- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Purification and Identification of Novel Host-derived Factors for Influenza Virus Replication from Human Nuclear Extracts
Published: Vol 6, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1934 Views: 11387
Reviewed by: Yannick DebingVasudevan AchuthanModesto Redrejo-Rodriguez

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Preparation of Respiratory Syncytial Virus with High or Low Content of Defective Viral Particles and Their Purification from Viral Stocks
Yan Sun and Carolina B. López
May 20, 2016 18717 Views

Selective Isolation of Retroviruses from Extracellular Vesicles by Intact Virion Immunoprecipitation
Tyler Milston Renner [...] Marc-André Langlois
Sep 5, 2018 12160 Views

Thermus thermophilus CRISPR Cas6 Heterologous Expression and Purification
Junwei Wei [...] Yingjun Li
Jul 20, 2025 2167 Views
Abstract
Recently, we identified two host cell-derived proteins as novel stimulatory factors of influenza virus RNA replication process, termed “Influenza virus REplication Factor-2 (IREF-2)”, from human nuclear extracts (NEs) by employing biochemical complementation assays (Sugiyama et al., 2015). Herein, we describe detailed methods for successive procedures for identification and purification of IREF-2, including large-scale suspension culture of HeLa S3 cells, preparation of NEs and separation of IREF-2 by sequential column chromatography steps. This protocol can be modified and used for purification and identification of the other unknown nuclear protein(s) of your interest.
Keywords: Nuclear ExtractsBackground
The influenza A virus genome is composed of 8 segmented- and single stranded-RNA (vRNA). Its transcription and replication are catalyzed by virus-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP). Several lines of evidence suggest that certain host-derived factors regulate the viral RNA syntheses (Nagata et al., 2008). Recently, a variety of host-derived proteins have been reported as regulator candidates related to the viral RNA syntheses by interactome analyses and genome wide RNAi screening studies. Among them, however, some false-positive interactors and factors involved indirectly in the viral RNA synthesis seem to be included. Instead, to identify reliable and important host factor(s) which play a direct role in the viral RNA synthesis process, we utilized a biochemical complementation assay system. In this system, the viral vRNA replication reaction occurring efficiently in infected cell nuclei is dissected and reconstituted in vitro using viral factors essential for the viral RNA replication such as viral RdRP derived from detergent-solubilized virion particle and model viral genomic RNA templates and uninfected nuclear extracts (NEs).
Recently, we have reported that an efficient vRNA replication is reproduced in vitro with viral factors and a crude fraction of NEs (Sugiyama et al., 2015). This stimulatory activity presented in NEs, designated IREF-2 that allows robust vRNA replication, was further fractionated and purified by sequential column chromatography. Finally, two host-derived paralogous proteins, pp32 (accession number NP_006296) and APRIL (accession number NP_006392), were identified by MS spectrometry analyses. Following experiments using recombinant pp32 and APRIL, and also in vivo analyses using siRNA confirmed that these host proteins are authentic proteins responsible for the IREF-2 activity (Sugiyama et al., 2015).
Materials and Reagents
- Tissue culture dish
- Centrifuge tubes [e.g., for F0650 rotor (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 363075 )]
- Conical centrifuge tubes (polypropylene, 50 ml) (e.g., Corning, catalog number: 430829 )
- Conical centrifuge tubes (polypropylene, 15 ml) (e.g., Corning, catalog number: 430791 )
- Dialysis membrane tube (Cellulose membrane, 14,000 dalton molecular weight cut off), (EIDIA, catalog number: UC27-32-100 )
- Bottle top filter (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: SCGPS01RE )
- Microcentrifuge tubes (polypropylene, 1.5 ml size and 0.6 ml size) (e.g., Eppendorf)
- HeLa S3 cell [National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Japanese Collection of Research Bioresources (JCRB), catalog number: JCRB0713 ]
- Minimum essential medium Eagle (MEM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4655 )
- Fatal bovine serum (FBS) (e.g., Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 26140-079 )
- S-MEM [Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4767 (production ceased, see Note 1). Alternatively, see also Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8167 , or similar products from other companies]
- Bovine serum (CS) (e.g., Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 16170-078 )
- Ultra-pure water (Milli-Q)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
- 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl] ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) buffer
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium chloride (KCl)
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2)
- Dithiothreitol (DTT)
- Trypsin-EDTA (for cell trypsinization)
- Glycerol
- di-Sodium dihydrogen ethylenediamine tetraacetate dihydrate (EDTA)
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
- Liquid N2
- Whatman® cation exchange cellulose (P11) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 4071010 )
- Ammonium sulfate [(NH4)2SO4]
- Silver staining kit (e.g., Cosmo Bio, catalog number: DCB-423413 )
- Silver staining kit (glutaraldehyde-free for MS analysis) (e.g., Wako Pure Chemical industries, catalog number: 299-58901 )
- Buffer A (see Recipes)
- Buffer C (see Recipes)
- Buffer D (see Recipes)
- Buffer HG (see Recipes)
- Buffer HGK (see Recipes)
- Buffer HGN1M (see Recipes)
- Buffer HGN2M (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Cell culture environments and equipment
- Clean bench
- CO2 incubator (37 °C for adherent cultivation)
- Microscope (phase-contrast)
- Hemocytometer
- Spinner flasks (small size for ~500 ml and large size for 8 L)
- Magnetic stirrer (Slow speed; enough size for spinner flask)
- 37 °C incubator (enough size for spinner flask and magnetic stirrer)
- Autoclave (enough size for spinner flask)
- Clean bench
- Large scale centrifuge (e.g., Beckman Coulter, model: Avanti® J-26XP )
- Large scale centrifuge rotor (Beckman Coulter, model: JLA-10.500 )
- Centrifuge bottles (500 ml-size for JLA-10.500 rotor) (e.g., Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 361691 )
- Benchtop high speed centrifuge (e.g., Beckman Coulter, model: Allegra® 64R )
- High-speed centrifuge rotor [e.g., F0650 (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 364610 )]
- Grass Dounce homogenizer with pestle, 15 ml (Capitol Scientific, Wheaton®, catalog number: 357544 )
- Grass Dounce homogenizer with pestle, 40 ml (Capitol Scientific, Wheaton®, catalog number: 357546 )
- Refrigerator (for dialysis)
- Deep freezer (-80 °C)
- pH meter
- Grass bottles (Pyrex®, dry heat-sterilizable)
- Tabletop centrifuge
- SDS-PAGE apparatus
- Column chromatography equipment (see Note 1)
- Fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) workstation (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: BioLogic HR )
- Chromato chamber (4 °C)
- Column housing (e.g., Bio-Rad Laboratories, Econo Column®, catalog number: 7371512 )
- Flow adaptor (e.g., Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 7380016 )
- Anion-exchanger, UNOTM Q1R (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 7200011 )
- Hydrophobic column, SOURCETM 15PHE PE 4.6/100 (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-5186-01 )
- Cation-exchanger, UNOTM S1 (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 7200021 )
- Anion-exchanger, Mono Q® HR 5/5 [GE Healthcare, model: Mono Q® HR 5/5 (production ceased). Alternatively, Mono Q® 5/50 GL (GE Healthcare, model: 17-5166-01 ) or similar products from other companies can be usable]
- Micro-Purification SMART system [GE Healthcare, Pharmacia Biotech, model: SMART® system (production ceased)]
- Gel filtration column (GE Healthcare, Pharmacia Biotech, model: Superdex® 75 PC 3.2/30 )
Note: This product has been discontinued.
- Fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) workstation (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: BioLogic HR )
- Razor blade
Procedure
- Large scale culture of HeLa S3 cells (see Note 2)
- Seed HeLa S3 cells on tissue culture dish(es) in MEM + 10% FBS medium.
- Incubate at 37 °C in 5% CO2 to grow until total cell number reaches to ≥ 1 x 107. Keep the density of adherent cells within 30-80% confluence. If necessary, passage all of the growing cells by increasing size and/or numbers of culture dish(es).
- Trypsinize the cells, resuspend in S-MEM + 5% calf serum (CS), and count the number of cells.
- Adjust the cell density to ~2 x 105 cells/ml by adding S-MEM + 5% CS.
- Place the cell suspension into a 500 ml-size spinner flask (sterilized), and incubate at 37 °C with gentle stirring by a magnetic stirrer (60-80 rotations/min).
- Monitor the cell growth by daily counting the number of cells, and add fresh medium (S-MEM + 5% CS) to maintain cells at 3-6 x 105 cells/ml. When the volume of cell culture reaches to 500 ml, transfer the culture to a large-scale spinner flask (8 L-size) and maintain incubation at 37 °C.
- When the cell culture reaches maximum volume (e.g., 8 L of 6 x 105 cells/ml; approximately 5 x 109 of total cells), proceed to the nuclear extracts preparation steps (see Note 3).
- Seed HeLa S3 cells on tissue culture dish(es) in MEM + 10% FBS medium.
- Nuclear Extracts (NEs) preparation from HeLa S3 cells (see Note 4)
- Harvest the cultured HeLa S3 cells by centrifugation (at 1,500 x g, 4 °C for 10 min).
- Suspend the cell pellet in PBS, and collect by centrifugation.
- Suspend the cells in ~5 packed cell volumes (PCV) (i.e., pellet mass of the collected cells) of ice-cold buffer A, and store on ice for 10 min (see Note 5).
- Collect by centrifugation at 1,500 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Suspend the cells in 2 PCV of the buffer A and allow cells to swell on ice for 10 min.
- Lyse the cells by 10-15 strokes of a Dounce homogenizer with “type B (tight)” pestle.
- Check for the cell lysis under a microscope (Figure 1). If the homogenization appears to be insufficient, homogenize additionally and check the lysis again.
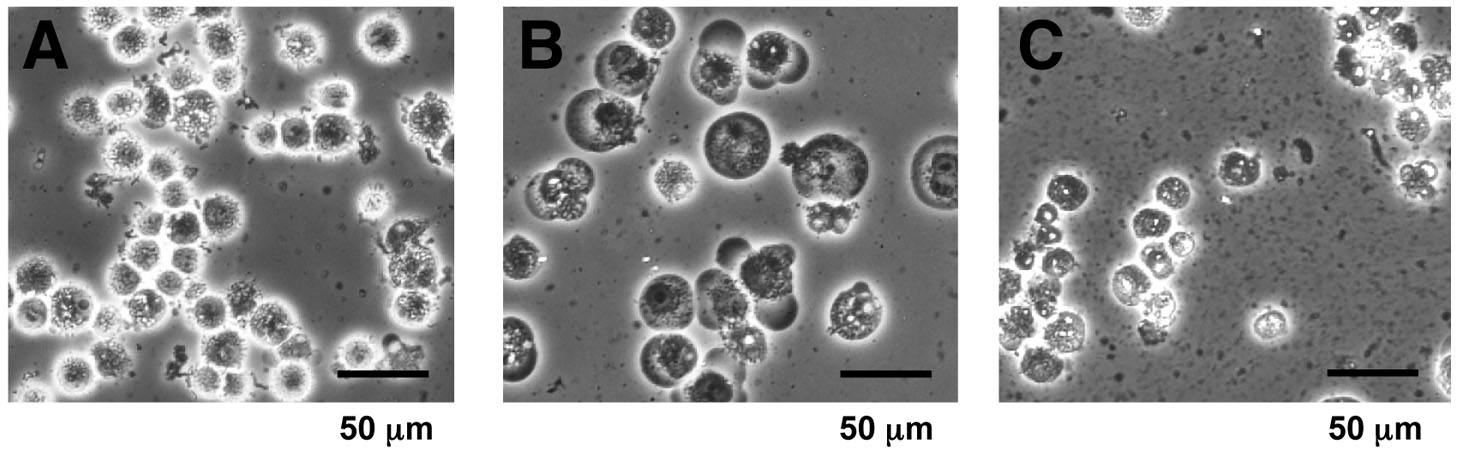
Figure 1. Microscopic view of the cell homogenate. Suspensions before and after homogenization (step B6) were observed at 200-fold magnification by phase-contrast microscopy. A. Cells suspended in PBS (step B2); B. Swollen cells in a hypotonic “buffer A” before homogenization (step B5); C. Homogenized cell suspension (step B6). Cytoplasmic debris and nuclei were observed. - Centrifuge the homogenate at 3,300 x g for 10 min at 4 °C, and remove the supernatant. The supernatant removed at this step can be saved as “S-100” cytoplasmic extracts (Dignam et al., 1983), and utilized for other purpose (Matsumoto et al., 1993).
- Re-centrifuge the remaining pellet (i.e., nuclei) at 14,000 x g for 20 min at 4 °C and remove the residual supernatant completely.
- Suspend the cells in an equal volume of packed nuclei (i.e., equal to pellet mass of the collected nuclei) with ice-cold buffer C (see Recipes and Note 6) and homogenate by 10 strokes of a Dounce homogenizer with “type B (tight)” pestle to ensure complete suspension.
- Transfer the homogenate to a centrifuge tube and invert gently by rotating for 30 min at 4 °C.
- Centrifuge the homogenate at 25,000 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Place the supernatant (NEs) in a dialysis membrane bag. The remaining pellet at this step can be frozen and stored at -80 °C, and utilized as a chromatin fraction (Simon and Felsenfeld, 1979; Schnitzler, 2001).
- Dialyze against ≥ 50 volumes of buffer D at 4 °C for 3 h. Change the buffer to fresh buffer D (≥ 50 volumes), and additionally dialyze at 4 °C for 3 h.
- Transfer the dialysate (white-turbid NEs) to a centrifuge tube and centrifuge for 20 min at 25,000 x g by benchtop centrifuge.
- Determine the protein concentration of NEs of the supernatant (see Note 7). Dispense aliquots into tubes (if desired), and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C until use (see Note 8).
- Harvest the cultured HeLa S3 cells by centrifugation (at 1,500 x g, 4 °C for 10 min).
