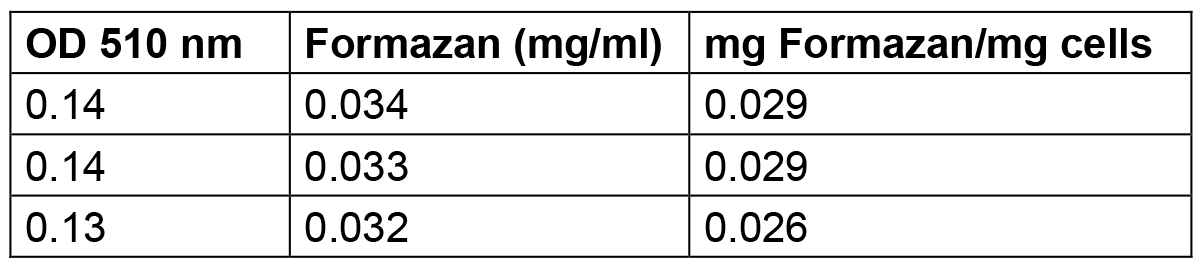
The amount of formazan reported in this Table was calculated by interpolating the standard solution points reported in Table 1 and elaborated in Figure1.
Recipes
- TYR broth medium (1 L)
5 g tryptone
3 g yeast extract
Add ddH2O to 1 L. Sterilize by autoclaving
After the solution has cooled add 12 ml sterile 0.5 M CaCl2 - Sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5)
- Prepare 1 M NaH2PO4 solution by dissolving 1.2 g in a final volume of 10 ml double distilled water
- Prepare 1 M Na2HPO4 solution by dissolving 1.42 g in a final volume of 10 ml double distilled water
- Mix 1.6 ml 1 M NaH2PO4 solution and 8.4 ml 1 M Na2HPO4 solution and dilute to 200 ml with double distilled water to prepare 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.5
Acknowledgments
The method for the TTC assay was adapted from Tachon et al. (2009). This work was partially supported by a dedicated grant from the Italian Ministry of Economy and Finance to the National Research Council for the project CISIA ‘Innovazione e Sviluppo del Mezzogiorno - Conoscenze Integrate per Sostenibilità ed Innovazione del Made in Italy Agroalimentare - Legge No. 191/2009’. This work was also partially supported by the European Commission for funding the ABSTRESS project (FP7 KBBE-2011-289562). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
References
- Berridge, M. V., Herst, P. M. and Tan, A. S. (2005). Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: new insights into their cellular reduction. Biotechnol Annu Rev 11: 127-152.
- Byth, H. A., Mchunu, B. I., Dubery, I. A. and Bornman, L. (2001). Assesment of a simple, non-toxic almar blue cell survival assay to monitor tomato cell viability. Phytochem Anal 12: 340-346.
- Hayashi, S., Kobayashi, T. and Honda, H. (2003). Simple and rapid cell growth assay using tetrazolium violet coloring method for screening of organic solvent tolerant bacteria. J Biosci Bioeng 96(4): 360-363.
- Lin, Y. C., Agbanyim, C. N., Miles, R. J., Nicholas, R. A., Kelly, D. P. and Wood, A. P. (2008). Tetrazolium reduction methods for assessment of substrate oxidation and strain differentiation among mycoplasmas, with particular reference to Mycoplasma bovigenitalium and some members of the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster. J Appl Microbiol 105(2): 492-501.
- Raut, U., Narang, P., Mendiratta, D. K., Narang, R. and Deotale, V. (2008). Evaluation of rapid MTT tube method for detection of drug susceptibility of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to rifampicin and isoniazid. Indian J Med Microbiol 26(3): 222-227.
- Tachon, S., Michelon, D., Chambellon, E., Cantonnet, M., Mezange, C., Henno, L., Cachon, R. and Yvon, M. (2009). Experimental conditions affect the site of tetrazolium violet reduction in the electron transport chain of Lactococcus lactis. Microbiology 155(Pt 9): 2941-2948.
- Tengerdy, R. P., Nagy, J. G. and Martin, B. (1967). Quantitative measurement of bacterial growth by the reduction of tetrazolium salts. Appl Microbiol 15(4): 954-955.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Defez, R., Andreozzi, A. and Bianco, C. (2017). Quantification of Triphenyl-2H-tetrazoliumchloride Reduction Activity in Bacterial Cells. Bio-protocol 7(2): e2115. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2115.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Bacterium
Biochemistry > Protein > Quantification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










