- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Catalase Activity Assay in Candida glabrata
Published: Vol 4, Iss 6, Mar 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1072 Views: 19910
Reviewed by: Fanglian HeAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Measurement of Energy-dependent Rhodamine 6G Efflux in Yeast Species
Yvetta Gbelska [...] Alexandra Konecna
Aug 5, 2017 8952 Views

An Assay to Determine NAD(P)H: Quinone Oxidoreductase Activity in Cell Extracts from Candida glabrata
Anamika Battu [...] Rupinder Kaur
Nov 5, 2021 3055 Views

Isolation of Mitochondria from Ustilago maydis Protoplasts
Juan Pablo Pardo [...] Lucero Romero-Aguilar
Jan 5, 2022 3578 Views
Abstract
Commensal and pathogenic fungi are exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) produced by macrophages of the host. Pathogenic fungi counteract the harmful effects of H2O2 with the enzyme catalase (EC 1.11.1.6), which decomposes two molecules of H2O2 to two molecules of H2O and O2. Contribution of antioxidant systems on fungal virulence is actively studied. Measurement of catalase activity can contribute to the elucidation of the factors that influence the regulation of this pivotal enzyme. Here we describe a simple spectrophotometric method in which the activity of catalase is measured in total yeast extracts. Decomposition of H2O2 by the yeast extract is followed by the decrease in absorbance at 240 nm. The difference in absorbance through time (ΔA240) is inferred as the measure of catalase activity.
Keywords: CatalaseMaterials and Reagents
- Yeast strains
Note: BG14 was used as the C. glabrata parental strain. The hst1Δ and the cta1Δ null mutants were used as a positive and the negative controls, respectively. - Catalase from bovine liver (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C9322 )
- Bradford reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: B6916 )
- Bovine serum albumin - fraction V (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 85040C )
- Zirconia/silica beads (0.5 mm diameter) (Bio Spec Products, catalog number: 11079105z )
- Sterile water
- Ice
- One tablet of protease inhibitors cOmplete ULTRA Mini EASYpack is used in 10 ml of phosphate buffer (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 05 892 970 001 )
- H2O2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 349887 )
- Catalase lyophilized powder (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C9322)
- YPD broth (see Recipes)
- 50 mM Phosphate buffer (PB) (pH 7.0) (see Recipes)
- 30 mM H2O2 (see Recipes)
- Catalase solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Orbital incubator shaker
- Microfuge tubes
- 50 ml conical tubes
- Corning 96 well clear flat bottom (Corning, catalog number: 3595 )
- Standard 10 mm light path quartz cuvette with PTFE cover
- UV/Vis Spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, model: UV-1700 , catalog number: 206-55401-92)
- Microplate spectrophotometer system (Benchmark Plus Microplate reader) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 170-6931 )
- Centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Allegra® 25R, catalog number: 369464 )
- Microfuge
- Stopwatch
- Parafilm
Procedure
- Preparation of total soluble extracts
- Yeast strains are grown overnight in 5 ml of Yeast extract-Peptone-Dextrose broth or selective media at 30 °C.
- Dilute overnight cultures in 50 ml of fresh medium in order that after seven duplications, the yeast cultures reach an OD600 = 0.5 at 30 °C.
- Centrifuge the cells for 5 min at 2,600 x g. Discard supernatant. Temperature of centrifuge is not relevant.
- Wash the cells with 25 ml of sterile water and discard supernatant.
- Resuspend the cells in 0.5 ml PB with protease inhibitors and transfer to a microfuge tube. Keep the samples on ice.
- Add 50 µl of zirconia/silica beads to each sample.
- Disrupt the cells by vortexing at maximum speed for 1 min and place on ice for another minute. Repeat 20 times.
- Centrifuge the lysate at 25,000 x g for 30 min at 4 °C to remove cell debris and zirconia/silica beads
- Transfer supernatant to a clean microfuge tube. At this point, lysates are ready for quantification of total protein and measurement of catalase activity. Alternatively, samples can be stored at -20 °C.
- Yeast strains are grown overnight in 5 ml of Yeast extract-Peptone-Dextrose broth or selective media at 30 °C.
- Bradford assay for protein quantitation
- Fill the wells of a microplate with 250 µl of Bradford regent.
- Prepare a standard curve of absorbance versus nanograms of protein using fresh BSA standards (100, 200, 400, 600, 800 ng/µl). Use PB as solvent.
- Dilute the lysates 1:20 or 1:50 with sterile water.
- Load 5 µl of the standards and diluted lysates to the Bradford reagent. Incubate room temperature for 5 min.
- Measure the absorbance at OD595 in a microplate spectrophotometer.
- Determine the amount of protein of the samples from the standard curve. Consider the dilution factor.
- Fill the wells of a microplate with 250 µl of Bradford regent.
- Catalase activity assay
- Set up the spectrophotometer by first turning on the instrument and then the UV light. Set up a kinetics program to record every 30 s at a wavelength of 240 nm for 2 min.
