- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Protocol to Treat Seedlings with Brassinazole and Measure Hypocotyl Length in Arabidopsis thaliana
Published: Vol 5, Iss 16, Aug 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1568 Views: 13159
Reviewed by: Arsalan DaudiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Quantification of Ethylene Production in Leaf and Bud Tissue of the Subtropical Tree Crop Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) Using Gas Chromatography and Flame Ionization Detection
Regina B. Cronje and Arnoldus J. Jonker
Mar 20, 2023 1548 Views

Bi-directional Dual-flow-RootChip for Physiological Analysis of Plant Primary Roots Under Asymmetric Perfusion of Stress Treatments
Claudia Allan [...] Claudia-Nicole Meisrimler
Aug 5, 2023 1942 Views

Enzymatic Starch Quantification in Developing Flower Primordia of Sweet Cherry
Nestor Santolaria [...] Afif Hedhly
Apr 5, 2025 1886 Views
Abstract
The plant hormones brassinosteroids (BR) promote hypocotyl elongation of Arabidopsis thaliana (A. thaliana) seedlings both under light and dark (etiolated) conditions. A common assay to determine if a mutant or transgenic line is affected in BR biosynthesis or response is a sensitivity assay to brassinazole (BRZ), an inhibitor of P450 cytochromes specific to BR biosynthesis.
Here we provide a protocol to compare BRZ sensitivity of different A. thaliana genotypes in terms of hypocotyl elongation (Bernardo-García et al., 2014).
Materials and Reagents
- A. thaliana seeds (background ecotype and mutant or transgenic line to be analysed)
Note: Seeds should be collected at the same time to avoid problems of differential germination rate.
- Murashige and Skoog (MS) media including vitamins and MES buffer (Duchefa M0255.0050)
- Sucrose
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- Bacto Agar (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 214010 )
- Ethanol
- Tween-20
- Brassinazole (TCI America, catalog number: B2829 )
Note: Stock solution is prepared at 2 mM in DMSO and kept at -20 °C. The appropriate volume of BRZ stock solution should be added in the fume hood to autoclaved media. The media should not be too hot (let it cool down to 55-65 °C before adding BRZ). BRZ concentration should range from 0.1 to 2 µM. We routinely use 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8 and 1.6 µM as a starting point.
- Growth media (see Recipes)
- Sterilization solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Plant growth chamber
- Sterile fume hood
- Autoclave
- Round (9 x 9 cm) and square (12 x 12 cm) polystyrene sterile Petri dishes
Software
- ImageJ software
Procedure
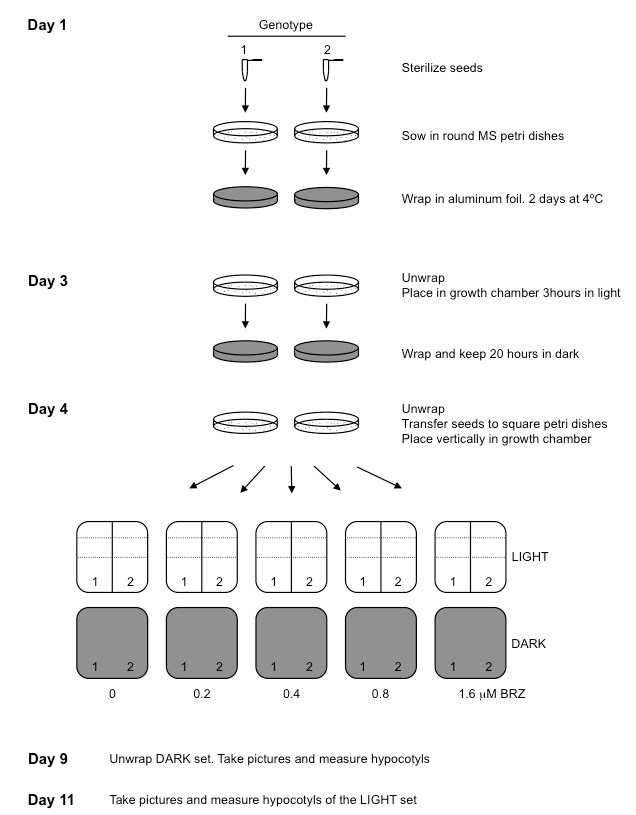
Figure 1. A flow chart of the steps described in our procedure
- Seed sterilization and sowing
- Seeds are surface sterilized in 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes by shaking for 15 min at 500-1,000 rpm at room temperature with 1 ml sterilization solution, and then washed twice in the sterile fume hood with 1 ml ethanol. Ethanol should be carefully removed with a p1000 pipette. Then close the tube and shake it to stick the seeds to the tube walls and remove ethanol from the tube bottom with a p200 pipette. After carefully removing ethanol, Eppendorf tubes are left open in the fume hood until the seeds are dry (30 min-1 h). Up to 50 µl seeds can be sterilized per tube. For bigger amount of seeds, divide them in several tubes. Drying time increases with larger amounts of seeds. To verify seeds are dry close the tube and shake gently. Dry seeds do not stick to the tube.
