- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Estimation of the Chromosomal Copy Number in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942
Published: Vol 6, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1855 Views: 8457
Reviewed by: Maria SinetovaChristian RothDamián Lobato-Márquez

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

CRISPR/Cas9 Editing of the Bacillus subtilis Genome
Peter E. Burby and Lyle A. Simmons
Apr 20, 2017 21556 Views

Method for Multiplexing CRISPR/Cas9 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Using Artificial Target DNA Sequences
Rachael M. Giersch and Gregory C. Finnigan
Sep 20, 2017 13368 Views

Markerless Gene Editing in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis
Alexandra M. Gehring [...] Thomas J. Santangelo
Nov 20, 2017 8600 Views
Abstract
Cyanobacteria are prokaryotic organisms that perform oxygenic photosynthesis. Freshwater cyanobacteria, such as Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 and Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, are model organisms for the study of photosynthesis, gene regulation, and biotechnological applications because they are easy to manipulate genetically. However, while studying these cyanobacteria, care has to be taken with respect to genetic heterogeneity in the establishment of gene disruptants, because these cyanobacteria contain multiple chromosomal copies per cell. Here, we describe a method for the estimation of chromosomal copy number in Synechococcus 7942. Using this method, we have recently observed that the chromosomal copy number of Synechococcus 7942 significantly changes during its growth phases. This technique is available for studying polyploidy not only in cyanobacteria, but also in other polyploid organisms.
Keywords: CyanobacteriaMaterials and Reagents
- Plastic disposable dish (for BG-11 plates)
- 1.5 ml microtubes
- Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942
- Escherichia coli K-12 W3110
- Chloramphenicol (Nacalai tesque, catalog number: 06285 )
- Glutaraldehyde solution (50% in water) (KANTO KAGAKU, catalog number: 17026-32 )
- Tween 20 (KANTO KAGAKU, catalog number: 40350-02 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5652 )
- Liquid nitrogen
- Trisodium citrate dihydrate (KANTO KAGAKU, catalog number: 37150-00 )
- SYTOX Green Nucleic Acid Stain (5 mM solution in DMSO) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S7020 )
- BG-11 liquid medium (Castenholz, 1988) (see Recipes)
- BG-11 plates (see Recipes)
- 50x BG-11 stock (see Recipes)
- 1,000x Micro elements A6 (see Recipes)
- 1,000x K2HPO4 (see Recipes)
- 1,000x CaCl2 (see Recipes)
- 1,000x Ammonium Iron(lll) citrate brown (see Recipes)
- 1,000x Na2S2O3 (see Recipes)
- 1 M HEPES-KOH (pH 8.2) (see Recipes)
- M9 medium (Sambrook et al., 1989) (see Recipes)
- 10x M9 salt (see Recipes)
- PBS buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Plant growth chamber (TOMY, model: CLE-405 )
- Growth chamber (YAMATO, model: IC602 )
- Laboratory shaker (TAITEC, model: PERSONAL11 )
- UV/Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, model: UV-1800 )
- Pharmaceutical refrigerator (Panasonic, model: MPR-3120CN-PJ )
- Rotator (TAITEC, model: RT-50 )
- FACS Calibur instrument (BD Biosciences, FACSCaliburTM)
- 100 ml test tubes (for culturing)
- Microtube centrifuge (TOMY, model: MX-107 )
Software
- Analytical software: BD CellQuest Pro (Becton-Dickinson)
Procedure
- Preparation of Synechococcus 7942 culture
- Synechococcus 7942 is streaked and pre-incubated on BG-11 agar plates at 30 °C under continuous illumination (40 µE/m2/s) for 1 week in the plant growth chamber.
- Cells from the plates are suspended in approximately 1 ml of BG-11 medium with high turbidity and diluted into 80 ml of BG-11 medium at an OD750 of 0.05.
- The culture is incubated at 30 °C under continuous illumination (40 µE/m2/s) with 2% CO2 bubbling for 10 days.
