- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Aorta Atherosclerosis Lesion Analysis in Hyperlipidemic Mice
Published: Vol 6, Iss 11, Jun 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1833 Views: 22271
Reviewed by: Ruth A. FranklinRakesh BamAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

In vivo Electroporation of Skeletal Muscle Fibers in Mice
Steven J. Foltz [...] Hyojung J. Choo
Jul 5, 2023 1823 Views

Cochlear Organ Dissection, Immunostaining, and Confocal Imaging in Mice
Chenyu Chen [...] Dongdong Ren
Jan 20, 2025 3758 Views

Isolation and Imaging of Microvessels From Brain Tissue
Josephine K. Buff [...] Sophia M. Shi
Aug 5, 2025 2627 Views
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease of large and medium-sized arteries. Apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/-) mice are used as experimental models to study human atherosclerosis. ApoE-/- mice are constitutively hyperlipidemic and develop intima plaques that resemble human plaques. Various issues including experimental design for lesion analysis, dietary conditions, isolation of the aorta, staining methods, morphometry, group size, age, the location within the arterial tree, and statistical analyses are important parameters that need to be addressed to obtain robust data. Here, we provide detailed methods to quantify aorta atherosclerosis.
Keywords: AtherosclerosisMaterials and Reagents
- Petri dish sets, glass (VWR International, catalog number: 89000-306 )
- Black dissection wax (CR Scientific, catalog number: C3541 )
- Minutien pins (0.15 mm diameter) to fix the aorta (Fine Scientific Tools, catalog number: 26002-15 )
- 50 ml Falcon tube (VWR International, CellStar®, catalog number: 188271 )
- 10 ml syringe (BD, catalog number: 309695 )
- 20 ml syringe (BD, catalog number: 301625 )
- Sterican single use needles-23G (B. Braun Medical Inc., catalog number: 4657640 )
- Poly-L-lysine coated glass slides (Menzel Glaeser, catalog number: J2800AMNZ )
- Coverslips (Menzel Glaeser, catalog number: BBAD02400500#A )
- OHP permanent marker pen (STAEDTLER MARS LIMITED)
- Microscope slide holder/mailer, 5 place (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z708313-25EA )
- Cryogenic freezer storage box (VWR International, catalog number: 82021-114 )
- Staining jar with cover (VWR International, catalog number: 25460-907 )
- Grade 410 filter paper (VWR International, catalog number: 28321-077 )
- Polystyrene petri dishes (150 mm x 15 mm) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5981 )
- Ethanol (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 1009832500 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E6758 )
- Phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4417-100TAB )
- Paraformaldehyde (PFA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 16005 )
- Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S0389 )
- Isopropanol (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 1096341011 )
- Acetone (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 1000141000 )
- Isopentane (VWR International, catalog number: 103614T )
Note: It is also named “2-Methylbutan” on VWR International website. - Dry ice (TKD KABEL GmbH)
- Sudan IV (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 198102 )
- OCT compound-Tissue-Tek (SAKURA FINETEK USA, catalog number: 4583 )
- Cryomold (SAKURA FINETEK USA, catalog number: 25608-924 )
- Oil Red O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 00625 )
- Hematoxylin solution, Mayer’s (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: MHS-16 )
- Faramount aqueous mounting medium (Dako, catalog number: S3025 )
- Distilled water
- NaOH
- Sudan IV staining solution (see Recipes)
- Oil Red O (ORO) working solution (see Recipes)
- EDTA (see Recipes)
- PBS (see Recipes)
- Paraformaldehyde (PFA) (see Recipes)
- Sucrose (see Recipes)
- PFA-sucrose (see Recipes)
- Black wax petri dish (see Recipes)
Equipment
- CO2 supply machine (Next Advance, model: Quietek CO2 induction system )
- Dissection scissors (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 91460-11 )
- Fine iris scissors (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 14094-11 )
- Spring scissors (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 15009-08 )
- Curved forceps (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11073-10 )
- Delicate suture tying forceps (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11063-07 )
- Dissection stereo microscope equipped with fibre-optic light source from top (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, model: Stemi 2000 )
- Measuring scale (LACO)
- Camera (Nikon, model: D5300 )
- -80 °C freezer (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Cryostat microtome (Microm GmbH, model: HM500 OM )
- Precision hotplate (HARRY GESTIGKEIT GMBH, model: PZ28-2T )
- Axio-Imager A2 microscope equipped with Axiovision release 4.8 software (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, model: 490022-0002-000 )
Software
- Statistical analysis software [IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0 (IBM Corporation, Released 2011, NY, USA)]
- Image J software [National Institutes of Health (NIH), USA]
- Axiovision release 4.8 software (Carl Zeiss)
Procedure
- Isolation of mouse aorta
- Measure the weight of mouse prior to euthanasia.
