- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In vitro Drug Susceptibility Assay for HBV Using Southern Blotting
Published: Vol 5, Iss 8, Apr 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1448 Views: 11317
Reviewed by: Yannick DebingAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Isolation of Exosomes from Semen for in vitro Uptake and HIV-1 Infection Assays
Marisa N. Madison [...] Chioma M. Okeoma
Apr 5, 2017 12837 Views

Sleeping Beauty Transposon-based System for Rapid Generation of HBV-replicating Stable Cell Lines
Jin-Wei Zheng [...] Quan Yuan
Jul 5, 2018 9702 Views
Abstract
Antiviral agents for the suppression of hepatitis B virus (HBV) have been used for treating chronic hepatitis B. However, the emergence of drug-resistant HBV is still a major problem for antiviral treatment. To identify and characterize the drug-resistant HBV, the construction of HBV replicon and in vitro drug susceptibility assay are essential. Here we describe the experimental methods to study drug-resistant HBV.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virusMaterials and Reagents
- Transfection HBV 1.2mer replicons
- Huh7 cells (Liver Research Center, Rhode Island Hospital, Brown Medical School, Providence, USA)
- Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11995 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 26140-079 )
- Penicillin-streptomycin (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 15140 )
- Lipofectamine 2000 (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 11668-019 )
- Opti-MEM® I Reduced Serum Medium (Opti-MEM) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 31985-088 )
- HBV 1.2mer replicon [WT or Drug-resistant HBV, WT HBV1.2 replicon was kindly provided from Prof. W. S. Ryu (Yonsei University, Korea)]
- Lamivudine (1~100 μM, provided by GlaxoSmithKline)
- Adefovir (1~100 μM, provided by Gilead Sciences)
- Clevudine (1~100 μM, provided by Bukwang Pharmaceutical Co.)
- Entecavir (0.05~1 μM, Moravek)
- Tenofovir (1~100 μM, provided by Gilead Sciences)
- Huh7 cells (Liver Research Center, Rhode Island Hospital, Brown Medical School, Providence, USA)
- Extraction of viral DNA from HBV core particles
- DNaseI (Takara Bio Company, catalog number: 2215B )
- MungBean Nuclease (Takara Bio Company, catalog number: 2420B )
- Proteinase K (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 03115801001 )
- Phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol 25:24:1 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 77617 )
- Sodium acetate trihydrate (NaOAc) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 236500 )
- HEPES lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Nuclease buffer (I) (see Recipes)
- 26% PEG solution (see Recipes)
- Nuclease buffer (II) (see Recipes)
- 0.5% SDS solution (see Recipes)
- DNaseI (Takara Bio Company, catalog number: 2215B )
- Southern blot assay and the construction of the HBV probe
- Certified Molecular Biology Agarose (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 161-3102 )
- Amersham Hybond-N+ membrane (GE Healthcare, catalog number: RPN203B )
- SSC Buffer (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 85639 )
- Salmon sperm DNA (Life Technologies, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: AM9680 )
- Poly ethylene glycol (PEG) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5413 )
- 50x Denhardt’s solution (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D2532 )
- 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0)
- Formamide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F7503 )
- HBV 1.2mer replicon
- Klenow fragment and 10x Klenow buffer (Takara Bio Company, catalog number: 2140B )
- dNTP (NEB, catalog number: N0446S )
- [α-32P] dCTP (3,000 Ci/mmole, Perkin Elmer, catalog number: BLU513H500UC )
- Quick Spin Columns for radiolabeled DNA purification (Sephadex G-50, Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11 273 973 001 )
- Aat II (New England BioLabs, catalog number: R0117S )
- Hind III (New England BioLabs, catalog number: R0104S )
- Random primer (Bioneer, catalog number: N-7052 )
- Na2HPO4 (Amresco, catalog number: 0404 )
- NaH2PO4 (Amresco, catalog number: 0571 )
- 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (see Recipes)
- Transfer solution (I) (see Recipes)
- Transfer solution (II) (see Recipes)
- Transfer solution (III) (see Recipes)
- Hybridization solution (see Recipes)
- Washing solution (I) (see Recipes)
- Washing solution (II) (see Recipes)
- Certified Molecular Biology Agarose (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 161-3102 )
Equipment
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 forced-air incubator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Forma®, model: 3131 )
- 100 mm cell culture dish (Nunc®, catalog number: 172958 )
- 6 well plate (Nunc®, catalog number: 140675 )
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5415R )
- Pipet Aid XP (Drummond Scientific Company)
- Electrophoresis system (Nihon Eido, catalog number: NB-1011 )
- Dry oven
- Hybridization bottle
- Hybridization chamber
- Heat block
Procedure
- Transfection of HBV 1.2mer replicons
- One day before transfection, plate 3 x 105 Huh7 cells per well in 2 ml of growth medium (DMEM with 10% FBS, 1% Penicillin-streptomycin) on 6 well plate.