- The culture is then diluted to OD750 = 0.2 with fresh BG-11 medium. After 18-h incubation under dark conditions at 30 °C with 2% CO2 bubbling, the culture is transferred to light conditions (40 µE/m2/s) to restart cell growth.
- A 1-ml aliquot of the cultured cells is used for the following assay (Procedure C, D and E).
- Synechococcus 7942 is streaked and pre-incubated on BG-11 agar plates at 30 °C under continuous illumination (40 µE/m2/s) for 1 week in the plant growth chamber.
- Preparation of E. coli culture as a standard
- E. coli is streaked and pre-incubated on M9 agar plates at 37 °C in the growth chamber.
- Cells from the plates are suspended in approximately 1 ml of M9 medium with high turbidity and then diluted into 10 ml of M9 medium at an OD600 of 0.2.
- The culture is incubated at 30 °C with shaking for 4 h.
- 10 µl of 20 mg/ml chloramphenicol is added to the culture (final concentration, 20 µg/ml).
- After incubation with shaking for 2 h, 1 ml of cell culture is subjected to the following assay.
- E. coli is streaked and pre-incubated on M9 agar plates at 37 °C in the growth chamber.
- Fixation
- To the 1-ml aliquots of cell culture, 10 µl of 0.5% Tween 20 and 20 µl of 50% glutaraldehyde are added (final conc. 0.005% and 1%, respectively), and incubated for 30 min at 4 °C with gentle agitation by a rotator.
- The cells are centrifuged at 20,000 x g for 1 min and then washed with 1 ml of PBS, and the cell pellets were stored at -30 °C until further analysis.
- To the 1-ml aliquots of cell culture, 10 µl of 0.5% Tween 20 and 20 µl of 50% glutaraldehyde are added (final conc. 0.005% and 1%, respectively), and incubated for 30 min at 4 °C with gentle agitation by a rotator.
- DNA staining
- Cell pellets were frozen with liquid N2, and then thawed at room temperature.
Note: This step is necessary for the permeation of SYTOX Green. - The cell pellets are resuspended in 50 µl of 10 µM SYTOX Green solution, which was diluted with 50 mM trisodium citrate (pH 8.0).
- The samples are incubated overnight at 4 °C.
- Cell pellets were frozen with liquid N2, and then thawed at room temperature.
- FACS analysis
- The SYTOX Green-stained cells are subjected to FACS analysis. The stained cell suspension (5 µl) is diluted with 250 µl of PBS and immediately analyzed by FACS.
- The cells could be selected by cell size and internal complexity by using forward (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) values. The SYTOX Green signal corresponds to the DNA amount, and is detected by the FL1 detector (laser: 488 nm, filter: 533/30 nm) (Figures 1 and 2).
Note: The signal of Synechococcus 7942 cells can be identified based on chlorophyll autofluorescence using FL3 (laser: 488 nm, filter: 610/20 nm). - The major peak of the chloramphenicol-treated E. coli sample, which corresponds to 1 copy of the chromosome per E. coli cell, is extracted and used as a standard for estimating the chromosomal copy number.
- The SYTOX Green-stained cells are subjected to FACS analysis. The stained cell suspension (5 µl) is diluted with 250 µl of PBS and immediately analyzed by FACS.
- Estimation of chromosomal copy number
The Synechococcus 7942 chromosome copy number (ca. 2.7 Mbp) is calculated based on the peak location of E. coli (ca. 4.7 Mbp) (Figure 3). The copy number of Synechococcus 7942 changes under our culture conditions (2-4 copies under dark and 3-8 copies under light conditions) (Watanabe et al. 2015) as reported previously (Binder and Chisholm, 1995; Griese et al., 2011).
