- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Intestinal Differentiation of Human ESCs
Published: Vol 3, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1010 Views: 8658
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Differentiation, Maintenance, and Contraction Profiling of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Cardiomyocytes
Matthijs Snelders [...] Jeroen Essers
Mar 5, 2025 3921 Views

Isolation and Culture of Ferret Airway Stem Cells
Ziying Yan [...] Feng Yuan
Jul 20, 2025 2412 Views

Optimization of Adipogenic Differentiation Protocol for Murine and Human Cell Culture Models
Junwan Fan [...] Wenyan He
Jan 20, 2026 222 Views
Abstract
ES cells (ESCs) are pluripotent and offer a good tool to study early embryonic development. Intestinal cells are derived from the definitive endoderm. In contrast to adult tissue stem cells, embryonic development and differentiation from ES cells have not been as well investigated in the intestine. There are four differentiated cell types of non-proliferative epithelial cells: enterocytes, goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells, and Paneth cells. Intestinal stem cells (ISCs) and progenitor cells reside in crypts, proliferate vigorously, and function as the source of differentiated epithelial cells. Here, we describe a protocol, in which differentiated cell types of the intestine are derived from human ESCs. In this protocol, we describe a protocol to differentiate mouse ES cells into Cdx2-expressing intestinal endoderm efficiently by co-culturing with M15, a mouse mesonephric cell line, and treatment with two chemical compounds. The chemical compounds used are BIO and DAPT. BIO is a Gsk3 inhibitor, that activate Wnt signaling pathway, and DAPT is a-secretase inhibitor that inhibit Notch signaling pathway. BIO and DAPT treatment yielded all representative cell lineages, enterocytes, goblet cells, enteroendocrine cells and paneth cells, to be derived from human ESCs. The protocol for human ESCs is principally very similar with that for the mouse ESCs, with some modifications.
Keywords: IntestineMaterials and Reagents
- Human embryonic stem cells (ESCs)
- M15 cells (ECACC, catalog number: 95102517 )
- Mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF)
- 0.1% gelatin
- PBS
- Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) high glucose (Gibco®, catalog number: 11995-075 )
- DMEM low glucose (Gibco®, catalog number: 11885-084 )
- KnockOut DMEM/F12 (Gibco®, catalog number: 12660-012 )
- RPMI1640 (Gibco®, catalog number: 11875-093 )
- Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) (Hyclone, catalog number: SH30310.03 )
- 200 mM L-glutamine (L-Gln) (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 16948-04 )
- 5,000 units/ml mixture of penicillin and streptomycin (PS) (Nacalai Tesque, catalog number: 26252-94 )
- 10 mM MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids Solution (NEAA) (Gibco®, catalog number: 11140-050 )
- 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M7522 )
- D-(+)-Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5146 )
- KnockOut Serum Replacement (KSR) (Gibco®, catalog number: 10828 )
- B27 supplements (Gibco®, catalog number: 17504044 )
- Recombinant human Activin A (R&D Systems, catalog number: 338-AC )
- Recombinant human bFGF (Pepro Tech, catalog number: 100-18B )
- BIO (Calbiochem®, catalog number: 361550 )
- DAPT (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 041-30983 )
- Y-27432 (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 688000 )
- Mitomycin C (MMC) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4287 )
- 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA (Life Technologies, catalog number: 2014-11 )
- 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (Life Technologies, catalog number: 25200-072 )
- EF medium (see Recipes)
- hESC Medium (see Recipes)
- EB medium (see Recipes)
- hESCs Endoderm Medium (see Recipes)
- Intestinal Medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 24 well plate (Corning, catalog number: 3526 )
- 10 mm dish (Corning, catalog number: 430167 )
- 60 mm dish (BD Biosciences, Falcon®, catalog number: 353004 )
- Centrifuge
- 37 °C 5% CO2 Cell culture incubator
Procedure
- Preparation of M15 cells
- 5x106 M15 cells are plated to a 100 mm dish with 10 ml EF medium.
- M15 cells are incubated in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C.
- When M15 cells are confluent (for 2-3 days), passage from a 100 mm dish to five 100 mm dishes.
- M15 cells are washed by PBS.
- M15 cells are trypsinized with 1 ml 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA at 37 °C for 5 min.
- M15 cells are pelleted at 190 x g for 5 min.
- M15 cells are plated to five 100 mm dishes.
- M15 cells are washed by PBS.
- When M15 cells are confluent, M15 cells are incubated with 10 μg/ml MMC containing EF medium in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 2 h to stop M15 cell from proliferation.
- MMC-treated M15 cells are washed by PBS.
- MMC-treated M15 cells are trypsinized with 1 ml 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA at 37 °C for 5 min.
- M15 cells are pelleted at 190 x g for 5 min.
- Resuspend and freeze MMC-treated M15 cells into cryovials with 22% FBS and 20% DMSO containing DMEM at 1 x 107 cells per tube at -150 °C.
- 5x106 M15 cells are plated to a 100 mm dish with 10 ml EF medium.
- Preparation of MEF
- MEF (5x106) are plated to a 100 mm dish with 10 ml EF medium.
- MEF are incubated in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C.