- Two hours before transfection, change 2 ml of growth media per well at 80% cells confluence.
- Dilute the 2 μg of HBV 1.2mer replicons in 125 μl of Opti-MEM and gently flick.
- Dilute 4 μl of Lipofectamine 2000 in 125 μl of Opti-MEM and gently flick. Then, incubate for 5 min at room temperature.
- After 5 min incubation, combine the diluted HBV 1.2mer replicons with the diluted Lipofectamine 2000 and gently mix by pipetting. Then, incubate for 20 min at room temperature.
- After 4~6 h transfection, change 2 ml of growth medium per well mixed with appropriate concentration anti-HBV drugs (see Figure 2).
- Replace the growth medium with anti-HBV drugs every day for 4 days and, then harvest the cells in 1.5 ml tube by centrifugation at 3,000 rpm for 1 min at 4 °C.
- One day before transfection, plate 3 x 105 Huh7 cells per well in 2 ml of growth medium (DMEM with 10% FBS, 1% Penicillin-streptomycin) on 6 well plate.
- Extraction of core particle relative HBV DNA
- Add 100 μl of cold HEPES lysis buffer in cell pellet and incubate on ice for 20 min.
- Centrifuge the lysates at 13,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C and transfer supernatant (cell lysate, cytoplasm fraction) into new 1.5 ml tube.
- Mix 5.67 μl of nuclease buffer (I) by pipetting and incubate for 30 min in 37 °C water bath.
- Briefly spin down, add 40 μl of 26% PEG solution and incubate for 2 h on ice (vortexing every 30 min) and centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 30 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant and centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Completely remove the supernatant (using pipet and KIMTECH Science Wipers).
- Add 100 μl of nuclease buffer (II) and physically resuspend the core particles.
- Incubate for 20 min in 37 °C water bath and briefly spin down.
- Add 282.5 μl of 0.5% SDS solution and 12.5 μl of proteinase K (20 mg/ml) and incubate for 2~4 h in 37 °C water bath (inverting every 30 min).
- After spin down, add 400 μl of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol and vigorously vortex for 10 sec. Then, centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 5 min at room temperature.
- Transfer aqueous upper layer into new 1.5 ml tube.
- Add 40 μl of 3 M NaOAc and 800 μl of 100% ethanol. After inverting several times, precipitate the mixture overnight at -20 °C.
- Centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 30 min at 4 °C and throw away the supernatant.
- Add 800 μl of 70% ethanol and gently inverting.
- Centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C and throw away the supernatant.
- Add 800 μl of 100% ethanol and gently inverting.
- Centrifuge at 13,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C and throw away the supernatant.
- Dry the HBV DNA pellet for 5~10 min (air-drying) and dissolve in 15 μl of TE buffer. Store HBV DNA at 4 °C until use.
- Add 100 μl of cold HEPES lysis buffer in cell pellet and incubate on ice for 20 min.
- Southern blot assay (gel transfer)
- Separate HBV DNA (procedure B, step 18) on 0.8% agarose gel for 2 h at 89 V.
- After electrophoresis, transfer the gel to tray and add transfer solution (I) to soak the gel.
- Incubate for 10 min on shaker and rinse the gel with distilled water.
- Add transfer solution (II) and incubate for 45 min on shaker.
- Rinse with distilled water and add transfer solution (III).
- Incubate over 30 min on shaker and rinse the gel with distilled water.
- Transfer the gel to Hybond-N+ membrane for overnight using capillary method (Figure 1) and bake the membrane to fix the HBV DNA for 2 h in 80 °C dry oven.
