- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Assays of Polyphenol Oxidase Activity in Walnut Leaf Tissue
Published: Vol 4, Iss 16, Aug 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1213 Views: 22622
Reviewed by: Saminathan ThangasamyZhaohui LiuAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Semi-throughput Procedure for Assaying Plant NADP-malate Dehydrogenase Activity Using a Plate Reader
Kevin Baudry and Emmanuelle Issakidis-Bourguet
Aug 20, 2023 1508 Views

An in vitro Assay to Probe the Formation of Biomolecular Condensates
Yu Zhang and Shen Lisha
Sep 5, 2023 3261 Views

Immunofluorescence for Detection of TOR Kinase Activity In Situ in Photosynthetic Organisms
Ana P. Lando [...] Giselle M. A. Martínez-Noël
Dec 20, 2024 1859 Views
Abstract
Polyphenol oxidase (PPO) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of monophenols into ortho-diphenols (cresolase activity) and the oxidation of o-diphenols into quinones (catecholase activity) (Figure 1). These quinones spontaneously polymerize to form dark-colored phytomelanins, most often seen in the browning of damaged plant tissue. PPO activity can be easily assayed in crude protein extracts from English walnut (Juglans regia) leaves and from many other plant tissue extracts. PPO activity is most commonly measured by spectrophotometric assay, in which the rate of phytomelanin production is quantified, or by oxygen electrode assay, in which the consumption of oxygen by the enzyme is quantified (Figure 1). Though simpler, the utility of the spectrophotometric assay is limited by variation in the absorption maxima of phytomelanins generated from different phenolic substrates. The oxygen electrode assay is generally considered the “gold standard” for measurement of PPO activity, but it is more time consuming and difficult to implement with monophenol substrates, since cresolase activity is typically quite low compared to catecholase activity. This protocol will describe crude protein extraction from walnut leaves, the spectrophotometric assay, and the oxygen electrode assay for determining PPO activity.
Keywords: Polyphenol oxidase
Figure 1. The activity of the polyphenol oxidase enzyme
Materials and Reagents
- Protein extraction
- Juglans regia leaf tissue
- Liquid nitrogen
- Insoluble polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 25249-54-1 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 9048-46-8 )
- Bradford reagent (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 500-0006 )
- Tris base (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 77-86-1 )
- Citric acid monohydrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Acros Organics, catalog number: 5949-29-1 )
- Cysteine hydrochloride (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 7048-04-6 )
- Ascorbic acid (Phyto Technology Laboratories®, catalog number: 50-81-7 )
- Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 8000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 25322-68-3 )
- Glycerol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 56-81-5 )
- Protein extraction buffer (see Recipes)
- Juglans regia leaf tissue
- Spectrophotometric assay
- Catalase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 9001-05-2 )
- Kojic acid (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 501-30-4 )
- Monobasic dihydrogen sodium phosphate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 7558-80-7 )
- Dibasic monohydrogen sodium phosphate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 7558-79-4 )
- Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 151-21-3 )
- Sodium phosphate buffer containing phenolic substrate (see Recipes)
- Catalase (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 9001-05-2 )
- Oxygraph assay
- Kojic acid (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 501-30-4)
- Sodium phosphate buffer containing phenolic substrate (see Recipes)
- Assay buffer (see Recipes)
- Kojic acid (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 501-30-4)
Equipment
- Ceramic mortar and pestle
- 50 ml centrifuge tubes
- 30 ml Oak Ridge tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Nalgene®, catalog number: 3114-0030 )
- 1.5 ml microfuge tubes
- Spectrophotometer cuvettes or clear, flat bottom 96-well microtiter plates
- Micropipettes
- Vortexer
- Floor centrifuge with rotor that accommodates 30 ml Oak Ridge tubes
- Spectrophotometer or microplate reader (e.g. Molecular Devices SpectraMax M5)
- Oxygen electrode with computer interface (e.g. Hansatech Instruments, Oxygraph)
- -80 °C freezer
Procedure
- Crude protein extract
- Collect several leaves from sample tree and gently wash off dirt with deionized (DI) water, then pat completely dry.