- Sterile seeds are sown in round 9 cm MS plates and vernalized for 2-4 days in the dark at 4 °C. Seeds are easily sown by gently tapping in the Eppendorf tube to let them drop in the plate. If many seeds stick together, they can be separated with the help of a sterile toothpick. Up to 200 seeds can be sown per plate. Plates are sealed with parafilm or saran wrap.
- Seeds are surface sterilized in 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes by shaking for 15 min at 500-1,000 rpm at room temperature with 1 ml sterilization solution, and then washed twice in the sterile fume hood with 1 ml ethanol. Ethanol should be carefully removed with a p1000 pipette. Then close the tube and shake it to stick the seeds to the tube walls and remove ethanol from the tube bottom with a p200 pipette. After carefully removing ethanol, Eppendorf tubes are left open in the fume hood until the seeds are dry (30 min-1 h). Up to 50 µl seeds can be sterilized per tube. For bigger amount of seeds, divide them in several tubes. Drying time increases with larger amounts of seeds. To verify seeds are dry close the tube and shake gently. Dry seeds do not stick to the tube.
- Germination induction and transfer to BRZ vertical plates
- To synchronize germination, 9 cm MS plates are placed horizontally in a culture chamber in the light for 3 h and then wrapped in aluminium foil and kept in dark for 20 h. This step is necessary because BRZ, at higher concentrations, inhibits germination and can give rise to differences in hypocotyl length due to slower germination.
- After germination induction, seeds are transferred to square 12 cm MS plates with increasing concentrations of BRZ keeping a control plate without BRZ (mock). Using a toothpick, seeds are transferred to square 12 cm petri dishes with appropriate concentration of BRZ. At least 20 seeds from each genotype are needed, with three replicates for each treatment. Each plate can accommodate up to 40 seeds per row. Seeds should be placed equally separated. One or two rows can be sown per plate. It can be useful to use a template (a piece of paper placed under the petri dish) (Figure 2).
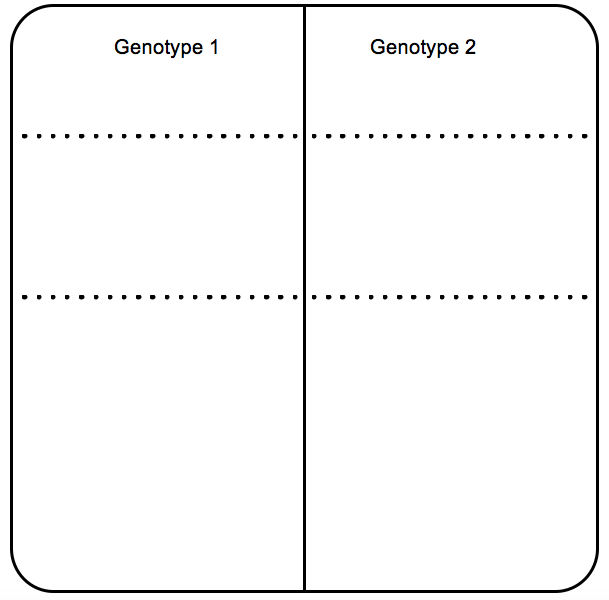
Figure 2. Template to help placing the seeds equally separated in the plate
- Square 12 cm petri dishes are placed in a vertical position in a growth chamber. To analyse etiolated growth, wrap them in aluminium foil and unwrap after 5 days to take pictures and measure hypocotyls. To analyse growth in the light, seedlings are grown for 7 days.