- Fractionation and purification of NEs by successive column chromatographies (see Figure 2 and Note 9). Herein, the procedures of the column chromatography are desired to purify and identify two host-derived factors, pp32 and APRIL (as known as ANP32A and B, respectively), termed as “influenza virus replication factor (IREF)-2” which stimulates influenza virus RNA replication process (Sugiyama et al., 2015).
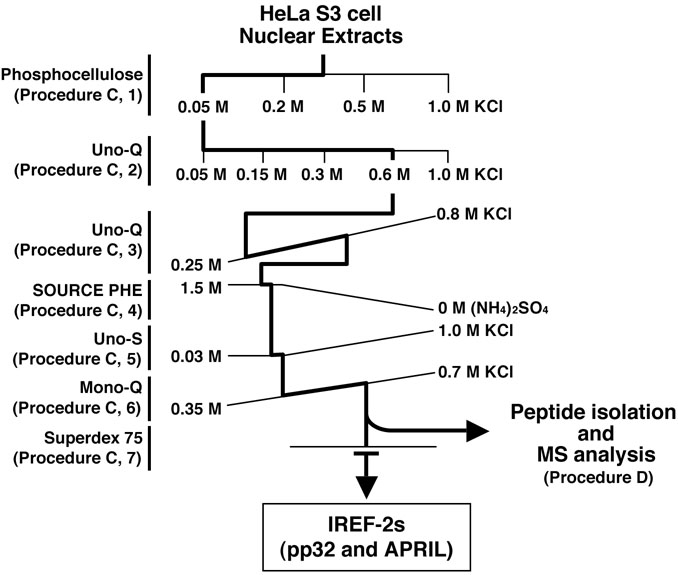
Figure 2. Purification scheme of IREF-2 from NEs. Chromatographic behavior of IREF-2 appears to be highly acidic and hydrophilic.- Stepwise fractionation on weak cation-exchanger column
- Prepare phosphocellulose (PC) column, as follows:
- Suspend the powder of PC resin (Whatman® cation exchange cellulose, P11) by gentle swirling in ≥ 20 volumes of water and keep for 30~60 min.
- Pour off supernatant, resuspend the resin in water, and repeat at least 8-10 times to remove any unsettled fine.
- Suspend the resin in 0.2 M NaOH, allow to settle for 30 min.
- Pour off supernatant and repeat until pH of supernatant is above 10.
- Wash the resin with water until pH of supernatant is below 8.
- Suspend the resin in 0.2 M HCl, allow to settle.
- Pour off supernatant and repeat until pH of supernatant is below 3.
- Wash the resin with water until pH of supernatant is about 5.
- Equilibrate the resins in buffer HG. If the PC resin is to be stored for longer than a week, add 0.1% sodium azide and store at 4 °C (never freeze).
- Suspend the PC resin and pour carefully into the column housing [approximately, 10 ml (bed volume) of the PC resin is enough for 10~15 ml of input NEs] and allow to settle. Then, attach the flow-adaptor carefully above the bed.
- Suspend the powder of PC resin (Whatman® cation exchange cellulose, P11) by gentle swirling in ≥ 20 volumes of water and keep for 30~60 min.
- Set up the FPLC system and column, routinely as follows:
- Wash the system (including a “sample loop”) with pure degassed water.
- Connect the prepared PC column (10 ml bed volume) to the system without introducing air, and wash the system including the column with enough water. Ensure no leakage from the column during flow.
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Wash the system with 100% solvent B (buffer HGK; 1 M KCl) and then equilibrate with 5% solvent B (i.e., 95% solvent A of buffer HG; 50 mM KCl).
- Wash the system (including a “sample loop”) with pure degassed water.
- Ensure the valve position to be “load”, and load the NEs (approximately, 12.5 ml in this protocol) into the sample loop.
- Change the valve position to “inject”, and run the program to start stepwise fractionation on the PC column (10 ml bed volume), as follows:
- Isocratic flow (0.15 ml/min) with 45 ml (4 volumes of the input NEs) of 5% solvent B (i.e., 95% solvent A; final 0.05 M KCl), collect the eluate (2 ml/fraction; total 23 fractions).
- Change the valve position from “inject” to “load” to bypass the flow channel through the sample loop. If forget this, following salt-elution steps would be delayed by the volume of the sample loop.
- Isocratic flow (0.15 ml/min) with 40 ml (4 column volumes) of 20% solvent B (i.e., 80% solvent A; final 0.2 M KCl), collect the eluate (2 ml/fraction; total 20 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.15 ml/min) with 40 ml (4 column volumes) of 50% solvent B (i.e., 50% solvent A; final 0.5 M KCl), collect the eluate (2 ml/fraction; total 20 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.15 ml/min) with 40 ml (4 column volumes) of 100% solvent B (i.e., 0% solvent A; final 1 M KCl), collect the eluate (2 ml/fraction; total 20 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.15 ml/min) with 45 ml (4 volumes of the input NEs) of 5% solvent B (i.e., 95% solvent A; final 0.05 M KCl), collect the eluate (2 ml/fraction; total 23 fractions).
- Make small aliquot(s) of each fractionated sample to avoid unnecessary freezing/thawing cycle in future, and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C.
- Check the activity (i.e., stimulation activity for influenza virus RNA replication, termed as “IREF-2” in this protocol) involved in the PC-fractions by employing a cell-free viral RNA replication assay using small aliquot (see Figure 3 and Note 10).