- Euthanize the mouse by CO2 inhalation as approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of local government. Death is noted by lack of respiration and motility.
- Lay down the mouse in a supine position and fix arms and legs onto a cork platform with needles.
- Disinfect the ventral side of mouse with 75% ethanol.
- Open the abdominal cavity by a ventral midline incision and traverse cuts in the abdominal wall.
- Cut the skin, subcutaneous tissue and peritoneum from the abdomen to the thorax along the middle line, and fix skin/subcutaneous tissue onto the cork plate with needles.
- Open the mediastinum and cut off the ribs lateral to the mediastinum. Cut the diaphragm to facilitate drainage.
- Make a small incision in the right atrium of heart to draw 500-800 µl blood before perfusion using a 1 ml syringe attached with a 23G needle. Perfuse the vasculature through apical left ventricular puncture by slowly injecting 10 ml of 5 mM EDTA in PBS using a 10 ml syringe followed by 20 ml of ice-cold PBS by using a 20 ml syringe attached with a 23G needle. Perfuse 2-3 times intermittently with 10-20 ml of ice-cold PBS during dissection to avoid dehydration of aorta tissue.
- Remove organs including lung, liver, spleen, gastrointestinal and reproductive organs using dissection scissors and curved forceps while leaving heart, aorta, and kidneys intact in-situ.
- Expose aorta from heart onto the level below the iliac bifurcation. Under a dissection microscope equipped with fibre-optic light source from top at 30-40x magnification, carefully dissect out the thymus using fine iris scissors and delicate forceps. Note that under dissection microscope, it is possible to distinguish the compact aorta adventitia from loose light yellow-colored brown adipose tissue in the thorax and loose pale white-colored white adipose tissue in abdomen as well as from solid light yellow/brown paraaortic lymph nodes in-situ (Figure 1, left). Caution should be taken to prevent aorta injury during removal of liver, mesentery, thymus and kidney.
- Remove perivascular connective tissue and adipose tissue around the aorta and the major artery branches including innominate, common carotid and subclavian arteries in the aortic arch of the thoracic aorta; and celiac, mesenteric, renal, and common iliac arteries of the abdominal aorta with caution using fine iris scissors and delicate forceps (Figure 1, right). Carefully dissect paraaortic lymph nodes that are close to the aorta for clarity.
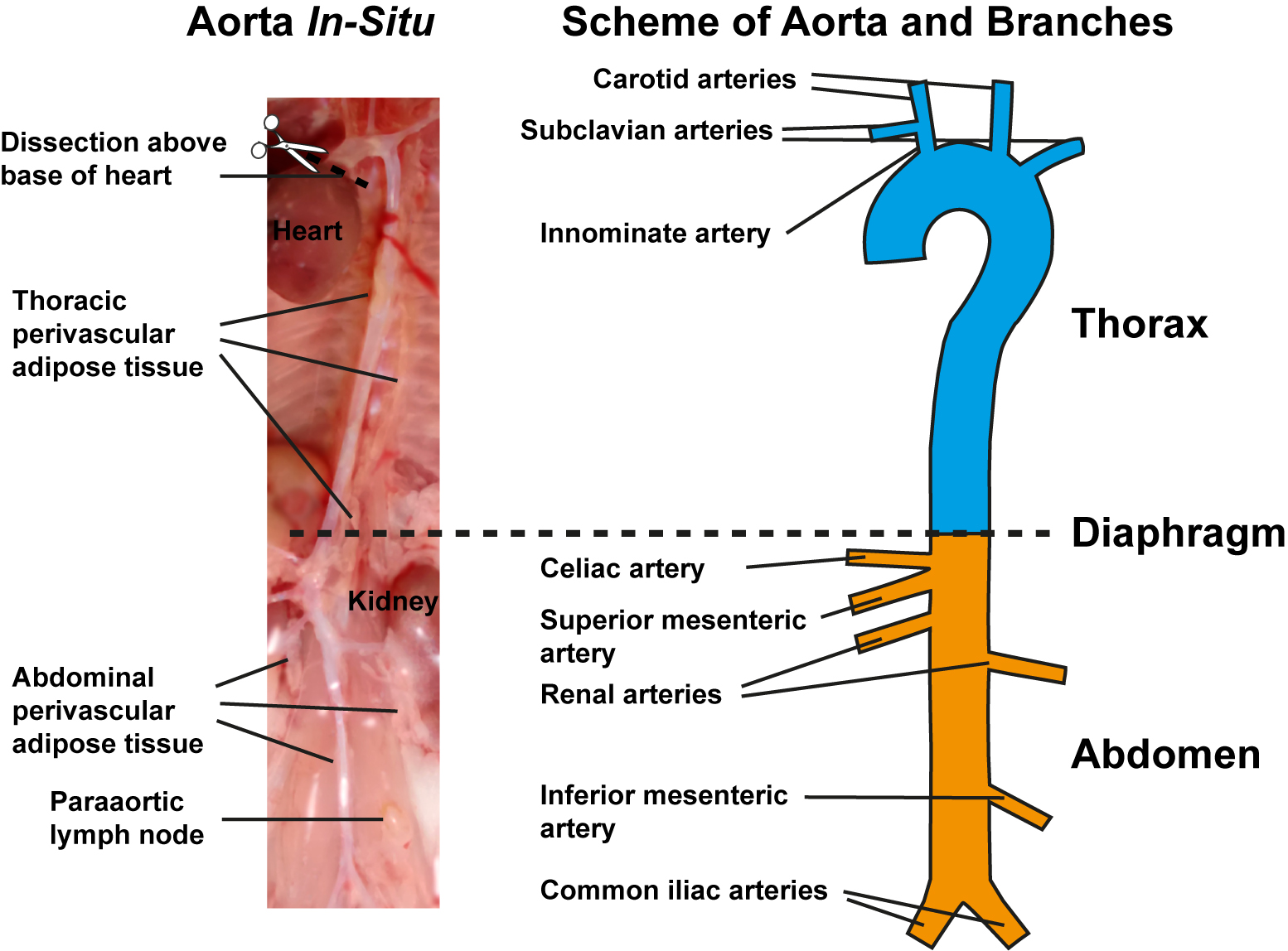
