- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Extraction and Quantification of Tryptophan and Kynurenine from Cultured Cells and Media Using a High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) System Equipped with an Ultra-sensitive Diode Array Detector
Published: Vol 6, Iss 7, Apr 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1781 Views: 9106
Reviewed by: Masahiro MoritaMichael EnosAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Measurement of Transferrin- and Non-transferrin-bound Iron Uptake by Mouse Tissues
Supak Jenkitkasemwong [...] Mitchell D. Knutson
Sep 5, 2016 9175 Views

Spectrophotometric Determination of Glutamine Synthetase Activity in Cultured Cells
I-Chen Peng [...] Wei-Xing Zong
Oct 5, 2016 13961 Views

Analysis of Leukemia Cell Metabolism through Stable Isotope Tracing in Mice
Nick van Gastel [...] David T. Scadden
Oct 5, 2021 5241 Views
Abstract
Evidence of the involvement of tryptophan and its metabolite, kynurenine, in various biological processes including cancer is constantly expanding. Analysis of cell extracts and culture media can allow for quick snapshots of the metabolic fluctuations occurring in vitro. Here, we describe a method for metabolite extraction from mammalian cells and analysis of extracted metabolites and cell culture media by HPLC with detection using an ultra-sensitive diode array detector.
Keywords: TryptophanMaterials and Reagents
- Disposable 2 ml plastic microcentrifuge tubes
- 1.5 ml glass vials (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5182-0715 ), screw top caps (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5182-0717 ) and 200 μl glass inserts (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 5182-0549 )
- AcroVac Filter Unit (Pall Life Sciences, catalog number: AVFP02L )
- Chloroform (HPLC grade) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C607 )
- L-Tryptophan (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0254 )
- L-Kynurenine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K8625 )
- 3-Nitro-L-tyrosine (nitrotyrosine) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N7389 )
- Methanol (HPLC grade) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A452 )
- Acetonitrile (HPLC grade) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: A998 )
- Potassium phosphate monobasic anhydrous (KH2PO4) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P285-500 )
- Potassium phosphate dibasic anhydrous (K2HPO4) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P288-500 )
- PIPES (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP292450 )
- EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S311-500 )
- Kynurenic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K3375 )
- Quinolinate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P63204 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
- 50% methanol/50% 3 mM PIPES-3 mM EDTA (pH 7.4) (see Recipes)
- Potassium phosphate (pH 6.4) with 2.7% (v/v) acetonitrile (see Recipes)
- Standard mix (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Refrigerated tabletop centrifuge
- HPLC system with binary pump, autosampler and UV diode array detector (DAD) (Agilent Technologies, model: 1100 )
- Hypersil GOLD C18 column (50 mm with 2.1 mm diameter) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25003-052130 )
Procedure
- Tryptophan and kynurenine extraction
- The protocol requires a minimum of 1 x 106 cells to accurately detect tryptophan and kynurenine levels. If tryptophan and kynurenine quantification is desired from fresh media, collect 2 ml of fresh media prior to cell addition for subsequent analysis and freeze at -80 °C. This sample will be used to measure the baseline levels of tryptophan and kynurenine in the media.
- If cells of interest are adherent cells, then proceed to step A2a. If cells of interest are suspension cells, then proceed to step A2b. If desired, the cell culture can be spiked with an internal standard such as 3-nitro-L-tyrosine (a final concentration of 20-50 µM is generally appropriate) at this time. The internal standard can be used to quantify metabolite recovery.
- At the completion of the treatment schedule, collect 2 ml media in 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes. Centrifuge at 2,000 x g at 4 °C in centrifuge to pellet cells/debris from the media. Without disturbing the pellet, transfer media into two labeled tubes of equal volume. One will be used for immediate analysis while the other will serve as a backup. At this point, cell-free, centrifuged culture media can be stored at -80 °C until analysis. Media can be analyzed by HPLC without the need for extraction. Next, aspirate off remaining media in plate/flask where cells are grown. Wash cells with cold (4 °C) phosphate buffered saline (PBS) twice. Afterwards, dislodge cells from culture plate/flask by scraping. Collect liberated cells and place into 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes. Centrifuge at 2,000 x g at 4 °C in centrifuge. Proceed to step A3.
- At the completion of the treatment schedule, collect all media containing cells into appropriate volume conical tubes. Centrifuge at 2,000 x g at 4 °C in centrifuge to pellet cells/debris from media. Without disturbing the pellet, transfer 1 ml of media into two labeled tubes. One will be used for immediate analysis while the other will serve as a backup. At this point, cell-free, centrifuged culture media can be stored at -80 °C until analysis. Media can be analyzed by HPLC without the need for extraction. Next, wash pelleted cells with cold (4 °C) phosphate buffered saline (PBS) twice. Proceed to step A3.
