- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Cell-based Assays to Monitor AID Activity
Published: Vol 6, Iss 3, Feb 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1724 Views: 9944
Reviewed by: Jia LiSmita NairAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Measurement of the Activity of Wildtype and Disease-Causing ALPK1 Mutants in Transfected Cells With a 96-Well Format NF-κB/AP-1 Reporter Assay
Tom Snelling
Nov 20, 2024 1603 Views

Fluorescence Polarization-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for Inhibitors Targeting Cathepsin L
Keyu Guo [...] Shuyi Si
Jul 20, 2025 2277 Views

Detecting the Activation of Endogenous Small GTPases via Fluorescent Signals Utilizing a Split mNeonGreen: Small GTPase ActIvitY ANalyzing (SAIYAN) System
Miharu Maeda and Kota Saito
Jan 5, 2026 483 Views
Abstract
The enzyme Activation induced deaminase (AID) underpins antibody affinity maturation and isotype switching through its mutagenic activity of deaminating deoxycytidine to deoxyuridine in DNA. Subsequent processing of the deoxyuridine initiates the processes of somatic hypermutation (SHM) and class switch recombination (CSR) in B cells. Structure-function analysis of AID requires sensitive and biologically relevant methods to measure its various activities. Here we describe simple but effective methods to measure 1) the ability of AID to mutate the Escherichia coli genome, which provides an indication of its catalytic activity; 2) the capacity of AID to perform SHM by complementing a derivative of the DT40 chicken B cell line; 3) the ability of AID to perform CSR by complementing AID-deficient primary mouse B cells. The combination of the three methods, accompanied by the necessary analysis of AID subcellular localization and protein expression levels and stability, as controls, allows detailed structure-function interrogation of AID.
Keywords: Activation induced deaminase
Part I. Measuring mutagenic activity of AID in E. coli
The following procedure has been adapted from Petersen-Mahrt et al. (2002). It provides a measurement of the capacity of AID to mutate the Escherichia coli genome by selecting for those mutations in the rpoB gene that confer resistance to Rifampicin. It can be used as a proxy for the catalytic activity of the enzyme, although it involves deamination of a transcribed gene, which might influence the results. When comparing different AID variants or mutants, it provides a measurement of their mutagenic activity compared to the wt enzyme, which often but not always correlates with the enzymatic activity of the corresponding recombinant enzymes measured on DNA oligonucleotide substrates.
Materials and Reagents
- Sterile multi-channel basin
- Competent Δung E coli. We use the BW310 strain (Duncan, 1985) (a gift from Dr. Bernard Weiss Department of Pathology, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta)
- Plasmids containing AID or AID variants cloned in an inducible prokaryotic expression vector. We use IPTG-inducible pTrcHis vectors (Life Technologies, catalog number: V360-20 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen™, catalog number: V360-20”. - Tryptone (BioShop Canada, catalog number: TRP402 )
- Yeast extract (BioShop Canada, catalog number: YEX401 )
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: SOD002 )
- Agar (bacteriological grade) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: AGR001 )
- Na2HPO4.7H2O (BioShop Canada, catalog number: SMP400 )
- Potassium Phosphate Monobasic (KH2PO4) (BioShop Canadap, catalog number: PPM666 )
- Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A0171 )
- Ampicillin (stock 100 mg/ml in ddH2O) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: AMP201 )
- Carbenicillin (100 mg/ml in ddH2O) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: CAR666 )
- Rifampicin (stock 100 mg/ml in DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: R3501 )
- IPTG (stock 1 M in ddH2O) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: IPT001 )
- Transparent sterile 96-well plates, flat bottom (Corning, catalog number: 3595 )
- LB media (see Recipes)
- LB agar (see Recipes)
- 2x TY media (see Recipes)
- 5x M9 media (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Bunsen burner
- Sterile glass beads (for bacteria plating) (Genlantis, EZ-spread, catalog number: C400050 )
- 37 °C incubator (for bacterial plates)
- 37 °C incubator with shaker (for bacterial cultures)
- 42 °C water bath
- Hand counter
- Multichannel pipettor
Procedure
Prepare as many 10 cm LB agar plates supplemented with rifampicin (100 μg/ml) + ampicillin (100 μg/ml) as samples will be tested (selection plates). Prepare also the necessary number of LB agar plates supplemented with ampicillin (100 μg/ml) for the initial transformation and for viability plates in the experiment (see below). For example, to compare 3 constructs prepare 3 plates supplemented with ampicillin for bacterial transformation plus 3 x 5 = 15 plates supplemented with ampicillin for the assay (for a total of 18 ampicillin plates), as well as 15 plates supplemented with rifampicin + ampicillin.
- Day 1: Transformations
- For each construct, mix 50 ng DNA with 50 μl competent BW310 in a sterile 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube.
- Incubate tube on ice for 30 min.
- Heat shock for 45 sec at 42 °C in a water bath.
- Return tube to ice for 5 min.
- Recover bacteria by transferring the whole volume of bacteria to a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube containing 950 μl 2x TY media and place in shaking incubator at 230 rpm for 45 min at 37 °C.
- Plate 40 μl of each bacterial culture from point 5 onto LB-ampicillin plates and incubate at 37 °C overnight.
