- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Purification of the GfsA-3x FLAG Protein Expressed in Aspergillus nidulans
Published: Vol 4, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1222 Views: 9641
Reviewed by: Kanika GeraFanglian He

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Purification of Native Dentilisin Complex from Treponema denticola by Preparative Continuous Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Functional Analysis by Gelatin Zymography
Pachiyappan Kamarajan [...] Yvonne L. Kapila
Apr 5, 2024 2121 Views

Thermus thermophilus CRISPR Cas6 Heterologous Expression and Purification
Junwei Wei [...] Yingjun Li
Jul 20, 2025 2202 Views
Abstract
GfsA is a fungal β-galactofuranosyltransferase involved in the biosynthesis of O-glycan. To investigate the enzymatic functions of GfsA, we attempted to obtain a recombinant protein of this enzyme from two heterologous host organisms. However, GfsA could not be expressed as a recombinant protein in either Escherichia coli (E. coli) or Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae). Therefore, we decided to employ Aspergillus nidulans (A. nidulans) as the host organism, and produced a strain that expressed 3x FLAG-tagged GfsA using chromosomal tagging. To confirm its expression, a solubilized protein was prepared from the tagged strain and analyzed with an anti-FLAG antibody. The strain that expressed 3x FLAG-tagged GfsA produced a functional protein with a mass of approximately 67 kDa. The method described in this manuscript allows purification of the GfsA-3xFLAG protein as expressed in A. nidulans cells.
Keywords: GalactofuranoseMaterials and Reagents
- Aspergillus nidulans expressing 3x FLAG-tagged GfsA (Komachi et al., 2013)
- 3x FLAG-peptide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F4799 )
- ANTI-FLAG M2-agarose produced from mouse (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2220 )
- Mouse IgG-agarose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A0919 )
- 2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl] ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, catalog number: GB10 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 198-13765 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 191-01665 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 163-03545 )
- Manganese (II) chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 133-00725 )
- Glycerol (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 075-00611 )
- 3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl) dimethylammonio]-2-hydroxypropanesulfonate (CHAPSO) (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, catalog number: C020 )
- CompleteTM protease inhibitor cocktail tablets (EDTA-free) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 1873580 )
- Liquid nitrogen
- Buffer A (see Recipes)
- Minimal medium (MM) (see Recipes)
- Hutner's trace elements (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Spreader
- 500-ml Sakaguchi flasks
- Mortar and pestle
- Aspirator
- Centrifuge with an angle rotor
- Centrifuge with a swing rotor
- Ultracentrifuge
- Spatula
- 15-ml plastic centrifuge tube (e.g., Greiner Bio-One GmbH)
- 4 °C incubator
- 30 °C incubator
- Rotator (e.g., TAITEC)
- Filter paper (Munktell & Filtrak GmbH, catalog number: 113053 )
Procedure
- Streak Aspergillus nidulans conidia from frozen stock onto Minimal medium (MM) plate and cultivate for 3 days at 30 °C.
- Collect the formed conidia with a spreader.
- Spread Aspergillus nidulans conidia (1 x 105) onto MM plates and cultivate for 3 days at 30 °C.
- Inoculate the collected conidia (2 x 107) into 100 ml of MM in 500-ml Sakaguchi flasks.
- Shake the flasks at 126 rpm at 30 °C for 24 h.
- Collect the mycelial cells by paper filtration.
- Wash the cells twice with approximately 30 ml of distilled water.
Note: Cells can easily be crushed by wringing wet cells out to dry using a scoopula after this step as much as possible. - Grind cells (25 g of wet cells) into a fine powder in liquid nitrogen using a mortar and pestle.
- Resuspend the lysed cells in 100 ml of buffer A containing CompleteTM protease inhibitor cocktail (EDTA-free).
- Remove cell debris by centrifugation with an angle rotor at 10,000 x g for 10 min.
- Centrifuge the supernatant at 100,000 x g for 45 min using an ultracentrifuge.
- Resuspend the resultant pellet in 10 ml of buffer A containing 0.5% CHAPSO using a spatula.
Note: Pilot experiments are needed to determine the suitable conditions under which the detergents solubilize the target protein. - Gently mix the sample for 1 h using a rotator to obtain solubilized membrane proteins.
- Centrifuge the sample at 100,000 x g for 30 min using an ultracentrifuge.
- Collect the supernatant (approximately 10 ml) into a 15-ml plastic centrifuge tube.
