- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Detection of Alternative Oxidase Expression in Arabidopsis thaliana Protoplasts Treated with Aluminium
Published: Vol 5, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1515 Views: 9779
Reviewed by: Arsalan DaudiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Plate Growth Assay to Quantify Embryonic Root Development of Zea mays
Jason T. Roberts [...] David M. Braun
Oct 20, 2023 2286 Views

Detection and Quantification of Programmed Cell Death in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: The Example of S-Nitrosoglutathione
Lou Lambert and Antoine Danon
Aug 5, 2024 1610 Views

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantification of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Ascorbate in Culture Medium and Microalgal Cells
Juan Manuel Ostera [...] Gabriela Malanga
Apr 5, 2025 1222 Views
Abstract
Aluminium (Al), a non-essential metal widespread in the environment that is known to be toxic to humans as well as to plants, can cause damage not only to the roots but also to the aerial parts of plants. Its toxicity has been recognized as one of the major factors that limit crop production on acid soil. Alternative oxidase, the respiratory terminal oxidase in plants, which contributes to maintain the electron flux and reduce mitochondrial ROS levels, is often dramatically induced to make plants to adapt better to stress conditions like Al stress. In this protocol, the expression of alternative oxidase induced by Al treatment was detected in Arabidopsis protoplasts using an adaptation of previous methods (Yamamoto et al., 2002; Li et al., 2011; Liu et al., 2014), which contribute to research on the mechanism of alternative oxidase in Al treatment.
Materials and Reagents
- Rosette leaves of Arabidopsis (Columbia, 3 weeks)
- AlCl3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 237051 )
- CaCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C7902 )
- HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 258148 )
- FDA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 596-09-8 )
- TRI reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 93289 )
- Cellulase R10 (Yakult Honsha, catalog number: C6260 )
- Macerozyme R10 (Yakult Honsha, catalog number: 8032-75-1 )
- Mannitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4125 )
- MES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8250 )
- KCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3911 )
- Bovine serum albumin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A-6793 )
- NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6150 )
- Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G7528 )
- Trition X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T-8787 )
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626 )
- Tris (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1378 )
- SDS (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L6026 )
- (NH4)2S2O8 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A3426 )
- TEMED (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9281 )
- Tween-20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416 )
- SuperScript II first-strand synthesis system (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11904-018 )
- SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, catalog number: RR420A )
- Bio-Rad protein assay kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 500-0001 )
- Anti-AOX antibody (Agrisera, catalog number: AS10699 )
- Anti-Rubisco antibody (Agrisera, catalog number: AS03037 )
- Anti-rabbit IgG (DylightTM 800 4x PEG Conjugate) secondary antibody (CST, catalog number: 5151 )
- Anti-mouse IgG (DylightTM 800 Conjugate) secondary antibody (CST, catalog number: 5257 )
- Enzyme solution (see Recipes)
- W5 solution (see Recipes)
- 5 mM AlCl3 solution in Ca medium
- Real time PCR reaction solution (see Recipes)
- Lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- 10 ml separating gel (see Recipes)
- 6 ml stacking gels (see Recipes)
- TBST (see Recipes)
Equipment
- pH meter
- Thermal Cycler (Roche, model: Light cycler 2.0 )
- Confocal laser-scanning microscope (Carl-Zeiss, model: LSM510/ConfoCor2 )
- Auto microplate reader (Tecan Trading AG, model: infinite M200 )
- Two-color infrared imaging system (Odyssey, model: 9120 )
- Centrifuge
- Orbital shaker
- PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 162-0177 )
- Nylon mesh
- 96-well plates
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube
- Generic razor blade
- Vacuum pump (Vacuubrand, model: MZ 2C )
- BioPhotometer (Eppendorf, model: AG 22331 )
Software
- Image J 1.43 software
Procedure
- Prepare for Arabidopsis protoplasts
- Healthy rosette leaves from Arabidopsis thaliana (3 weeks) were sliced with a razor blade into small leaf strips (0.5-1 mm).