- At the completion of the treatment schedule, collect 2 ml media in 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes. Centrifuge at 2,000 x g at 4 °C in centrifuge to pellet cells/debris from the media. Without disturbing the pellet, transfer media into two labeled tubes of equal volume. One will be used for immediate analysis while the other will serve as a backup. At this point, cell-free, centrifuged culture media can be stored at -80 °C until analysis. Media can be analyzed by HPLC without the need for extraction. Next, aspirate off remaining media in plate/flask where cells are grown. Wash cells with cold (4 °C) phosphate buffered saline (PBS) twice. Afterwards, dislodge cells from culture plate/flask by scraping. Collect liberated cells and place into 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes. Centrifuge at 2,000 x g at 4 °C in centrifuge. Proceed to step A3.
- Centrifuge cells at 2,000 x g at 4 °C and aspirate PBS without disturbing the cell pellet. Keep cells on ice while pipetting PBS. To quench metabolism and extract metabolites, add 200 µl ice-cold 50% methanol/50% PIPES-EDTA to the cell pellet.
- To the quenched cell mixture, add 200 µl ice-cold chloroform and vortex vigorously for 45 min at -20 °C. (Note: This extraction length is important when extracting metabolites from organisms with cell walls including bacteria and yeast. A shorter extraction time of 5-10 min is adequate for mammalian cells. Vigorous vortexing is most effective for metabolite extraction. Use of a multi-tube vortex mixer head is recommended.) Afterwards, centrifuge at 21,000 x g at 4 °C for 10 min.
- Collect upper, water/methanol phase in a clean labeled tube. This is the first metabolite extract. Place tube on ice.
- Re-extract the chloroform phase by adding 200 µl of ice-cold 50% methanol/ 50% PIPES-EDTA. Vortex for 1 min and centrifuge again at 21,000 x g at 4 °C for 10 min.
- Just as before collect the upper, water/methanol with the extract from step A5. Freeze the extract until analysis.
- The protocol requires a minimum of 1 x 106 cells to accurately detect tryptophan and kynurenine levels. If tryptophan and kynurenine quantification is desired from fresh media, collect 2 ml of fresh media prior to cell addition for subsequent analysis and freeze at -80 °C. This sample will be used to measure the baseline levels of tryptophan and kynurenine in the media.
- Detection and quantification of tryptophan and kynurenine
- Analyze metabolites from cell culture media and from cell extracts by HPLC. To separate and quantify tryptophan and kynurenine, inject 5-20 µl (Note: The required injection volume will vary depending on the concentration of metabolite in the sample and is a recommended range.) of the cell extract obtained from step A7, spent culture media collected in step A2, or the cell-free media collected from step A1 in an HPLC equipped with an ultra-sensitive diode array detector and a Hypersil GOLD C18 column (50 x 2.1 mm, 3 µm), which is a reverse phase column packed with spherical, fully porous ultrapure silica. Set column temperature to be maintained at 30 °C. Use an isocratic mobile phase of 15 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.4), with 2.7% (v/v) acetonitrile with a flow rate of 0.8 ml/min. The run time should be set for 10 min.
- Quantify the area under the peaks that display absorbance at 286 nm and 360 nm to calculate the concentration of tryptophan and kynurenine, respectively, in the samples. Generate standard curves ranging from 0 to 200 µM for both tryptophan and kynurenine and other metabolites of interest as well as any internal standard (if applicable) using authentic standards. Standards of each concentration should be prepared in triplicate and measured in triplicate. A recipe for a standard mix is included in the Recipes section.
Note: Details of standard curve generation will vary depending on the chromatography system and data analysis software used. Consult the manufacturer’s documentation to generate a standard curve with your instrument’s software.
- Analyze metabolites from cell culture media and from cell extracts by HPLC. To separate and quantify tryptophan and kynurenine, inject 5-20 µl (Note: The required injection volume will vary depending on the concentration of metabolite in the sample and is a recommended range.) of the cell extract obtained from step A7, spent culture media collected in step A2, or the cell-free media collected from step A1 in an HPLC equipped with an ultra-sensitive diode array detector and a Hypersil GOLD C18 column (50 x 2.1 mm, 3 µm), which is a reverse phase column packed with spherical, fully porous ultrapure silica. Set column temperature to be maintained at 30 °C. Use an isocratic mobile phase of 15 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.4), with 2.7% (v/v) acetonitrile with a flow rate of 0.8 ml/min. The run time should be set for 10 min.