Equation: Copy number of the Synechococcus 7942 chromosome = FL1 valueSynechococcus x 4.7 (Genome size in E. coli)/FL1 valueE.coli x 2.7 (Genome size in Synechococcus)
Representative data
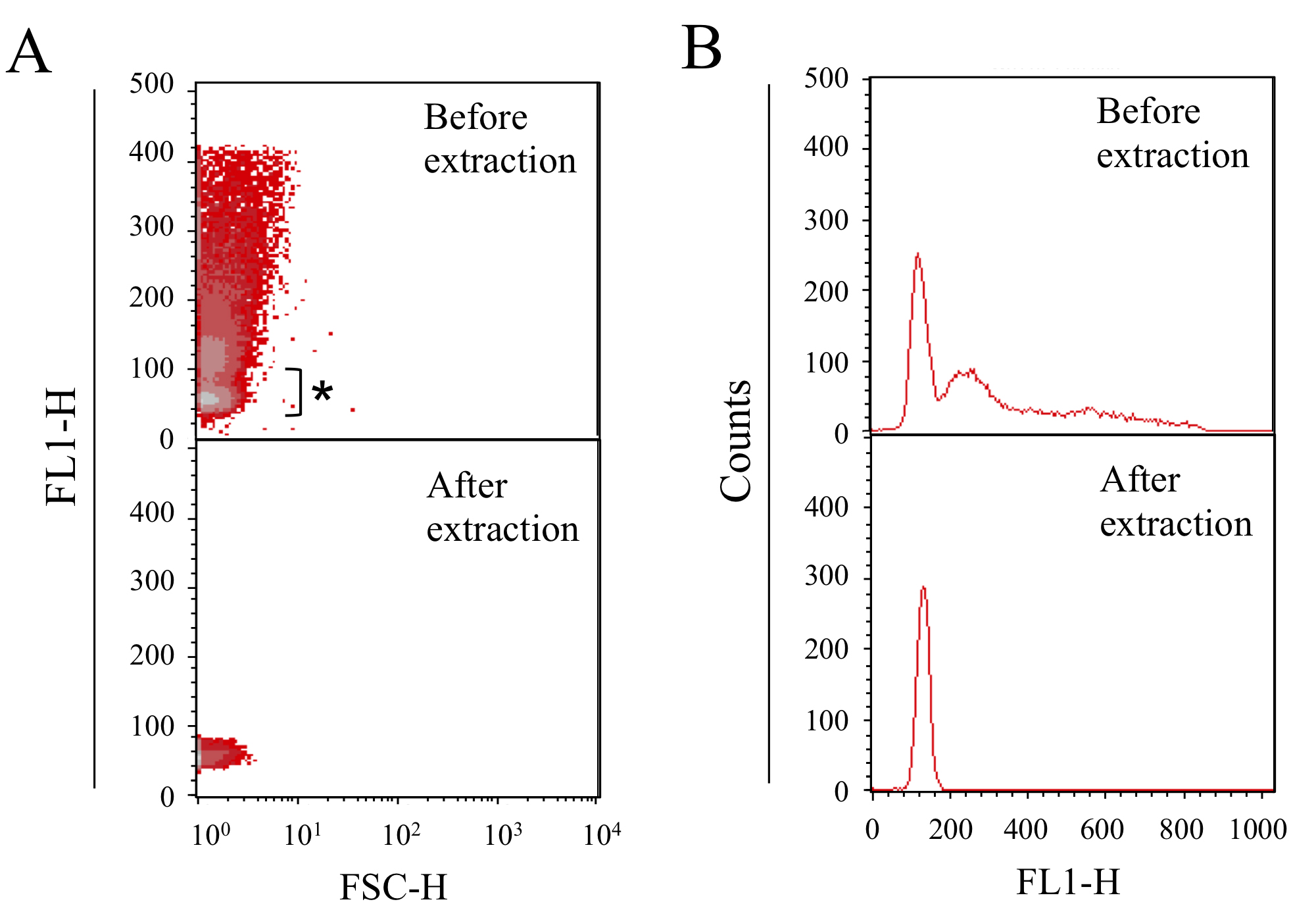
Figure 1. DNA content profiles of chloramphenicol-treated E. coli cells. After culturing for 2 h in M9 medium with 20 µg/ml chloramphenicol, the cells are fixed and analyzed. A. Profiles of cell size (X axis: FSC-H) and DNA content (Y axis). B. Profiles of DNA content (X axis) and cell number (Y axis). For preparing the standard peak, which corresponds to single copy chromosome in E. coli, the major peak (asterisk) was extracted. The bottom panel represents the profiles obtained after extraction by gating.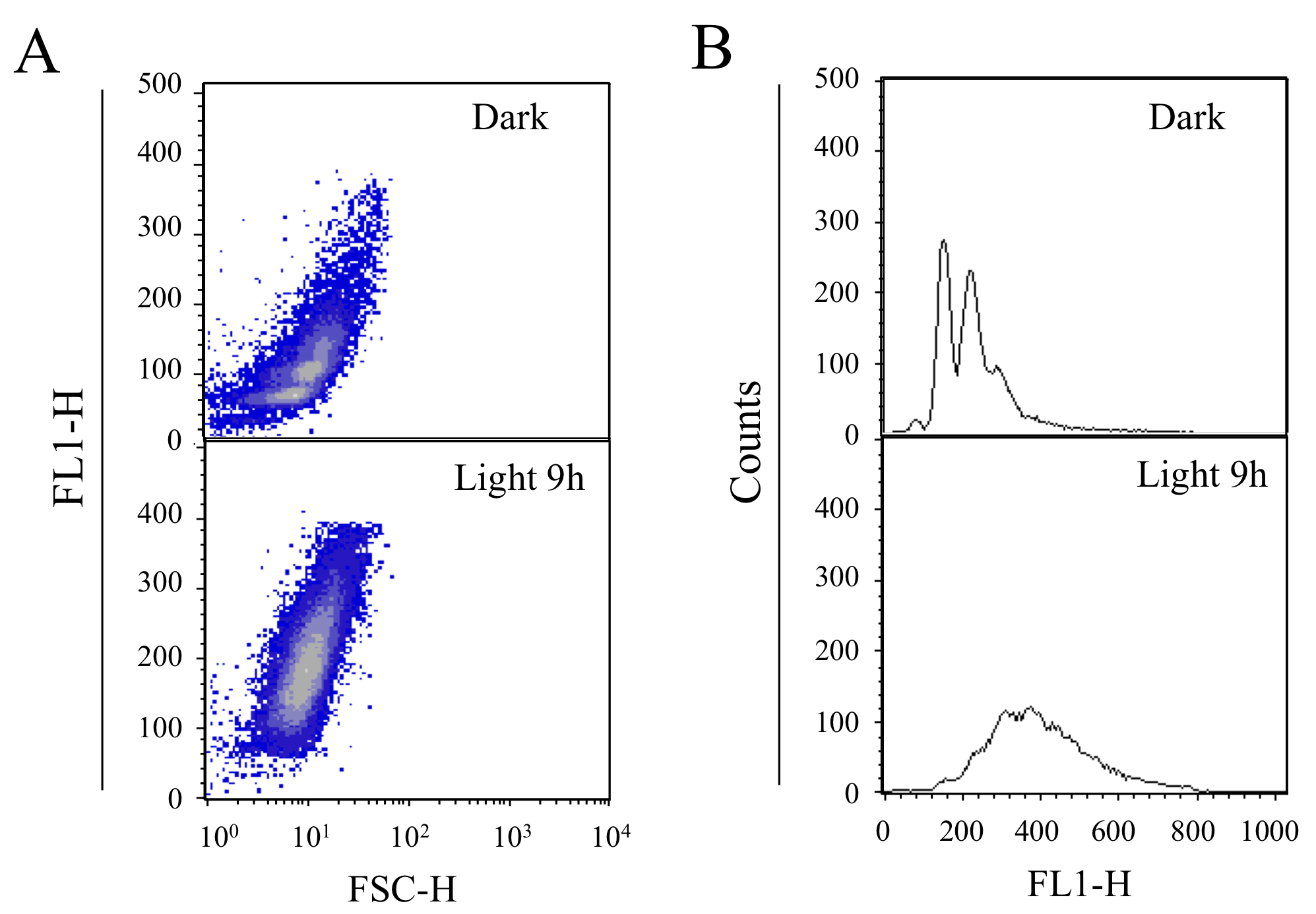