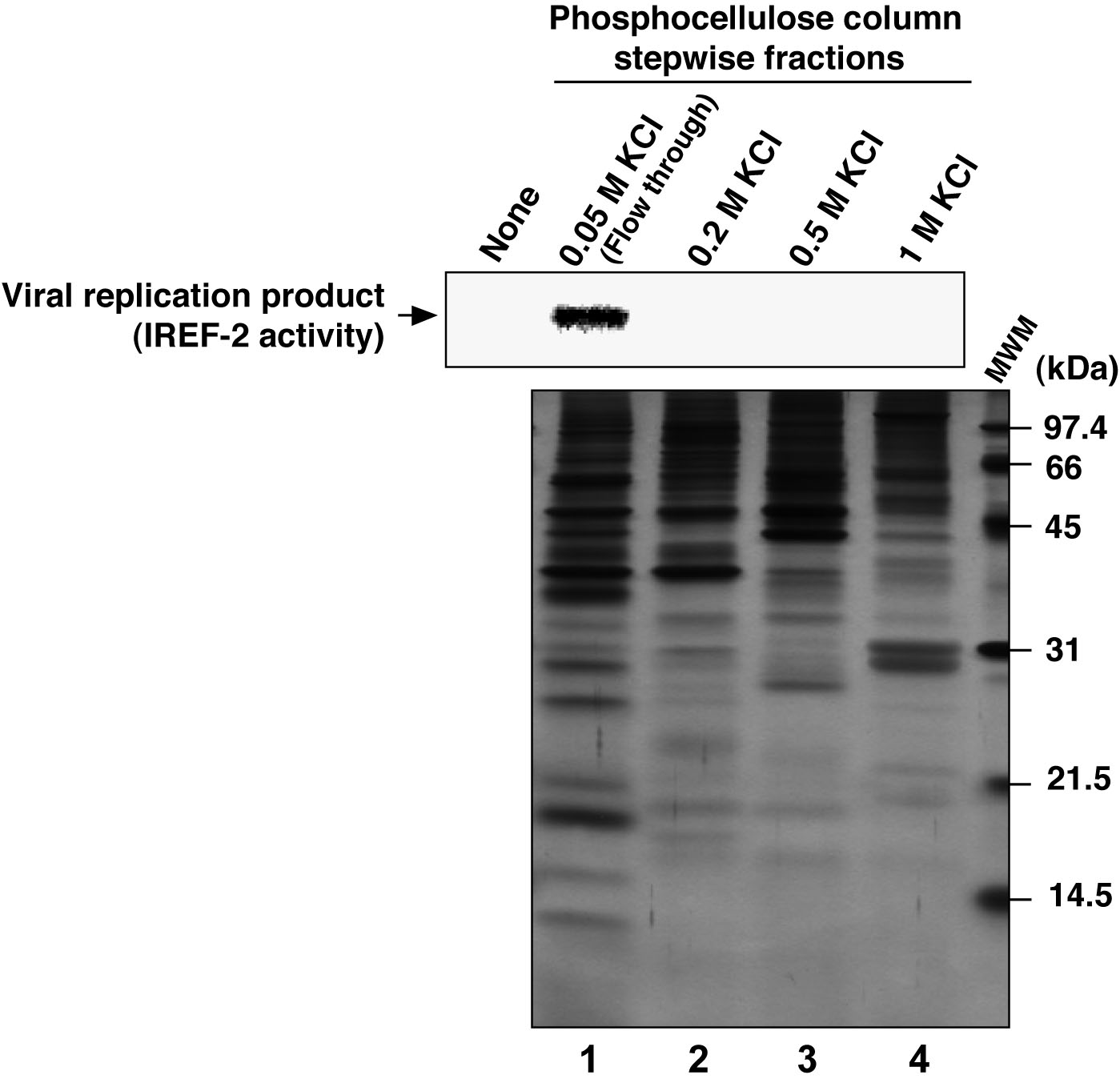
Figure 3. Profile of the fractions from phosphocellulose column chromatography for IREF-2. Each stepwise fraction of NE from the phosphocellulose (PC) column chromatography was individually added to the cell-free viral RNA replication reaction (1.75 μg of each fraction/reaction), as follows; unbound fraction (i.e., flow-through) eluted with 0.05 M KCl buffer (lane 1), materials eluted with buffer containing 0.2 M KCl (lane 2), 0.5 M KCl (lane 3) and 1 M KCl (lane 4), respectively. For the detail of the cell-free viral RNA replication assay, see Note 10 and the original article (Sugiyama et al., 2015). Robust viral RNA product was detected (upper panel, lane 1), suggesting that certain activity stimulating a viral RNA replication reaction, termed as IREF-2, was present in the flow-through fraction from the PC column chromatography. Each fraction was also subjected to 14% SDS-PAGE (1 μg of each fraction/lane), and polypeptides were visualized by silver staining (lower panel). The arrow indicates viral RNA replication products. The molecular weight (kDa) positions are denoted on the right side of the lower panel. MWM: molecular weight marker.
- Prepare phosphocellulose (PC) column, as follows:
- Stepwise fractionation on a strong anion-exchanger column
- Set up the FPLC system and pre-packed UNO Q1R column, routinely
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Wash the column with 100% solvent B, and equilibrate with 5% solvent B (i.e., 95% solvent A).
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Thaw the IREF-2 activity-positive fraction (total 9 ml in this protocol) of the PC column chromatography (i.e., the unbound “flow-through” fraction, see Figure 3) and centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min at 4 °C to remove insoluble material.
- Load the supernatant into the sample loop and change the valve position to “inject”. Run the program to start stepwise fractionation on the UNO-Q column (1.3 ml column volume) as follows:
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 18 ml (2 volumes of the input) of 5% solvent B (i.e., 95% solvent A; final 0.05 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 18 fractions).
- Change the valve position from “inject” to “load”.
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 7.8 ml (6 column volumes) of 15% solvent B (i.e., 85% solvent A; final 0.15 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 8 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 7.8 ml (6 column volumes) of 30% solvent B (i.e., 70% solvent A; final 0.3 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 8 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 7.8 ml (6 column volumes) of 60% solvent B (i.e., 40% solvent A; final 0.6 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 8 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 7.8 ml (6 column volumes) of 100% solvent B (i.e., 0% solvent A; final 1 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 8 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 18 ml (2 volumes of the input) of 5% solvent B (i.e., 95% solvent A; final 0.05 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 18 fractions).
- Make small aliquot(s) of each stepwise-fractionated sample by the UNO-Q column, and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C.
- Check the IREF-2 activity present in each fraction (see Note 10).
- Set up the FPLC system and pre-packed UNO Q1R column, routinely
- Gradient fractionation on a strong anion-exchanger column
- Set up the FPLC system and the UNO Q1R column, routinely
- Set degassed buffer HG as “solvent A” to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as “solvent B” to inlet B, respectively.
- Wash the column with 100% solvent B, and equilibrate with 25% solvent B (i.e., 75% solvent A).
- Set degassed buffer HG as “solvent A” to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as “solvent B” to inlet B, respectively.
- Thaw the IREF-2-active fractions of the stepwise fractionated sample on the UNO-Q column chromatography (= total 8 ml), the eluate with 0.6 M KCl [i.e., mixture of 60% of buffer HGK (as solvent B) and 40% of buffer HG (as solvent A)], and dilute with 1.5 volume of buffer HG to decrease the salt concentration in the sample (finally, 20 ml as an input volume). Centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min at 4 °C to remove insoluble material.
- Load the supernatant into the sample loop and change the valve position to “inject”. Run the program for gradient fractionation on the UNO-Q column (1.3 ml column volume) as follows:
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 30 ml (~1.5 volumes of the input) of 25% solvent B (i.e., 75% solvent A; final 0.25 M KCl), collect the eluate (1.5 ml/fraction; total 20 fractions).
- Change the valve position from “inject” to “load”.
- Linear gradient flow (0.5 ml/min) ranging from 25% to 80% of solvent B with 15 ml, collect the eluate (0.5 ml/fraction; total 30 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 30 ml (~1.5 volumes of the input) of 25% solvent B (i.e., 75% solvent A; final 0.25 M KCl), collect the eluate (1.5 ml/fraction; total 20 fractions).
- Make small aliquot(s) of each fractionated sample on the UNO-Q column chromatography, and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C.
- Check the IREF-2 activity present in each fraction (see Note 10).
- Set up the FPLC system and the UNO Q1R column, routinely
- Gradient fractionation on a hydrophobic column chromatography
- Prepare the FPLC system and pre-packed hydrophobic column, SOURCE 15PHE PE 4.6/100, routinely
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGN1M as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Wash the column with 100% solvent A, and equilibrate with 100% solvent B.
