- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Phenol-based Total Protein Extraction from Lily Plant Tissues
Published: Vol 5, Iss 4, Feb 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1399 Views: 11962
Reviewed by: Pablo Bolanos-VillegasArsalan DaudiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Streamlining Protein Fractional Synthesis Rates Using SP3 Beads and Stable Isotope Mass Spectrometry: A Case Study on the Plant Ribosome
Dione Gentry-Torfer [...] Federico Martinez-Seidel
May 5, 2024 2855 Views

An Activity-Based Proteomics with Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (2D-PAGE) for Identifying Target Proteases in Arabidopsis Apoplastic Fluid
Sayaka Matsui and Yoshikatsu Matsubayashi
Mar 5, 2025 1975 Views

Advancing 2-DE Techniques: High-Efficiency Protein Extraction From Lupine Roots
Sebastian Burchardt [...] Emilia Wilmowicz
Oct 5, 2025 1763 Views
Abstract
The phenol-based total protein extraction method is unique in that water-soluble components such as polyphenolic compounds and nucleic acids can be easily removed. Thus, total protein is free from contaminants and allows for high quality two–dimensional gel electrophoresis. The phenol-based extraction of total protein was used in various lily organs and may likely apply to other plants whose content of polyphenolics is high (Note 1). An additional advantage of this extraction method is that nucleic acids can be easily removed and thus, avoid adverse effects of nucleic acids on protein resolution in the gel. This method is modified from that of Hurkman and Tanaka (1986).
Keywords: Protein extratctionMaterials and Reagents
- Sucrose (United States Biological, catalog number: 21938 )
- Tris base (United States Biological, catalog number: 75825 )
- HCl (fuming, at 37%) (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 100317 )
- EDTA (United States Biological, catalog number: 15699 )
- KCl (SERVA, catalog number: 26868 )
- 2-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M6250 )
- Phenol (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 100206 )
- NH4OAc (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 101116 )
- 100% MeOH (J.T. Baker®, catalog number: 9093-03 )
- Urea (United States Biological, catalog number: 75826 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9284 )
- K2CO3 (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 106683 )
- L-lysine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L5501 )
- DTT (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 111474 )
- Extraction buffer (see Recipes)
- Dissolving buffer (see Recipes)
- 0.1 M NH4OAc in 100% MeOH (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Ceramic mortar and pestles
- Beaker
- Stir bar
- Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5424 )
- AVANTI® J-26 XP High-Performance centrifuge with a JA 25.50 fixed-angle rotor (Beckman Coulter)
- COREX® tube,DuPont Instruments (catalog number: 00152 )
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes
- Fume hood
- Speed vacuum (Savant Systems LLC, model: SC110 )
- Mixer (Vortex Genie 2, Scientific Industries, Inc.)
- Stirrer (Corning)
Procedure
- Lily plant tissue collection
- Various vegetative and floral organs of young lily plants, including flower buds with a length around 4 cm were collected. The first three whorls of young leaves around the buds, plus the entire roots (approximately 8 cm from the apex) were also collected.
- Each organ was dissected from lily plants in the field and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C.
- Various vegetative and floral organs of young lily plants, including flower buds with a length around 4 cm were collected. The first three whorls of young leaves around the buds, plus the entire roots (approximately 8 cm from the apex) were also collected.
- Homogenization
- Work in the fume hood. Add liquid nitrogen into a mortar (12.5 cm) and pestle and keep them frozen.
- Add and grind 1 g of fresh or frozen tissue into powder in the frozen mortar and pestle in liquid nitrogen. Keep the sample frozen at all times.
- Add 5 ml of water-saturated phenol and 5 ml of extraction buffer to the sample powder.
- Add more liquid nitrogen into the mortar for easy grinding and mixing of the plant sample. Repeat one more time.
- Leave the frozen sample mix in the mortar until it melts and turns into a slurry.
- Grind the sample mix vigorously as soon as it turns into slurry.
Video 1. Homogenization of lily plant tissues - Transfer the melting solution into a glass beaker (25 or 50 ml in volume) and gently mix with a stir bar for 30 min at room temperature.
- Work in the fume hood. Add liquid nitrogen into a mortar (12.5 cm) and pestle and keep them frozen.
- Phase separation-partition of protein into the phenol phase
- Transfer the sample mixture into a COREX® tube.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer the upper phase (phenol phase) into a new 50 ml tube.
- Add an equal volume of phenol to the aqueous phase.
- Mix thoroughly by vigorous vortexing for 1 min.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Remove and pool the upper phase (phenol phase).
