- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Sample Preparation of Telomerase Subunits for Crystallization
Published: Vol 5, Iss 16, Aug 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1565 Views: 8776
Reviewed by: Arsalan DaudiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Thermus thermophilus CRISPR Cas6 Heterologous Expression and Purification
Junwei Wei [...] Yingjun Li
Jul 20, 2025 2202 Views

Prokaryotic Expression and Purification of the hSox2-HMG Domain
Lijie Yang [...] Jingjun Hong
Aug 20, 2025 2440 Views

On-Column Dual-Gradient Refolding for Efficient Recovery of Insoluble Affinity-Tagged Recombinant Proteins
Anna Vlaskina [...] Maxim Patrushev
Feb 5, 2026 188 Views
Abstract
Telomerase is a large ribonucleoprotein complex that replicates the linear chromosome ends in most eukaryotes. Large-scale preparation of the telomerase core components in vitro has long been a big challenge in this field, hindering the understanding of the catalytic mechanism of telomerase, as well as slowing down the development of telomerase inhibitors for cancer therapy. We have successfully developed a protocol for large-scale preparation of the TRBD-CR4/5 complex of the medaka telomerase in vitro, and used this method to study the high-resolution structure of the TRBD-CR4/5 complex by X-ray crystallography. This procedure may be also adapted to purify other protein-RNA complexes for structural studies.
Materials and Reagents
- pMAL-C2X vector (New England Biolabs, catalog number: N8076S ) with an insertion of the protease 3C recognition site between MBP and the fusion protein
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain ScarabXpress T7lac cells (Scarab Genomics, catalog number: C-1709-05K )
- LB (Luria-Bertani) medium (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 214906 ) and LB agar (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 244520 )
- Ampicillin (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0339 )
- Glucose (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0188 )
- Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0487 )
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11359061001 )
- Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) (AMRESCO, catalog number: K831 )
- Benzamidine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 12072 )
- Leupeptin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 62070 )
- Pepstatin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 77170 )
- Amylose resin (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E8021S )
- Ammonium sulfate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A4418 )
- Sodium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S3014 )
- Magnesium Chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 63068 )
- Tris-HCl (Amresco, catalog number: 0 497 )
- Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516 )
- Maltose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 1B1184 )
- HEPES-KOH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 54457 )
- Spermidine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 85558 )
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10708984001 )
- Recombinant RNasin Ribonuclease Inhibitor (Promega Corporation, catalog number: N2511 )
- Nuclease-Free Water (Promega Corporation, catalog number: P1193 )
- T7 RNA polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0251S )
- Pyrophosphatase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0361S )
- Glucosamine-6-phosphoate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5509 )
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Column buffer (see Recipes)
- RNA buffer (see Recipes)
- 5x transcription buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Incubator shaker (Eppendorf, model: New BrunswickTM Innova 44 )
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5810R )
- Ultracentrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Optima TM)
- 45Ti rotor (Beckman Coulter)
- Sonicator (Branson Sonifier)
- AKTA purifier (GE)
Procedure
- Preparation of recombinant proteins of the TRBD subunit of telomerase
- Medaka TRBD subunit (residues 318-579) was inserted into a modified pMAL-2CX vector and the plasmid was transformed into the E. coli strain ScarabXpress T7lac cells.
- Pick a single colony from a freshly streaked plate. Inoculate a starter culture of 5 ml LB medium containing 100 µg/ml ampicillin in a sterile plastic tube. Incubate at 37 °C overnight with shaking at 250 rpm.
- Dilute the overnight culture into 2 L LB medium containing 0.2% glucose and 100 µg/ml ampicillin, and grow the culture at 37 °C with shaking at 250 rpm until the cell density reaches OD600 = 0.5.
- Induce the expression of the recombinant TRBD proteins with 0.1 mM IPTG at 20 °C for 16 h with shaking at 250 rpm.
- Harvest cells by centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 15 min at 4 °C (Beckman centrifuge).
- Resuspend the cell pellet in 50 ml lysis buffer supplemented with 1 mM PMSF, 5 mM benzamidine, 1 µg/ml leupeptin, and 1 µg/ml pepstatin.
- Sonicate the cell suspension with 6 short burst of 30 sec followed by intervals of 30 sec for cooling (sonication power 100 W).
- Remove cell debris by ultracentrifuge at 4 °C for 40 min at 46,000 rpm using a 45Ti rotor.
- Slowly add ammonium sulfate (powder) into cell lysate to 55% saturation (add 16.3 g ammonium sulfate per 50 ml cell lysate). Mix for 30 min at 4 °C with slow stirring.