- Add mouse-IgG-agarose (100 µl) to the supernatant and gently shake the mixture for 1 h (Video 1).
Video 1. Shaking the mixture using a rotator - Remove the mouse-IgG-agarose by centrifugation with a swing rotor at 1,400 x g for 10 min.
- Add 200 µl anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel to the supernatant and gently shake the resultant mixture for 1 h.
- Collect the Anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel by centrifugation with a swing rotor at 1,400 x g for 10 min.
- Gently remove the supernatant with an aspirator.
- Resuspend the resultant agarose with 15 ml of buffer A containing 0.1% CHAPSO.
- Repeat steps 18-20 five times.
- Elute GfsA protein with 20 µl of buffer A with 0.1% CHAPSO containing 0.5 µg/µl 3x FLAG peptide.
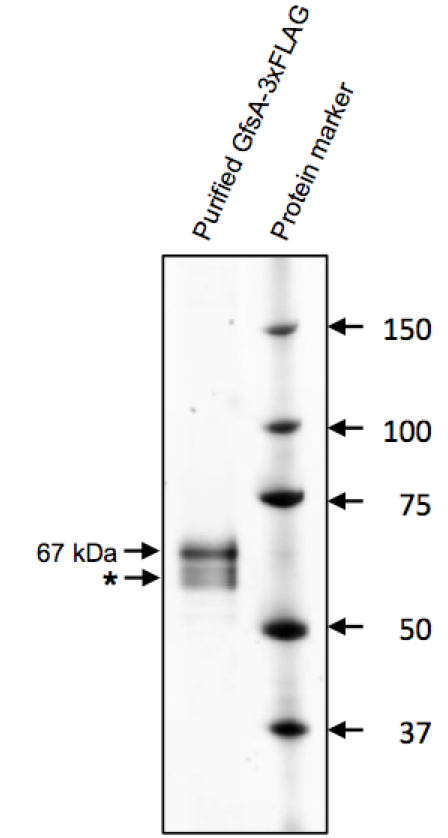
Figure 1. Purification of GfsA-3xFLAG protein. A total of 0.5 mg (silver staining) proteins were separated by 5%-20% SDS-PAGE, and were then assayed by silver staining. GfsA-3xFLAG was detected as a 67 kDa protein. Asterisk indicates a degradation product or insufficiently N-glycosylated product of GfsA-3xFLAG.
Notes
- Perform all manipulations on ice or at 4 °C.
Recipes
- Buffer A (1 L)Add water to bring the final solution to 1 L total volume
Compounds Amounts HEPES 11.9 g NaCl 5.84 g KCl 2.24 g MnCl2.4H2O 0.2 g Glycerol 50 g
Filter sterilize the solution using a 0.45 μm filter
Stored at 4 °C - Minimal medium (1 L)Adjust pH to 6.8 using NaOH
Compounds Amounts NaNO3 6.0 g KCl 0.52 g MgSO4.7H20 0.52 g KH2PO4 1.52 g Glucose 10.0 g Hutner's trace elements 2 ml
Add water to bring the final solution to 1 L total volume
Autoclave for 20 min - Hutner's trace elementsAdjust the pH value to 6.5-6.8 using KOH
Compounds Amounts H2O (60 °C) 100 ml ZnSO4.7H2O 2.2 g H3BO3 1.1 g MnCl2.4H2O 0.5 g FeSO4.7H2O 0.5 g CoCl2.6H2O 0.16 g CuSO4.5H2O 0.16 g (NH4) 6Mo7O24.4H2O 0.11 g EDTA 5.0 g
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from the previously published paper Komachi et al., 2013. The work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) from the Japan Society of the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (21780313, 23780350 and 26450106) (to T.O.).
References
- Komachi, Y., Hatakeyama, S., Motomatsu, H., Futagami, T., Kizjakina, K., Sobrado, P., Ekino, K., Takegawa, K., Goto, M., Nomura, Y. and Oka, T. (2013). GfsA encodes a novel galactofuranosyltransferase involved in biosynthesis of galactofuranose antigen of O-glycan in Aspergillus nidulans and Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol Microbiol 90(5): 1054-1073.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Oka, T., Katafuchi, Y., Fukuda, K., Ekino, K., Goto, M. and Nomura, Y. (2014). Purification of the GfsA-3x FLAG Protein Expressed in Aspergillus nidulans. Bio-protocol 4(17): e1222. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1222.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein > Isolation and purification
Biochemistry > Protein > Expression
Biochemistry > Protein > Labeling
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