- Transfer the sample mixture into a COREX® tube.
- Phase separation-repetitive removal of contaminants from the phenol phase
- Add an equal volume of extraction buffer to the pooled phenol phase.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer the upper phase (phenol phase) into a new 50 ml tube.
- Add an equal volume of extraction buffer to the pooled phenol phase.
- Protein precipitation
- Add 5x volume of 0.1 M NH4OAc in 100% MeOH (cold) and mix well by vortexing for 1 min.
- Precipitate protein at -20 °C for 2 h or overnight (approximately 16 h) (Note 2).
- Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Decant the supernatant.
- Add 5x volume of 0.1 M NH4OAc in 100% MeOH (cold) and mix well by vortexing for 1 min.
- Protein wash
- The protein pellet is added with 10 ml of 0.1 M NH4OAc in 100% MeOH (cold).
- Wash the pellet by vigorous vortexing.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Repeat the washing step twice.
- Decant the supernatant.
- Add 10 ml of acetone.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Repeat the washing step twice.
- The pellet is shortly dried by speed vacuum for 30-60 sec.
- Dissolve the pellet in 300-500 μl (Note 3) of dissolving buffer and mix constantly by vortexing for 30 min. If the pellet is big, break it down into small pieces with a glass bar in order to increase protein solubility.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Collect supernatant (protein). The pellet (Note 4) in the tube is redissolved in 300-500 μl of dissolving buffer.
- This process of protein dissolution may be repeated several times until the concentration of protein in the dissolving buffer becomes insignificant.
- The collected supernatant may be pooled together.
- The protein pellet is added with 10 ml of 0.1 M NH4OAc in 100% MeOH (cold).
Representative data
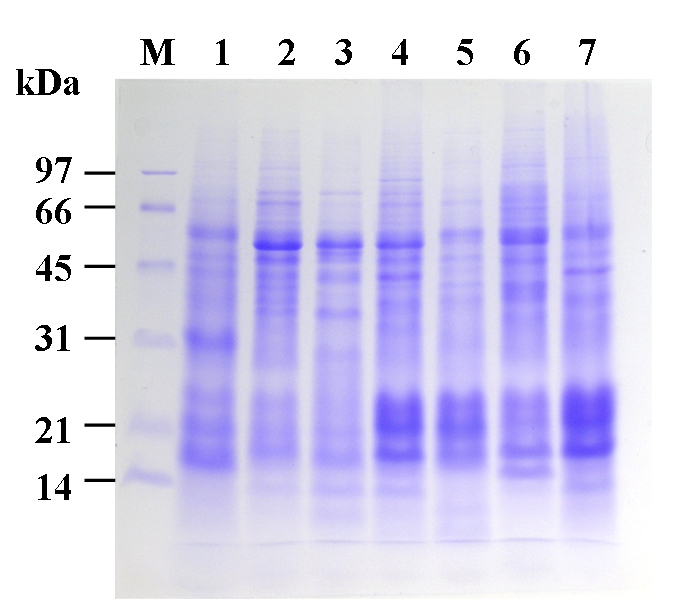
Figure 1. Anther-specificity analysis of lily protein by SDS-PAGE. Total protein (40 μg) was isolated from various organs of L. longiflorum, separated by 12% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. 1, root; 2, stem; 3, leaf; 4, tepal; 5, filament; 6, anther; 7, pistil; M, marker.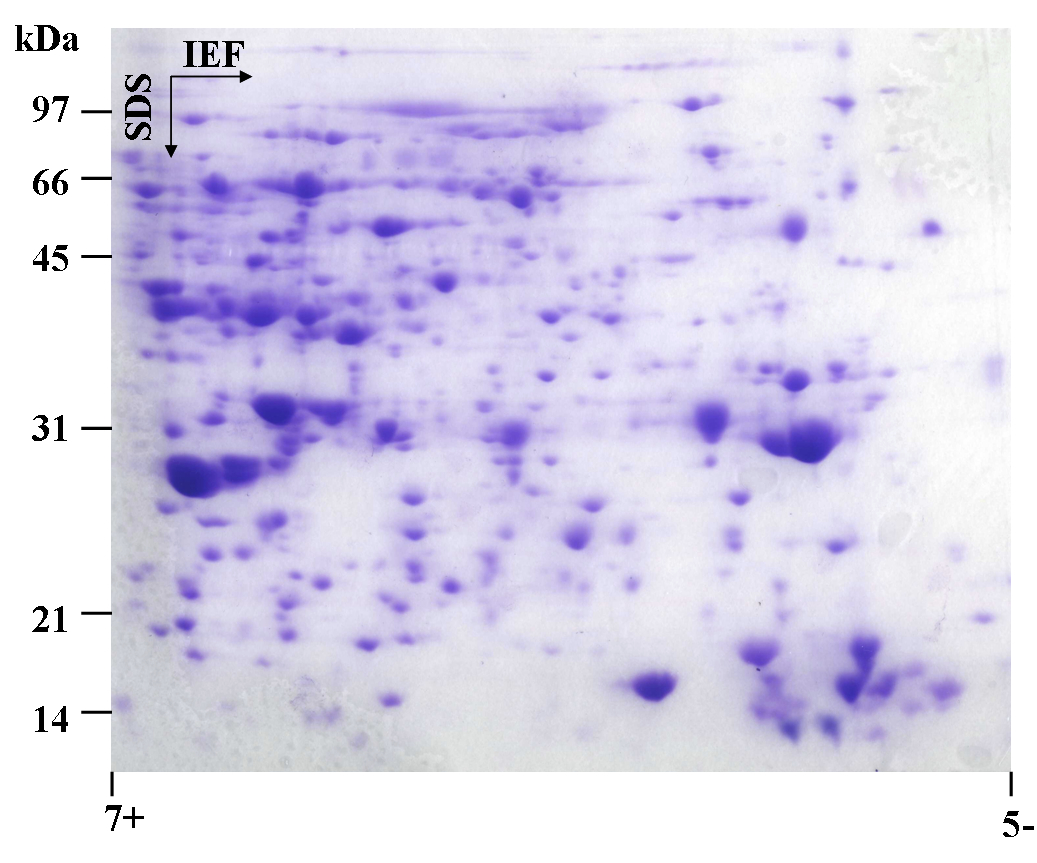
Figure 2. 2D-PAGE analysis of lily pollen protein. Total protein (1.5 mg) was isolated from pollen of L. longiflorum, separated by 2D-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. Marker proteins are indicated in the left.
Recipes