- Seal leaves into 50 ml centrifuge tube and place in liquid nitrogen to flash freeze. Frozen leaf tissue may be stored at -80 °C.
- Grind tissue in a liquid nitrogen cooled mortar and pestle, being sure to keep adding liquid nitrogen to ensure the tissue does not thaw. A fine powder is desired.
- Add 6.0 ml of protein extraction buffer and 0.5 g of insoluble PVP to a 30 ml Oak Ridge tube. Place the tube on a balance and tare.
- Add ~1 g of ground, frozen leaf tissue to the tube. Tissue can be added using a liquid nitrogen cooled metal spatula, with mass read directly on the balance.
- Vortex the tissue slurry immediately to allow the frozen tissue to thaw in the presence of the buffer. Continue vortexing for 2 min.
- Centrifuge sample at 20,000 x g for 20 min at 4 °C.
- Aliquot ~200 µl volumes of the supernatant into 1.5 ml microfuge tubes and transfer the tubes to -80 °C for storage. (It is ideal to reduce freeze/thaw cycles so only the needed volume should be thawed at one time. If a sample is thawed three times, it should be discarded.)
- To determine total protein concentration, perform a Bradford assay according to the reagent manufacturer’s instructions with BSA standard concentrations of 25 µg/ml, 20 µg/ml, 12.5 µg/ml, 10 µg/ml, 5 µg/ml, and 1 µg/ml.
- Dilute the crude protein extract to 1/400 with ultrapure water for the Bradford assay. This dilution should be within the range of the BSA standards.
- Collect several leaves from sample tree and gently wash off dirt with deionized (DI) water, then pat completely dry.
- Spectrophotometric assay
- Prepare sodium phosphate buffer with phenolic substrate per recipe.
- Obtain protein samples from -80 °C and place on ice to thaw.
- Warm up the plate reader or spectrophotometer, setting at 490 nm (for tyrosine or L-DOPA substrates) and choosing the kinetic option. Read times range from 3 min (most diphenol substrates) to 3 h (many monophenol substrates). If using a plate reader, it should be set to read every two minutes, with shaking for 15 sec before each read. If using a spectrophotometer, it should be set to read every 15 sec. See notes on latency below.
- Determine the buffer quantity needed for the experiment (200 µl/well for plate reader or 1 ml/cuvette for spectrophotometer). 2-3 technical replicates of each sample are typically performed. In addition, parallel assays containing 1 mM Kojic acid should be performed. Kojic acid is a specific inhibitor of PPO, so these experiments provide a negative control, assuring that measured activity derives from PPO enzymes.
- Transfer the necessary buffer volume to a centrifuge tube and then add 280 Units of catalase per milliliter of buffer. The catalase eliminates any H2O2, preventing the activity of peroxidases, some of which also oxidize phenolic compounds.
- Aliquot buffer samples into a 96-well plate or a cuvette. If using the plate reader, be careful to avoid bubbles caused by the SDS since they can interfere with accurate readings. Bubbles are best avoided by placing the pipette tip against the wall of the well and steadily dispensing the buffer.
- Add desired volume of thawed, mixed protein extract to buffer (typically 5 µl per 200 µl of buffer).
- Place the plate/cuvette into the plate reader/spectrophotometer and begin the read. If using a spectrophotometer, the sample should be manually mixed between readings (with a pipet tip or stir stick) to aerate. Pre-programmed shaking provides aeration in the plate reader. Given that the reaction catalyzed by PPO enzyme consumes oxygen (Figure 1), aeration is important to ensure adequate oxygen availability and thus accurate activity data.
- Typical PPO activity data (plate reader assay, tyrosine substrate) is provided in Figures 2 and 3.