- For each construct, mix 50 ng DNA with 50 μl competent BW310 in a sterile 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube.
- Day 2: Picking colonies and inducing AID expression
- Pick at least 5 isolated colonies from each transformation plate (i.e. construct) into a 15 ml tube containing 1.5 ml LB media supplemented with 100 μg/ml carbenicillin and 1 mM IPTG.
- Grow overnight at 37 °C.
- Day 3: Plating
- Selection plates
- Plate 50 μl of each induced culture in 10 cm Petri dishes with LB rifampicin + ampicillin.
- Incubate ~48 h at 37 °C until colonies are clearly visible.
Note: That colony sizes can be heterogeneous, as different mutations will allow different growth rates in rifampicin. In addition, hypo- or hyperactive AID variants may require ad hoc plating (i.e. larger volumes or diluting the sample, respectively) to obtain a number of colonies that can be accurately counted. Do not plate volumes smaller than 50 μl to prevent too rapid absorption and clustering of the colonies.
- Plate 50 μl of each induced culture in 10 cm Petri dishes with LB rifampicin + ampicillin.
- Viability plates
- Make 10-fold serial dilutions of the induced cultures in 1x M9 media using a sterile 96-well plate and a multichannel pipettor for convenience. Dilute up to 10-6.
- Plate 50 μl of the 10-6 in 10 cm petri dish LB ampicillin.
Note: Depending on the conditions of growth, induction and expression, other dilutions (10-4 or 10-5) may be necessary to obtain a number of colonies that can be easily and accurately counted (Figure 1). - Incubate overnight at 37 °C.
- Make 10-fold serial dilutions of the induced cultures in 1x M9 media using a sterile 96-well plate and a multichannel pipettor for convenience. Dilute up to 10-6.
- Selection plates
- Day 4: Count LB ampicillin plates
- Day 5: Count LB rifampicin plates
Note: Count all colonies. In the case of rifampicin plates count colonies of all sizes. If there are too many colonies, (i.e., small and close together) 1/2-1/4 of the plate could be counted to estimate the total number of colonies without affecting the accuracy of the measurement, as long as isolated colonies can be distinguished. If colonies are confluent repeat the experiment, do not replate cultures that were kept overnight since viability diminishes significantly. If there are too few or no colonies the measurement may not be accurate; repeat and adjust the volume or dilution to plate accordingly.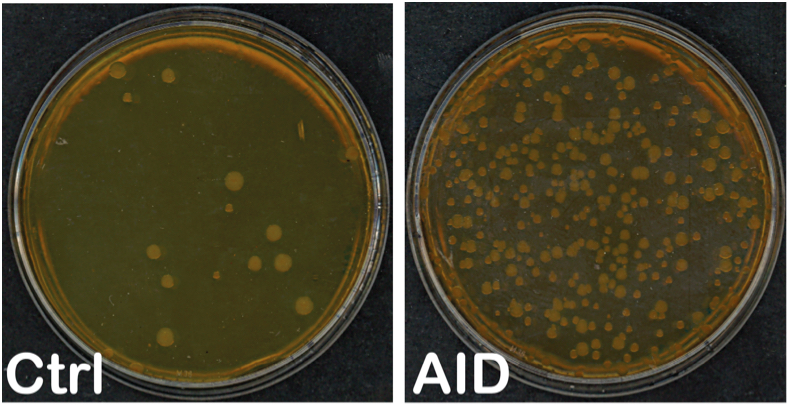
Figure 1. Example of LB ampicillin + rifampicin plates incubated at 37 °C for two days with bacteria transformed with pTrc-His (Ctrl) and pTrc-His-AID (AID) - Calculating rpoB mutation frequency
- For each culture calculate the number (N) of Colony Forming Unit (CFU) per ml using the formula
N=(n x d x Vo)/Vp
n: Number of colonies counted in the plate; d: Dilution factor; Vo: Original culture volume (μl); Vp: Plated volume (μl)
The LB ampicillin plate will provide the viable CFU/ml (NV) and the LB rifampicin plate will provide the mutant CFU/ml (NM) - Calculate the number of Rifampicin resistant (RIFR) mutants per /109 CFU as:
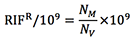
Calculate the median RifR/109 of all the values obtained for each construct and evaluate significance using the appropriate statistical method depending on the number of samples compared. At least 3 independent experiments with 5 colonies per construct are necessary for accurate comparisons of relative frequencies between AID variants.
- For each culture calculate the number (N) of Colony Forming Unit (CFU) per ml using the formula
Recipes
Note: Media must be autoclaved after preparation and kept sterile.
