- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Trypsin Sensitivity Assay to Study the Folding Status of Proteins
Published: Vol 6, Iss 19, Oct 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1953 Views: 11123
Reviewed by: Ralph BottcherMelike ÇağlayanGregory C. Finnigan

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

An NMR Approach for Investigating Membrane Protein–Lipid Interactions Using Native Reverse Micelles
Sara H. Walters and Brian Fuglestad
Jul 20, 2024 2310 Views

A Protocol to Purify Human Mediator Complex From Freestyle 293-F Cells
Hui-Chi Tang [...] Ti-Chun Chao
Feb 20, 2025 2186 Views

Purification of the Active-State G Protein-Coupled Receptor ADGRL4 for Cryo-Electron Microscopy Using a Modular Tag System and a Tethered mini-Gq
David M. Favara and Christopher G. Tate
Mar 5, 2026 173 Views
Abstract
This protocol aims to evaluate folding status of proteins, utilizing trypsin sensitivity. Unfolded/misfolded proteins are more susceptible to trypsin than folded proteins, because trypsin easily accesses and cleaves loosely folded parts of proteins. This method is especially useful to compare tightness of the folding among wild-type and mutant proteins. As trypsin generally cleaves a peptide bond at the carboxyl-terminal side of the amino acids lysine or arginine, this method can be used to analyze the folding status of different types of proteins such as integral membrane or soluble proteins (Ninagawa et al., 2015) and is applicable to cell lysates of any species and tissues as well as to recombinant proteins. You can use this technique with regular molecular and cell biology equipment.
Keywords: TrypsinMaterials and Reagents
- 6 well dish (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 353046 )
- PVDF membrane (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 10600023 )
- DT40 cell line (DT40 is a B cell line derived from an avian leukosis virus induced bursal lymphoma in a white leghorn chicken) (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-2111 )
- Homo sapiens colon colorectal carcinoma cell line (HCT116) (ATCC, catalog number: CCL-247 )
- Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 08458-45 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10270-106 )
- 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (NACALAI TESQUE)
- RPMI (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 30263-95 )
- Chicken serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 16110-082 )
- Opti-mem (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 31985-070 )
- Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11668019 )
- 2.5 g/L trypsin (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 32777-44 )
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (100x) (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 25955-11 ) (for inhibition of various proteases’ activity such as trypsin, in ddH2O; stored at -20 °C)
- NaCl (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 191-01665) (for DT40)
- Na2HPO4
- KCl
- KH2PO4
- Tris/HCl (pH 8.0) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6791 ) (Stored at room temperature)
- Glycerol
- Bromophenol blue (BPB)
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- Nonidet P-40 (NACALAI TESQUE, catalog number: 23640-94 ) (for HCT116)
- 20 mM carbobenzoxy-valyl-alanyl-aspartyl-[O-methyl]-fluoromethylketone (Z-VAD-fmk) (Promega, catalog number: G7231 ) (for inhibition of PNGase activity)
- 10 mM Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-CHO (MG132) (PEPTIDE INSTITUTE, catalog number: 3175-v ) (in DMSO; inhibition of proteasomal activity, stored at -20 °C)
- 1 M dithiothreitol (DTT) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 041-08976 ) (in water; for reduction of proteins)
- Anti-β-actin antibody (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 017-24573 )
- Anti-myc antibody (MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LABORATORIES, catalog number: 562 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (see Recipes)
- 2x sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer (pH 6.8) (see Recipes)
- Buffer A (see Recipes)
- Buffer B (see Recipes)
Equipment
- High speed refrigerated micro centrifuge (Tomy, model: MX-301 )
- mPAGE (ATTO, model: AE-6530 ) (Using hand-made 10% gel)
- Transfer equipment (ATTO, model: WSE-4020 )
- Heat block (TAITEC, model: DTU-1BN )
- Micro porator (Digital Bio, model: MP-100 )
Software
- ImageJ
Procedure
- Culture adherent HCT116 cells in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (glucose 4.5 g/L) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics (100 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin) at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2/95% air atmosphere. Culture suspended DT40 cells at a density of 1 x 105-1 x 106 cells per ml in RPMI1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% chicken serum and antibiotics (100 U/ml penicillin and 100 ug/ml streptomycin) at 39.5 °C in a humidified 5% CO2/95% air atmosphere.