- Calibrate the spectrophotometer using 3 ml of PB in a 3-ml quartz cuvette as a blank.
- Dilute the lysate samples 1:50 with PB.
- In a quartz cuvette, mix 1 ml PB with 1 ml of the diluted sample. To begin the assay, add 1 ml of the H2O2 solution (H2O2 to a final concentration of 10 mM). The initial absorbance must be between 0.550 and 0.520. If necessary, add H2O2 to increase the absorbance and Phosphate Buffer to decrease the absorbance.
- Mix the content by inversion and Immediately place the cuvettes into the spectrophotometer. Follow the decrease in absorbance at OD240 with a stopwatch for 2 min.
- A catalase solution must be used as a control. Pippete 2.9 ml of PB in the cuvette, add 1 ml 30 mM H2O2 and 100 µl of the catalase solution (~10 units). Record the initial and final absorbance in a one-minute period. Use 2 ml of PB and 1 ml of 30 mM H2O2 as blank.
- Calculate the catalase activity using the following formula (Cuellar-Cruz et al., 2009)
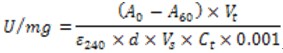
Where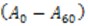 is the difference between the initial and final absorbance.
is the difference between the initial and final absorbance. is the total volume of the reaction (3 ml).
is the total volume of the reaction (3 ml). is the molar extinction coefficient for H2O2 at OD240 (34.9 mol-1 cm-1).
is the molar extinction coefficient for H2O2 at OD240 (34.9 mol-1 cm-1). is the optical length path of cuvette (1 cm).
is the optical length path of cuvette (1 cm). is the volume of the sample in ml.
is the volume of the sample in ml. is the protein concentration of the sample in mg/ml.
is the protein concentration of the sample in mg/ml. - Example of catalase activities of extracts from C. glabrata strains in exponential phase of growth:
Note: Catalase activity of the BG14 strain is higher in stationary phase ≈ 10 U/mg. However catalase activity of a cta1Δ is always < 2 U/mg or undetectable.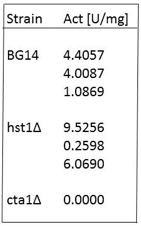
- Set up the spectrophotometer by first turning on the instrument and then the UV light. Set up a kinetics program to record every 30 s at a wavelength of 240 nm for 2 min.
Notes
- For catalase, the dependence of the H2O2 decomposition on temperature is small, so measurements can be carried out between 0 and 37 °C, however 20 °C is recommended.
- For the catalse assay, each test cuvette will need to be run one at a time, so do not prepare the next test cuvette until the run with the preceding cuvette is complete.
- Low concentrations of H2O2 are used to avoid bubbling.
- Mixing of the samples can be facilitated by the use of parafilm.
Recipes
- Yeast extract-Peptone-Dextrose broth (1 L)
Dissolve 10 g yeast extract and 20 g peptone in 950 ml of distilled water
Autoclave (121 °C, 15 lb/in2 for 15 min)
Add 50 ml 40% (w/v) dextrose (2% final; sterilized separately by autoclaving or filtering) - 50 mM Phosphate Buffer (PB) (pH 7.0) (1 L)
Dissolve 2.724 g KH2PO4 in 400 ml of distilled water
Dissolve 5.34 g Na2HPO4 in 600 ml of distilled water
Mix solutions [proportion (1:1.5)]
pH to 7.0 with 1 M KOH
To obtain cell lysates, prepare 10 ml of PB and add one tablet of cOmplete protease inhibitors. - 30 mM H2O2 (100 ml)
Dilute 0.26 ml of 35% H2O2 with PB to 100 ml. Prepare fresh to each activity assay. The solution can be at room temperature during the experiment. - Catalase solution
Dissolve 10 mg of catalase lyophilized powder in 1 ml of cold PB
Immediately before use, dilute 5 µl of catalase solution to 1 ml cold PB to obtain a solution with ~100 U/ml. Stored at -20 °C for 6 months.
Acknowledgments
This protocol is based on the methodology reported by Aebi (1984), and by Weydert and Cullen (2010). Our adapted method was first published in Cuellar-Cruz et al. (2009). This work was funded by a CONACYT grant no. CB-2010-153929 to A.D.L.P. Finally, we thank Guadalupe Gutierrez-Escobedo for technical assistance.
References
- Aebi, H. (1984). Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105: 121-126.
- Cuellar-Cruz, M., Castano, I., Arroyo-Helguera, O. and De Las Penas, A. (2009). Oxidative stress response to menadione and cumene hydroperoxide in the opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida glabrata. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104(4): 649-654.
- Weydert, C. J. and Cullen, J. J. (2010). Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat Protoc 5(1): 51-66.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Orta-Zavalza, E., Briones-Martin-del-Campo, M., Castano, I. and Penas, A. D. L. (2014). Catalase Activity Assay in Candida glabrata. Bio-protocol 4(6): e1072. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1072.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Other compound > Reactive oxygen species
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










