- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Determination of Quinone Reductase Activity
Published: Vol 5, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1581 Views: 8790
Reviewed by: Fanglian HeKanika GeraAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

H2 Production from Methyl Viologen–Dependent Hydrogenase Activity Monitored by Gas Chromatography
Nuttavut Kosem
Dec 5, 2023 1794 Views

Monitoring Protein Stability In Vivo Using an Intein-Based Biosensor
John S. Smetana [...] Christopher W. Lennon
Apr 20, 2025 1617 Views

Endo-1,4-β-D-xylanase Assay Using Azo-Xylan and Variants Thereof
Luca Bombardi [...] Salvatore Fusco
Apr 20, 2025 1959 Views
Abstract
We recently demonstrated the presence of a quinone detoxification pathway present in Firmicutes. It is based on two enzyme activities, namely a quinone reductase, YaiB, described here, and a hydroquinone dioxygenase, YaiA, described in a separate protocol. In Lactococcus lactis (L. lactis), these enzymes are encoded by the yahCD-yaiAB operon. The operon is induced by copper to prevent the synergistic toxicity of quinones and copper. The quinone reductase, YaiB, reduces p-benzoquinone and a range of quinone derivatives to hydroquinone, using NADPH as a reductant, according to the reaction: p-benzoquinone + NADPH + H+ → hydroquinone + NADP+. We here describe the measurement of quinone reductase activity, based on the spectrophotometric measurement of NADPH-oxidation.
Materials and Reagents
- Quinone reductase purified from Escherichia coli (E. coli) by Ni-NTA chromatography as described in Mancini et al. (2015).
- p-Benzoquinone (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B10358 )
Note: optionally other quinone substrates like 1, 4-penzoquinone, 2-methyl-1, 4-benzoquinone, 2, 5-dimethyl-1, 4-benzoquinone, menadione, naphthoquinone, or 2, 6-dichloro-1, 4-benzoquinone, all available from Sigma-Aldrich.
- 50 mM NADPH in water; prepare on the day of use (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N5130 )
- 20 mM Tris-Cl buffer (pH 7.5)
- Flavin mononucleotide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F1392 )
- p-Benzoquinone (see Recipes)
- NADPH (see Recipes)
- 20 mM Tris-Cl (see Recipes)
- 100 µM flavin mononucleotide (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Thermostated spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, model: UV2600 or similar)
Procedure
- Mix 970 µl of 20 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5), with 10 µl of 100 mM NADPH (final concentration 1 mM) and 10 µl of 100 mM p-benzoquinone (final concentration 1 mM) in a cuvette and equilibrate at 30 °C.
- Zero the spectrophotometer and start the reaction at 30 °C by adding purified quinone reductase and immediately start recording the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm due to the oxidation of NADPH to NADP (approximately a 0.1 OD increase at 340 nm in 10 min should be observed, requiring 1 to 10 µg of purified enzyme). In a double-beam spectrophotometer, the measurement can be conducted in the reference beam, which will result in an apparent increase in absorbance. Since YaiB is an enzyme from L. lactis which grows best at 30 °C, this temperature was chosen for the assay,
- A linear absorbance change should be observed within a few seconds. Let the reaction proceed for 5 to 10 min or until a steady reaction rate is observed. Calculate the activity as nmol/min, using an extinction coefficient for NADPH of 6,220 M-1 cm-1.
Enzyme kinetics
- Both, NADPH and quinones are substrates of the enzyme reaction. NADPH is the reductant and quinones are the substrates being reduced. To determine the Km for a substrate (either quinones or NADPH), run enzyme reactions with one substrate at 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 1,000 µM, while keeping the other substrate at 1 mM.
- Determine the initial reaction rates, v0, from the slopes of the earliest linear regions of the recordings and plot v0 versus the substrate concentrations, S.
- Fit the curve to obtain the affinity for the substrate, Km, and the maximal velocity, vmax. Alternatively, plot v0 versus 1/S to obtain a Lineweaver-Burk plot, from which Km and vmax can be determined.
- Both, NADPH and quinones are substrates of the enzyme reaction. NADPH is the reductant and quinones are the substrates being reduced. To determine the Km for a substrate (either quinones or NADPH), run enzyme reactions with one substrate at 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 1,000 µM, while keeping the other substrate at 1 mM.
Representative data
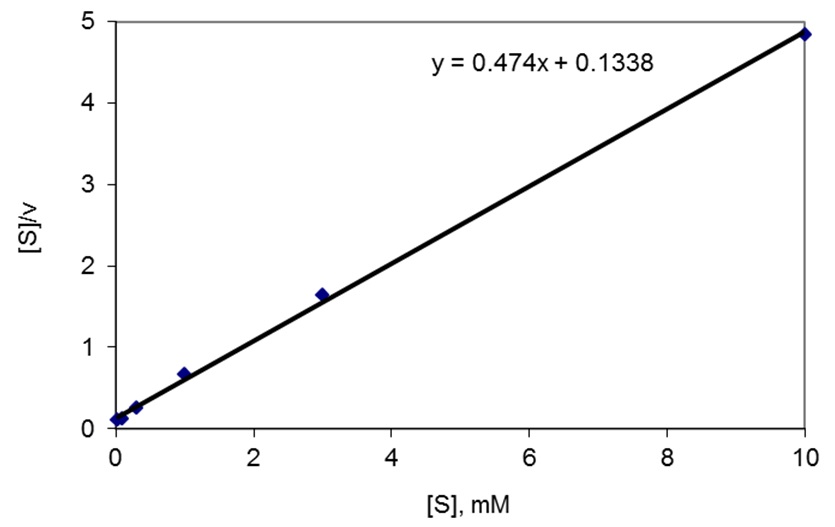
Figure 1. Representative data. Hanes-Woolf plot of p-benzoquinone reduction by YaiB of L. lactis. [S] is the mM substrate concentration and v the reaction rate in mmol/min. The slope of the linear regression line equals 1/vmax: vmax = 1/0.474 = 2.11 mmol/min/mg. Km is defined by the intercept of the regression line with the ordinate, which equals Km/vmax: Km = 0.1338*2.11 = 0.28 mM.
Notes
- Quinone reductases are flavoproteins which lose their cofactor quite readily; therefore, all the buffers used for purification or dilution of the enzyme should be supplemented with 10 µM flavin mononucleotide.
- NADPH tends to auto-oxidize to NADP in the presence of oxygen; therefore, it must be prepared fresh.
Recipes
- p-Benzoquinone (optionally other quinone substrates like 1,4-penzoquinone, 2-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone, 2,5-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone, menadione, naphthoquinone, or 2,6-dichloro-1,4-benzoquinone)
Dissolve substrates at 50 mM in dimethylsulfoxide
Stable at room temperature
- NADPH
50 mM in water
Prepare fresh on the day of use.
- 20 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5)
Stable at room temperature.
- 100 µM flavin mononucleotide
Stored frozen
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Russian Federation Government Grant 14.Z50.31.0011 to leading scientists. The procedure has previously been described in Mancini et al. (2015).
References
- Mancini, S., Abicht, H. K., Gonskikh, Y. and Solioz, M. (2015). A copper-induced quinone degradation pathway provides protection against combined copper/quinone stress in Lactococcus lactis IL1403. Mol Microbiol 95(4): 645-659.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Mancini, S. and Solioz, M. (2015). Determination of Quinone Reductase Activity. Bio-protocol 5(17): e1581. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1581.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