- The leaves were covered with enzyme solution in a petri dish and placed in a vacuum chamber connected to a vacuum pump, and approx. 100 to 400 mmHg of vacuum was applied for 30 min. The leaves were then incubated in the dark for 3 h without shaking at room temperature.
- The digested sample was filtrated through a 75 µm nylon mesh, the crude protoplast filtrates were sedimented by centrifugation for 3 min at 100 x g at room temperature.
- The purified protoplasts were suspended in W5 solution.
- Healthy rosette leaves from Arabidopsis thaliana (3 weeks) were sliced with a razor blade into small leaf strips (0.5-1 mm).
- Al treatment for Arabidopsis protoplasts
- 10 μl AlCl3 solution in Ca medium was added to 90 µl of protoplast solution in 96-well plates.
- The protoplasts were incubated for 1 h at room temperature in darkness.
- The protoplasts were incubated with 50 µM FDA for 5 min and Al-induced protoplast death was observed by confocal microscopy (Figure 1).
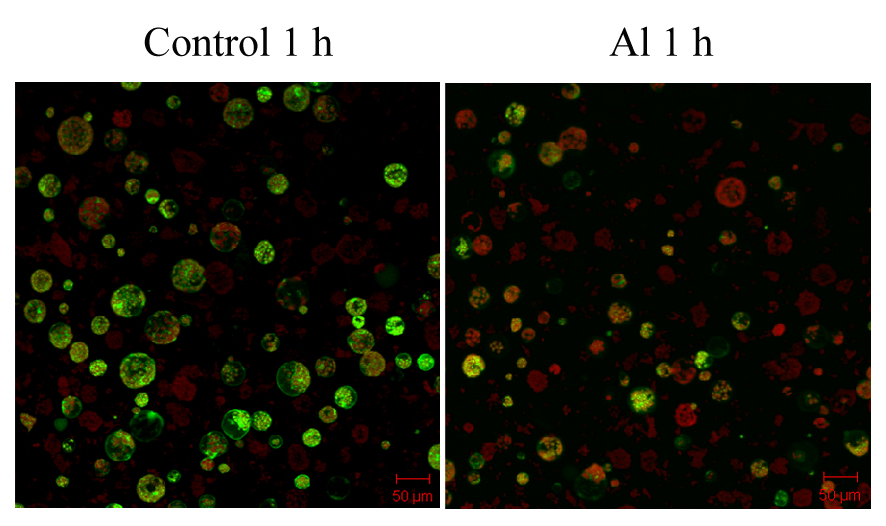
Figure 1. Al-induced protoplast death. Viability of wild-type (WT) Arabidopsis protoplasts after 0.5 mM Al treatment. Protoplasts (2 x 105/ml) were incubated with 50 µM FDA and observed with a confocal laser-scanning microscope.
- 10 μl AlCl3 solution in Ca medium was added to 90 µl of protoplast solution in 96-well plates.
- RNA extraction and quantitative RT-PCR
- Total RNA was extracted from Arabidopsis protoplasts according to the manufacturer’s instructions using TRI reagent.
- The concentration of RNA was determined by measuring A260 using BioPhotometer. 4 μg RNA was used for reverse transcription PCR.
- First strand cDNA was synthesized with SuperScript II First strand synthesis system for qRT-PCR. Eppendorf BioPhotometer was used to determine the concentrations of cDNA.
- The transcript of AOX genes were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR using ACTIN2 as an endogenous control. The AOX1a gene was amplified with the primers 5’-ATGATGATAACTCGCGGTGGAGC-3’ and 5’-GCAACATTCAAAGAAAG CCGAATC-3'. PCR was carried out using 50 ng of cDNA and SYBR PCR Master Mix following the manufacturer’s protocol. For quantitative RT-PCR analyses, the Light Cycler 2.0 instrument was used to run the two-step program. PCR cycling conditions for amplification were 95 °C for 30 sec followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 sec, 55 °C for 30 sec.
- Relative expression levels were calculated using the 2(-∆∆Ct) analysis method.