- Place membrane in hybridization bottle contained with 25 ml hybridization solution and incubates the membrane for 4 h in 42 °C hybridization chamber (pre-hybridization step).
- Separate HBV DNA (procedure B, step 18) on 0.8% agarose gel for 2 h at 89 V.
- The construction of the HBV probe
- To construct a template for the HBV specific probe, digest HBV 1.2mer replicon with Aat II and Hind III for 2 h at 37 °C and gel purification (Ahn et al., 2015).
- To synthesis HBV specific probe, mix the 48 ng of template (step 8) and 80 ng of random primer in 50 μl of distilled water.
Note: Step 10 should be carried out during pre-hybridization step.
- Heat the probe mixtures for 5 min at 100 °C and snap cooling on ice for 5 min.
- After spin down, add 5ul of 10x Klenow buffer, 2.5 μl of the dNTPs mixtures (2.5 mM, except dCTP), 5 μl of 32P-labled dCTP (50 μCi=5 μl/labeling), and 1 μl of Klenow fragment in probe mixtures.
- Incubate the probe mixture for 30 min at 37 °C.
- Remove the non-labeled probe using Quick Spin Columns for radiolabeled DNA purification.
- To construct a template for the HBV specific probe, digest HBV 1.2mer replicon with Aat II and Hind III for 2 h at 37 °C and gel purification (Ahn et al., 2015).
- Southern blot assay (membrane hybridization)
- Replace pre-warmed 25 ml of hybridization solution with 32P-labled HBV probe and incubate overnight in 42 °C hybridization chamber.
- After hybridization step, wash the membrane with washing solution (I) for 15~20 min in 63 °C hybridization chamber.
Note: If need more washing step, repeat wash with washing solution (II). Steps 9~16 should be performed in the Radio isotope room.
- Expose membrane to film and incubate overnight at -80 °C deep freezer. Then, develop the film.
- Replace pre-warmed 25 ml of hybridization solution with 32P-labled HBV probe and incubate overnight in 42 °C hybridization chamber.
Representative data
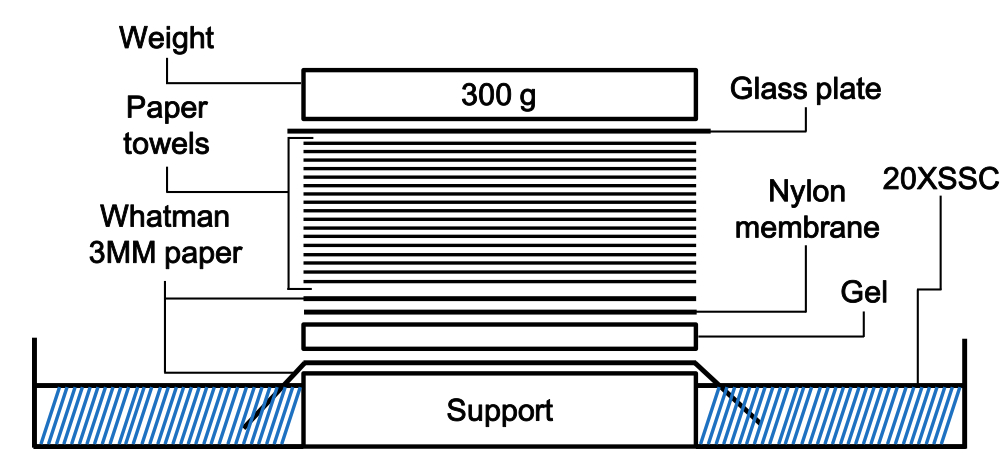
Figure 1. Scheme of capillary transfer method for Southern blotting
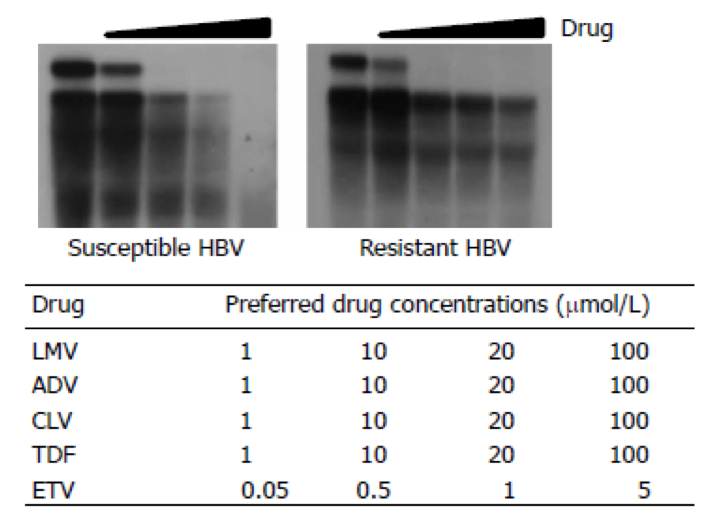
Figure 2. In vitro susceptibility assay of drug-resistant HBV (Kim et al., 2014). The replication of drug-resistant HBV was analyzed by Southern blot. TDF and ETV were treated with concentration as followed table (below).