- LB media (for 1 L in ddH2O)
10 g tryptone
5 g yeast extract
5 g NaCl - LB agar (for 1 L in LB media)
LB media
15 g agar - 2x TY media (for 1 L in ddH2O)
16 g tryptone
10 g yeast extract
5 g NaCl - 5x M9 media (for 1 L in ddH2O)
64 g Na2HPO4.7H2O
15 g KH2PO4
2.5 g NaCl
5 g NH4Cl
Part II. Measuring somatic hypermutation activity of AID in DT40 cells
DT40 cells are a chicken B cell lymphoma line that constitutively expresses IgM at the plasma membrane, as well as AID (Arakawa et al., 2002). Chickens diversify their Ig genes by gene conversion, a homologous recombination-based mechanism. However, the DT40-derived cell line used here (DT40 ΔΨV IgM+) has been engineered to eliminate the V pseudogenes that act as homology donors for gene conversion, causing that AID deaminations accumulate as mutations, mostly at C:G pairs with a bias towards transversion mutations (Arakawa et al., 2004). The protocol below takes advantage of the fact that a fraction of AID-induced mutations at the Ig loci will disrupt IgM expression. This can be quantified by flow cytometry as IgM-loss cells, and is a convenient proxy to monitor SHM frequency. When starting from a DT40 ΔΨV IgM+ population, the proportion of IgM-loss cells is a function of the time the cells spent in culture as well as of the SHM frequency, which depends directly on AID activity. A DT40 ΔΨV IgM+ line in which AID expression has also been eliminated by knock out (KO) can be complemented with expression vectors encoding AID or AID mutants, either tagged with GFP or linked to GFP expression by an internal ribosomal entry site, in order to compare their relative ability for SHM. GFP expression is used to monitor infection efficiency and to evaluate lgM-loss on infected cells only.
Materials and Reagents
- 6-well plate, sterile and tissue-treated (Corning, catalog number: 3516 )
- 24-well plate, sterile and tissue-treated (Corning, catalog number: 3526 )
- 96-well plate, round-bottom, sterile and tissue-treated (Corning, catalog number: 3799 )
- 15 ml sterile conical tubes
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes
- 5 ml round-bottom tubes (facs tube)
- HEK 293T cells (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3216 )
- DT40 AID KO ΔΨV IgM+ cells (these are non adherent cells) (Arakawa et al., 2004) (a gift from Dr. J-M Buerstedde, National University of Ireland, Galway)
- DMEM culture media (Wisent, catalog number: 319-005-CL )
- RPMI 1640 culture media (Wisent, catalog number: 350-000-CL )
- FBS (Wisent, catalog number: 080150 )
- Chicken serum (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 16110-082 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 16110-082 ”. - Penicillin-Streptomycin (Wisent, catalog number: 450-201-EL )
- β-Mercaptoethanol (BioShop Canada, catalog number: MER002 )
- TransIT-LT1 reagent (Mirus Bio LLC, catalog number MIR 2305 )
- Polybrene (8 mg/ml in water) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9268 )
- HEPES 1 M (Wisent, catalog number: 330-050-EL )
- Mouse Anti-Chicken IgM-PE (SouthernBiotech, catalog number: 8310-09 )
- PBS (1x) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: PBS404 )
- BSA (BioShop Canada, catalog number: ALB001 )
- Expression vector encoding the VSV G envelop protein (pVSVG)
- Expression vector encoding for MLV polyprotein and reverse transcriptase (pGagPol)
- Retroviral expression vector containing AID variants and selection or reporter marker (we use pMXs-ires-GFP)
- Direct PCR Lysis reagent (VIAGEN BIOTECH, catalog number: 301-C )
- Proteinase K (stock 10 mg/ml in water at -20 °C) (Bio Basic Canada Inc., catalog number: PB0451 )
- KOD (Merck Millipore Corporation, Novagen, catalog number: 71086-3 ) or Pfu Turbo (Agilent, catalog number: 600250-52 ) high fidelity DNA polymerase
- Any Taq DNA polymerase for A-tailing
- QiaexII gel purification Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 20021 )
- pGEMT easy (Promega Corporation, catalog number: A1360 )
- Complete DMEM media (see Recipes)
- Complete DT40 media (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 40 μm cell strainer
- Centrifuge
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 cell culture incubator
- Flow cytometer
- PCR machine
- Oven
- Vortex (Scientific industries, model: Vortex-genie 2 )
Procedure
- Day 1: Plating HEK 293T cells for retrovirus packaging
Plate 0.5 x 106 cell/well in a 6-well plate in 2 ml complete DMEM media. At the moment of plating, cells should be 75-90% confluent. - Day 2: HEK 293T transfection
- Prepare the following for each well of cells to be transfected:
- Mix the following in this order in a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube by gentle tapping at room temperature:
RPMI 1640 (without additives) 250 μl
TransIT-LT1 reagent 7.5 μl
Mix well and then add:
pGagPol 0.625 μg
pVSVG 0.625 μg
Retroviral vector 1.25 μg
Note: The indicated masses of the plasmids are for achieving a molar DNA ratio of 1 [pVSVG]: 1 [pGagPol]: 2 [Retroviral vector], adjust the masses according to your plasmid sizes. - Let sit 20 min then add to the cells dropwise.
- Rock the plate gently and incubate at 37 °C.
- Prepare the following for each well of cells to be transfected:
- Day 3
- Carefully remove media from each well of transfected HEK 293T cells.
- Add 2 ml complete DT40 media supplemented with 10 mM HEPES to each well.
- Carefully remove media from each well of transfected HEK 293T cells.
- Day 4: DT40 infection
- Transfer the media (viral supernatant) from each transfected HEK 293T cells well to a 15 ml conical tube. Centrifuge at 200 x g, 5 min at room temperature.
