- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Efficient Isolation of Influenza Specific CTLs
Published: Vol 6, Iss 12, Jun 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1847 Views: 9157
Reviewed by: Jia LiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Selective Enrichment and Identification of Cerebrospinal Fluid-Contacting Neurons In Vitro via PKD2L1 Promoter-Driven Lentiviral System
Wei Tan [...] Qing Li
Nov 20, 2025 1372 Views

Revisiting Primary Microglia Isolation Protocol: An Improved Method for Microglia Extraction
Jianwei Li [...] Guohui Lu
Dec 5, 2025 1549 Views

Non-Enzymatic Isolation of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts From Human Prostate Tumor Explants
Giulia Gangarossa [...] Paola Chiarugi
Mar 5, 2026 95 Views
Abstract
Human antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell clones are valuable tools for dissecting CD8+ T-cell responses against antigens derived from infectious agents, cancer and self antigens. Here we describe a protocol for isolating human antigen-specific CD8+ T cells. This protocol uses surface capture of IFNγ to identify antigen responsive cells that are then cloned by single-cell sorting. Here we use CD8+ T-cell responses to influenza matrix protein (MP) as an example, but this approach can be applied to any antigen specificity.
Keywords: CloningMaterials and Reagents
- 50 ml Falcon tubes
- Greiner CELLSTAR®, 96-well round-bottom tissue culture plates (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M9311 )
- Corning® Costar® 24 and 48 well tissue culture plates (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CLS3524 and CLS3548 )
- 10 ml tube
- Vials
- Peripheral blood
- EBV-transformed B-cell lines (HLA-A2)
- Ficoll (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 17-1440-03 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (DPBS) (Lonza, catalog number: 17-512F )
- Trypan blue solution (0.4%) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8154 )
- RPMI 1640 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R8758 )
- Synthetic peptide(s) (Purar Chemicals)
- Influenza matrix peptide 58-66 (MP58-66; GILGFVFTL) (GL-Biochem)
- 5% pooled human serum
- Cytokines IL-2 (Peprotech, catalog number: AF-200-02 ), IL-15 (Peprotech, catalog number: AF-200-15 )
- Human IFNγELISA Kit (BioLegend, catalog number: 430106 )
- Miltenyi IFN-γ secretion assay kit-PE (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-054-202 )
- CD8-FITC (SK1) mAb (clone SK1) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, eBiosciencesTM, catalog number: 11-0087-42 )
- Fungizone (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15290-018 )
- Propidium iodide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 81845 )
- Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8139 )
- Ionomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I0634 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2650 )
- HEPES (1 M) (Life technologies, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15630-080 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15630-080”. - Non-essential amino acids (NEAA) (Life Technologies, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11140-050 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11140-050”. - GlutaMAXTM (Life Technologies, GibcoTM, catalog number: 35050-061 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 35050-061”. - UltraPureTM 0.5 M EDTA, pH 8.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 15575-020 )
- Penicillin-Streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P0781 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7906 )
- Stock concentration of cytokines and peptides (see Recipes)
- Cell culture media (see Recipes)
- Staining buffer (see Recipes)
- Stock concentration of propidium iodide (PI) (see Recipes)
- Stock concentration of PMA and ionomycin (see Recipes)
- Stock concentration of fungizone (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Megafuge 40R centrifuge (ThermoFisher, catalog number: 75004503 )
- Neubauer chamber
- Freezing container, Nalgene® Mr. Frosty (Sigma-Aldrich, C1562 )
- Cell culture CO2 incubator (Panasonic Healthcare Co., model: MCO-20AIC ) with 5% CO2
- Flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, model: BD FACSAria III )
- Liquid nitrogen dewar
Procedure
- Collect approximately 25 ml of blood from HLA*A02:01 positive donor. Prepare peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) by centrifuging over 10 ml of Ficoll (20 °C, 805 x g, no brake). Collect PBMC from above the Ficoll and wash twice in DPBS. Count live PBMC using trypan blue exclusion on a Neubauer chamber. Dilute the PBMC to 2 x 106 cells/ml in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 5% pooled human serum. A total of 6.0 ml of cell suspension (12 x 106 cells) is used for peptide stimulation. PBMC were cultured (at 37 °C, 5% CO2) with 1 μM influenza matrix peptide 58-66 (MP58-66; GILGFVFTL) for 3 days in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 5% pooled human serum [The Australian Red Cross Blood Service (ARBCS), Melbourne, Australia]. Freeze remaining PBMC at 5 x 106 cells/vial and store in liquid nitrogen for later to use (step 3) as antigen presenting cells (APCs) in re-stimulation and screening step.