Representative data
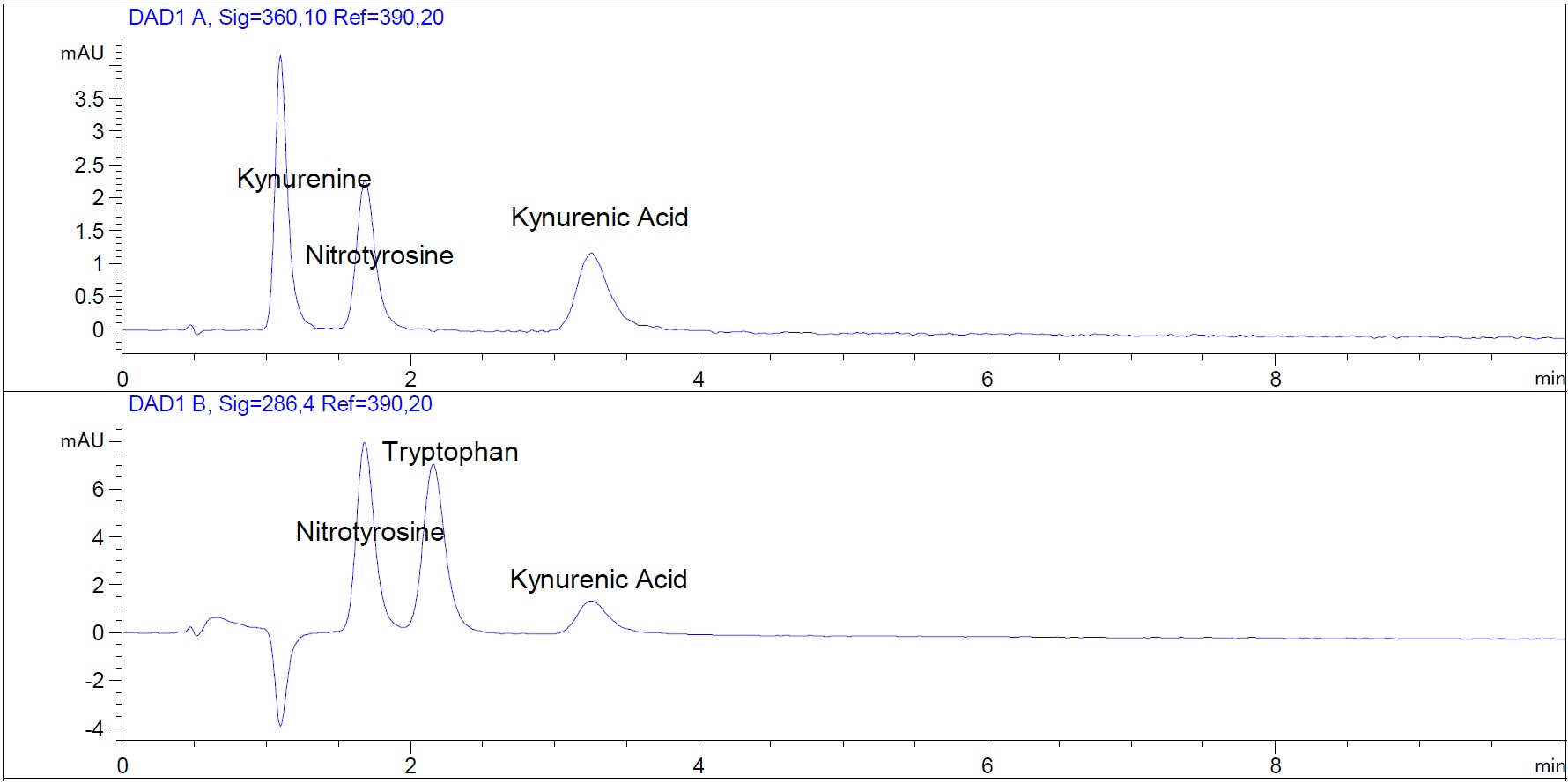
Figure 1. HPLC chromatogram showing separation of tryptophan, kynurenine, kynurenic acid and nitrotyrosine standards. Quinolinate is also present in the standard mix but below the limit of quantification. The upper panel shows absorbance at 360 nm, and the lower panel shows absorbance at 286 nm. The tryptophan metabolite kynurenic acid and 3-nitro-L-tyrosine (nitrotyrosine), which can be used as an internal standard, are also separated. All analytes are present at a concentration of 12.5 µM. The standard solution was prepared as described in the Recipes section.
Notes
This method can be modified for compatibility with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry by using a mobile phase consisting of 10 mM ammonium formate (pH 6.4), containing 2.7% acetonitrile. Other chromatographic conditions remain unchanged. If desired, a known quantity of 3-nitro-L-tyrosine can be added to samples prior to extraction for use as an internal standard.