- In a 24-well plate, plate 1 x 106 DT40 cells/well in 500 μl DT40 media (Cells growing exponentially and harvested at a density of ~0.5-1 x 106 cells/ml should be used).
- Add 1.5 ml/well of centrifuged viral supernatant to the plated DT40 cells.
- Add Polybrene to 8 μg/ml and HEPES to 10 mM final concentrations to each well.
- Centrifuge the plate at 600 x g for 1.5 h at 32 °C.
- Place the plate for 4 h in the cell culture incubator (37 °C, 5% CO2).
- After 4 h, remove media from each well and add 2 ml DT40 media supplemented with 10 mM HEPES.
- GFP infection frequency can be checked by flow cytometry and sorted 24-48 h later. The expected efficiency is ~40-90%, depending on the construct.
- Transfer the media (viral supernatant) from each transfected HEK 293T cells well to a 15 ml conical tube. Centrifuge at 200 x g, 5 min at room temperature.
- Sorting
Note: Work in sterile conditions.- For each sample, prepare 1 to 4 round-bottom 96-well plates containing 200 μl/well of filtered complete DT40 media.
Note: The number of plates will depend on the number of cells sorted per well, for single cell deposition prepare 4 plates to account for cloning efficiency, for 5 cells/well two plates are enough, for >5 cells/well one plate will be enough to obtain sufficient populations for the fluctuation analysis. - Transfer 107 infected cells into a sterile FACS tube.
- Centrifuge 200 x g, 5 min at 4 °C.
- Wash with 4 ml PBS and centrifuge 200 x g, 5 min at 4 °C.
- Add anti-chicken IgM-PE (1:200) in 200 μl PBS-1%BSA.
- Mix well by vortexing gently and incubate for 30 min on ice and in the dark.
- Wash cells with 4 ml PBS and centrifuge 200 x g, 5 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend cells in 300 μl PBS and filter the sample through a 40 μm cell strainer.
- Sort 1-3,000 cells/well (GFP+, IgM-).
Note: The number of cells sorted in each well will depend on the application. The fluctuation analysis for surface IgM-loss will show less variation when the initial populations are large. However, when subsequently analyzing V region sequences, all shared mutations should be removed to prevent biasing by clonal expansion of pre-existing mutations. Using 1 cell per well will yield single cell clones, which have larger variations in the fluctuation analysis but allow a more accurate analysis of SHM upon sequencing. A larger number of clones should be analyzed in this case to obtain accurate median values of IgM-loss.
- For each sample, prepare 1 to 4 round-bottom 96-well plates containing 200 μl/well of filtered complete DT40 media.
- Identifying clones/populations
- Clones/populations will be visible at naked eye 3-5 d after sorting and should be transferred to a 24-well plate containing 1 ml of filtered complete DT40 media. Isolate 12-24 clones/populations for each transduced construct (see Note above).
- When cells get confluent (3-4 days after isolating the clones), add 1 ml DT40 media to each well.
- Dilute 1:2 by carefully resuspending the cells using a P1000 and swirling around. Remove 1 ml of cells, then add 1 ml of fresh DT40 media to each well, everyday, for 2-4 weeks.
Note: Monitor cell density by looking at the cells every day. Certain conditions or AID variants may slow down proliferation. Dilution of the cells and the length of expansion should be adjusted accordingly. The frequency of IgM should increase with time; the total time of expansion will depend on the signal to noise ratio of each particular experiment.
- Flow cytometry for surface IgM
- Transfer 500 μl of cells from each well to a flow cytometry tube.
- Centrifuge 200 x g, 5 min at 4 °C.
- Wash with 4 ml PBS and centrifuge 200 x g, 5 min at 4 °C.
- Add anti-chicken IgM-PE (1:200) in 100 μl PBS-1% BSA.
- Mix well by vortexing and let sit for 30 min (on ice and in the dark).
- Wash with 4 ml PBS and centrifuge 200 x g, 5 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend in 300 μl PBS.
- Analyze samples in a flow cytometer. Acquire 20,000 events. Always have a mixture of IgM+ and IgM- DT40 cells as controls to set the gating (Figure 2).
- Analyze IgM-loss % for each clone and calculate median values for each construct or condition. Analyze statistically.
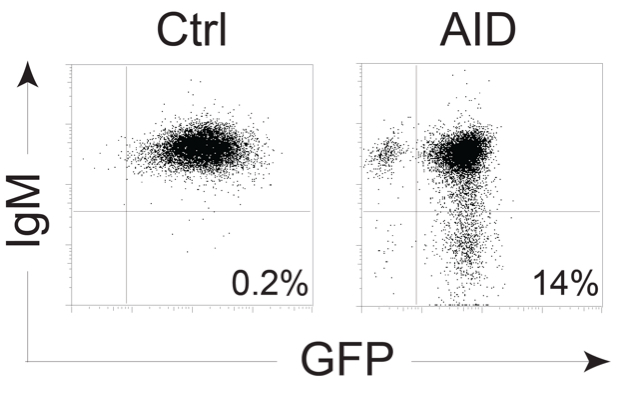
Figure 2. Example of DT40 AID KO ΔΨV IgM+ cells expressing control vector or pMXs-AID-ires-GFP expanded for 3 weeks and stained for IgM - Transfer 500 μl of cells from each well to a flow cytometry tube.