Notes:- Choose donors who have the appropriate HLA class I allele(s) for the peptide antigen.
- Other sera, such as foetal bovine serum, can be used. We prefer to use human serum because this results in a lower background response in the absence of peptide.
- Choose donors who have the appropriate HLA class I allele(s) for the peptide antigen.
- After three days add IL-2 (final concentration of 20 U/ml) and IL-15 (final concentration of 5 ng/ml) to the cells. The culture is continued for a further 7 days making the total culture time 10 days.
- IFNγ-secreting CD8+ cells are detected after overnight restimulation with peptide (1 μM final concentration) and thawed, autologous, irradiated (60 Gy) PBMC (from step 1 above), by surface-capture staining. IFNγ secretion and capture was performed according to Miltenyi’s instructions. Autologous, irradiated PBMC are used at a 1:1 ratio with the PBMC culture with peptide and cytokines. After 1 h of culture at 37 °C/5% CO2, 2 ml of ice cold staining buffer is added to each tube and cells are washed once at 515 x g for 5 min, at room temperature. Washed cells are resuspended with 90 μl of staining buffer and 10 μl of IFNγ capture reagent and incubated on ice for 5 min. Cells are then transferred to 50 ml Falcon tubes and warm (37 °C) culture media is added to dilute the cells to 1 x 105 cells/ml. The diluted cells are then incubated at 37 °C/5% CO2 for 60 min with occasional mixing. In parallel, a small sample of cells (~0.5 x 106) is ‘restimulated’ in the absence of peptide. After 1 h captured IFNγ was detected using a PE-labeled detection mAb. For IFNγ detection, the cells are diluted in ice-cold staining buffer and centrifuged at 515 x g for 5 min, at 4 °C. Cells are resuspended in 90 μl staining buffer for up to 5 x 106 cells. For staining, 10 μl of IFNγ detection antibody and 10 μl of CD8-FITC is added to stain for CD8. Tubes were incubated on ice for 10 min then the cells are washed once with ice-cold staining buffer and transferred to FACS tubes for sorting.
Note: A small number of cells are restimulated in the absence of peptide to determine how many CD8+ IFNγ+ cells are present without restimulation. We expect to see >5x increase in the number of IFNγ+ cells after restimulation with peptide. - Flow cytometry. Compensation settings were determined using single-colour stained samples. Propidium iodide (final concentration of 1 μg/ml) was added to exclude dead cells. Negative control sample (without peptide) and positive control sample (PMA/ionomycin-stimulated) can be used to set sorting gates. Doublets are excluded using a FSC-w (forward scatter width) vs FSC-h (forward scatter height) gate (Figure 1). A single CD8+, IFNγ+ cells is sorted into the 60 inner wells of a 96-well plate containing feeder cells [irradiated (60 Gy)] PBMC, anti-CD3 (OKT3, 30 ng/ml) and IL-2 (20 U/ml) and IL-15 (5 ng/ml) and fungizone, as described in Mannering et al. (2003).
Notes: - We prefer not to use the outer wells of the 96-well plate because these often become infected with fungus.
- Fungizone (final concentration of 2.5 μg/ml) is routinely included in the cultures. This markedly reduces the rate of fungal contamination in the plates.
- Plates containing the sorted IFNγ+, CD8+ cells, irradiated feeder cells, cytokines, anti-CD3 and fungizone are cultured (37 °C/5% CO2). After a week 50 μl of culture media containing 60 U/ml of IL-2 and 15 ng/ml of IL-15 is added to each well of the 96-well, round-bottom plate. This gives a final concentration of 20 U/ml of IL-2 and 5 ng/ml of IL-15.
Each well is ‘fed’ again, with IL-2 and IL-15 in 50 μl of media, after another week of culture. This gives a final volume of 200 μl in each well.
By ~14 days after sorting growing clones should start to become be visible in some of the wells.
Notes: - By this time the irradiated feeder cells should be dead.
- Growing clones are best identified using an inverted microscope.