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGN1M as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Thaw the IREF-2-active fractions of the gradient-fractionated sample by the UNO-Q column chromatography and combine them as an input sample (= total 3 ml), and mix an equal volume of ice-cold buffer HGN2M, gradually. Centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min at 4 °C to remove insoluble material.
- Load the diluted supernatant (~6 ml) into the sample loop and change the valve position to “inject”. Run the program for gradient fractionation on the SOURCE 15PHE column (1.7 ml column volume) by reducing the concentration of (NH4)2SO4, as follows:
- Isocratic flow (0.3 ml/min) with 15 ml (~2.5 volumes of the input) of 100% solvent B [i.e., 0% solvent A, final 1 M (NH4)2SO4], collect the eluate (0.75 ml/fraction; total 20 fractions).
- Change the valve position from “inject” to “load”.
- Linear gradient flow (0.3 ml/min) ranging from 100% to 0% of solvent B (i.e., from 0% to 100% of solvent A) with 12 ml, collect the eluate (0.75 ml/fraction; total 16 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.3 ml/min) with 15 ml (~2.5 volumes of the input) of 100% solvent B [i.e., 0% solvent A, final 1 M (NH4)2SO4], collect the eluate (0.75 ml/fraction; total 20 fractions).
- Dialyze each fraction against 50 volumes of buffer HG for 5 h at 4 °C.
- Make small aliquot(s) of each fractionated and dialyzed sample by the hydrophobic column chromatography, and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C.
- Check the IREF-2 activity present in each fraction (see Note 10).
- Prepare the FPLC system and pre-packed hydrophobic column, SOURCE 15PHE PE 4.6/100, routinely
- Gradient fractionation on a strong cation-exchanger column chromatography
- Set up the FPLC system and pre-packed UNO S1 column, routinely.
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Wash the column with 100% solvent B, and equilibrate with 3% solvent B (i.e., 97% solvent A).
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Thaw the IREF-2-active fraction of the hydrophobic column chromatography, (i.e., unbound “flow-through” fraction). Centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min at 4 °C to remove insoluble material.
- Load the supernatant (approximately 5 ml) to the sample loop and change the valve position to “inject”. Run the program for gradient fractionation on the UNO-S column (1.3 ml column volume) as follows:
- Isocratic flow (0.4 ml/min) with 10 ml (2 volumes of the input) of 3% solvent B (i.e., 97% solvent A; final 0.03 M KCl), collect the eluate (0.65 ml/fraction; total 16 fractions).
- Change the valve position from “inject” to “load”.
- Linear gradient flow (0.5 ml/min) ranging from 3% to 100% of solvent B with 15.6 ml (12 column volumes), collect the eluate (0.65 ml/fraction; total 24 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.4 ml/min) with 10 ml (2 volumes of the input) of 3% solvent B (i.e., 97% solvent A; final 0.03 M KCl), collect the eluate (0.65 ml/fraction; total 16 fractions).
- Make small aliquot(s) of each fractionated sample on the UNO-S column chromatography, and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C.
- Check the IREF-2 activity present in each fraction (see Note 10).
- Set up the FPLC system and pre-packed UNO S1 column, routinely.
- Gradient fractionation on a strong anion-exchanger column
- Set up the FPLC system and pre-packed Mono-Q column, routinely.
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Wash the column with 100% solvent B, and equilibrate with 35% solvent B (i.e., 65% solvent A).
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Thaw the IREF-2-active fraction from the fractionated samples by the cation exchanger (UNO-S) column chromatography (i.e., unbound “flow-through” fraction). Centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min at 4 °C to remove insoluble material.
- Load the supernatant (approximately 5 ml) to the sample loop and change the valve position to “inject”. Run the program for gradient fractionation on the Mono-Q column (1 ml column volume) as follows:
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 10 ml (2 volumes of the input) of 35% solvent B (i.e., 65% solvent A; final 0.35 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 10 fractions).
- Change the valve position from “inject” to “load”.
- Linear gradient flow (0.4 ml/min) ranging from 35% to 70% with 12 ml, collect the eluate (0.4 ml/fraction; total 30 fractions).
- Isocratic flow (0.5 ml/min) with 10 ml (2 volumes of the input) of 35% solvent B (i.e., 65% solvent A; final 0.35 M KCl), collect the eluate (1 ml/fraction; total 10 fractions).
- Make small aliquot(s) of each fraction from the Mono-Q column chromatography, and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C.
- Check the IREF-2 activity present in each fraction (see Note 10 and Figure 4).
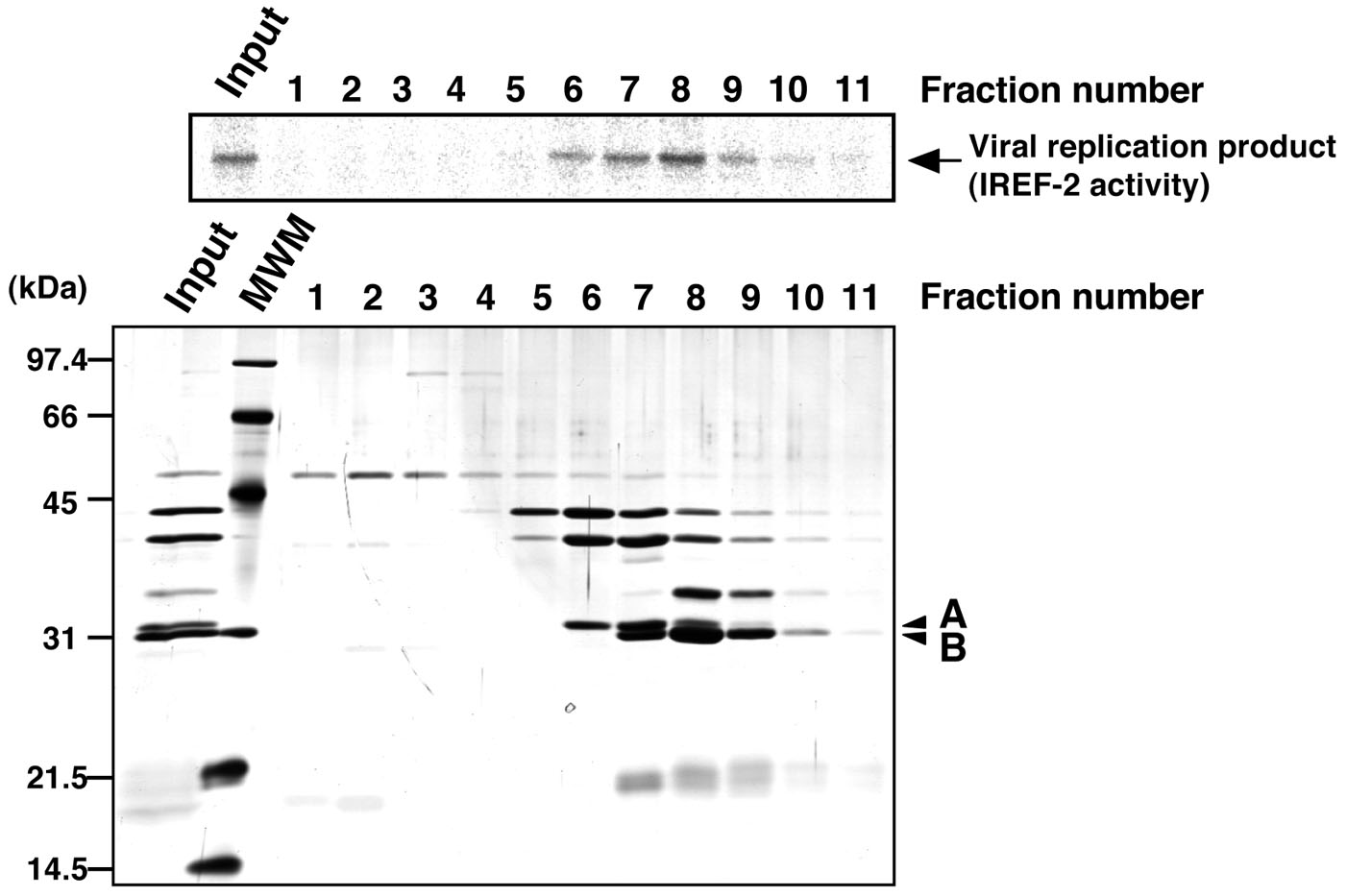
Figure 4. Profile of the fractions from Mono-Q column chromatography for IREF-2. Each Mono-Q fraction (fraction numbers 1-11) or input material for the Mono-Q column chromatography (i.e., unbound fraction of the UNO-S column chromatography at procedure C, 5) was individually added to the cell-free viral RNA synthesis reaction (upper panel). Each fraction was also subjected to 11.5% SDS-PAGE, and polypeptides were visualized by silver staining (lower panel). The arrow indicates viral RNA replication products. By comparing carefully between the IREF-2 activity level and the elution pattern of each peptide, two peptides (arrowheads A and B) migrated at 31 and 30 kDa are expected to be candidates for the IREF-2 activity. The molecular weight (kDa) positions are denoted on the left side of the panel. MWM: molecular weight marker.
