- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
XTT Assay of Antifungal Activity
Published: Vol 5, Iss 15, Aug 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1543 Views: 11141
Reviewed by: Emilia Krypotou Belen SanzFanglian He

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Intracellular cAMP Measurements in Candida albicans Biofilms
Liuliu Jiang [...] Xin Wei
Dec 5, 2019 4678 Views

Competition Assays to Quantify the Effect of Biocontrol Yeasts against Plant Pathogenic Fungi on Fruits
Electine Magoye [...] Florian M. Freimoser
Feb 5, 2020 5417 Views

Determination of the Cellular Ion Concentration in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Using ICP-AES
Louise Thines [...] Pierre Morsomme
Aug 20, 2020 3443 Views
Abstract
XTT assay is a colorimetric method that uses the tetrazolium dye, 2,3-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulphenyl)-(2H)-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide (XTT) to quantify cell-mediated damage to fungi. Actively respiring fungal cells convert the water-soluble XTT to a water-soluble, orange colored formazan product (Meshulam et al., 1995). Here, we describe the protocol that measures the ability of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) to exert antifungal activity. This approach was first established with human polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) by Meshulam et al. (1995) and then adapted to pDC by Ramirez-Ortiz et al. (2011) and Loures et al. (2015). It can be modified for use with other effector cells and to test compounds for antifungal activity.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatusMaterials and Reagents
- Aspergillus fumigatus (A. fumigatus) clinical isolate Af293 (Nierman et al., 2005)
- Human pDCs obtained from healthy donors
- RPMI-1640 medium without phenol red (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11875119 )
- Penicillin G/ streptomycin sulfate (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 15140122 )
- L-glutamine (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 25030081 )
- Sodium pyruvate (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11360070 )
- Sterile distilled water (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 10977015 )
- Sterile PBS (Corning Incorporated, catalog number: 21040CM )
- 96 well half area plates (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 07200309 )
- Tips
- 15 ml Centrifuge tube (Falcon®,catalog number: 352059 )
- XTT (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X4251 )
- Coenzyme Q (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D9150 )
- Tween 20 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP337500 )
- Sabouraud dextrose agar (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: R454472 )
- Supplemented media (see Recipes)
- Slants (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 30 μm Nylon mesh (Genesee Scientific Corporation, catalog number: 57105 )
- 10 ml Syringe (BD Bioscience, catalog number: 305482 )
- Inverted microscope (Nikon)
- Pipettes
- Multichannel pipette
- Neubauer chamber
- Reagents reservoir (Corning, Costar®, catalog number: 07200127 )
- Microplate reader with capacity to measure OD450 and OD650 (Versamax)
- Water bath (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- CO2 Incubator (37 °C)
- Vortex (Fisher Vortex Genie 2) (Scientisfic Industries, Inc., catalog number: 12812 )
- Autoclavec
Procedure
- Grow A. fumigatus (Af293) on Sabouraud dextrose agar slants for 3-5 days at 37 °C. The culture will turn white as hyphae grow and then green as sporulation (conidia formation) occurs.
Note: The assay can be adapted for other species of fungi. - Harvest the conidia with 2-3 ml of PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 (PBS T20) gently removing the conidia from the slants with a tip. The conidia can be kept at 4 °C for up to 7 days before use in assays. Maintain sterile conditions when working with conidia.
- Suspend the conidia by mixing on a vortex for few seconds. Draw the suspension into a 10 cc syringe. Fold 30 μm nylon mesh inside the top of a 15 ml centrifuge tube. Filter the conidial suspension drop wise through the nylon mesh. Remove and discard the nylon mesh from the centrifuge tube.
- Wash the conidia three times by suspension in 10 ml PBS T20 followed by centrifugation at 3,000 rpm/10 min.
- Suspend the filtered conidia in 5 ml supplemented media.
- Count the conidia in a Neubauer chamber.
- Add 5 x 103 A. fumigatus conidia in 96-well half area plates in 100 μl supplemented media per well. If desired for a dose response curve, the number of conidia per well can be varied; however, fewer conidia may not give adequate OD readings.
- Keep the plates in the dark at room temperature (21 °C) in static conditions for 16 h in supplemented media to swell the conidia and then incubate for an additional 3 h at 37 °C to promote germination of hyphae. Note that after putting the plates in the incubator check the germination process every 15 min until you get hyphae of 10-20 μm average length.
- Withdraw the plate from the incubator when you get hyphae of 10-20 μm average length. If your pDCs are not ready yet keep the plate at 4 °C to avoid overgrowing of the hyphae. We suggest 2 h as the maximum period of storage at 4 °C.
- Gently wash the hyphae 2 times with sterile PBS (200 µl).