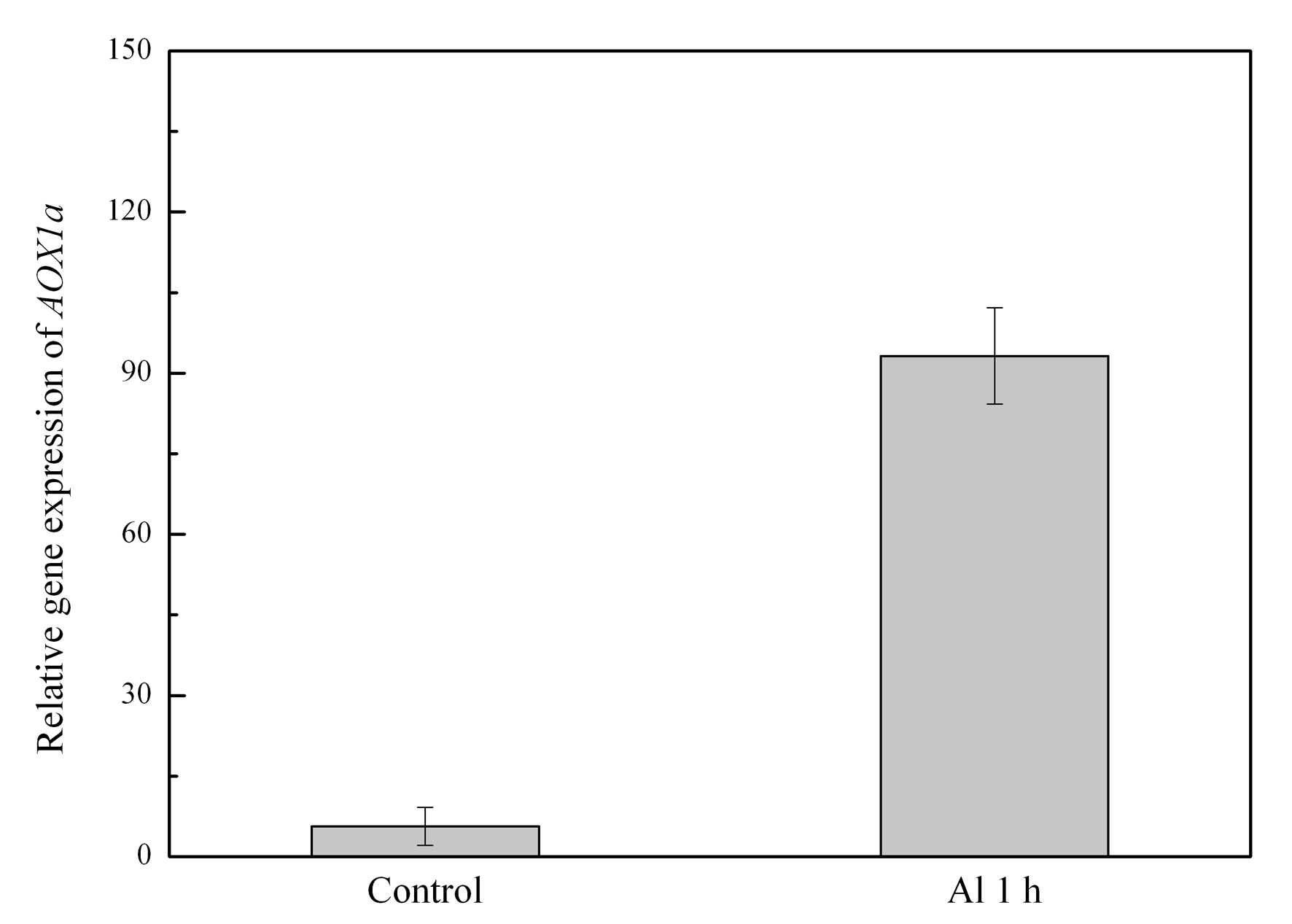
Figure 2. qRT-PCR analysis of the gene expression levels of AOX1a gene in Al-treated WT protoplasts
- Total RNA was extracted from Arabidopsis protoplasts according to the manufacturer’s instructions using TRI reagent.