- It is most convenient to use a felt-tipped pen to put a circle on the lid of the plate over the well(s) with growing clones.
- Transfer the growing clones to a 48-well plate. Add another 200 μl of culture media containing IL-2 (40 U/ml) and IL-15 (10 ng/ml) to give a final concentration of 20 U/ml of IL-2 and 5 ng/ml of IL-15 in a final volume of 400 μl.
- The clones are tested for antigen specificity by ELISA assay.
Antigen specificity testing is done in duplicate-two wells with HLA-A2+ APC and peptide and two wells with APC, but no peptide. Each of the clones in the 48-well plate is resuspended in ~400 μl. One to two hundred microliters of this cell suspension is transferred to a 10 ml tube, washed in 10 ml of DPBS and then with 1.0 ml of culture media. For an ELISA assay, the washed clones are resuspended in 400 μl of culture media and dispense 100 μl into four wells in 96-well round-bottom plate containing APC (50,000 EBV transformed B cells/well) with (two wells) and without (two wells) peptide (1.0 μM). After overnight culture collect 100 μl of the supernatant and assay for IFNγ by ELISA (http://www.biolegend.com/human-ifn-gamma-elisa-max-standard-2226.html).
Notes: - We routinely use EBV-transformed B-cell lines that express the required HLA molecule, HLA-A2 in this case. Alternative APC, such as irradiated PBMC (60 Gy) or transfected cell lines can also be used.