- Add 5 x 104 pDCs to the hyphae in a final volume of 100 μl supplemented media. Note that you can use a different number of pDCs or another effector cell type. Generally, each condition is tested in at least triplicate. Keep the co-culture under sterile conditions.
- To determine background activity, 4 to 5 wells should contain pDC only.
- To determine XTT reduction by fungi in the absence of pDC, 4 to 5 wells should be left with A. fumigatus hyphae only.
- To determine blank values, 4 to 5 wells should have media only.
- Following 2 h incubation at 37 °C, the pDCs are subjected to hypotonic lysis by three washes with 100 μl distilled water. It is critical that the washes are performed very gently and carefully to avoid removing hyphae.
- Incubate for 30 min with 100 μl distilled water at 37 °C.
- During the 30 min of incubation, the RPMI-1640 containing 400 μg/ml of XTT and 50 μg/ml of Coenzyme Q must be prepared. Stock solutions each containing 10 mg/ml XTT and Coenzyme Q should be prepared individually in PBS. Both compounds need high temperature to dissolve. Usually a 1 min incubation in a 60 °C water bath is sufficient. When more than 1 min is necessary, it is important to take the solutions out of the water bath (at 60 °C) immediately after they dissolve. The XTT and Coenzyme should be added to the RPMI-1640 a few minutes before adding to the wells. As phenol red can interfere with colorimetric readings, the RPMI-1640 should not contain phenol red.
- Remove the supernatants, again taking great care taken not to remove the hyphae.
- 100 μl RPMI media containing 400 μg/ml of XTT and 50 μg/ml of Coenzyme Q, are added, and the wells are incubated for 2 h at 37 °C.
- The OD450 and OD650 are measured on the microplate reader.
- Data are expressed as percent antifungal activity according to the formula:
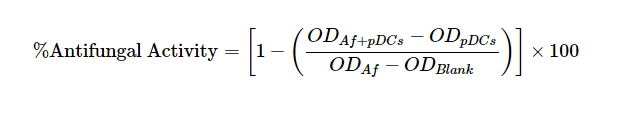
ODAf + pDC is (OD450 - OD650) of wells containing A. fumigatus hyphae with pDCs.
ODpDC is (OD450 - OD650) of wells containing pDCs.
ODAf is (OD450 - OD650) of wells containing A. fumigatus hyphae alone.
ODblank is (OD450 - OD650) of wells containing media alone.
Recipes
- Supplemented media
RPMI-1640 (without phenol red) with 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml streptomycin, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 1 mM sodium pyruvate - Slants
Add 4.5 of Sabouraud dextrose agar to 100 ml distillated water
Autoclave it for 15 min
Add 3 ml per 15 ml tube
Tilt the tube at a 45° to 60° angle and let it solidify. Keep at 4 °C until use.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grants RO1HL112671, RO1AI025780, and RO1AI072195. FVL acknowledges support from Fundação de Amparo Pesquisa de São Paulo (FAPESP) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
References
- Loures, F. V., Rohm, M., Lee, C. K., Santos, E., Wang, J. P., Specht, C. A., Calich, V. L., Urban, C. F. and Levitz, S. M. (2015). Recognition of Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells is mediated by dectin-2 and results in formation of extracellular traps. PLoS Pathog 11(2): e1004643.
- Meshulam, T., Levitz, S. M., Christin, L. and Diamond, R. D. (1995). A simplified new assay for assessment of fungal cell damage with the tetrazolium dye, (2,3)-bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulphenyl)-(2H)-tetrazolium-5-carboxanil ide (XTT). J Infect Dis 172(4): 1153-1156.
- Nierman, W. C., Pain, A., Anderson, M. J., Wortman, J. R., Kim, H. S., Arroyo, J., Berriman, M., Abe, K., Archer, D. B., Bermejo, C., Bennett, J., Bowyer, P., Chen, D., Collins, M., Coulsen, R., Davies, R., Dyer, P. S., Farman, M., Fedorova, N., Fedorova, N., Feldblyum, T. V., Fischer, R., Fosker, N., Fraser, A., Garcia, J. L., Garcia, M. J., Goble, A., Goldman, G. H., Gomi, K., Griffith-Jones, S., Gwilliam, R., Haas, B., Haas, H., Harris, D., Horiuchi, H., Huang, J., Humphray, S., Jimenez, J., Keller, N., Khouri, H., Kitamoto, K., Kobayashi, T., Konzack, S., Kulkarni, R., Kumagai, T., Lafon, A., Latge, J. P., Li, W., Lord, A., Lu, C., Majoros, W. H., May, G. S., Miller, B. L., Mohamoud, Y., Molina, M., Monod, M., Mouyna, I., Mulligan, S., Murphy, L., O'Neil, S., Paulsen, I., Penalva, M. A., Pertea, M., Price, C., Pritchard, B. L., Quail, M. A., Rabbinowitsch, E., Rawlins, N., Rajandream, M. A., Reichard, U., Renauld, H., Robson, G. D., Rodriguez de Cordoba, S., Rodriguez-Pena, J. M., Ronning, C. M., Rutter, S., Salzberg, S. L., Sanchez, M., Sanchez-Ferrero, J. C., Saunders, D., Seeger, K., Squares, R., Squares, S., Takeuchi, M., Tekaia, F., Turner, G., Vazquez de Aldana, C. R., Weidman, J., White, O., Woodward, J., Yu, J. H., Fraser, C., Galagan, J. E., Asai, K., Machida, M., Hall, N., Barrell, B. and Denning, D. W. (2005). Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 438(7071): 1151-1156.
- Ramirez-Ortiz, Z. G., Lee, C. K., Wang, J. P., Boon, L., Specht, C. A. and Levitz, S. M. (2011). A nonredundant role for plasmacytoid dendritic cells in host defense against the human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Cell Host Microbe 9(5): 415-424.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Loures, F. V. and Levitz, S. M. (2015). XTT Assay of Antifungal Activity. Bio-protocol 5(15): e1543. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1543.
Category
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Antifungal assay
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Other compound
Biochemistry > Other compound > Antimicrobial
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link