Hypocotyl length is affected by light intensity, photoperiod and temperature. Higher light intensity, longer photoperiods and high temperature promote hypocotyl growth.
To assess the effect of BRZ, we use the following conditions:
Photoperiod: Short day (8 h light/16 h darkness)
Light intensity: 10 µmol m-2 s-1
Temperature: Constant 22 °C
- To synchronize germination, 9 cm MS plates are placed horizontally in a culture chamber in the light for 3 h and then wrapped in aluminium foil and kept in dark for 20 h. This step is necessary because BRZ, at higher concentrations, inhibits germination and can give rise to differences in hypocotyl length due to slower germination.
- Hypocotyl measurement and analysis
- To measure hypocotyls, the plates can be photographed or scanned. Hypocotyl lengths are measured with ImageJ software (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij) (Abràmoff et al., 2004).
For details on how to use ImageJ please read the following protocol (Corrales et al., 2014).
To measure hypocotyls, choose the “segmented line” option (right-click in the highlighted button, Figure 3).
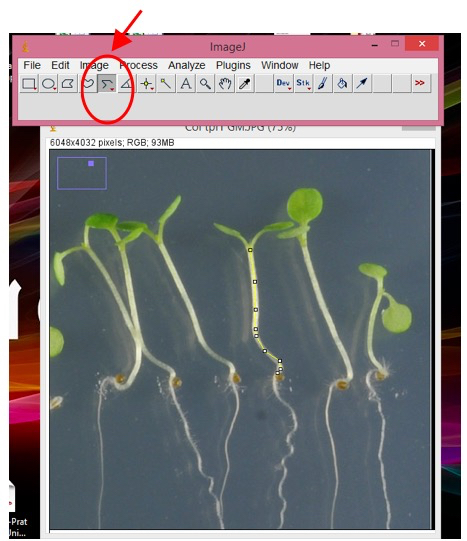
Figure 3. Snapshot from ImageJ program showing hypocotyl measurement
- A graph bar is used to represent the media and standard deviation of each genotype and treatment measurement (Figure 5).
- Statistical analyses are carried out by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Student’s t-test (P < 0.01).