Recipes
- 50% methanol / 50% 3 mM PIPES -3 mM EDTA (pH 7.4)
- Prepare 3 mM PIPES-3 mM EDTA (pH 7.4) (for 500 ml).
Mix 0.453 g PIPES and 0.438 g EDTA in 400 ml of sterile water (HPLC grade). After the solution becomes completely dissolved, complete to 500 ml with sterile water. Filter the solution. - Mix the above with 500 ml of Methanol (HPLC grade).
- Degas and store at 4 °C.
- Prepare 3 mM PIPES-3 mM EDTA (pH 7.4) (for 500 ml).
- 15 mM potassium phosphate, pH 6.4, with 2.7% (v/v) acetonitrile (for 1 L)
Make 1 M stock solutions of both monobasic anhydrous (KH2PO4) and dibasic anhydrous (K2HPO4).- Mix 72.2 ml of KH2PO4 and 27.8 ml of K2HPO4 dilute with 900 ml of sterile water (HPLC grade) to make 100 mM stock.
- Take 150 ml of the 100 mM stock and dilute with 850 ml of sterile water (HPLC grade) to make 15 mM potassium phosphate stock. Filter the solution.
- Add appropriate amount of acetonitrile (HPLC grade) fresh when running HPLC separation.
- Degas and store at room temperature.
- Mix 72.2 ml of KH2PO4 and 27.8 ml of K2HPO4 dilute with 900 ml of sterile water (HPLC grade) to make 100 mM stock.
- Standard mix (200 µM each of tryptophan, nitrotyrosine, kynurenine, kynurenic acid, and quinolinate)
- Prepare each standard separately at a concentration of 1 mM in 50 ml mobile phase [15 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.4) with 2.7% acetonitrile]. For each solution, weigh out an appropriate quantity of each standard and place in a 50 ml volumetric flask. Record the actual mass of each standard.
- To each volumetric flask, add 50 ml mobile phase and mix. The standards, especially kynurenic acid, may require more than an hour to go into solution. A stir bar can be added to each flask and stirred on a stir plate to facilitate dissolution of the standard.
- When each solution is ready, add 2 ml of each standard 1 mM standard solution to a 15 ml tube and vortex mix. The final concentration of each standard in this standard mix will be 200 µM. Perform replicate serial dilutions as required to make a series of standards for use in generation of a standard curve.
Note: Serial dilutions of standards are generally satisfactory but can propagate concentration errors if the stock solution concentration is not correct.
- Prepare each standard separately at a concentration of 1 mM in 50 ml mobile phase [15 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.4) with 2.7% acetonitrile]. For each solution, weigh out an appropriate quantity of each standard and place in a 50 ml volumetric flask. Record the actual mass of each standard.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants 1R01CA135401-01A1, and 1R01DK082690-01A1, the Medical Service of the US Department of Veterans’ Affairs, and Dialysis Clinics, Inc. (DCI) (all to R. H. W.). This work was performed in part at the Research Resource for Biomedical Accelerator Mass Spectrometry, which is operated at LLNL under the auspices of the U. S. Department of Energy under contract DEAC52-07NA27344. The Research Resource is supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences under Grant P40 RR13461. The extraction protocol was adapted from Villas-Boas et al. (2005). The HPLC method was adapted from Laich et al. (2002).
References
- Laich, A., Neurauter, G., Widner, B. and Fuchs, D. (2002). More rapid method for simultaneous measurement of tryptophan and kynurenine by HPLC. Clin Chem 48(3): 579-581.
- Villas-Boas, S. G., Hojer-Pedersen, J., Akesson, M., Smedsgaard, J. and Nielsen, J. (2005). Global metabolite analysis of yeast: evaluation of sample preparation methods. Yeast 22(14): 1155-1169.
- Wettersten, H. I., Hakimi, A. A., Morin, D., Bianchi, C., Johnstone, M. E., Donohoe, D. R., Trott, J. F., Aboud, O. A., Stirdivant, S., Neri, B., Wolfert, R., Stewart, B., Perego, R., Hsieh, J. J. and Weiss, R. H. (2015). Grade-dependent metabolic reprogramming in kidney cancer revealed by combined proteomics and metabolomics analysis. Cancer Res 75(12): 2541-2552.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kim, J., Stewart, B. and Weiss, R. H. (2016). Extraction and Quantification of Tryptophan and Kynurenine from Cultured Cells and Media Using a High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) System Equipped with an Ultra-sensitive Diode Array Detector. Bio-protocol 6(7): e1781. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1781.
Category
Cancer Biology > Cellular energetics > Biochemical assays
Cell Biology > Cell metabolism > Amino acid
Biochemistry > Other compound
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