Figure 1. Preparation of aorta and schematic view of aorta with its major branches. Image of in-situ aorta preparation before isolation showing preparation of aorta segments corresponding to the right schematic view, perivascular adipose tissue in thorax and abdomen, and paraaortic lymph nodes (left). Schematic view of freshly isolated aorta depicting the upper thoracic part with its branches (cyan) and lower abdominal part with its branches (yellow). Diaphragm indicates border between thorax and abdomen (right).
- Measure the weight of mouse prior to euthanasia.
B1. En-face staining of whole aorta (Zhao et al., 2014; Hu et al., 2015)
- Follow steps 1-11 in Procedure A of aorta isolation.
- Fix the aorta tissue in-situ by injecting 5 ml of 4% PFA in PBS into the left ventricle using 10 ml syringe attached with a 23G needle and wait for 10 min, then inject/rinse with 10 ml of 5% sucrose in PBS.
- Harvest the whole aorta from the level above the coronary artery at the base of heart near the atria until 2-3 mm below the iliac bifurcation of the abdominal aorta after severing all major arteries in-situ. Be careful while dissecting and do not cut the thoracic or abdominal aorta.
- Put the whole aorta onto a previously prepared smooth surfaced black wax petri dish containing PBS.
- Gently clean all soft/loose perivascular adipose tissue around the aorta from thorax and abdomen under the dissection microscope at 20-25x magnification using fine iris scissors and delicate forceps (Figure 2, left). Note that applying more force or improper cutting can damage the adventitia or injure the aorta.
- Refill the black wax petri dish with fresh PBS after perivascular adipose tissue cleaning.
- Sever innominate, carotid, and subclavian arteries of aortic arch in thoracic aorta, and iliac arteries in abdominal aorta 3-5 mm after the bifurcations. Sever renal arteries in abdominal aorta for clarity (Figure 2, middle left)
- Pin the open end of one common iliac artery with minutien pin. Cut the aorta longitudinally from the unfixed common iliac artery using spring scissors and proceed anteriorly along the inner curvature of the aortic arch. Pin the split aorta onto the black dissection wax using minutien pins. (Figure 2, middle right)
- Cut along the outer curvature of the aorta from aortic root through innominate, carotid, and subclavian arteries until the aortic arch resembles a Y shaped split. Flatten out the Y-shaped aortic arch onto the black wax and pin the aorta parts (Figure 2, middle right).