- Variable region sequencing
The following procedure is for amplifying and sequencing the IgVL region from each DT40 subpopulation. If no phenotypic selections are applied, many sequences will be unmutated. The number of mutations over the total number of bases sequenced will provide an accurate estimation of the mutation frequency. However, obtaining sufficient (>50) independent mutations to evaluate changes in the mutation patterns may require extensive sequencing. Calculating mutation rates will additionally require to measure the doubling time of the cells and record the total number of population doublings during the expansion of the cells. On the other hand, IgM-loss cells can be purified by FACS, which will select cells bearing more mutated sequences on average. The latter is better suited for analyzing mutation patterns but less accurate to calculate mutation frequency. - DNA extraction
- Prepare DNA extraction buffer (485 µl Direct PCR + 15 µl 10 mg/ml Proteinase K).
Note: Direct PCR needs to be warmed up and make sure any precipitates go back in solution before using. - Spin 5 x 104 to 5 x 105 cells for 15 sec at max speed in the tabletop microcentrifuge.
- Carefully remove the supernatant.
- Resuspend cells gently in 50 μl DNA extraction buffer by pipetting up and down.
- Incubate for 5 h at 55 °C. Use an oven rather than a heat block to prevent condensation on the lid (this step can be done overnight).
- Incubate for 45 min at 85 °C to inactivate the Proteinase K.
- Store DNA at -20 °C or proceed to PCR.
- Prepare DNA extraction buffer (485 µl Direct PCR + 15 µl 10 mg/ml Proteinase K).
- PCR reaction
- Use 1-5 μl DNA template from above as template.
- Primers:
5’-gcggggccgtcactgattgccg -3’
5’-ccccagcctgccgccaagtccaag -3’ - PCR has to be made with high fidelity DNA polymerase (such as KOD or Pfu turbo). Use all reagents and concentrations as suggested in the polymerase’s instructions.
- Perform PCR in 50 μl final volume.
Note: Always include a no template control, using some of the left over DNA extraction buffer instead, which controls for possible reagents contamination. - Annealing temperature: perform a touch down PCR of 8 cycles at 68-60 °C followed by 23 cycles at 60 °C for annealing temperatures. Extension time and temperature, as well as denaturing temperature, will depend on the DNA polymerase used. The expected PCR product is 520 base pairs.
- Use 1-5 μl DNA template from above as template.
- Cloning and sequencing
Note: From here on keep away from the PCR hood to avoid contaminations with final product in future experiments.- Run 50 µl of the PCR product in an agarose gel. A single band of 520 bp should be visible and no band should be visible in the water control.
- Gel purify following QIAEX II kit instructions.
- Elute the purified fragment in 20 µl of 10 mM Tris pH 8.
- Cloning in T-vector (alternatively, restriction sites could be added to the oligonucleotides or use your cloning method of choice).
Poly-A tailing (high fidelity polymerase do not add A-overhangs):
Incubate for 20 min at 72 °C in PCR cycler.Purified PCR product from step K3 17 µl 10x DNA pol buffer with Mg2+(2.5 mM Mg2+ final) 2 µl 10 mM dATP (0.2 mM final) 0.4 µl Taq DNA Polymerase 1 µl - Immediately ligate into pGEM-T easy following the protocol provided by the manufacturer.
- Transform the ligation in E. coli DH5α competent bacteria.
- Perform minipreps to purify vectors containing cloned PCR products and sequence using Sp6 primer. The total number of sequences to analyze will depend on the average mutation load per sequence and the aim of the experiment.
- Run 50 µl of the PCR product in an agarose gel. A single band of 520 bp should be visible and no band should be visible in the water control.
Recipes
- Complete DMEM media
DMEM
FBS 10%
Penicillin-Streptomycin 1% - Complete DT40 media
RPMI 1640
FBS 10%
FCS 1%
β-Mercaptoethanol 100 μM
Penicillin-Streptomycin 1%
Part III. Measuring AID class switch recombination activity
This method uses retroviral complementation of primary B cells obtained from the spleen of AID-deficient (Aicda-/-) mice, to assay the capacity of AID variants to produce CSR.
