- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
RNase H Polymerase-independent Cleavage Assay for Evaluation of RNase H Activity of Reverse Transcriptase Enzymes
Published: Vol 5, Iss 16, Aug 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1561 Views: 13627
Reviewed by: Modesto Redrejo-RodriguezToshitsugu FujitaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

An Improved Focus-Forming Assay for Determination of the Dengue Virus Titer
Maharah Binte Abdul Mahid [...] Kitti Wing Ki Chan
Oct 20, 2024 2401 Views

Flotation Assay With Fluorescence Readout to Study Membrane Association of the Enteroviral Peripheral Membrane Protein 2C
Kasturika Shankar [...] Lars-Anders Carlson
Apr 5, 2025 1613 Views

Detection and Analysis of S-Acylated Proteins via Acyl Resin–Assisted Capture (Acyl-RAC)
Dina A. Abdulrahman and Michael Veit
Apr 5, 2025 1841 Views
Abstract
The ribonuclease H (RNase H) polymerase-independent cleavage assay allows detection and quantification of RNase H activity of reverse transcriptase (RT) enzymes with a hybrid substrate formed by a fluorescein labeled RNA annealed with Dabcyl DNA (Figure 1). Here we describe a protocol that we have adapted for HIV-1 RT expressed from a p(His)6-tagged p66/p51 HIV-1HXB2 RT-prot plasmid and for RT of the prototype foamy virus (PFV RT). 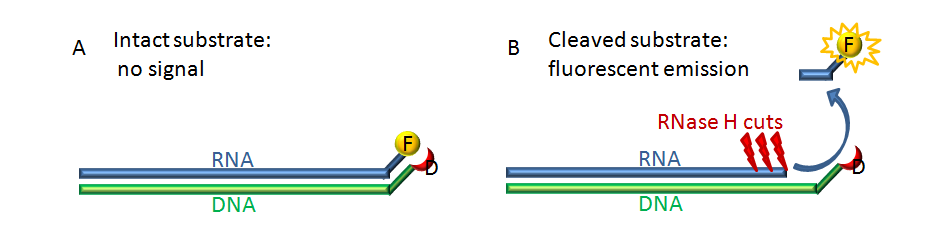
Figure 1. Scheme of the principle of the experiment. The RNA substrate (blue) labeled with the fluorophore fluorescein (F, yellow) is annealed with complementary DNA strand (green) labeled with a quencher molecule Dabcyl (D, red). Panel A. In the intact substrate the quencher is so close to the fluorophore that it can quench the fluorescence emitted after excitation. Panel B. After the RNA substrate is cut by the RNase H a few ribonucleotides oligo labeled with the fluorescein is free to escape from the quencher, and to release fluorescence after excitation.
Materials and Reagents
- Reverse transcriptase enzyme (HIV-1 RT or PFV RT). HIV-1 RT expressed and purified from p(His)6-tagged p66/p51 HIV-1HXB2 RT-prot plasmid (Corona et al., 2014a), PFV RT provided by Birgitta M. Wöhrl from Universität Bayreuth, Lehrstuhl Biopolymere, Bayreuth, Germany (Corona et al., 2014b).
- Distilled water (DNase/RNase-free UltraPureTM) (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 10977-015 )
- 5'-GAUCUGAGCCUGGGAGCU-FLUORESCEIN-3' (HPLC, dry, QC: Mass Check) (Metabion)
- 5'-DABCYL-AGCTCCCAGGCTCAGATC-3' (HPLC, dry, QC: Mass Check) (Metabion)
- 1 M KCl solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 60142-100ML-F )
- 1 M MgCl2 solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 63069-100ML )
- 1 M Dithiothreitol (DTT) solution (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: P2375 )
- 1 M Tris-HCl Solution (pH 7.8) prepared from Trizma base® (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number 93352 )
- 1 M Tris-HCl Solution (pH 8.1) prepared from Trizma base® (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93352)
- 5 M NaCl solution (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9760G )
- EDTA (0.5 M, pH 8.0) UltraPureTM (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 15575-020 )
- Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) >=99.5% (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5879-1 L )
- Microcentrifuge tubes, extended capacity, volume 0.65 ml, graduated, siliconized polypropylene (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T3406-250EA )
- OPTIPLATE-96 F /50B (PerkinElmer, catalog number: 6005270 )
- HIV-1 RT reaction mix (1.25x) (see Recipes)
- PFV RT reaction mix (1.25x) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Thermal cycler
- Refrigerated tabletop microcentrifuge
- Sonicator Bath (Elma Ultrasonic bath Transonic T 310)
- Vortex mixer
- Multi Thermo-Shaker for microplates (Bionics)
- Multilabel counter plate reader Victor 3 (PerkinElmer, model: 1420-051 ) equipped with filters for fluorescein fluorophore 490/528 nm (excitation/emission wavelength)
Procedure
- Preparation of the RNA/DNA hybrid as the substrate
- Resuspend carefully each RNA and DNA oligos at final concentration of 500 µM in 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.1), 0.5 mM EDTA (pH 8.0).