- Pellet the precipitated proteins by centrifuge at 4 °C for 15 min at 15,000 rpm using a 45Ti rotor.
- Solubilize the protein pellet in lysis buffer and mix it with 5 ml pre-equilibrated amylose resin in a 50-ml conical tube. Rock the tube for 2 h at 4 °C.
- Transfer the bead-protein mixture to a BIO-RAD Econo-Pac column and allow all of the liquid to flow through the column. Then, wash beads with 100 ml lysis buffer.
- Elute the MBP-TRBD proteins with 15 ml lysis buffer added with 10 mM maltose.
- Apply the eluted MBP-TRBD proteins to a HiLoad Superdex 200 chromatography column to perform gel filtration purification. The column is pre-equilibrated with 120 ml lysis buffer.
- Collect the fractions that contain the MBP-TRBD proteins, and treat them with 200 μg protease 3C at 4 °C overnight to cleave the fusion proteins.
- Slowly pass the protease 3C-digested protein solution through 5 ml pre-equilibrated amylose resin by gravity to remove MBP and the uncleaved MBP-TRBD proteins.
- Apply the TRBD proteins to a HiLoad Superdex 200 chromatography column to perform gel filtration purification. The column is pre-equilibrated with 120 ml column buffer.
- Concentrate the purified proteins using Amicon 15 ml centrifugal filter to a concentration of 10 mg/ml (determined by UV280 absorbance) and store them at -80 °C in small aliquots.
- Medaka TRBD subunit (residues 318-579) was inserted into a modified pMAL-2CX vector and the plasmid was transformed into the E. coli strain ScarabXpress T7lac cells.
- Preparation and purification of the CR4/5 RNAs
- Prepare the DNA templates for the in vitro transcription of the medaka telomerase CR4/5 RNA (nucleotides 170-220), with a glucosamine-6-phosphate-activated ribozyme (GlmS ribozyme) fused at its 3’ terminus, by PCR amplification.
- Set up 5 ml of the following in vitro transcription reaction and carry it out at 37 °C overnight.
1 ml 5x transcription buffer 1 ml NTP mix (25 mM of each NTP) 0.5 ml DNA template (200 µg/ml) 2.375 ml Nuclease-free water 50 µl Recombinant RNasin ribonuclease inhibitor 50 µl T7 RNA polymerase (3 mg/ml) 25 µl Pyrophosphatase (100 U/ml) - After the in vitro transcription, purify the CR4/5-GlmS-ribozyme RNAs from the DNA templates and the excess NTPs by gel-filtration chromatography on a HiLoad Superdex 200 column with the RNA buffer.
- Pool and concentrate the RNA fractions. Treat them with 1 mM glucosamine-6-phosphate at 25 °C for 30 min to cleave the GlmS ribozyme from the 3’ site of CR4/5.
- Run another gel-filtration chromatography on HiLoad Superdex 200 with the column buffer to purify the CR4/5 RNAs from the GlmS ribozyme.
- Concentrate the CR4/5 RNAs to 10 mg/ml.
- Prepare the DNA templates for the in vitro transcription of the medaka telomerase CR4/5 RNA (nucleotides 170-220), with a glucosamine-6-phosphate-activated ribozyme (GlmS ribozyme) fused at its 3’ terminus, by PCR amplification.
- Preparation of the TRBD-CR4/5 complex for crystallization
- Mix the TRBD proteins and the CR4/5 RNAs at a molar ratio of 1:2, and incubate the mixture on ice for 1 h.
- Purify the TRBD-CR4/5 mixture from the excess CR4/5 RNA by gel-filtration chromatography on a HiLoad Superdex 200 column with the column buffer.
- Concentrate the TRBD-CR4/5 protein-RNA complexes to 12 mg/ml. Proceed to crystallization trials or store them at -80 °C in small aliquots.
- Mix the TRBD proteins and the CR4/5 RNAs at a molar ratio of 1:2, and incubate the mixture on ice for 1 h.