- Transfect 8.0 x 105 HCT116 cells (40-60% confluent in 6-well plate) using 1 μg of plasmid DNA, 300 μl of Opti-mem and 10 μl of Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) for one well according to the manufacturers’ instructions (After the transfection medium is not replaced). To obtain 1.05 x 107 cells transfected cells, electroporate three times 3.5 x 106 DT40 cells with 8 µg plasmid DNA with two pulses at 1,500 V for 15 msec according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Collect approximately 2.0 x 106 HCT116 cells or 4.0 x 106 DT40 cells for further analysis 24 h (HCT116 cell) or 16 h (DT40 cells) after transfection. For this the cells are washed with 1 ml PBS three times, scraped off and centrifuged at 3,000 x g for 2 min at 4 °C. Discard the supernatants of samples and suspend cell pellets in 400 μl (for HCT116 cells) or 250 µl (for DT40 cells) buffer A and incubate for 20 min on ice to lyse the cells. We used smaller amount of buffer A for DT40 cells, because DT40 cells do not contain as much proteins as HCT116 cells. After this step, samples from HCT116 cells and DT40 cells are treated in the same manner.
Note: Important, the buffer A must NOT contain protease inhibitor cocktail as it would inhibit trypsin activity. - Clarify cell lysates by centrifugation at 17,800 x g for 10 min at 4 °C and transfer the supernatants to new tubes. Pellets are discarded.
- To allow trypsin processing of misfolded proteins, incubate 50 µl aliquots (in case of protein concentrations of 1 mg/ml) of the cleared lysates with 1 µl trypsin solution (Test different concentrations from 1 µg/ml to 100 µg/ml) for 15 min at 4 °C. To stop the trypsin reaction, mix samples with 40-50 μl of buffer B supplemented with 10x protease inhibitor cocktail (We usually use high inhibitor concentrations: 5x final) and incubate at 100 °C for 5 min. Important, every 3 min four samples could be handled for equal incubation time with trypsin.
- Separate 10 µl of the samples (approximately 5 µg) by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting using PVDF membrane and probing with an antibody against the protein of interest. Percentage of SDS-PAGE depends on the molecular weight of the protein of interest. Band intensities can be analyzed and compared to each other by ImageJ or similar programs (Figure 1).
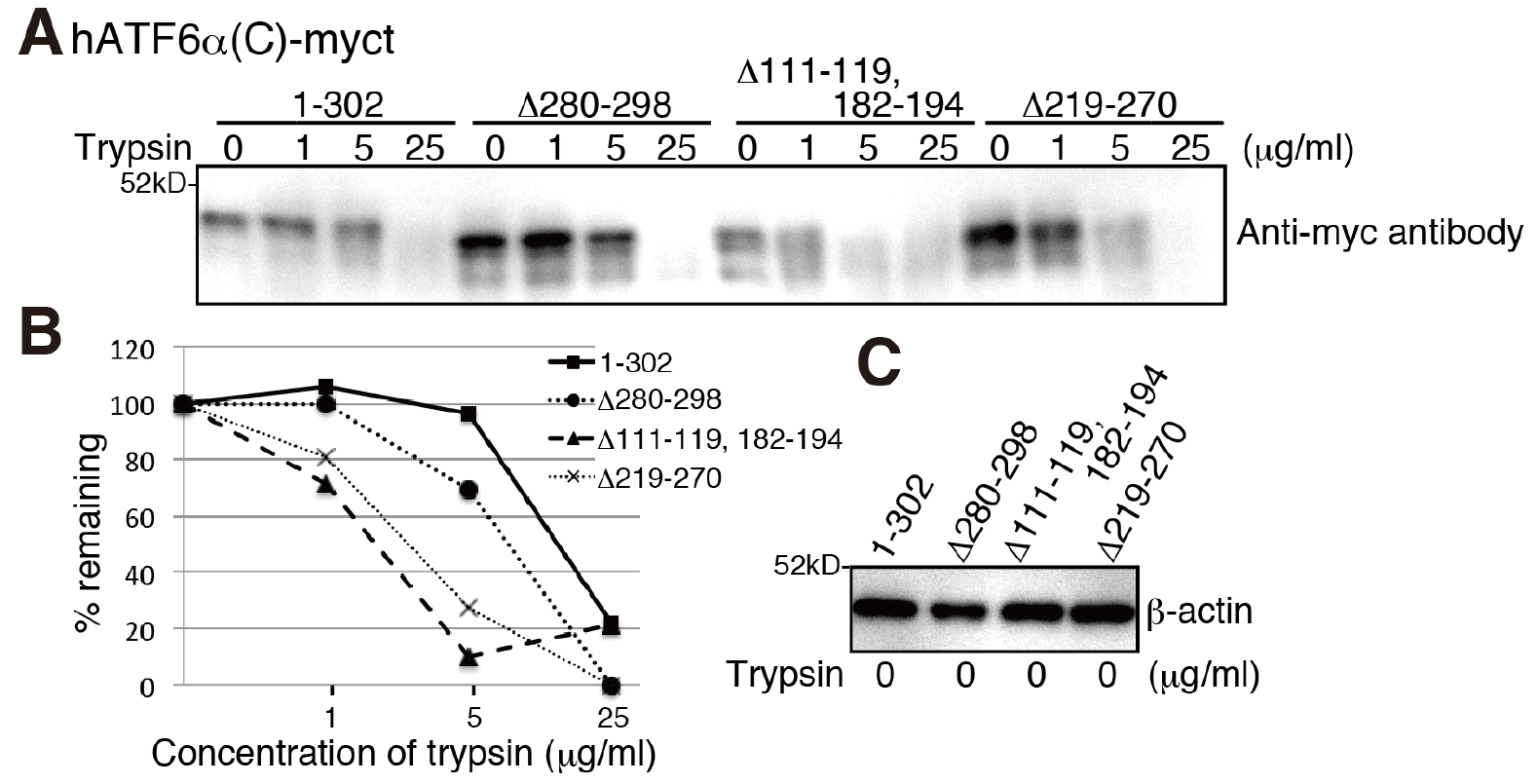
Figure 1. Severely misfolded mutants were more sensitive to trypsin. A. Chicken EDEM1/2/3 triple KO cells (gEDEM TKO) were described previously (Ninagawa et al., 2015). The indicated myc-tagged hATF6α(C) variants were transiently express in gEDEM-TKO cells and subjected to trypsin sensitivity assay. After the indicated time points the trypsin reaction was stopped and samples analyzed by a 12% SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against the myc-tag. The data shown represents a single representative experiment out of three repeats. Less folded proteins are more sensitive to trypsin, so the hATF6α(C)-myct mutants, Δ111-119, 182-194 mutant and Δ219-270 mutant were cleaved by lower trypsin concentrations. B. Quantification of band intensities shown in (A) by ImageJ and calculation of the percentage of remaining protein. C. Equal loading of cell lysates shown by immunoblotting of the lysates and probing with an antibody against β-actin.