- Fix the pinned aorta in the black wax petri dish overnight with PFA-sucrose at room temperature.
- Rinse 3 times for 10 min each with 1x PBS and fix 5 min with 70% ethanol at room temperature. Use of shaker is optional.
- Stain with Sudan IV staining solution for 10 min at room temperature. Sudan IV will stain lipid-rich plaque red leaving other non-plaque containing areas pale (Figure 2, right). It is advisable to clear all visible perivascular adipose tissue before staining because Sudan IV stained perivascular adipose tissue can give false background and interfere with plaque morphometry.
- Rinse 2 times for 3 min each with 70% Ethanol at room temperature. Note that over rinsing can destain the plaque. Rinse for 5 min with 1x PBS to remove ethanol.
- Fill the black wax petri dish with 1x PBS until it covers the stained aorta and pins.
- Place a measuring scale near the pinned aorta in the black wax petri dish.
- Take image with a digital camera from the top attached to a holding stand.
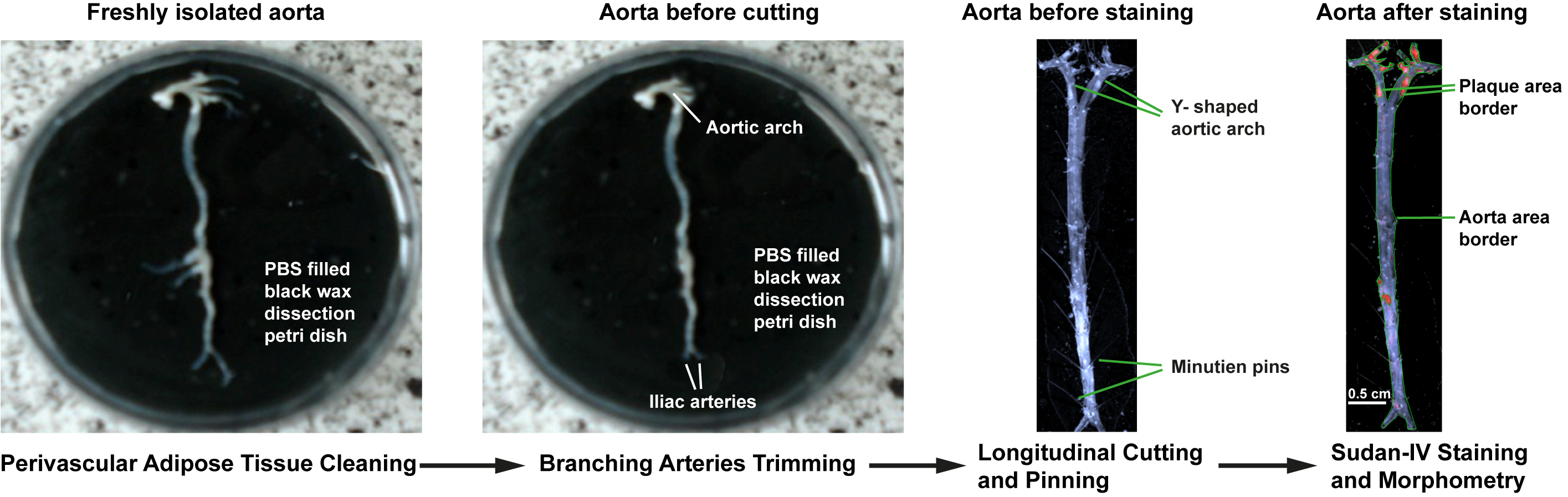
Figure 2. Atherosclerosis lesion analysis of whole aorta. Removal of perivascular adipose tissue from freshly isolated aorta and trimming of branching arteries under the dissection microscope (left, middle left). Longitudinally split and pinned whole aorta before en-face staining (middle right). Enumeration of total aorta surface area and plaque surface area for morphometric analysis of Sudan-IV-stained whole aorta (right).
B2. Staining of aorta cross sections (Hu et al., 2015; Grabner et al., 2009)
- Follow steps 1-10 in procedure A of aorta isolation.
- Sever all thoracic and abdominal branching arteries 3-5 mm after their bifurcations from the aorta.