- Set up the FPLC system and pre-packed Mono-Q column, routinely.
- Fractionation on a gel filtration column (see Note 11)
- Set up the SMART system and gel filtration column, routinely.
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Wash the column with 100% solvent B, and equilibrate with 20% solvent B (i.e., 80% solvent A).
- Set degassed buffer HG as solvent A to inlet A and degassed buffer HGK as solvent B to inlet B, respectively.
- Thaw the IREF-2-active fraction number 8 of the anion exchanger column chromatography (see Figure 4). Centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min at 4 °C to remove insoluble material.
- Load a small part of the supernatant (approximately 40 μl) into the sample loop and change the valve position to “inject”. Run the program for fractionation on the Superdex 75 gel filtration column (2.4 ml column volume) as follows:
- Isocratic flow (50 μl/min) with 2.4 ml (1 column volume) of 20% solvent B (i.e., 80% solvent A; final 0.2 M KCl).
- At 0.78 ml of the total flow, start collecting the eluate from the gel filtration column (30 μl/fraction).
- Isocratic flow (50 μl/min) with 2.4 ml (1 column volume) of 20% solvent B (i.e., 80% solvent A; final 0.2 M KCl).
- Make small aliquot(s) of each fraction on the gel filtration column chromatography, and freeze in liquid N2 and store at -80 °C.
- Check the IREF-2 activity present in each fraction (see Note 10 and Figure 5).
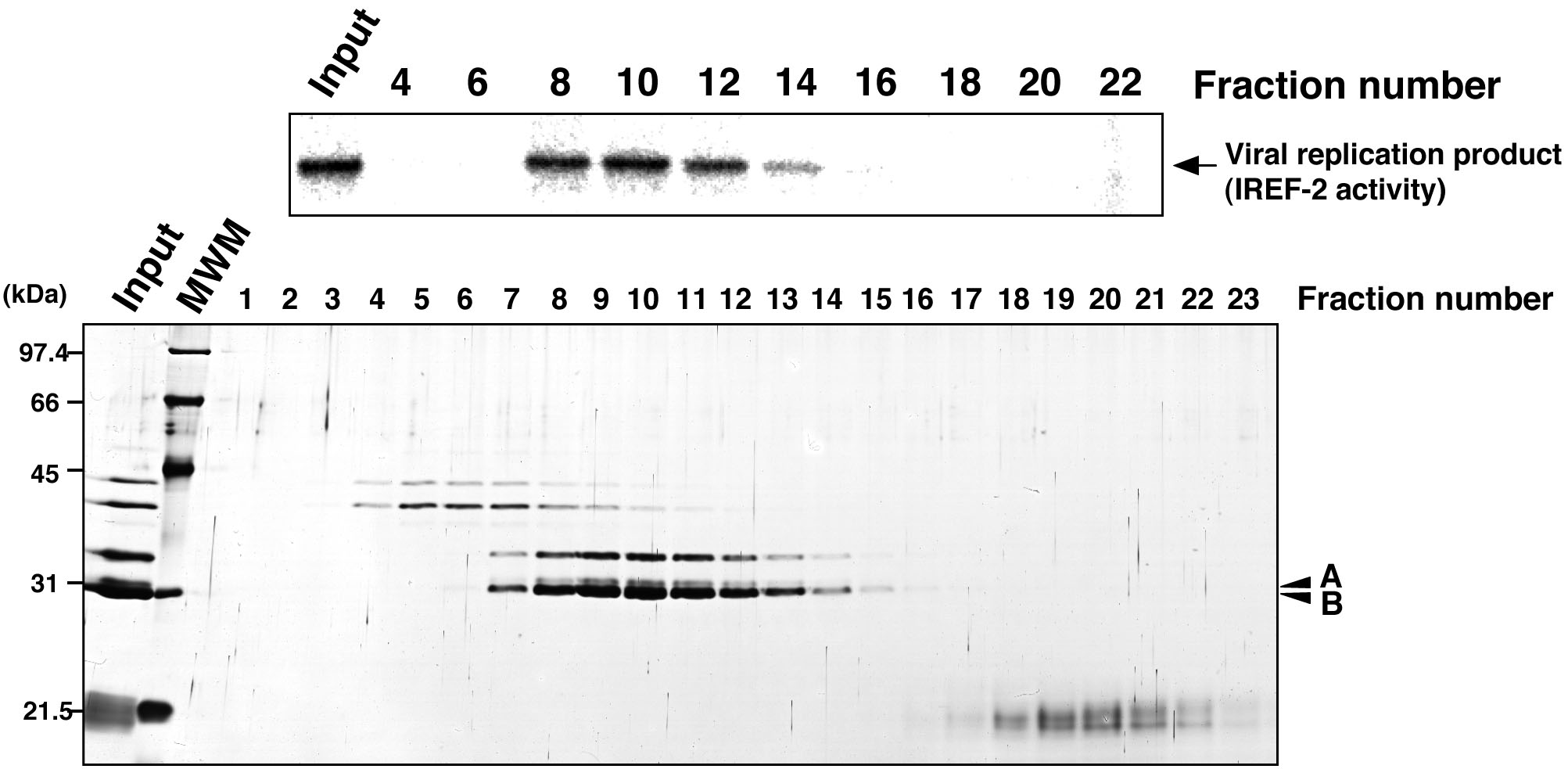
Figure 5. Profile of the fractions from gel filtration chromatography for IREF-2. Each gel-filtrated fraction (fraction numbers 1-23) or input material for the gel-filtration chromatography (i.e., the fraction number 8 of the Mono-Q column chromatography in step C6) was individually added to the cell-free viral RNA synthesis reaction (upper panel). Each fraction was also subjected to 11.5% SDS-PAGE, and polypeptides were visualized by silver staining (lower panel). The arrow indicates viral RNA replication products. The arrowheads indicate two candidate peptides responsible for the IREF-2 activity. The molecular weight (kDa) positions are denoted on the left side of the panel. MWM: molecular weight marker.