Materials and Reagents
- 6-well plate, sterile and tissue-treated (Corning, catalog number: 3516 )
- 24-well plate, sterile and tissue-treated (Corning, catalog number: 3526 )
- 12-well plate, sterile and tissue-treated (Corning, catalog number: 3513 )
- 50 ml sterile conical tubes
- 15 ml sterile conical tubes
- 1.5 ml eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf or similar)
- 10 ml flat syringe plunger
- 5 ml pipettes
- 5 ml round-bottom tubes (Falcon®, catalog number: 352008 )
- 70 μm cell strainer (Corning, catalog number: 352350 )
- 40 μm cell strainer
- PLAT-E ecotropic retrovirus packaging cells (Morita et al., 2000) (a gift from Dr. T Kitamura, University of Tokyo, Japan)
- Aicda-/- mice (Muramatsu et al., 2000) (a gift from Dr. Tasuku Honjo, Kyoto University, Japan)
- Retroviral vector encoding AID variants (such as pMX-ires-GFP or pMIG)
- RPMI 1640 culture media (Wisent, catalog number: 350-000-CL )
- FBS (Wisent, catalog number: 080150 )
- Penicillin-Streptomycin (Wisent, catalog number: 450-201-EL )
- β -Mercaptoethanol (BioShop Canada, catalog number: MER002 )
- TransIT-LT1 transfection reagent (Mirus Bio LLC, catalog number: MIR 2305 )
- PBS (1x) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: PBS404 )
- BSA (BioShop Canada, catalog number: ALB001 )
- EDTA (BioShop Canada, catalog number: EDT001 )
- β-Mercaptoethanol (BioShop Canada, catalog number: MER002.100 )
- Lympholyte-M (Cedarlane Labs, catalog number: CL5031 )
- MACS anti-CD43 microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-049-801 )
- Anti-mouse CD180 (BD, Pharmingen, catalog number: 552128 )
- HEPES 1M (Wisent, catalog number: 330-050-EL )
- Polybrene (stock resuspended at 8 mg/ml in ddH2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9268 )
- LPS (stock resuspended at 1 mg/ml in RPMI without additives stored at -20 °C) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L-4391 )
- Recombinant murine IL-4 (stock resuspended at 5 μg/ml, in PBS + BSA 0.1% stored at -20 °C) (PREPROTECH, catalog number: 214-14 )
- Recombinant human TGF-β1 (stock resuspended at 1 μg/ml in 4 mM HCl + 1 mg/ml BSA stored at -20 °C) (R&D Systems, catalog number: 240-B )
- FcR Blocking Reagent, mouse (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-092-575 )
- Biotinylated Rat Anti-Mouse IgG1 (BD, Pharmingen, catalog number: 553441 )
- Biotinylated Rat Anti-Mouse IgG3 (BD, Pharmingen, catalog number: 553401 )
- Biotinylated Rat Anti-Mouse IgG2b (BD, Pharmingen, catalog number: 553393 )
- Anti-biotin–APC (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-090-856 )
- Propidium Iodide (stock resuspended at 100 mg/ml in ddH2O, stored protected from light at 4 °C) (BioShop Canada, catalog number: PPI777 )
- Complete RPMI media (see Recipes)
- MACS column buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuge
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 tissue culture incubator
- AutoMACS Pro Separator (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-092-545 )
- Flow cytometer
Procedure
Note: All procedures are performed in a tissue culture hood to prevent contaminations.
- Day 1: Plating PLAT-E cells
Transfection
Plate 0.5 x 106 cell/well in a 6-well plate in 2 ml complete RPMI media.
Note: At the moment of plating, cells should be 75-90% confluent. The quality of the cells will highly impinge on the transfection frequency and thereby on retroviral production for infection.
B cell purification- Sacrifice Aicda-/- mice and extract the spleen using sterile utensils and place into a well of a 6-well plate containing sterile PBS.
Note: From here on work in the cell culture hood. A filmed example of the procedure to remove the spleen and extracting the lymphocytes by the method described in points 2-4 below has been previously published (Zaheen and Martin, 2010). - Put the spleen on a 70 µm cell strainer placed on top of a 50 ml falcon. Add 1 ml complete RPMI media onto the spleen and gently press using the flat end of a 10 ml flat syringe plunger.
- Add complete RPMI media 1 ml at a time and continue squishing the spleen until all the cells have been extracted from the organ (should only be left with clear tissue on the strainer and lead to a final volume of 5 ml).
- Pipette up and down gently with a 5 ml pipette to produce a homogeneous suspension and transfer cells to a 15 ml conical tube.
- Introduce a sterile, long Pasteur pipette in the tube.
- Slowly pipette 3 ml of Lympholyte-M into the Pasteur pipette to underlay the cell suspension.
- Handle the tube gently to avoid disturbing the phases
- Centrifuge 1,250 x g for 20 min at RT-with no break.
Note: Brake must be turned off in order to maintain the lymphocyte interphase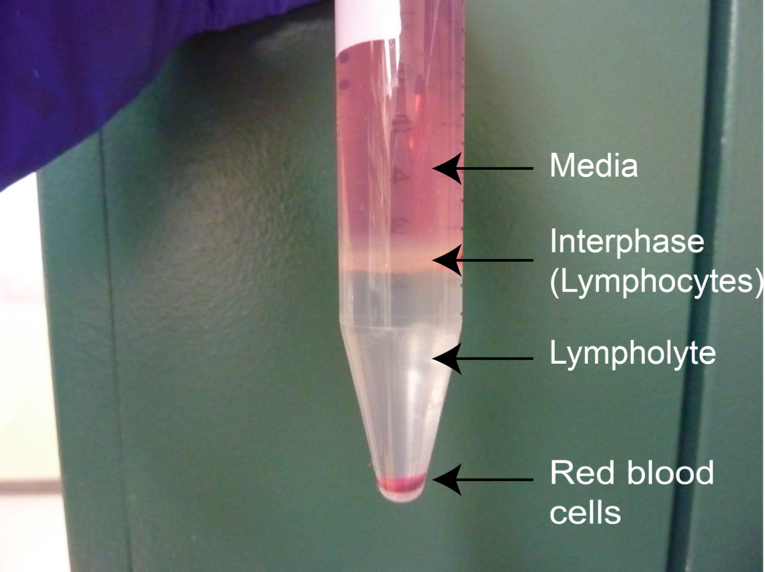
Figure 3. Typical aspect of the lymphocyte-rich interphase between medium and lympholyte after centrifugation - Collect the interphase using a 5 ml pipette, avoiding as much Lympholyte-M as possible. Tilt the 15 ml conical tube and place the tip of the pipette slightly on top of the interphase, touching the side of the canonical tube. Aspirate gently avoiding as much of the Lympholyte phase as possible (Figure 3).