- Isolate whole aorta with adjacent adipose tissue 1 mm peripheral of the external lamina of the aorta under dissection microscope from the level above the coronary artery near the atria at the base of heart of the thorax onto the level below the iliac bifurcation (2-3 mm) of the abdominal aorta. (Figure 3, left).
- Cut the aorta into 4 parts: Thorax-I from the base of heart, to the level of 5th rib that included the aortic root, short ascending aorta, aortic arch containing the innominate, the right subclavian, the right common carotid, the left carotid, and the left subclavian arteries, and long descending thoracic aorta; thorax-II from the level of the 7th rib to the diaphragm including intercostal arteries; abdomen-I below the diaphragm to the middle of the abdominal aorta including the celiac, the superior mesenteric, the right and left renal arteries; and abdomen-II from the middle of the abdominal aorta to below the level of iliac bifurcation including the inferior mesenteric, and the common iliac arteries at the iliac bifurcation (Figure 3, left).
- Put OCT embedding medium tissue-tek into a labeled cryomold and then transfer 4 parts into the mold as described in Figure 3 (middle). Draw the direction of embedded aorta parts on the posterior part of cryomold using a permanent marker pen (Figure 3, middle).
- Refill the cryomold with tissue-tek until all aorta parts are completely embedded. Adjust the aorta segments to the same level within the embedding medium.
- If measurement of atherosclerosis in the innominate artery is to be done, embed thorax-I into a separate mold (optional).
- Snap freeze the mold containing aorta segments in tissue-tek in isopentane chilled with dry ice for 3 - 5 min until the tissue block becomes solid and white.
- Keep the frozen tissue block on dry ice for 30 min and store in -80 °C freezer until cryosectioning.
- Transfer the frozen tissue block onto the -20 °C chamber of a cryostat microtome 1 h before tissue sectioning. Mark the cutting side on the tissue block based on the direction of embedded aorta parts in step 5 in procedure B2.
- Prepare 10 µm thick fresh frozen aorta cross sections using cryostat microtome at -20 °C and collect them carefully onto labeled Poly-L-lysine-coated glass slides. To get good quality flat cryosections use new blade, apply even force to the wheel of the microtome and do not move the slide during tissue collection. New users should practice at least 10 times with practice tissue like liver or spleen before cutting the aorta.
- Collect every 10th serial aorta section at 100 µm intervals for Oil Red O and hematoxylin staining and reserve other sections for further staining.
- Air dry the glass slide containing tissue sections at room temperature for 1 h, keep them in slide holder within the moisture repellant coated freezer boxes and store in -80 °C freezer until further use.
- Prior to staining, take the slides out of -80 °C freezer and thaw them on hotplate for 1 min at 37 °C followed by air dry for 1 h.
- Fix the slides with 4% PFA for 5 min followed by 60% isopropanol for 5 min in a staining jar.
- Stain the slides with Oil Red O working solution for 10 min at room temperature.
- Rinse the slides 3 times 2 sec each with 60% isopropanol followed by brief wash in tap water.
- Stain the slides with hematoxylin for 6 min at room temperature.
- After a thorough wash in tap water dip the slides in tap water for 10 min.
- Mount the coverslips on the slides with faramount aqueous mounting medium. Do not air dry the slides before mounting, use 2-3 drops of mounting medium per slide, avoid air bubbles by slowly mounting the coverslip from one side of the slide.
- Leave the slide for 30-60 min after mounting in RT until the coverslip becomes firmly attached to the slide. Do not move or shake the slide to avoid air bubbles or damage of tissue.

Figure 3. Atherosclerosis lesion analysis of aorta cross sections. Freshly isolated aorta with thoracic and abdominal perivascular adipose tissue (left). Note that perivascular adipose tissue in aortic arch was removed for better visibility of the branching arteries. Schematic presentation of isolation and embedding of different aorta segments including thorax-I with its branches (cyan) and thorax-II (green) above diaphragm, abdomen-I with its branches (yellow) and abdomen-II with its branches (red) below diaphragm (middle). Rotate thorax-I at 180° angle before embedding. Arrow indicates direction of cutting. Enumeration of lumen area, internal elastic lamina (IEL) and external elastic lamina (EEL) area for morphometric analysis of Oil Red O and hematoxylin-stained innominate artery (right).
C1. Morphometry of en-face stained aorta (Hu et al., 2015; Daugherty and Rateri, 2015; Schmitt et al., 2014)
- Transfer the images of en-face stained total aorta to a computer equipped with Image J software.