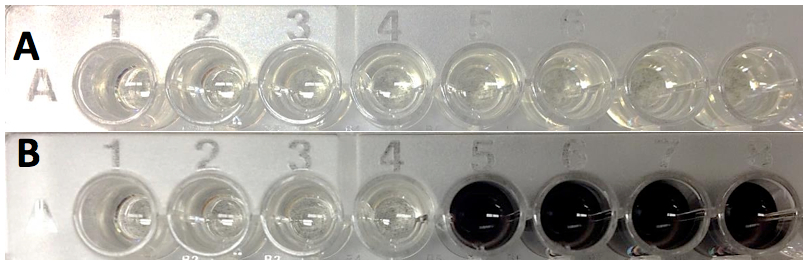
Figure 2. Spectrophotometric PPO activity assay using a microplate reader. A. Assay at time 0 (just after addition of protein extract). B. Assay after two hours. All wells contain tyrosine (4 mM) as substrate. Wells 1-4 also contain 1 mM kojic acid, a PPO inhibitor.
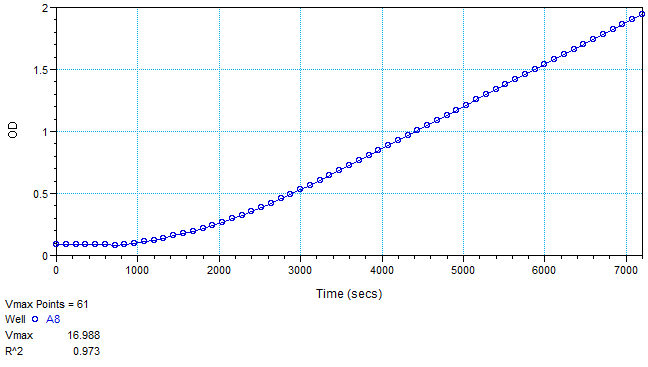
Figure 3. Sample data (Abs490) of well A8 from Figure 2
- Prepare sodium phosphate buffer with phenolic substrate per recipe.
- Oxygen electrode assay
- Prepare sodium phosphate buffer with substrate solution as per recipe.
Note: Omit catalase in this assay since the catalase can substantially alter dissolved oxygen levels and give inaccurate data. This makes Kojic acid controls especially critical.
- Obtain protein samples from -80 °C and place on ice to thaw.
- Set up and calibrate the oxygen electrode apparatus according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Pipette 1 ml (may vary depending on equipment) of buffer into the oxygen electrode chamber.
- Pipette desired volume of crude protein extract (typically 25 µl) into the chamber and seal.
- Measure oxygen consumption. Assay time can range from 10 min-4 h. Monophenol substrates typically require long measurement times due to relatively low activity and long PPO latency times.
- Prepare sodium phosphate buffer with substrate solution as per recipe.
- Calculating PPO enzyme activity
- For spectrophotometric and plate reader assays, calculate change in Abs490/min/mg total protein. Calculate based on initial rate of takeoff because the quinone products of PPO activity will oxidize proteins (including PPO), thus reducing activity over time.
- For oxygen electrode assay, calculate nmoles O2 consumed per milliliter per minute per mg total protein. Again, calculate based on initial rate using software to obtain nmol/ml/min value and then dividing by the amount of protein that was added to the sample in mg.
