- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Influenza Virus-cell Fusion Inhibition Assay
Published: Vol 3, Iss 24, Dec 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1004 Views: 11390
Reviewed by: Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Micro Neutralization (MN) Assay of Influenza Viruses with Monoclonal Antibodies
Ying Wu [...] Ruben O. Donis
Jun 5, 2016 16177 Views

Nab Escaping AAV Mutants Isolated from Mouse Muscles
Zheng Chai [...] Chengwen Li
May 5, 2018 7593 Views

Intestinal Enteroid Culture for Human Astroviruses
Irene A. Owusu [...] Abimbola O. Kolawole
Jul 20, 2020 4768 Views
Abstract
During viral infection to host cells, several viruses undergo the process of endocytosis and pH-dependent fusion. By fusion of viral membrane with host cellular membrane, the viral core invades to host cytoplasm. A part of monoclonal antibodies against viral membrane protein have potential to inhibit the viral fusion step. Here we describe in vitro influenza virus-cell fusion inhibition assay. The infected cells expressing viral membrane protein, such as hemagglutinin (HA), on cellular surface are incubated with monoclonal antibodies targeting viral membrane protein. Then the cells are incubated under low pH condition. If the antibody does not inhibit the fusion step, we can see multinucleated giant cells.
Keywords: EndocytosisMaterials and Reagents
- Monkey kidney cell line CV-1 cells
- MDCK-propagated Influenza B viruses (B/Florida/4/2006 and B/Malaysia/2506/2004) provided by the National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Japan
- Minimal Essential Medium (MEM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4655 )
- Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 2917054 )
- Phosphate buffered saline without Ca2+ and Mg2+ (PBS)
- Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium F12 (DMEMF12) (Life Technologies, catalog number: 11320-033 )
- Acetylated trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6763 )
- Giemsa stain solution (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 079-04391 )
- Methanol (Nacalai tesque, catalog number: 21915-93 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9576 )
- Specific pathogen
- Monoclonal antibody
- MEM powder (Nisshin EM, catalog number: 05901 )
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- MES (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 344-08351 )
- Fusion medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 96-well cell culture plate (Corning, catalog number: 3596 )
- CO2 incubator (37 °C, 5% CO2)
- Light microscope
Procedure
- (Day 1) CV-1 cells in 100 μl MEM including 10% FBS are passaged to 96-well plate at 2.5 x 105/ml and incubated in the CO2 incubator for 24 h.
- (Day 2) The cells are rinsed with 100 μl PBS once, adsorbed with 50 μl viruses in MEM at an MOI of 0.3 for 1 h in the CO2 incubator.
- The cells are rinsed with 100 μl PBS once, added 100 μl DMEMF12 including 0.2% BSA and incubated for 24 h in the CO2 incubator.
- (Day 3) The cells are rinsed with 100 μl MEM twice.
- The cells in 100 μl MEM including 2.5 μg/ml acetyrated trypsin are incubated in the CO2 incubator for 15 min.
- They are rinsed with 100 μl MEM twice.
- 50 μl MEM containing different concentration of monoclonal antibody (concentration is 100, 25, 6.25, 1.5, 0.4 and 0.1 μg/ml) is incubated with the cells in different wells for 30 min in the CO2 incubator.
- After aspiration of medium, 100 μl fusion medium with each of pH is added and then incubated for 2 min in the CO2 incubator.
- The cells are rinsed with 100 μl MEM twice.
- The cells are suspended with 100 μl DMEMF12 including 0.2% BSA and incubated in the CO2 incubator for 3 h.
- After aspiration of medium, the cells are fixed using 100 μl absolute methanol for 30 sec.
- After aspiration of methanol, the cells are stained with 100 μl diluted Giemsa staining solution (1 drop per ml dH2O) for 30 min at room temperature.
- After rinsing the cells on tap water, the cells are observed by microscope (Figure 1).
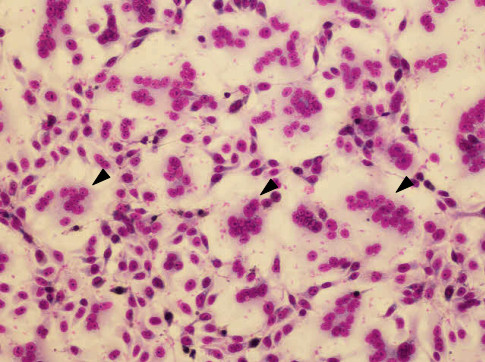
Figure 1. Giemsa staining of CV-1 cells in fusion inhibition assay. Arrow heads show multinuclear giant cells.
Recipes
- Fusion medium
Mix 2x MEM with 10 mM MES and 10 mM HEPES
Adjust to pH 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5 and 7.0
Mess up to 1x MEM
Autoclaved
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Japan Science and Technology Agency/Japan International Cooperation Agency, Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (JST/JICA, SATREPS) (http://www.jst.go.jp/global/kadai/h2011_thailand.html); and a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to MY (#23790660).
References
- Yasugi, M., Kubota-Koketsu, R., Yamashita, A., Kawashita, N., Du, A., Sasaki, T., Nishimura, M., Misaki, R., Kuhara, M., Boonsathorn, N., Fujiyama, K., Okuno, Y., Nakaya, T. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Human monoclonal antibodies broadly neutralizing against influenza B virus. PLoS Pathog 9(2): e1003150.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Yasugi, M. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Influenza Virus-cell Fusion Inhibition Assay. Bio-protocol 3(24): e1004. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1004.
- Yasugi, M., Kubota-Koketsu, R., Yamashita, A., Kawashita, N., Du, A., Sasaki, T., Nishimura, M., Misaki, R., Kuhara, M., Boonsathorn, N., Fujiyama, K., Okuno, Y., Nakaya, T. and Ikuta, K. (2013). Human monoclonal antibodies broadly neutralizing against influenza B virus. PLoS Pathog 9(2): e1003150.
Category
Immunology > Host defense > General
Immunology > Antibody analysis > Antibody function
Cell Biology > Cell-based analysis > Cytosis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