- Adjust the measuring scale distance of the digital image to the pixel scale of the Image J program.
- Encircle outer border line of the aorta manually and measure the area of the total aorta.
- Encircle each Sudan-IV stained plaque surfaces (intense red spots) within the aortic surface and measure their areas. Be careful to exclude any Sudan IV stained adipose tissues that are usually located below the aorta adventitia and less red compare to plaque (Figure 2, right).
- Export all the measurements to an excel file to calculate the ratio of plaque area from total aorta area and normalize the value as percentage of plaque area.
- Optionally, plaque area can be measured in the aortic arch (from aortic root to 3 mm below the subclavian artery branch), the descending thorax (from the level of aortic arch up to the level of diaphragm above the celiac artery branch), and the abdominal aorta (below the diaphragm until iliac bifurcation) after morphometry of plaque area in total aorta.
- For statistics, use 8-10 mice.
C2. Morphometry of Oil Red O-and hematoxylin-stained aorta cross sections (Hu et al., 2015; Grabner et al., 2009)
- Adjust brightness and contrast of the microscope. Take the bright field images of the aorta sections with an Axio-Imager microscope using 10x objective for imaging innominate artery and 5x objective for imaging abdominal aorta sections.
- Use Axiovision release 4.8 software to measure the areas after manually encircling them (Figure 3, right):
- Measure the area encircled by the intima/lumen border.
- Measure the area encircled by of internal elastic lamina (IEL) of arterial media.
- Measure the area encircled by external elastic lamina (EEL) of arterial media.
- Note that the contrast-rich elastin fibers in the media, the intima/media or media/adventitia border can be readily identified and the adventitia can be easily distinguished from adjacent adipose tissue using the Axiovision microscope.
- Export measurement data to an excel file to calculate the intima and media area.
- Calculate intima area by subtracting IEL area from lumen area and media area by subtracting EEL area from IEL area.
- Calculate ratio of intima area versus media area: Equation: intima/media ratio = intima area (IEL-lumen area)/media area (EEL-IEL area). Intima/media ratio represents the normalized value of plaque size.
- Calculate the intima/media ratio in at least 10 serial aorta cross sections (every 10th section) in 8-10 ApoE-/- mice.
- For statistical analyses of morphometry data comparison among multiple mouse groups, it is advisable to use generalized estimating equation model (GEE) model to estimate the parameters of a generalized linear models with the software IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0 (Hu et al., 2015).
- Express the data as means and standard error of mean (SEM). Calculate P values of significance using multiple testing with Bonferroni post-hoc test.
Notes
- During dissection of the aorta, infuse PBS into the left ventricle at regular intervals to keep the aorta wet and to prevent dehydration.
- Remove all perivascular adipose tissues to get a clear Sudan-IV staining with less background.
- Because the level of atherosclerosis varies among individual ApoE-/- mouse, it is advisable to use 8-10 mice of same gender and age per experimental group.
- In case of multiple comparison data sets with repeated measurements per mouse, i.e., several data points from the same mouse, the GEE model takes the correlation of these measurements per individual into account and provides robust estimates for the standard errors of the regression coefficients. This means that, even under misspecification of the chosen correlation structure, inferences regarding the group differences are still unbiased, which is a clear advantage compared to traditional linear regression models including analysis of variance (ANOVA). The major reason not to use ANOVA is that it assumes each data point as a separate entity and ignores the random effects, i.e., the biological differences between the mice. In contrast, GEE treats each mouse as a separate entity; plaque area or size as dependent variable; and genotype, aorta regions (innominate artery or abdominal aorta) as response.