Figure 2. The DNA content profiles of cells cultured in the dark (Top) and lag-phase Synechococcus 7942 cells (bottom) cultured in light conditions for 9 h. A. Profiles of cell size (X axis: FSC-H) and DNA content (Y axis). B. Profiles of DNA content (X axis) and cell number (Y axis).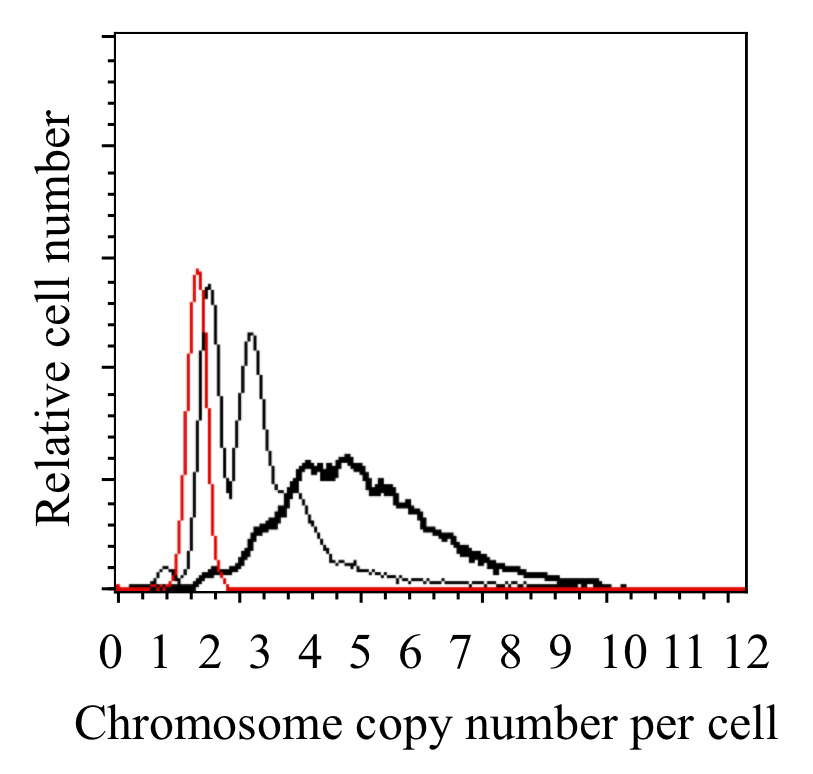
Figure 3. DNA content profiles of cells cultured in the dark (thin line), lag-phase Synechococcus 7942 cells cultured in light conditions for 9 h (bold line), and the chloramphenicol-treated E. coli culture (thin red line). The copy number of the Synechococcus 7942 chromosome (ca. 2.7 Mbp) was calculated based on the peak location of E. coli (ca. 4.7 Mbp).
Recipes
- BG-11 liquid medium (pH 8.2)/1 L
50x BG-11 stock 20 ml
1,000x Micro elements A6 1 ml
1,000x K2HPO4 1 ml
1,000x CaCl2 1 ml
1,000x Ammonium Iron(lll) citrate brown 1 ml
1 M HEPES-KOH (pH 8.2) 20 ml
H2O up to 1 L
Autoclave (A. C.) (120 °C, 20 min) - BG-11 plates (pH 8.2)/1 L
- 2x BG-11 stock
50x BG-11 stock 20 ml
1,000x Micro elements A6 1 ml
1,000x K2HPO4 1 ml
1,000x CaCl2 1 ml
1,000x Ammonium Iron(lll) citrate brown 1 ml
1,000x Na2S2O3 1 ml
1 M HEPES-KOH (pH 8.2) 20 ml
H2O up to 500 ml
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - 2x Agar stock
Bacto agar (Nissui) 15 g
H2O 500 ml
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min)
After dissolve Recipe 2b, mix with Recipe 2a.