- Prepare an annealing solution of 50 µM final of both RNA and DNA oligos with 50 mM NaCl in DNase/RNase-free water then aliquot 50 µl in a 0.2 ml PCR tube. Vortex carefully and then and then spin down briefly at 5,000 rpm to allow all the liquid to lay in the bottom of the tube.
- Do not overlay mineral oil on the solution. Place the tube in a thermal cycler and set up a program to perform the following profile:
Heat to 95 °C and remain at 95 °C for 2 min;
Ramp cool to 25 °C over a period of 45 min;
Proceed to a storage temperature of 4 °C.
- The RNA/DNA hybrid solution (50 μM) is ready to be used (see Recipes). The solution can be stored at -20 °C.
- Resuspend carefully each RNA and DNA oligos at final concentration of 500 µM in 100 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.1), 0.5 mM EDTA (pH 8.0).
- Preparation of dilutions of inhibitors
- Dissolve the powder of compound in DMSO at 10 mM final concentration, sonicate it (e.g.: 10” at 50 Hz) and warm it if needed (e.g.: 2’ 45 °C), to be sure all the compound goes in solution.
- Starting from the 10 mM solution in DMSO make the serial dilutions of compound in Milli-Q purified water: Starting from 1 mM dilution and making three fold dilution 10 fold more concentrate with respect to the final concentration needed. e.g.: 1 mM -> 333.33 µM->111.11 µM dilution will result 100 µM->33.33 µM -> 11.11 µM in the samples. Please see Notes.
- Dissolve the powder of compound in DMSO at 10 mM final concentration, sonicate it (e.g.: 10” at 50 Hz) and warm it if needed (e.g.: 2’ 45 °C), to be sure all the compound goes in solution.
- RNase H assay
- Plan an experiment without RT enzymes (blank), with the RT enzyme in the absence of inhibitors (control), and in the presence of increasing concentration of inhibitors (samples). It is better to use a wide range of concentrations to have a better curve of inhibition. The reaction volume is 100 µl.
- In one OPTIPLATE-96 F/50B, first add water (20 µl in blanks and 10 µl in controls).
- Add 80 µl of RT reaction mix (1.25x).
- Add 10 µl of the inhibitor dilution at the established concentration in the samples (see Figure 2 as an example).
- Finally add 10 µl of the enzyme (20 ng of HIV-1 RT) or (2 nM of PFV RT) to each well (control and samples).
- Cover the plate with the lid and incubate the reaction for 1 h at 37 °C at 200 rpm in the Multi Thermo-Shaker for microplates.
- Stop the reaction by addition of 50 µl EDTA (0.5 M, pH 8.0) to each well.
- Quantify the reaction with the Victor 3 at 490/528 nm (excitation/emission wavelength).
- Elaborate the results by subtracting the value of the blank from all the samples and reporting the obtained values in the samples with the inhibitor as a percentage of the control.
- Calculate by interpolation the IC50 value of the inhibitors as the concentration that reports a 50% of reduction of the signal of the product respect to the control.
- Plan an experiment without RT enzymes (blank), with the RT enzyme in the absence of inhibitors (control), and in the presence of increasing concentration of inhibitors (samples). It is better to use a wide range of concentrations to have a better curve of inhibition. The reaction volume is 100 µl.