- Resuspend the cells by pipetting up and down a few times in 15 ml PBS 1% BSA.
- Centrifuge 800 x g for 10 min at RT-break is ok now.
- Resuspend the cells in 15 ml PBS 1% BSA.
- Centrifuge 400 x g for 10 min at RT.
- Resuspend in 100 µl PBS 1% BSA.
- Add anti-CD43 microbeads. Use 20 µl per spleen.
Note: Resting B cells are CD43-. Depleting the splenic cell suspension of CD43+ cells will eliminate most T and activated B cells (note that this protocol is very inefficient in extracting dendritic cells or macrophages). A typical purity of >90% naïve B cells is achieved. - Incubate 45 min at 4 °C mixing gently every now and then.
- Add 15 ml of cold PBS 1% BSA.
- Centrifuge 400 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend in 1 ml MACS column buffer and pass the cells through a 40 μm cell strainer to avoid cell clumps in the AutoMACS.
- Proceed to AutoMACS separator and use DEPLETE program with quick washes in between samples.
Note: Remember this is a depletion of activated cells (i.e., you want the cells that flow through, not the retained ones). - Collect the flow through cells from the AutoMACS and wash with cold PBS 1% BSA, then centrifuge 400 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend in 1 ml complete RPMI media.
- Count the cells (do a 1/20 dilution in PBS and then 1/2 with trypan blue).
Note: The quality of the depletion could be monitored by flow cytometry using anti-CD43 and anti-B220 markers. Typically, this procedure yields >90% pure resting B cells. - Plate 106 B-cells per well in a 24-well plate in 1 ml complete RPMI media. Plate as many wells as constructs you want to test + one well as uninfected control.
- Add 1 ml of medium containing 0.5 μg/ml anti-CD180 (final concentrations of 0.5 x 106 B cells/ml and 0.25 μg/ml anti-CD180). Anti-CD180 antibody promotes B cell proliferation without inducing AID expression or CSR.
- Put cells in the tissue culture incubator.
- Sacrifice Aicda-/- mice and extract the spleen using sterile utensils and place into a well of a 6-well plate containing sterile PBS.
- Day 3
Observe the cells, B cells should start to proliferate and clump. Remove media from transfected PLAT-E cells and add 2.5 ml fresh RPMI media supplemented with 10 mM HEPES. - Day 4: B cell infection
- Transfer the viral supernatant from transfected PLAT-E cells to a 15 ml conical tube. Centrifuge at 200 x g, 5 min at room temperature.
- Transfer viral supernatant to a new tube.
- Adjust the concentration of viral supernatant to 20 mM HEPES and 16 μg/ml Polybrene.
- Remove 1 ml media from the top of each well containing B cells avoiding disturbing the cells, and add 1 ml of supplemented viral supernatant for a final concentration of 8 μg/ml Polybrene and 10 mM HEPES.
- Centrifuge the 24-well plate at 515 x g for 1.5 h at 30 °C.
- Place the plate for 4 h in the tissue culture incubator at 37 °C.
- After 4 h remove most of the media from each well, and add 2 ml complete RPMI media containing appropriate mitogens and cytokines as follows.
For IgG1 switching: 5 μg/ml LPS + 25 ng/ml IL-4 (for saturating conditions) or 5 μg/ml LPS + 5 ng/ml (for non-saturating conditions)//
For IgG3 switching: 25 μg/ml LPS
For IgG2b switching: 5 μg/ml LPS (+TGF-β1 next day, see below)
- Transfer the viral supernatant from transfected PLAT-E cells to a 15 ml conical tube. Centrifuge at 200 x g, 5 min at room temperature.
- Day 5: For IgG2b, add 1 ng/ml TGF-β1 (it is added 24 h after infection because it delays proliferation)
- Day 6: For IgG1 or IgG3, transfer cells to a 12-well plate and add 2 ml of fresh RPMI (no cytokines needed). For IgG2b leave cells alone.