Recipes
- Sudan IV staining solution
Solve 500 mg Sudan IV in a mixture of 35 ml ethanol, 50 ml acetone and 20 ml distilled water
Agitate from time to time until Sudan IV dissolves - Oil Red O (ORO) working solution
Dissolve 0.5 g of ORO with100 ml iso-propanol to prepare ORO stock solution
Mix 6 parts of stock solution with 4 parts of distilled water
Allow the solution to stand for 24 h
Filter the solution before use using grade 410 filter paper
Stored at room temperature - 3.5 mM EDTA
Mix 14.612 g of EDTA with 80 ml distilled water to prepare 50 mM EDTA
Stir the solution vigorously using a magnetic stirrer
Adjust pH to 8.0 using NaOH
Adjust volume to 100 ml with distilled water
Mix 10 ml of 50 mM EDTA stock solution with 90 ml of distill water
Stored at room temperature - 1x PBS
Dissolve 1 PBS tablet in 200 ml distilled water
Stored at room temperature - 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA)
Mix 40 gm of PFA with 800 ml of 1x PBS
Stir the solution at 62 °C under a fume hood
Adjust pH to 7.4 using NaOH
Add distilled water make up the solution to 1,000 ml
Stored at 4 °C - 5% sucrose
Dissolve 5 g of sucrose in 100 ml of 1x PBS
Adjust pH to 7.4 using NaOH
Stored at room temperature - PFA-sucrose
Dissolve 5 g of sucrose in 100 ml of 4% PFA
Adjust pH to 7.4 using NaOH
Stored at room temperature - Black wax petri dish
Melt black dissection wax in the oven at 80 °C for 2-3 h
Pour the melted wax on to several polystyrene petri dishes (150 mm x 15 mm) up to 1/3 of the petri dish
Cool it down overnight at room temperature
Stored at room temperature
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the German Research Council (HA 1083/15-4; to A. J. R. H.; MO 3052/1-1 to S. M.; and YI 133/2-1 to C. Y.) and the European Research Council (AdG 249929 to C.W.).
References
- Daugherty, A. and Rateri, D. L. (2005). Development of experimental designs for atherosclerosis studies in mice. Methods 36(2): 129-138.
- Grabner, R., Lotzer, K., Dopping, S., Hildner, M., Radke, D., Beer, M., Spanbroek, R., Lippert, B., Reardon, C. A., Getz, G. S., Fu, Y. X., Hehlgans, T., Mebius, R. E., van der Wall, M., Kruspe, D., Englert, C., Lovas, A., Hu, D., Randolph, G. J., Weih, F. and Habenicht, A. J. (2009). Lymphotoxin beta receptor signaling promotes tertiary lymphoid organogenesis in the aorta adventitia of aged ApoE-/- mice. J Exp Med 206(1): 233-248.
- Hu, D., Mohanta, S. K., Yin, C., Peng, L., Ma, Z., Srikakulapu, P., Grassia, G., MacRitchie, N., Dever, G., Gordon, P., Burton, F. L., Ialenti, A., Sabir, S. R., McInnes, I. B., Brewer, J. M., Garside, P., Weber, C., Lehmann, T., Teupser, D., Habenicht, L., Beer, M., Grabner, R., Maffia, P., Weih, F. and Habenicht, A. J. (2015). Artery tertiary lymphoid organs control aorta immunity and protect against atherosclerosis via vascular smooth muscle cell lymphotoxin beta receptors. Immunity 42(6): 1100-1115.
- Hu, D., Mohanta, S. K., Yin, C., Weber, C. and Habe nicht, A. J. R. (2016). Preparation of single cell suspensions from mouse aorta. Bio-protocol 6(11): e1832.
- Schmitt, M. M., Megens, R. T., Zernecke, A., Bidzhekov, K., van den Akker, N. M., Rademakers, T., van Zandvoort, M. A., Hackeng, T. M., Koenen, R. R. and Weber, C. (2014). Endothelial junctional adhesion molecule-a guides monocytes into flow-dependent predilection sites of atherosclerosis. Circulation 129(1): 66-76.
- Mohanta, S. K., Yin, C., Peng, L., Srikakulapu, P., Bontha, V., Hu, D., Weih, F., Weber, C., Gerdes, N. and Habenicht, A. J. (2014). Artery tertiary lymphoid organs contribute to innate and adaptive immune responses in advanced mouse atherosclerosis. Circ Res 114(11): 1772-1787.
- Zhao, L., Moos, M. P., Grabner, R., Pedrono, F., Fan, J., Kaiser, B., John, N., Schmidt, S., Spanbroek, R., Lotzer, K., Huang, L., Cui, J., Rader, D. J., Evans, J. F., Habenicht, A. J. and Funk, C. D. (2004). The 5-lipoxygenase pathway promotes pathogenesis of hyperlipidemia-dependent aortic aneurysm. Nat Med 10(9): 966-973.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Mohanta, S., Yin, C., Weber, C., Hu, D. and Habenicht, A. J. R. (2016). Aorta Atherosclerosis Lesion Analysis in Hyperlipidemic Mice. Bio-protocol 6(11): e1833. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1833.
Category
Cell Biology > Tissue analysis > Tissue isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