Recipes
- HEPES lysis buffer
10 mM Hepes (pH 7.5)
100 mM NaCl
1 mM EDTA
1% NP-40
- Nuclease buffer (I)
10 mM CaCl2
12 mM MgCl2
DNaseI 0.5 unit
Mung Bean nuclease 7.5 unit
- 26% PEG solution
1.2 M NaCl
60 mM EDTA
30% sucrose
26% PEG 8000
- Nuclease buffer (II)
10 mM Tris (pH 7.5)
8 mM CaCl2
6 mM MgCl2
DNaseI 2 unit
Mung Bean nuclease 3 unit
- 0.5% SDS solution
25 mM Tris (pH 7.5)
10 mM EDTA
100 mM NaCl
0.5% SDS
- 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0)
57.7 ml of 1 M Na2HPO4
42.3 ml of 1 M NaH2PO4
- Transfer solution (I)
0.25 N HCl
0.6 M NaCl
- Transfer solution (II)
0.5 M NaOH
1 M NaCl
- Transfer solution (III)
1 M Tris (pH 7.5~8.0)
1 M NaCl
- Hybridization solution
Formamide 25 ml
20x SSC 12.5 ml
0.1 M sodium phosphate buufer (pH 7.0) 2.5 ml
0.5 M EDTA 0.2 ml
50x Denhardt’s solution 3 ml
10% SDS 1 ml
Salmon sperm DNA (10 mg/ml) 1 ml
Distilled water 4.8 ml
- Washing solution (I)
2x SSC
0.1% SDS
- Washing solution (II)
0.5x SSC
0.1% SDS
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Konkuk University.
References
- Ahn, S. H., Park, Y. K., Park, E. S., Kim, J. H., Kim, D. H., Lim, K. H., Jang, M. S., Choe, W. H., Ko, S. Y., Sung, I. K., Kwon, S. Y. and Kim, K. H. (2014). The impact of the hepatitis B virus polymerase rtA181T mutation on replication and drug resistance is potentially affected by overlapping changes in surface gene. J Virol 88(12): 6805-6818.
- Ahn, S. H., Park, Y. K. and Kim, K. (2015). Introduction and sequencing of patient-isolated HBV RT sequences into the HBV 1.2-mer replicon. Bio-protocol 5(8): e1449.
- Kim, J. H., Park, Y. K., Park, E. S. and Kim, K. H. (2014). Molecular diagnosis and treatment of drug-resistant hepatitis B virus. World J Gastroenterol 20(19): 5708-5720.
- Kwon, S. Y., Park, Y. K., Ahn, S. H., Cho, E. S., Choe, W. H., Lee, C. H., Kim, B. K., Ko, S. Y., Choi, H. S., Park, E. S., Shin, G. C. and Kim, K. H. (2010). Identification and characterization of clevudine-resistant mutants of hepatitis B virus isolated from chronic hepatitis B patients. J Virol 84(9): 4494-4503.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Ahn, S. H., Park, Y. K. and Kim, K. (2015). In vitro Drug Susceptibility Assay for HBV Using Southern Blotting. Bio-protocol 5(8): e1448. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1448.
Category
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Antiviral assay
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Virus
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > In vitro model > Cell line
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