- Other assay, such as 51Cr release, can also be used to screen clones. We prefer to use IFNγ secretion as the initial screen because all the responding cells should secrete this cytokine because they were selected based on IFNγ secretion.
- Clones that responded specifically to MP58-66 were grown to large numbers by restimulation with anti-CD3 (OKT3) and feeding with IL-2 and IL-4 as described in Ciantar and Mannering (2011).
- Following expansion the clones were re-tested for antigen specificity and stored in liquid nitrogen until required. To freeze the clones they centrifuged, (515 x g, 5 min, room temperature). After pouring off the supernatant the cells are resuspended in FCS (usually to 10 x 106 cells/ml). An equal volume of FCS containing 20% DMSO is slowly added while mixing gently. Aliquots of 1.0 ml (~5 x 106 cells/vial) are dispensed in vials suitable for freezing in liquid nitrogen. The vials are placed in a freezing container containing propanol and stored in a -80 °C freezer overnight. The next day the vials are transferred to a liquid nitrogen dewar and stored until required.
Note: We have found that killing function of CD8+ T cells can improve if they are cultured in IL-2 (20 U/ml) overnight after being thawed.
Representative data
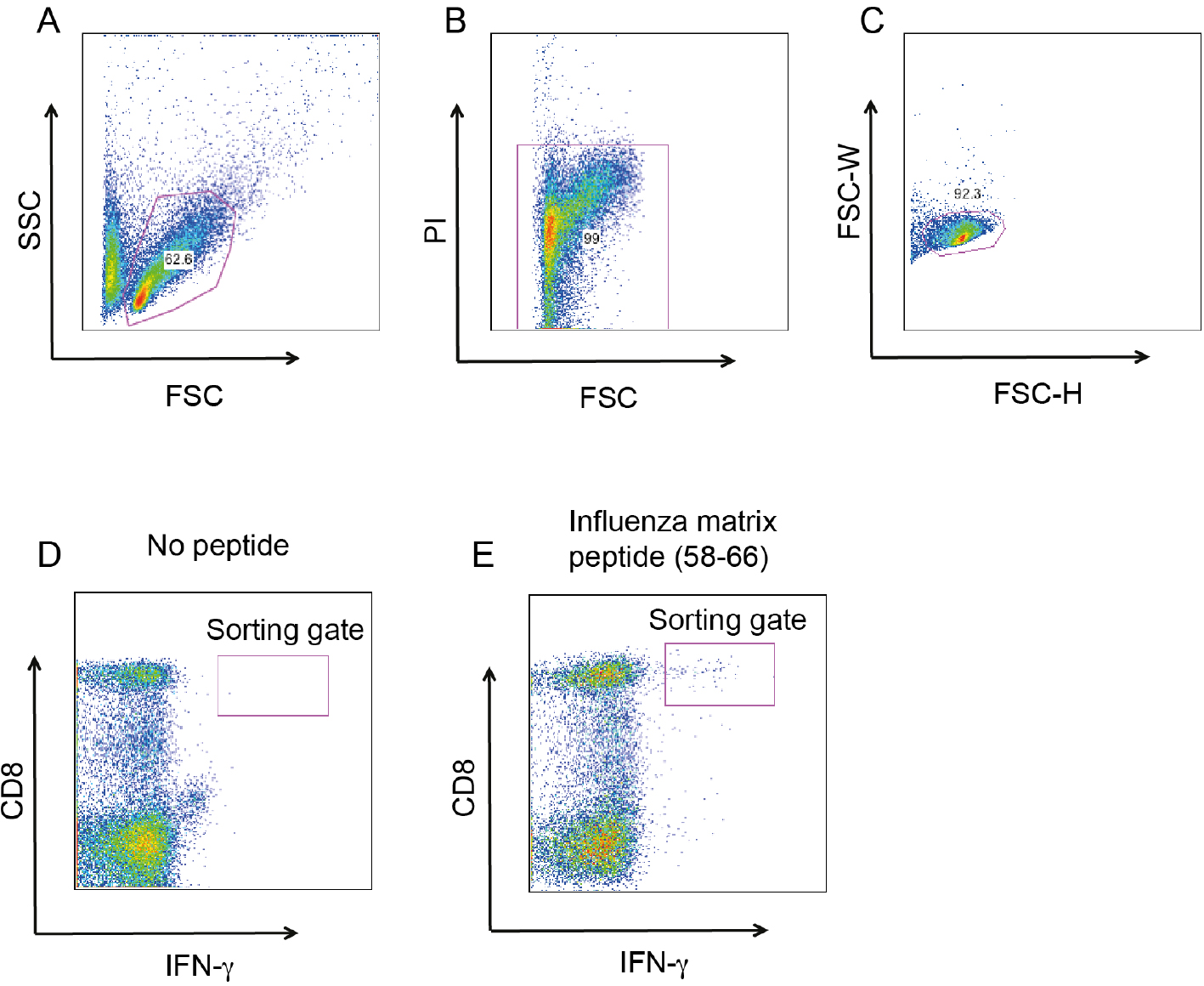