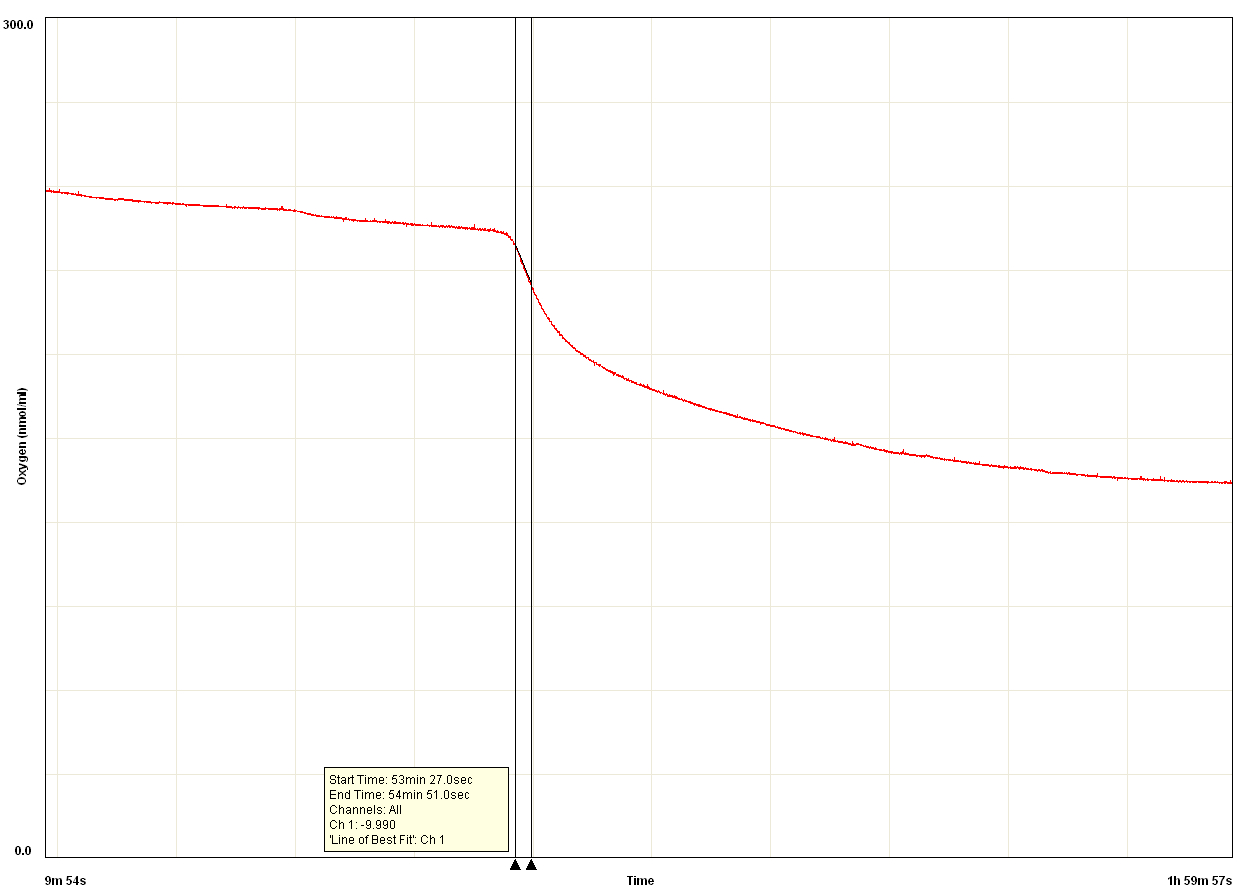
Figure 4. PPO activity data measured using an oxygen electrode. After a latent period of ~50 min, rapid oxygen consumption commenced. PPO activity was calculated based on this initial rapid rate of oxygen consumption (slope between the two black vertical lines). The rate slows over time due to oxidative damage of proteins (including PPO) caused by the product quinones. X axis is oxygen concentration (nmol/ml), Y axis is time elapsed.
- For spectrophotometric and plate reader assays, calculate change in Abs490/min/mg total protein. Calculate based on initial rate of takeoff because the quinone products of PPO activity will oxidize proteins (including PPO), thus reducing activity over time.
Notes
- Most or all plant PPOs have a characterized property of latency (a time lag before full enzyme activity) which may affect the way tests are conducted. In walnut tissue extracts, PPO has shown latency from a few minutes to a few hours, depending on the substrate. Latency is substantially longer when using monophenol substrates than when using diphenol substrates. The inclusion of SDS in the assay buffer is designed to minimize latency.