- If compared genotypes show different hypocotyl length in control MS mock media, sensitivity to BRZ should be represented as the percentage of hypocotyl length reduction relative to control conditions.
- To measure hypocotyls, the plates can be photographed or scanned. Hypocotyl lengths are measured with ImageJ software (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij) (Abràmoff et al., 2004).
Representative data
Representative data showing hypocotyl measurements of type Col-0 and bes1D mutant are shown in Figures 4 and 5. BES1 is a transcription factor essential for BL response. bes1D mutation renders a constitutively active form of BES1. bes1D plants display constitutive response to BL and therefore are less sensitive to BRZ.
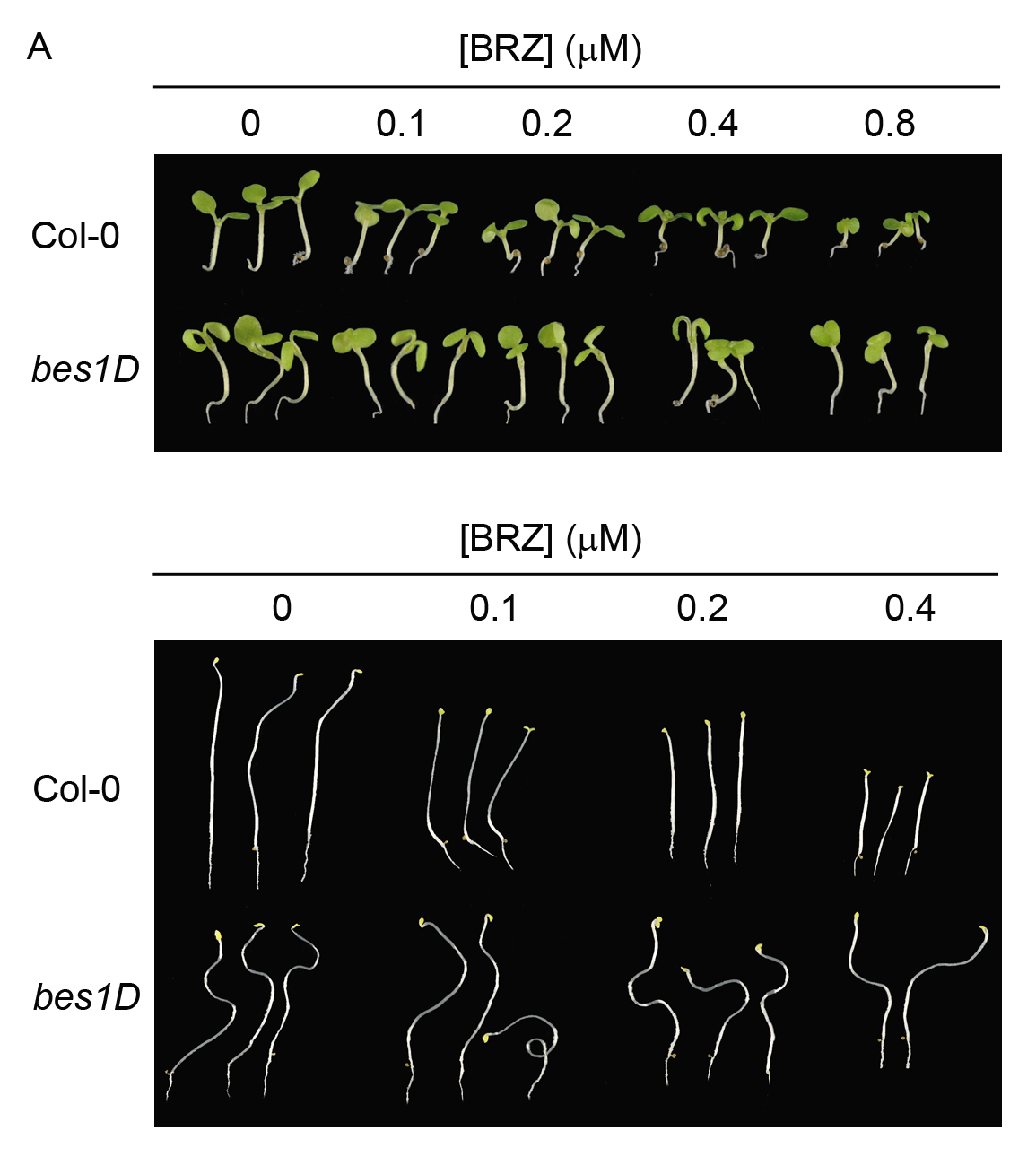
Figure 4. 7-days old Col-0 and bes1D seedlings grown under light (A) and dark conditions (B) in the indicated BRZ concentrations
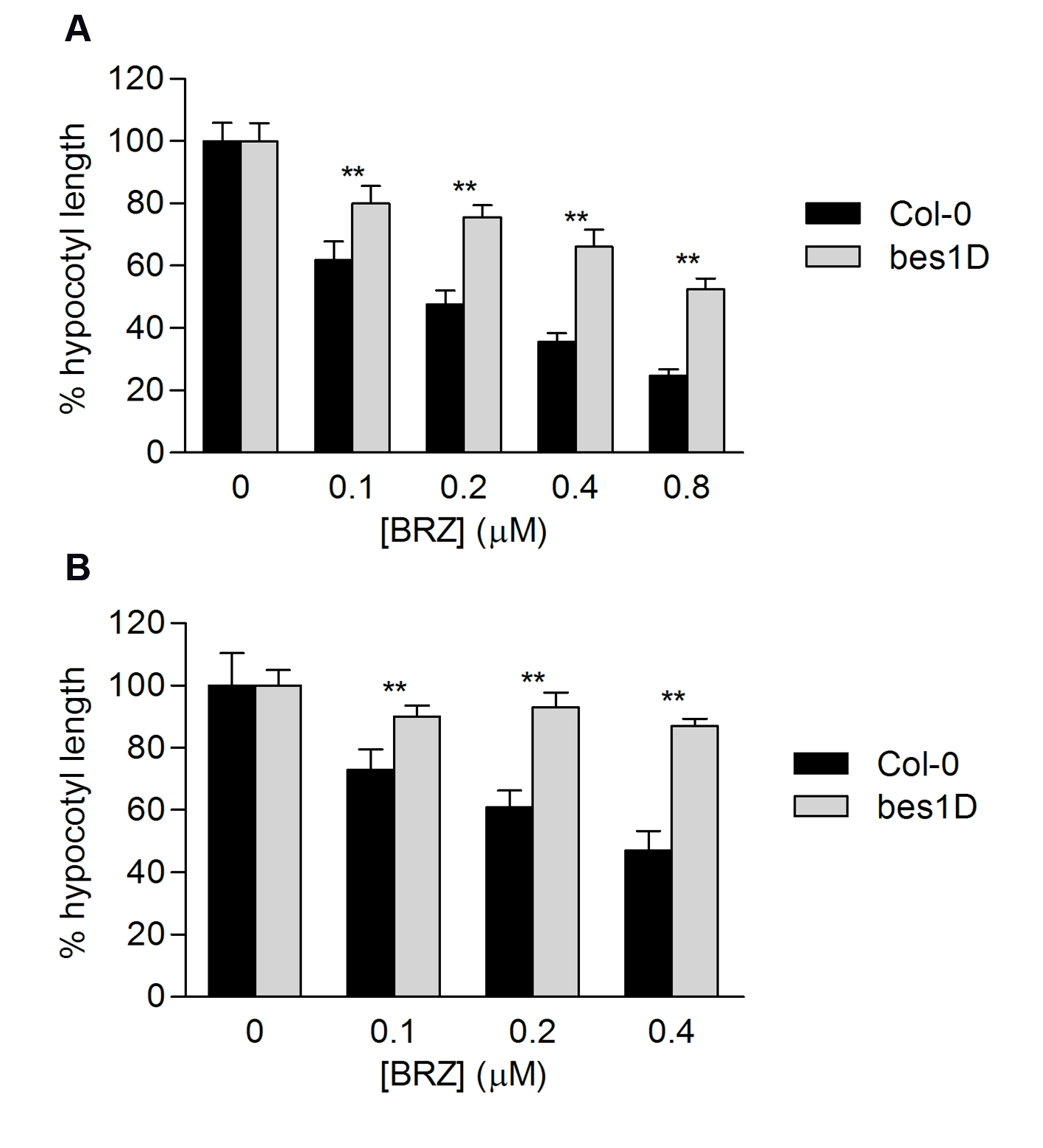
Figure 5. BRZ sensitivity of Col-0 and bes1D estimated by determining hypocotyl length reduction by increasing BRZ concentrations under light (A) and dark conditions (B). Error bars represent standard deviation. Asterisks indicate significant differences between Col-0 and bes1-D for each BRZ concentration (n = 20, p<0.01).
Recipes
- Growth media
2.45 g/L Murashige and Skoog media (half strength)
10 g/L sucrose
Water to final volume
Adjust pH to 5.8 with 0.5 M KOH
Add Bacto agar to 8 g/L (horizontal plates, 9 cm round) or 11 g/L (vertical plates, 12 cm square)
Autoclave
Let the media cool down to 55-65 °C before adding BRZ and pour the plates.