- When MEF are confluent (for 2-3 days), passage from a 100 mm dish to five 100 mm dishes.
- MEF are washed by PBS.
- MEF are trypsinized with 1 ml 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA at 37 °C for 5 min.
- MEF are pelleted at 190 x g for 5 min.
- MEF cells are plated to five 100 mm dishes.
- MEF are washed by PBS.
- When MEF cells are confluent, MEF are incubated with 10 μg/ml MMC containing EF medium in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C for 2 h. MEF are treated with MMC to stop M15 cell from proliferation.
- MMC-treated MEF are washed by PBS.
- MMC-treated MEF are trypsinized with 1 ml 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA at 37 °C for 5 min.
- M15 cells are pelleted at 190 x g for 5 min.
- Resuspend and freeze MMC-treated M15 cells into cryovials in 22% FBS and 20% DMSO containing DMEM at 2 x 106 cells per tube at -150 °C.
- MEF (5x106) are plated to a 100 mm dish with 10 ml EF medium.
- Maintenance of human ESCs
- 1 x 105 MMC-treated MEF cells are plated to a gelatin-coated 60 mm dish with EF medium.
Note: Lower number of MEF cells is used compared to that of the mouse ESCs.
- MMC-treated MEF cells are incubated in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C overnight.
- 5x106 Human ESCs are plated on MEF-coated dish with hESC Medium in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C (day 0), until passage (4-7 days).
- Medium is changed daily.
- 1 x 105 MMC-treated MEF cells are plated to a gelatin-coated 60 mm dish with EF medium.
- Intestinal differentiation of human ESCs
- 1 x 107 MMC-treated M15 cells are plated to two gelatin-coated 24 well plates in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C overnight.
- ESCs plated on MEF-coated dishes (step C3) are treated hESC Medium with 10 μM Y-27632, which is a ROCK inhibitor and is added to inhibit apoptosis, in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C overnight (day 1).
- ESCs are washed by PBS.
- ESCs are trypsinized with 1 ml 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA at 37 °C for 5 min.
- ESC cells are pelleted at 190 x g for 5 min.
- The supernatant is removed and 1 x 106 cells/ml resuspended in EB medium.
- 5 x 104 ESCs in 500 μl EB medium are plated to a M15-pre-coated well (day 0).
- Medium is changed to hESCs Endoderm Medium at day 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9.
Note: Human ES cells-derived definitive endodermal induction is different with that of the mouse ESCs.
- Medium is changed to 2 ml Intestinal Medium at day 10.
- Medium is changed with 2 ml Intestinal Medium at every two days (Figure 1).
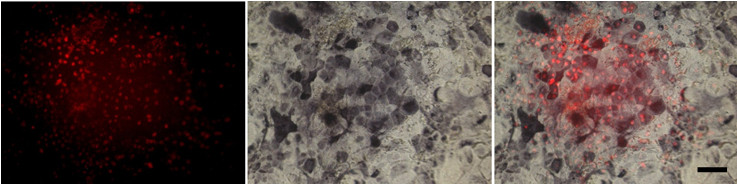
Figure 1. Human ESC-derived enterocyte at day 30. Cells expressing the intestinal transcription factor CDX2 are stained positive for alkaline phosphatase (ALP), a marker for the absorptive enterocytes. Red: CDX2, Black: ALP. Scale bar indicates 100 μm.
- 1 x 107 MMC-treated M15 cells are plated to two gelatin-coated 24 well plates in the 5% CO2 incubator at 37 °C overnight.
Recipes
- EF medium
DMEM high glucose containing 10% FBS
2 mM L-Gln
50 units/ml PS
- hESC Medium
DMEM/F12 containing 20% FBS
2 mM L-Gln
50 units/ml PS
100 μM NEAA
100 μM 2-ME
5 ng/ml bFGF
- EB medium
DMEM high glucose containing 10% FBS
2 mM L-Gln
50 units/ml PS
100 μM NEAA
100 μM 2-ME
- hESCs Endoderm Medium
RPMI1260 with 100 ng/ml Activin A
2% B27 supplements
2 mM L-Gln
50 units/ml PS
100 μM NEAA
100 μM 2-ME
- Intestinal Medium
DMEM low glucose with 1 mg/ml D-(+)-Glucose
10% KSR
2 mM L-Gln
50 units/ml PS
100 μM NEAA
100 μM 2-ME
5 μM BIO
10 μM DAPT
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from Ogaki et al. (2013). This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid (#21390280 to S.K. and #21790671 to N.S.), and in part by a Global COE grant (Cell Fate Regulation Research and Education Unit, to S.K.), and a grant from the Project for Realization of Regenerative Medicine from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) Japan.
References
- Ogaki, S., Shiraki, N., Kume, K. and Kume, S. (2013). Wnt and Notch signals guide embryonic stem cell differentiation into the intestinal lineages. Stem Cells 31(6): 1086-1096.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Ogaki, S. and Kume, S. (2013). Intestinal Differentiation of Human ESCs. Bio-protocol 3(24): e1010. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1010.
Category
Stem Cell > Embryonic stem cell > Maintenance and differentiation
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell differentiation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link