Figure 1. Cloning MP58-66 specific, IFNγ+ CD8+ T cells. The gating strategy for MP58-66 specific, IFNγ+ CD8+. A. Gating on lymphocytes based on forward (FSC) and side scatter (SSC); B. Exclusion of dead cells by propidium iodide staining, viable cells are PI negative; C. Exclusion of doublets by FSC-Height (FSC-H) and FSC-width (FSC-W) gating strategy; D. IFNγ+ CD8+ T cells when PBMC are cultured without peptide; E. The same gate with PBMC cultured with MP58-66 and re-stimulated with the same peptide.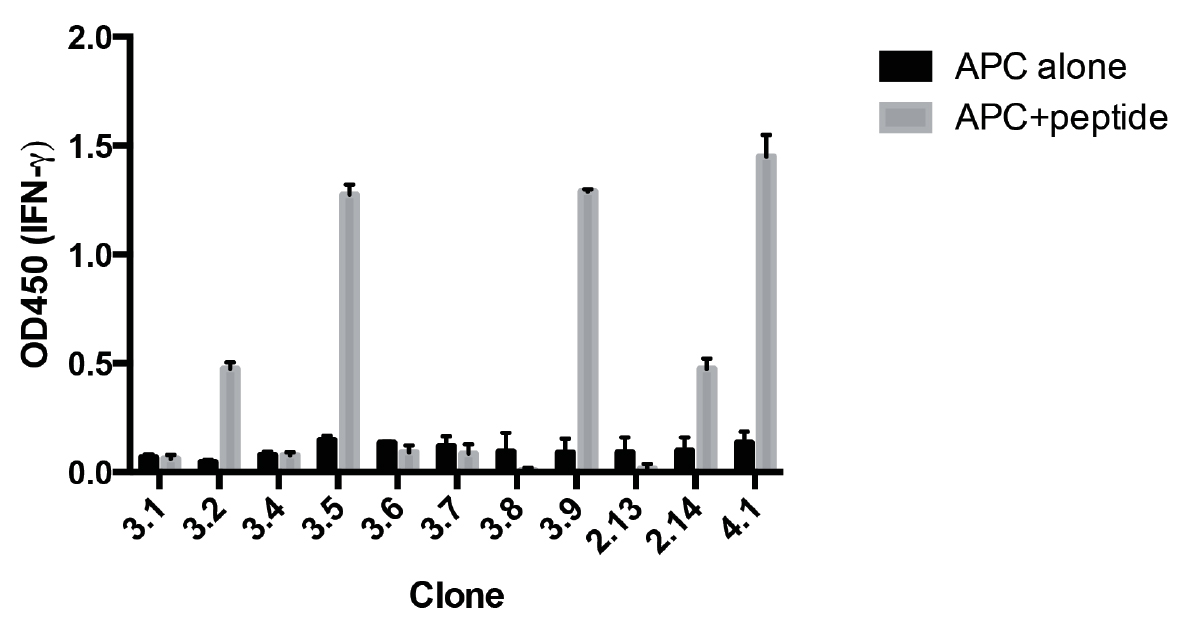
Figure 2. Screening of antigen specificity for growing CD8+ T-cell clones. HLA-A2+ EBV cells were pulsed with either MP58-66, or without peptide. A sample of each growing clone was washed and incubated with these APCs overnight. The next day the concentration of IFNγ in the supernatant is determined by ELISA. Data represents mean ± standard deviation of duplicate cultures for each clone. The clones that secreted IFNγ in response to MP58-66 were selected for further expansion.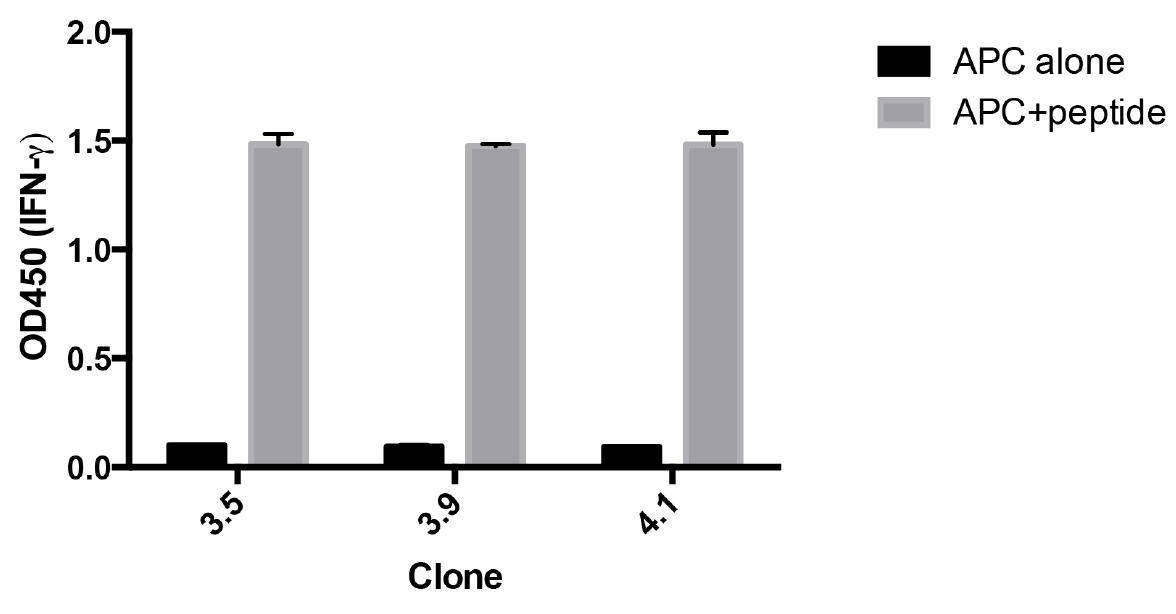
Figure 3. Re-screening of antigen specificity after expansion of CD8+ T-cell clones. Clones were incubated with HLA-A2+ EBV cells pulsed with, or without, MP58-66. After overnight incubation the IFNγ in the supernatant was measured by ELISA. The data represent the means ± standard deviation of triplicate samples for each clone.