- Extraction bufferThen fill ddH2O up to 10 ml.
10 ml Final concentration Sucrose 2.4 g 0.7 M Tris base 0.61 g 0.5 M EDTA 0.19 g 50 mM HCl fuming 37% 24.8 μl 30 mM 1.0 M KCl 1 ml 100 mM 2-Mercaptoethanol 200 μl 2% - Dissolving bufferddH2O is added to a volume of 3 ml, filter-sterilized (0.22 μm), aliquoted and stored at -20 °C.
3 ml Final concentration Urea 1.7 g 9.5 M 10% Triton X-100 600 μl 2% 2.5 M K2CO3 6 μl 5 mM L-lysine 1.5 mg 500 μg/ml 1 M (15.4%) DTT 97.4 μl 0.5 % - 0.1 M NH4OAc in 100% MeOH
0.771 g of NH4OAc (MW = 77.08) is added into 100 ml of 100 % MeOH
Notes
- In our experience, total protein extracted from various organs of Arabidopsis and Tobacco plants using the phenol-based total protein extraction method yields high quality protein.
- Protein precipitated at -20 °C overnight (approximately 16 h) may allow a better yield of total protein. However, if yield is not a concern, most proteins can be precipitated at -20 °C for 2 h.
- It is important to maintain protein samples in a high concentration (at least 15 μg/μl) given that the maximum of sample loading in isolectric focusing of 2D-PAGE is around 100 μl. If protein is prepared for SDS-PAGE only, a larger volume of dissolving buffer can be applied.
- Protein in the pellet can be dissolved with the dissolving buffer. However, insoluble materials may remain in the pellet after centrifugation.
Acknowledgments
The protocol is mainly modified from that of Hurkman and Tanaka (1986). We appreciate their original contribution.
References
- Hurkman, W. J. and Tanaka, C. K. (1986). Solubilization of plant membrane proteins for analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol 81(3): 802-806.
- Wang, C. S., Walling, L. L., Eckard, K. J. and Lord, E. M. (1992). Patterns of protein accumulation in developing anthers of Lilium longiflorum correlate with histological events. Am J Bot. 118-127.
- Yang, C. Y., Chen, Y. C., Jauh, G. Y. and Wang, C. S. (2005). A Lily ASR protein involves abscisic acid signaling and confers drought and salt resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139(2): 836-846.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Chen, Y., Hsiao, Y. and Wang, C. (2015). Phenol-based Total Protein Extraction from Lily Plant Tissues. Bio-protocol 5(4): e1399. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1399.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Tissue analysis
Biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