- Protein extraction and western blot
- The treated protoplasts were re-suspended in lysis buffer and incubated on ice with gentle shaking on a level shaker for 30 min.
- The samples were centrifuged for 5 min at 1,2000 x g at 4 °C, and the supernatants were transferred to new 1.5 ml tubes.
- Protein concentrations were determined by the Bradford method using bovine serum albumin as a standard (Bio-Rad protein assay kit).
- Proteins extracts were separated by 12% sodium dodecyl sulphate- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
- The gel was transferred to PVDF membranes and then electrophoresis for 45 min.
- The membrane was blocked with TBST containing 5% non-fat milk for 1 h.
- The membrane was incubated with anti-AOX antibody or anti-Rubisco antibody at 4 °C overnight.
- The membrane was washed with TBST three times (about 10 min each time), and then incubated with secondary antibody [AOX: Anti-rabbit IgG (DylightTM800 4x PEG Conjugate) secondary antibody; Rubisco: Anti-mouse IgG (DylightTM800 Conjugate) secondary antibody] at room temperature for 2 h.
- When the membrane was dried, detected by using Odyssey two-color infrared imaging system.
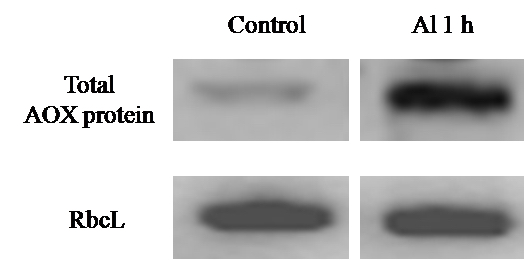
Figure 3. Western blot analysis of the level of total AOX proteins in Al-treated WT protoplasts. Blots were probed with monoclonal anti-AOX antibody.
Quantitative analysis was carried out using Image J 1.43 software (Figure 4). A step-by-step guide on how to use Image J for this purpose is shown in Supplementary data 1.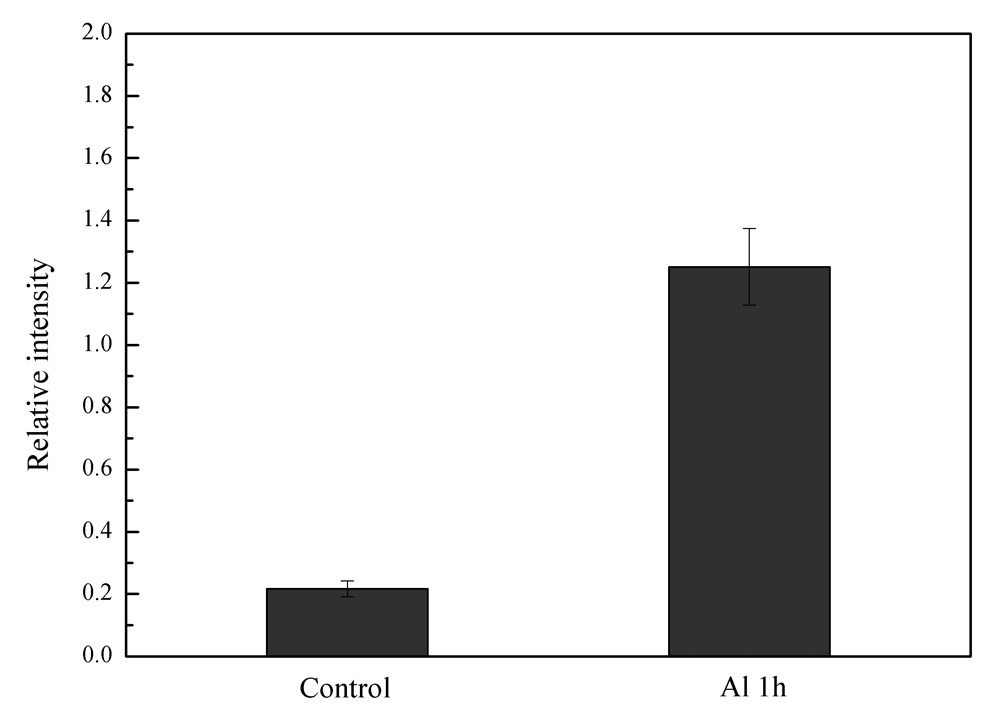
Figure 4. Quantitative analysis of western blot. Quantitative analysis was carried out using Image J software.