- 2x BG-11 stock
- 50x BG-11 stock, 1 L
NaNO3 75 g
MgSO4·7H2O 3.75 g
Citric acid 0.33 g
EDTA-3Na Salt 0.05 g
Na2CO3 1.0 g
H2O up to 1 L
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - 1,000x Micro elements A6, 1 L
H3BO3 2.86 g
MnCl2·4H2O 1.81 g
ZnSO4·7H2O 0.222 g
Na2MoO4·2H2O 0.391 g
Co(NO3)2·6H2O 0.0494 g
CuSO4·5H2O 0.08 g
H2O up to 1 L
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - 1,000x K2HPO4, 100 ml
K2HPO4 3.0 g
H2O up to 100 ml
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - 1,000x CaCl2, 100 ml
CaCl2·2H2O 3.6 g
H2O up to 100 ml
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - 1,000x Ammonium Iron(lll) citrate brown, 100 ml
Ammonium Iron(lll) citrate brown 0.6 g
H2O up to 100 ml
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - 1,000x Na2S2O3, 100 ml
Na2S2O3 15.81 g
H2O up to 100 ml
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - 1 M HEPES-KOH (pH 8.2), 1 L
HEPES 238.3 g
pH adjusted to 8.2 with KOH
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - M9 medium, 1 L
H2O (A. C.) 895 ml
10x M9 salt 100 ml
1 M MgSO4 (A. C.) 1 ml
40% Glucose (A. C., 120 °C, 15 min) 5 ml
1% Thiamine-HCl (A. C.)1 ml
1M CaCl2 (A. C.) 100 µl - 10x M9 salt, 1 L
Na2HPO4 60 g
KH2PO4 30 g
NaCl 5 g
NH4Cl 10 g
H2O up to 1 L
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min) - PBS buffer
PBS powder 9.6 g
H2O up to 1 L
A. C. (120 °C, 20 min)
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from Watanabe et al. (2012). This work was supported in part by a Grants-in-Aid 25850056 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan to S. W.
References
- Binder, B. J. and Chisholm, S. W. (1995). Cell cycle regulation in marine Synechococcus sp. strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(2): 708-717.
- Castenholz, R. W. (1988). Culturing methods for cyanobacteria. Meth Enzymol 167: 68-93.
- Griese, M., Lange, C. and Soppa, J. (2011). Ploidy in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 323(2): 124-131.
- Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. and Maniatis, T. (1989). Bacterial media, antibiotics, and bacterial strains. In: Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, A.1-13.
- Watanabe, S., Ohbayashi, R., Shiwa, Y., Noda, A., Kanesaki, Y., Chibazakura, T. and Yoshikawa, H. (2012). Light-dependent and asynchronous replication of cyanobacterial multi-copy chromosomes.Mol Microbiol 83(4): 856-865.
- Watanabe, S., Ohbayashi, R., Kanesaki, Y., Saito, N., Chibazakura, T., Soga, T. and Yoshikawa, H. (2015). Intensive DNA replication and metabolism during the lag phase in cyanobacteria. PLoS One 10(9): e0136800.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Watanabe, S. and Yoshikawa, H. (2016). Estimation of the Chromosomal Copy Number in Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942. Bio-protocol 6(13): e1855. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1855.
- Watanabe, S., Ohbayashi, R., Kanesaki, Y., Saito, N., Chibazakura, T., Soga, T. and Yoshikawa, H. (2015). Intensive DNA replication and metabolism during the lag phase in cyanobacteria. PLoS One 10(9): e0136800.
Category
Molecular Biology > DNA > DNA quantification
Microbiology > Microbial genetics > DNA > Chromosomal
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