- Day 7: Measure class switch recombination to IgG1 or IgG3 (Figure 4)
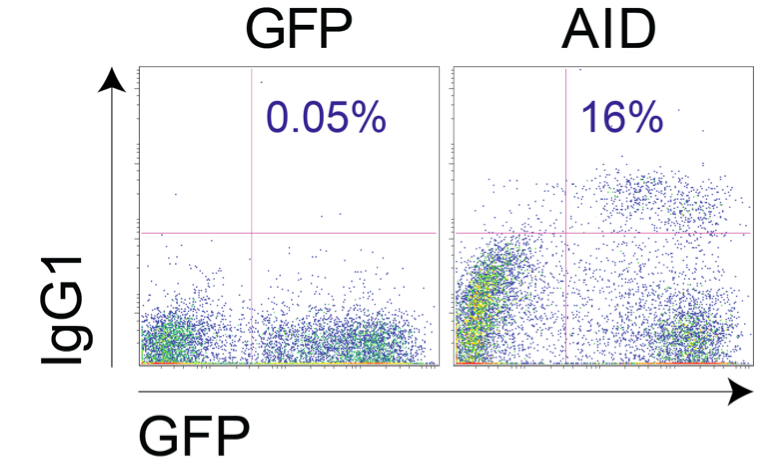
Figure 4. Example of Aicda-/- B cells transduced with vector control or pMXs-AID-ires-GFP and stimulated as explained above - Day 8: Measure class switch recombination to IgG2b if desired
Measuring Class Switch Recombination:- Resuspend the cells GENTLY and transfer 500 µl of cells into FACS tubes.
- Top up tube with PBS and centrifuge at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Block by incubating cells in 100 µl PBS 1% BSA containing 1:10 dilution of FcR block for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Add 100 µl PBS 1% BSA containing 1:100 dilution of anti-IgG1/anti-IgG3 or 1:50 dilution of anti-IgG2b.
- Incubate at 4 °C for 30 min.
- Top up the tube with cold PBS and centrifuge at 400 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend cells in 100 µl of anti-biotin-APC at 1:50 dilution in PBS 1% BSA by gently vortexing.
- Incubate 10 min at 4 °C in the dark.
- Top up the tube with cold PBS and centrifuge 400 x g for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Resuspend the cells in 200 µl PBS.
- Bring to flow cytometer.
- Add 5 µl of 100 µg/ml propidium iodide per tube to exclude dead cells.
Note: Infection efficiency can be affected by the AID variant used. With wild type AID in pMX-ires-GFP we typically obtain ~40-60% infection efficiency and ~20% switching to IgG1 among the GFP+ cells.
- Resuspend the cells GENTLY and transfer 500 µl of cells into FACS tubes.
Recipes
- Complete RPMI media
RPMI 1640
10% FBS
100 μM β-Mercaptoethanol
1% Penicillin-Streptomycin - MACS column buffer
PBS
0.5% BSA
2 mM EDTA
Acknowledgments
The protocols described here were adapted from our publications (Methot et al., 2015; Zahn et al., 2014). Our studies are supported in part by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Cancer Research Society Inc and a Canada Research Chair tier 2 to JMDN. LCL is supported in part by a Cole Foundation Fellowship and SPM is supported by a fellowship from Fonds de recherche Quebec-Santé (FRQ-S).
References
- Arakawa, H., Hauschild, J. and Buerstedde, J. M. (2002). Requirement of the activation-induced deaminase (AID) gene for immunoglobulin gene conversion. Science 295(5558): 1301-1306.
- Arakawa, H., Saribasak, H. and Buerstedde, J. M. (2004). Activation-induced cytidine deaminase initiates immunoglobulin gene conversion and hypermutation by a common intermediate. PLoS Biol 2(7): E179.
- Duncan, B. K. (1985). Isolation of insertion, deletion, and nonsense mutations of the uracil-DNA glycosylase (ung) gene of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 164(2): 689-695.
- Methot, S. P., Litzler, L. C., Trajtenberg, F., Zahn, A., Robert, F., Pelletier, J., Buschiazzo, A., Magor, B. G. and Di Noia, J. M. (2015). Consecutive interactions with HSP90 and eEF1A underlie a functional maturation and storage pathway of AID in the cytoplasm. J Exp Med 212(4): 581-596.
- Morita, S., Kojima, T. and Kitamura, T. (2000). Plat-E: an efficient and stable system for transient packaging of retroviruses. Gene Ther 7(12): 1063-1066.
- Muramatsu, M., Kinoshita, K., Fagarasan, S., Yamada, S., Shinkai, Y. and Honjo, T. (2000). Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 102(5): 553-563.
- Petersen-Mahrt, S. K., Harris, R. S. and Neuberger, M. S. (2002). AID mutates E. coli suggesting a DNA deamination mechanism for antibody diversification. Nature 418(6893): 99-103.
- Zaheen, A. and Martin, A. (2010). Induction and assessment of class switch recombination in purified murine B cells. J Vis Exp(42).
- Zahn, A., Eranki, A. K., Patenaude, A. M., Methot, S. P., Fifield, H., Cortizas, E. M., Foster, P., Imai, K., Durandy, A., Larijani, M., Verdun, R. E. and Di Noia, J. M. (2014). Activation induced deaminase C-terminal domain links DNA breaks to end protection and repair during class switch recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(11): E988-997.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Litzler, L. C., Methot, S. P., Patenaude, A., Zahn, A. and Di Noia, J. M. (2016). Cell-based Assays to Monitor AID Activity. Bio-protocol 6(3): e1724. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1724.
Category
Immunology > Antibody analysis > Antibody function
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