Pour approximately 25 ml of growth media per round 9 cm petri dishes and 50 ml of growth media per 12 cm square petri dishes.
- Sterilization solution
70% ethanol
0.01% Tween 20
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge funding through grants BIO2008-04160 and BIO2011-30546 from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation.
References
- Abràmoff, M. D., Magalhães, P. J. and Ram, S. J. (2004). Image processing with ImageJ. Biophot Internat 11(7): 36-43.
- Bernardo-García, S., de Lucas, M., Martínez, C., Espinosa-Ruiz, A., Davière, J.-M. and Prat, S. (2014). BR-dependent phosphorylation modulates PIF4 transcriptional activity and shapes diurnal hypocotyl growth. Genes Dev 28(15): 1681-1694.
- Corrales, A. R., Carrillo, L., Nebauer, S. G., Renau-Morata, B., Sánchez-Perales, M., Fernández-Nohales, P., Marqués, J., Granell, A., Pollmann, S., Vicente-Carbajosa, J., Molina, R. V. and Medina, J. (2014). Salinity assay in Arabidopsis. Bio-protocol 4(16): e1216.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Espinosa-Ruiz, A., Martínez, C. and Prat, S. (2015). Protocol to Treat Seedlings with Brassinazole and Measure Hypocotyl Length in Arabidopsis thaliana. Bio-protocol 5(16): e1568. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1568.
Category
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Plant growth
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Plant hormone
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Tissue analysis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