- Set up the SMART system and gel filtration column, routinely.
- Stepwise fractionation on weak cation-exchanger column
- Identification of two polypeptides responsible for IREF-2 activity by mass spectrometry
- Subject two Mono-Q fractions involving two candidate peptides, the fraction number 6 enriched with the peptide A and the fraction number 9 enriched with the peptide B (see Figure 4), to 11.5% SDS-PAGE.
- Visualize the peptides separated in the gel by using a glutaraldehyde-free silver staining kit (for MS analysis).
- Excise the gel pieces containing the bands of the peptide A and B, respectively (by using a clean razor blade).
- Tryptic digestion in the gel pieces, followed by mass analysis (MALDI-TOF MASS).
- Subject two Mono-Q fractions involving two candidate peptides, the fraction number 6 enriched with the peptide A and the fraction number 9 enriched with the peptide B (see Figure 4), to 11.5% SDS-PAGE.
Data analysis
Finally, pp32 (peptide A) and APRIL (peptide B) were identified as peptides derived from IREF-2 by database search using MS-Fit program in Protein Prospector (University of California San Francisco; http://prospector.ucsf.edu/prospector/mshome.htm). Top 3 hits of each mass analysis were summarized in Table 1. Observed mass (m/z) and theoretical mass for each digested peptide were summarized as “supplementary file 1 (http://elifesciences.org/content/4/e08939v2/supp-material1)” in the original article (Sugiyama et al., 2015).
Table 1. Top 3 hit proteins identified by MALDI-TOF MASS analyses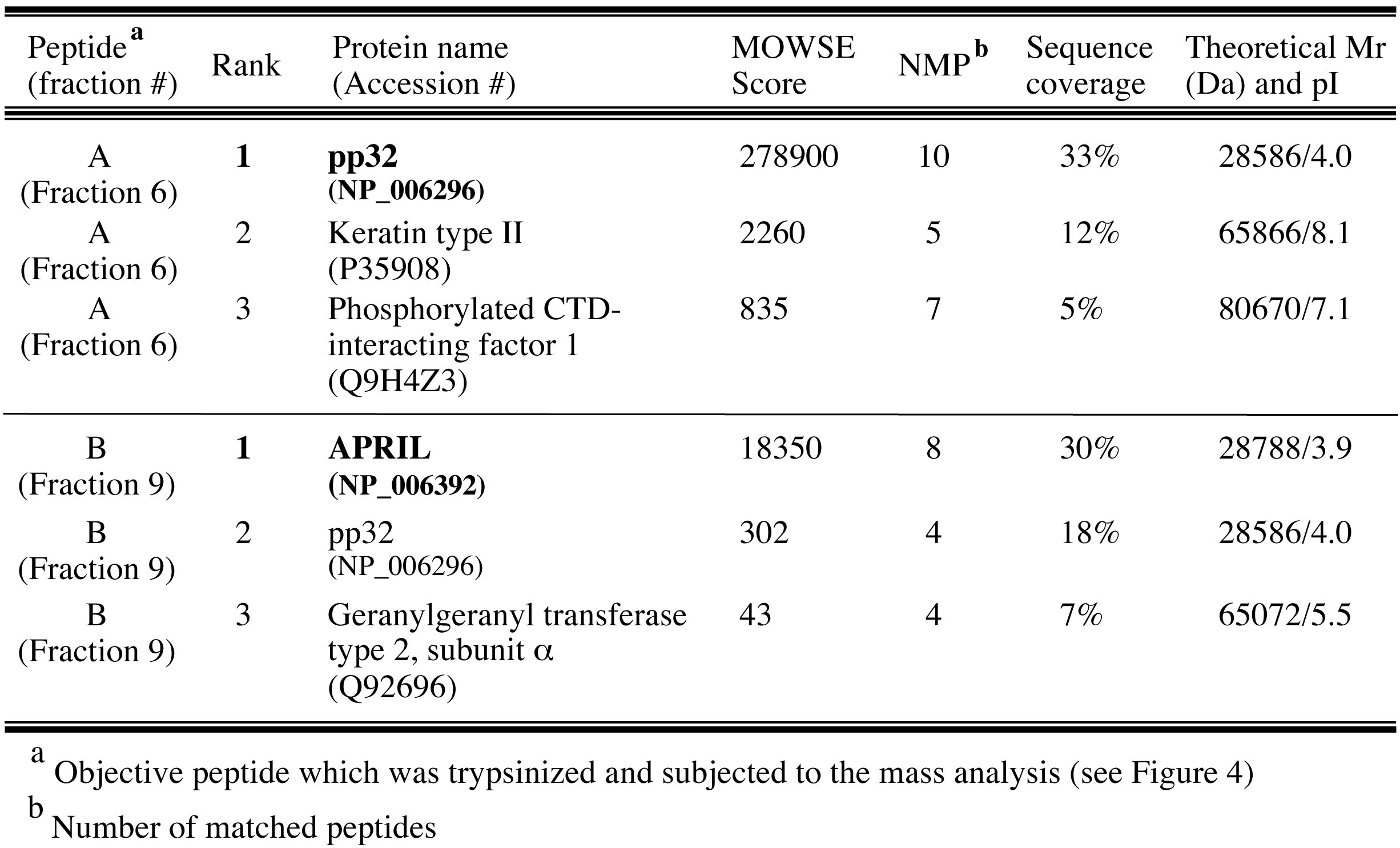
Notes
- Several materials/reagents and equipment listed here, which were actually used in this protocol, are unavailable now. Of course, you can substitute these with other company’s or industry’s products.
- For 8-L scale culture, it usually takes ~2 weeks from the beginning.
- If more NEs are required for your purpose, a part of the cell culture (e.g., ~200 ml) should be aseptically kept and used for another round of large-scale culture.
- All procedures for preparation of the nuclear extracts should be carried out as rapidly as possible at 4 °C or on ice.
- Packed cell volume obtained from 8-L scale culture is usually 10-15 ml.
- Packed nuclear volume obtained from 8-L scale culture is usually 8-12 ml.
- The protein concentration usually results in about 5-10 mg/ml.