Recipes
- Stock concentration of cytokines and peptides
Prepared according to manufacturer’s instructions - Staining buffer
0.5% BSA and 2 mM EDTA in DPBS - Cell culture media-RPMI with 5% pooled human serum (Table 1)
Table 1. Preparation of T-cell culture medium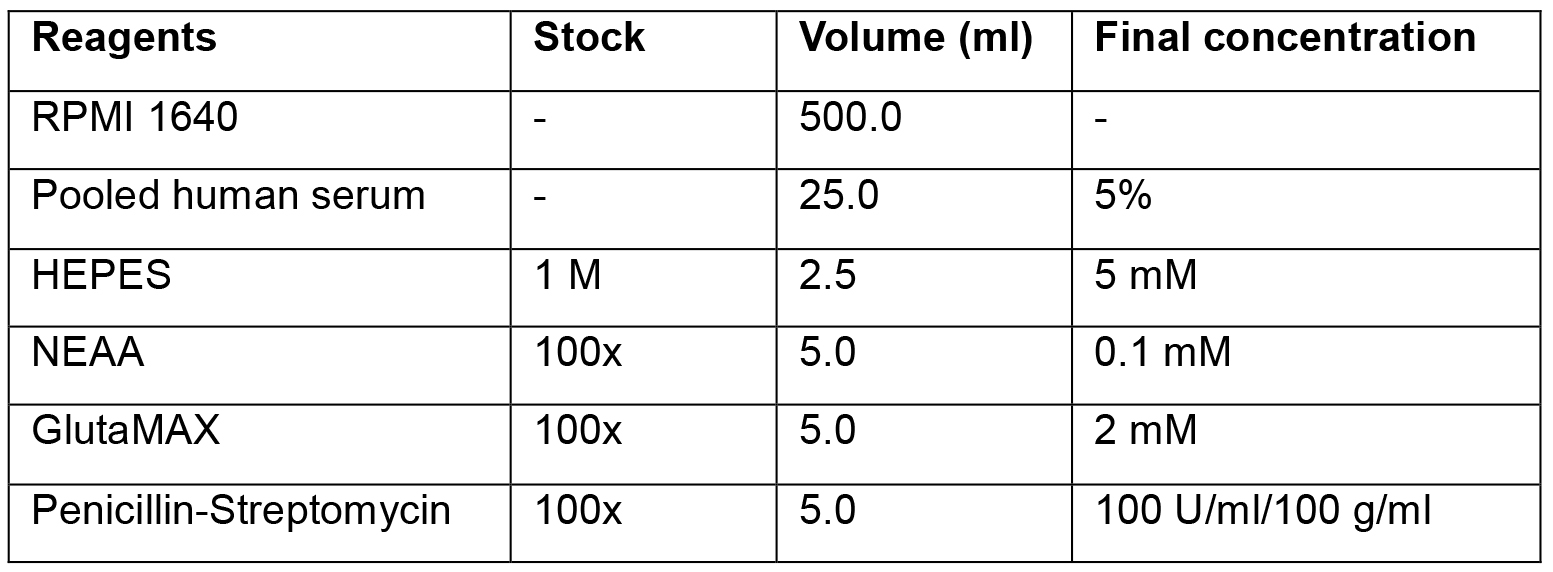
- Stock concentration of propidium iodide (1 mg/ml)
Prepared by dissolving propidium iodide in sterile filtered water - Stock concentration of PMA (0.1 mg/ml) and ionomycin (0.5 mg/ml)
Prepared by dissolving in DMSO - Stock concentration of fungizone (50 μg/ml)
Prepared by dissolving fungizone into sterile filtered water
Acknowledgments
We thank Eleanora Tresoldi for technical assistance and blood donors for providing blood samples for research. SIM is supported by The Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC, APP1061961, APP1087341) and a JDRF Career Development Award 5-CDA2014210-A-N. St Vincent’s Institute of Medical Research receives support from the Operational Infrastructure Support Scheme of the Government of Victoria. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Ciantar, J. P. and Mannering, S. I. (2011). An improved method for growing and analysing human antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell clones. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 27(8): 906-912.
- Mannering, S. I., Morris, J. S., Jensen, K. P., Purcell, A. W., Honeyman, M. C., van Endert, P. M. and Harrison, L. C. (2003). A sensitive method for detecting proliferation of rare autoantigen-specific human T cells. J Immunol Methods 283(1-2): 173-183.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Trivedi, P. and Mannering, S. I. (2016). Efficient Isolation of Influenza Specific CTLs. Bio-protocol 6(12): e1847. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1847.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell function > Antigen-specific response
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