Representative data
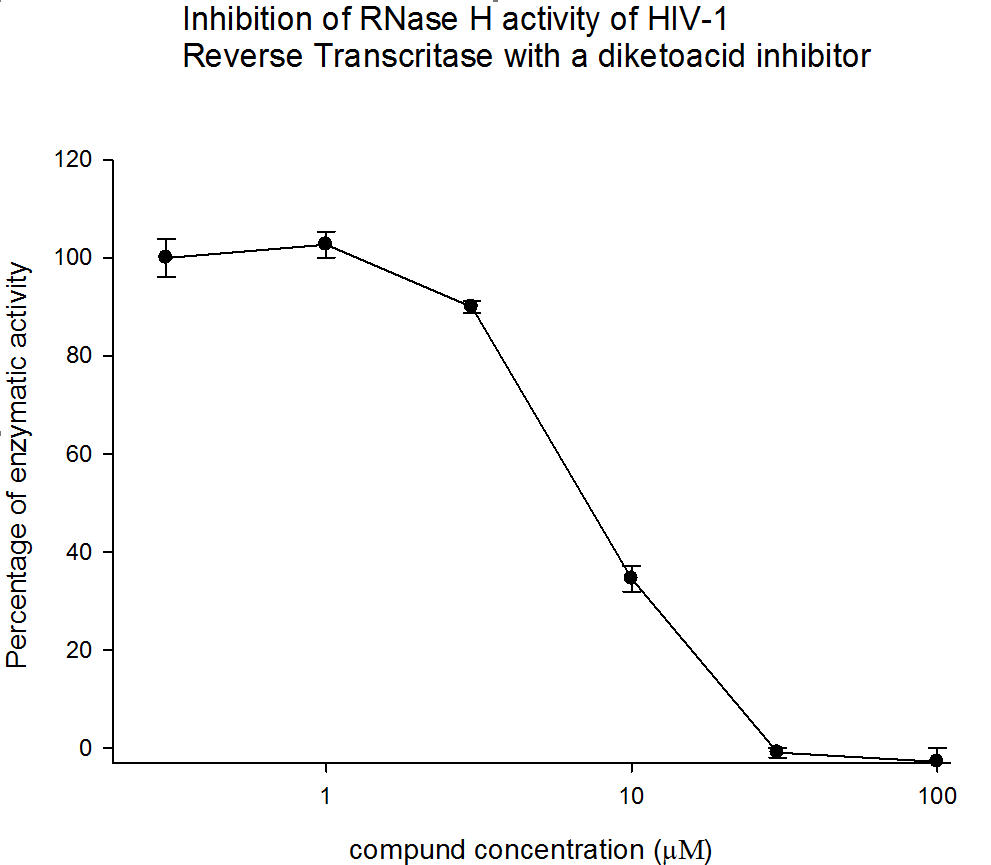
Figure 2. The results from three independent experiments (biological replicates) are shown as percentage of control. Error bars represent the standard deviation.
Notes
- This protocol has been applied to the HIV-1 and PFV RT enzymes. However, it can be used with virtually any RT enzymes with an RNase H activity.
- We recommend to make the inhibitor dilutions in water since the DMSO solvent affects the RNase H activity so its concentration in the sample should never overcome 1.01%.
Recipes
- Reaction mix (1.25x)
For HIV-1 RT:
62.5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.8)
7.25 M MgCl2
1.25 M DTT
100 mM KCl
0.3125 µM of RNA/DNA hybrid
- PFV RT reaction mix (1.25x)
62.5 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.1)
7.25 mM MgCl2
1.25 mM DTT
100 mM KCl
0.3125 µM of RNA/DNA hybrid
Acknowledgments
The p(His)6-tagged p66/p51 HIV-1HXB2 RT-prot plasmid was kindly provided by Stuart Le Grice Laboratory (NCI Frederick). The foamy virus reverse transcriptase was kindly provided by Birgitta M. Wöhrl Universität Bayreuth, Lehrstuhl Biopolymere, Bayreuth, Germany. This protocol was modified and adapted from Parniak et al. (2003).
References
- Corona, A., Di Leva, F. S., Thierry, S., Pescatori, L., Cuzzucoli Crucitti, G., Subra, F., Delelis, O., Esposito, F., Rigogliuso, G., Costi, R., Cosconati, S., Novellino, E., Di Santo, R. and Tramontano, E. (2014a). Identification of highly conserved residues involved in inhibition of HIV-1 RNase H function by Diketo acid derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(10): 6101-6110.
- Corona, A., Schneider, A., Schweimer, K., Rösch, P., Wöhrl, B. M. and Tramontano, E. (2014b). Inhibition of foamy virus reverse transcriptase by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNase H inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(7): 4086-4093.
- Parniak, M. A., Min, K. L., Budihas, S. R., Le Grice, S. F. and Beutler, J. A. (2003). A fluorescence-based high-throughput screening assay for inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H activity. Anal Biochem 322(1): 33-39.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Corona, A. and Tramontano, E. (2015). RNase H Polymerase-independent Cleavage Assay for Evaluation of RNase H Activity of Reverse Transcriptase Enzymes. Bio-protocol 5(16): e1561. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1561.
Category
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Antiviral assay
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