- It is preferable to proceed continuously to the next procedure (i.e., first fractionation on the phosphocellulose column chromatography in this protocol) without freezing and thawing of NEs. To this end, the phosphocellulose column and FPLC system should be prepared on ahead to be ready-to-use (steps C1a and C1b).
- Procedures of column chromatography (e.g., choice of column and fractionation way in stepwise or gradient, etc.) must be highly dependent on the chromatographic behavior and the purity of the protein of your interest at each column chromatography step. In addition to the column chromatography, you can utilize “ammonium sulfate precipitation” or “(glycerol or sucrose) density gradient centrifugation” method. For other cases of purification procedures, refer also to previous reports from our laboratory (Momose et al., 2001; Okuwaki et al., 2001; Momose et al., 2002; Kawaguchi and Nagata, 2007) and other laboratories.
- Cell-free influenza virus RNA replication assay is carried out, as described briefly below: Single reaction (final volume of 20 μl) contains 50 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9), 3 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, 500 μM each ATP, UTP and CTP and 25 μM GTP, 5 mCi of [α-32P] GTP (3,000 Ci/mmol), 8 U of RNase inhibitor from human placenta, 10 ng of 53 nt-long influenza virus artificial model RNA template (termed “cRNA”) and 58 fmol of the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase prepared from influenza virion particles (termed “mnRNP”) as an enzyme source. In addition, NE fractions at each column chromatography step were individually added in the reactions to address whether IREF-2 activity was involved in the fraction, or not. After incubation at 30 °C for 2 h, reactions were terminated by extraction with phenol/chloroform followed by precipitation of RNA products with ethanol. The precipitated materials were subjected to 10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of 7 M urea (Urea-PAGE), and visualized by autoradiography. For the detail of the cell-free viral RNA replication assay, see Sugiyama et al. (2015).
- This gel filtration chromatography was performed for further confirmation that the peptides A and B (see Figure 4) were really responsible for the IREF-2 activity, not for further purification. Therefore, a small part of the IREF-2 active fraction (fraction number 8 in Figure 4) was subjected to the gel filtration chromatography with the Micro-Purification SMART system.
Recipes
Note: All buffers listed below should be prepared before use (not prepared long before) as ultra-pure “nuclease-free” grade.
- Buffer A (used in steps B3 and B5)
10 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9 at 4 °C)
10 mM KCl
1.5 mM MgCl2
0.5 mM DTT (add 1 M stock just before use) - Buffer C (used in step B10)
20 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9 at 4 °C)
420 mM NaCl
1.5 mM MgCl2
200 mM EDTA
25% (v/v) glycerol
0.5 mM PMSF [add 1 M stock (in DMSO) just before use]
0.5 mM DTT (add 1 M stock just before use) - Buffer D (used in step B14)
20 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9 at 4 °C)
100 mM KCl
12.5 mM MgCl2
200 mM EDTA
25% (v/v) glycerol
0.5 mM PMSF [add 1 M stock (in DMSO) just before use]
0.5 mM DTT (add 1 M stock just before use) - Buffer HG (used in step C)
50 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9 at 4 °C)
20% (v/v) glycerol- Filtrate and degas with bottle top filter under vacuum.
- Chill in 4 °C.
- Add DTT (1 M stock, final 1 mM) just before use.
- Filtrate and degas with bottle top filter under vacuum.
- Buffer HGK (used in step C)
50 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9 at 4 °C)
1 M KCl
20% (v/v) glycerol- Filtrate and degas with bottle top filter under vacuum.
- Chill in 4 °C.
- Add DTT (1 M stock, final 1 mM) just before use.
- Filtrate and degas with bottle top filter under vacuum.
- Buffer HGN1M (used in step C4)
50 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9 at 4 °C)
1 M (NH4)2SO4
20% (v/v) glycerol- Filtrate and degas with bottle top filter under vacuum.
- Chill in 4 °C.
- Add DTT (1 M stock, final 1 mM) just before use.
- Filtrate and degas with bottle top filter under vacuum.
- Buffer HGN2M (used in step C4b)
50 mM HEPES-NaOH (pH 7.9 at 4 °C)
2 M (NH4)2SO4
20% (v/v) glycerol
1 mM DTT (add 1 M stock just before use)
Acknowledgments
The protocol for preparation of NEs preparation was based on Dignam et al. (1983). This work was supported in part by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (to K. N.).
References
- Dignam, J. D., Lebovitz, R. M. and Roeder, R. G. (1983). Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res 11(5): 1475-1489.
- Kawaguchi, A. and Nagata, K. (2007). De novo replication of the influenza virus RNA genome is regulated by DNA replicative helicase, MCM. EMBO J 26(21): 4566-4575.
- Matsumoto, K., Nagata, K., Ui, M. and Hanaoka, F. (1993). Template activating factor I, a novel host factor required to stimulate the adenovirus core DNA replication. J Biol Chem 268(14): 10582-10587.
- Momose, F., Basler, C. F., O'Neill, R. E., Iwamatsu, A., Palese, P. and Nagata, K. (2001). Cellular splicing factor RAF-2p48/NPI-5/BAT1/UAP56 interacts with the influenza virus nucleoprotein and enhances viral RNA synthesis. J Virol 75(4): 1899-1908.
- Momose, F., Naito, T., Yano, K., Sugimoto, S., Morikawa, Y. and Nagata, K. (2002). Identification of Hsp90 as a stimulatory host factor involved in influenza virus RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem 277(47): 45306-45314.
- Nagata, K., Kawaguchi, A. and Naito, T. (2008). Host factors for replication and transcription of the influenza virus genome. Rev Med Virol 18(4): 247-260.
- Okuwaki, M., Iwamatsu, A., Tsujimoto, M. and Nagata, K. (2001). Identification of nucleophosmin/B23, an acidic nucleolar protein, as a stimulatory factor for in vitro replication of adenovirus DNA complexed with viral basic core proteins. J Mol Biol 311(1): 41-55.
- Simon, R. H. and Felsenfeld, G. (1979). A new procedure for purifying histone pairs H2A + H2B and H3 + H4 from chromatin using hydroxylapatite. Nucleic Acids Res 6(2): 689-696.
- Schnitzler, G. R. (2001). Isolation of histones and nucleosome cores from mammalian cells. Curr Protoc Mol Biol Chapter 21: Unit 21 25.
- Sugiyama, K., Kawaguchi, A., Okuwaki, M. and Nagata, K. (2015). pp32 and APRIL are host cell-derived regulators of influenza virus RNA synthesis from cRNA. Elife 4: e08939.
Article Information
Copyright
Sugiyama and Nagata. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0).
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Sugiyama, K. and Nagata, K. (2016). Purification and Identification of Novel Host-derived Factors for Influenza Virus Replication from Human Nuclear Extracts. Bio-protocol 6(18): e1934. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1934.
- Sugiyama, K., Kawaguchi, A., Okuwaki, M. and Nagata, K. (2015). pp32 and APRIL are host cell-derived regulators of influenza virus RNA synthesis from cRNA. Elife 4: e08939.
Category
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > In vitro model
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