- The treated protoplasts were re-suspended in lysis buffer and incubated on ice with gentle shaking on a level shaker for 30 min.
Recipes
- Enzyme solution
1%-1.5% (w/v) cellulose R10
0.2%-0.4% (w/v) macerozyme R10
0.4 M mannitol
20 mM MES
20 mM KCl
10 mM CaCl2
0.1% (w/v) bovine serum albumin
pH 5.7 - W5 solution
154 mM NaCl
125 mM CaCl2
5 mM KCl
5 mM Glc
15 mM MES-KOH (pH 5.6) - 5 mM AlCl3 solution in Ca medium
5 mM AlCl3
30 mM CaCl2
pH 4.5 - Real time PCR reaction solution
SYBR premix Ex Taq 10.0 µl PCR forward primer (10 µM) 0.4 µl PCR reverse primer (10 µM) 0.4 µl cDNA 2.0 µl ddH2O 7.2 µl - Lysis buffer
15 mM NaCl
1% Triton X-100
100 mg/ml phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) - 10 ml separating gel
30% polyacrylamide 4.0 ml 1.5 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.8) 2.5 ml 10% SDS 100 µl 10% (NH4)2S2O8 100 µl TEMED 10 µl ddH2O 3.29 ml - 6 ml stacking gels
30% polyacrylamide 1.0 ml 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) 0.75 ml 10% SDS 60 µl 10% (NH4)2S2O8 60 µl TEMED 6 µl ddH2O 4.124 ml - TBST
10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4)
150 mM NaCl
0.1% Tween-20
Acknowledgments
This protocol was supported by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT0829), the Key Program of NSFC-Guangdong Joint Funds of China (U0931005) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (2007AA10Z204). This protocol was adapted from previous work (Yamamoto et al., 2002; Ye et al., 2013; Sun et al., 2012).
References
- Liu, J., Li, Z., Wang, Y. and Xing, D. (2014). Overexpression of ALTERNATIVE OXIDASE1a alleviates mitochondria-dependent programmed cell death induced by aluminium phytotoxicity in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 65(15): 4465-4478.
- Li, Z. and Xing, D. (2011). Mechanistic study of mitochondria-dependent programmed cell death induced by aluminium phytotoxicity using fluorescence techniques. J Exp Bot 62(1): 331-343.
- Sun, A., Nie, S. and Xing, D. (2012). Nitric oxide-mediated maintenance of redox homeostasis contributes to NPR1-dependent plant innate immunity triggered by lipopolysaccharides. Plant Physiol 160(2): 1081-1096.
- Yamamoto, Y., Kobayashi, Y., Devi, S. R., Rikiishi, S. and Matsumoto, H. (2002). Aluminum toxicity is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and the production of reactive oxygen species in plant cells. Plant Physiol 128(1): 63-72.
- Ye, Y., Li, Z. and Xing, D. (2013). Nitric oxide promotes MPK6-mediated caspase-3-like activation in cadmium-induced Arabidopsis thaliana programmed cell death. Plant Cell Environ 36(1): 1-15.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Liu, J., Li, Z. and Xing, D. (2015). Detection of Alternative Oxidase Expression in Arabidopsis thaliana Protoplasts Treated with Aluminium. Bio-protocol 5(13): e1515. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1515.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Other compound
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Abiotic stress
Biochemistry > Other compound > Reactive oxygen species
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