Notes
- Incubation time with trypsin and concentration of trypsin should be optimized for proteins of interests.
- The lot and freshness of trypsin can affect the result and can change the outcome between independent experiments (We use trypsin stored at 4 °C). Anyway, you can compare the tightness of the folding among proteins of interests.
- Dilute trypsin in PBS to obtain the expected concentration.
- We used gEDEM TKO cells. This method is applicable for a wide variety of cells lines and recombinant proteins.
- This method can be applied to recombinant proteins. In this case, you might reduce concentration of trypsin.
- CPY and CPY* (Izawa et al., 2012), and GFP and GFP variants (Xu et al., 2013) were other examples used in this assay. We can provide plasmids to express hATF6α(C)-myct 1-302 and Δ280-298 for positive controls (Folded), and Δ111-119, 182-194 and Δ219-270 for negative controls (Less folded).
Recipes
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
137 mM NaCl
8.1 mM Na2HPO4
2.68 mM KCl
1.47 mM KH2PO4 - 2x sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer (pH 6.8)
100 mM Tris/HCl (pH 6.8)
20% glycerol
0.2% bromophenol blue (BPB)
4% sodium dodecyl sulfate - Buffer A
50 mM Tris/HCl (pH 8.0)
1% NP-40
150 mM NaCl
2 μM Z-VAD-fmk (Add before use)
20 μM MG132 (Add before use)
Stored at 4 °C. - Buffer B
1x SDS sample buffer
100 mM dithiothreitol (Add before use)
10x protease inhibitor cocktail (Add before use, and 10 times diluted from original protease inhibitor cocktail)
Stored at room temperature.
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from and used in Ninagawa et al. (2015), Izawa et al. (2012) and Xu et al. (2013).
References
- Izawa, T., Nagai, H., Endo, T. and Nishikawa, S. (2012). Yos9p and Hrd1p mediate ER retention of misfolded proteins for ER-associated degradation. Mol Biol Cell 23(7): 1283-1293.
- Ninagawa, S., Okada, T., Sumitomo, Y., Horimoto, S., Sugimoto, T., Ishikawa, T., Takeda, S., Yamamoto, T., Suzuki, T., Kamiya, Y., Kato, K. and Mori, K. (2015). Forcible destruction of severely misfolded mammalian glycoproteins by the non-glycoprotein ERAD pathway. J Cell Biol 211(4): 775-784.
- Xu, C., Wang, S., Thibault, G. and Ng, D. T. (2013). Futile protein folding cycles in the ER are terminated by the unfolded protein O-mannosylation pathway. Science 340(6135): 978-981.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Ninagawa, S. and Mori, K. (2016). Trypsin Sensitivity Assay to Study the Folding Status of Proteins. Bio-protocol 6(19): e1953. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1953.
-
Ninagawa, S., Okada, T., Sumitomo, Y., Horimoto, S., Sugimoto, T., Ishikawa, T., Takeda, S., Yamamoto, T., Suzuki, T., Kamiya, Y., Kato, K. and Mori, K. (2015). Forcible destruction of severely misfolded mammalian glycoproteins by the non-glycoprotein ERAD pathway. J Cell Biol 211(4): 775-784.
Category
Biochemistry > Protein > Modification
Biochemistry > Protein > Structure
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