Representative data
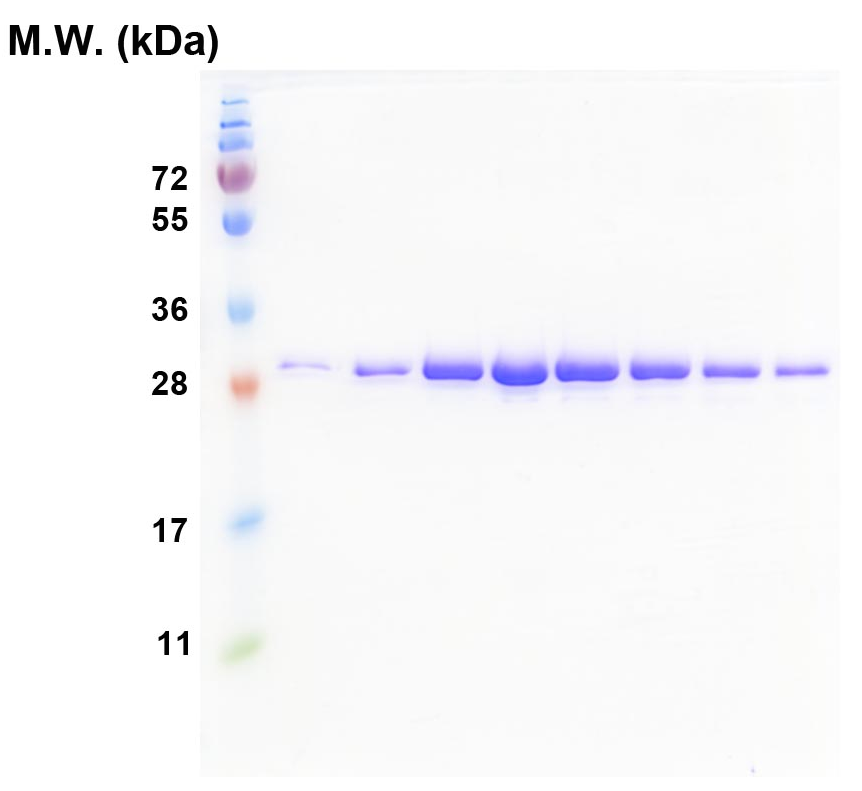
Figure 1. SDS-PAGE of the TRBD proteins after the final-step gel filtration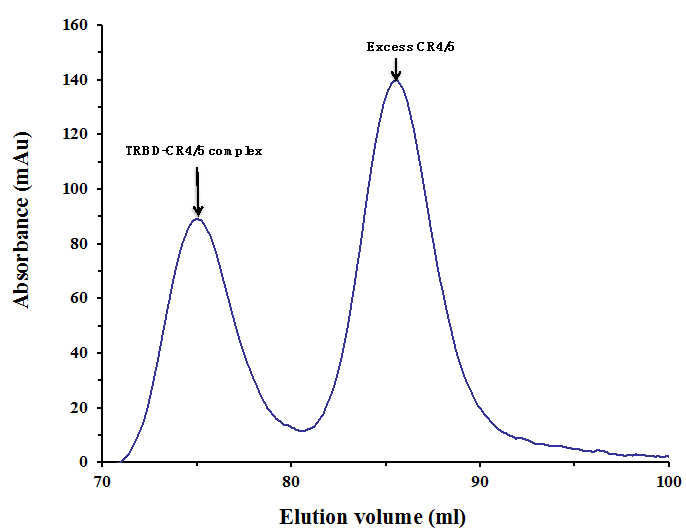
Figure 2. Gel filtration profile of the final-step purification of the TRBD-CR4/5 complex
Recipes
- Lysis buffer
50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) 500 mM NaCl 1 mM MgCl2 10% (v/v) Glycerol 1 mM Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TECP) - Column buffer
50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) 500 mM NaCl 1 mM MgCl2 1 mM Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TECP) - RNA buffer
50 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5) 150 mM NaCl 10 mM MgCl2 - 5x transcription buffer
400 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5) 120 mM MgCl2 10 mM spermidine 200 mM DTT
Acknowledgments
M. L. is supported as a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Early Career Scientist. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2013CB910400 to M. L.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31330040 to M. L.), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB08010201 to M. L.) and the US National Institutes of Health (RO1GM094450 to J. J.L. C.).
References
- Bley, C. J., Qi, X., Rand, D. P., Borges, C. R., Nelson, R. W. and Chen, J. J. (2011). RNA-protein binding interface in the telomerase ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(51): 20333-20338.
- Huang, J., Brown, A. F., Wu, J., Xue, J., Bley, C. J., Rand, D. P., Wu, L., Zhang, R., Chen, J. J. and Lei, M. (2014). Structural basis for protein-RNA recognition in telomerase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21(6): 507-512.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Huang, J., Bley, C. J., Rand, D. P., Chen, J. J. and Lei, M. (2015). Sample Preparation of Telomerase Subunits for Crystallization. Bio-protocol 5(16): e1565. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1565.
Category
Biochemistry > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Biochemistry > Protein > Structure
Biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