- When performing the spectrophotometric assay with substrates other than L-DOPA and tyrosine, alternative absorbance wavelengths may be preferable for measuring activity. A wavelength scan can be used to determine the absorbance maximum for phytomelanins derived from other substrates.
- Although walnut PPO displays both cresolase and catecholase activities, many plant PPOs display catecholase activity only (i.e. they can only act upon diphenol substrates). As such, initial assays are preferably performed using a diphenol substrate such as L-DOPA to assure that PPO activity is present. Later studies can evaluate whether the examined PPO also possesses cresolase activity.
Recipes
- Protein extraction buffer (pH 8.3)
- 6.5 g/L tris base
- 1.5 g/L citric acid monohydrate
- 1.0 g/L cysteine hydrochloride
- 1.0 g/L ascorbic acid
- 10.0 g/L PEG 8000
- 110 ml/L glycerol
- Ultrapure water to volume
Mix components well and adjust to pH to 8.3 with KOH or HCl
May be stored at 4 °C up to one week
- 6.5 g/L tris base
- Assay buffer (pH 7.0)
- 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) (monobasic dihydrogen sodium phosphate; dibasic monohydrogen sodium phosphate)
- 0.15% SDS
- 4 mM phenolic substrate
- Ultrapure water to volume
- Negative control samples only: 1 mM Kojic acid
Amount of monobasic and dibasic sodium phosphate is calculated using the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation. A 1 M sodium phosphate buffer stock solution (pH 7.0) can be made by combining 57.7 ml of 1 M Na2HPO4 and 42.3 ml of 1 M NaH2PO4. This stock can be diluted to make the assay buffer above. See Reference 4.
Note: The solubility of some phenolic substrates may not allow a substrate concentration of 4 mM.
- 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) (monobasic dihydrogen sodium phosphate; dibasic monohydrogen sodium phosphate)
Acknowledgments
Protocols for the spectrophotometric assay of PPO activity were adapted from Constabel and Ryan (1998). This work was supported in part by a University of California/California State University Collaborative Research Grant.
References
- Constabel, C. P. and Ryan, C. A. (1998). A survey of wound-and methyl jasmonate-induced leaf polyphenol oxidase in crop plants. Phytochemistry 47(4): 507-511.
- Escobar, M. A., Shilling, A., Higgins, P., Uratsu, S. L. and Dandekar, A. M. (2008). Characterization of polyphenol oxidase from walnut. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 133(6): 852-858.
- Lucia, V., Mesquita, V. and Queiroz, C. (2013). Chapter 10 - Enzymatic Browning. In: Eskin, N. A. M. and Shahidi, F. (eds). Biochemistry of Foods (Third Edition). Academic Press, 387-418.
- Sambrook, J., Russell, D. W. (2001). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (3rd ed.) Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
- Stewart, R. J., Sawyer, B. J., Bucheli, C. S. and Robinson, S. P. (2001). Polyphenol oxidase is induced by chilling and wounding in pineapple. Funct Plant Biol 28(3): 181-191.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Gertzen, R. and Escobar, M. A. (2014). Assays of Polyphenol Oxidase Activity in Walnut Leaf Tissue. Bio-protocol 4(16): e1213. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1213.
- Araji, S., Grammer, T. A., Gertzen, R., Anderson, S. D., Mikulic-Petkovsek, M., Veberic, R., Phu, M. L., Solar, A., Leslie, C. A., Dandekar, A. M. and Escobar, M. A. (2014). Novel roles for the polyphenol oxidase enzyme in secondary metabolism and the regulation of cell death in walnut. Plant Physiol 164(3): 1191-1203.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Plant Science > Plant metabolism > Phenolics
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










