Advanced Search
Heat Induced Epitope Retrieval (HIER) Assisted Protein Immunostaining in Maize
Published: Jun 5, 2019 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3260 Views: 3479
Edited by: Marisa Rosa Reviewed by: Annis Elizabeth Richardson
Abstract
Protein immunostaining provides important spatio-temporal information about gene expression. Even using high quality antibodies, signal reproducibility and specificity can be problematic depending on tissue fixation methods. For example, formaldehyde fixed tissues often require an epitope retrieval step to expose epitopes of interest for binding to antibodies. One way to achieve this is by using Proteinase K-assisted partial protein degradation (Smith, 1994). However, this process can often reduce, or even abolish immunostaining signals. Here we provide an alternative protocol employing heat induced epitope retrieval (HIER) that gives an improved performance for signal detection (Figure 1).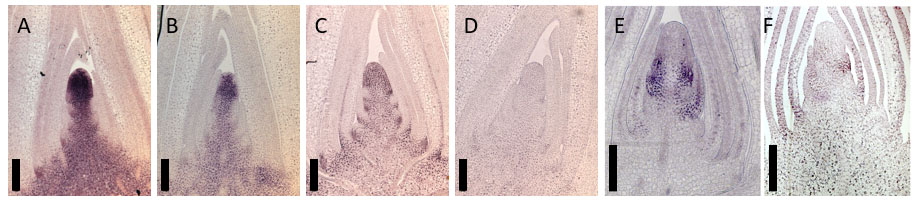
Figure 1. Comparison of HIER and ProK-assisted epitope retrieval. Immunolocalization images detected using anti-KN1 (A and B), anti-BLH14 antibodies (C and D) and anti-TSH4 (E and F). Tissue sections are subjected to HIER (A, C and E) or Proteinase K (B, D and F)-assisted epitope retrieval. For the Proteinase K treatment, slides are incubated in 1x PBS buffer containing 20 μg/μl of Proteinase K for 30 min at room temperature instead of HIER (Procedure B). Bars are 200 μm.
Materials and Reagents
- Consumables
- Paper towels
- Saran wrap
- Tupperware (e.g., 15 cm x 25 cm x 5 cm for 10 slides laid flat on the bottom. See Figure 4.)
- Glass slides (Probe-on-Plus slides) (Fisher, catalog number: 22-230-900)
- Cover slips
- Biological material
Tissue sections (~10 μm thickness) of maize vegetative shoot apices, fixed in FAA (see Recipes)
under vacuum and embedded in paraplast plus, on glass slides. - Reagents
- Distilled water
- Ethanol (99.5) (Wako, catalog number: 054-07225)
- Ethanol solutions (Dilute ethanol (99.5) to 95, 85, 70, and 50% distilled water. Stored at RT)
- Histoclear (National Diagnostics, catalog number: HS-202)
- Trisodium citrate dihydrate (C6H5Na3O7·2H2O) (Wako, catalog number: 191-01785)
- Citric acid monohydrate (C6H8O7·H2O) (Wako, catalog number: 033-20155)
- Sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate (Na2HPO4·7H2O) (Wako, catalog number: 592-11065)
- Potassium Dihydrogen Phosphate (KH2PO4) (Wako, catalog number:169-04245)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Wako, catalog number:192-10745)
- Potasium chloride (KCl) (Wako, catalog number:163-03545)
- 1x phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, dilute 10x PBS with distilled water)
- BSA (Bovine serum albumin) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9418-100G)
- Triton X-100 (Wako, catalog number: 590-18624)
- 2-Amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol (Tris) (Wako, catalog number: 204-07885)
- Magnesium chlorate (MgCl2) (Wako, catalog number: 136-03995)
- Ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt Dihydrate (2NA) (EDTA) (Wako, catalog number: 345-01865)
- Primary antibody [Affinity purified KNOTTED1 (KN1), BELL1-like homeobox 14 (BLH14), and TASSELSHEATH4 (TSH4) polyclonal rabbit antibodies] (Chuck et al., 2010; Tsuda et al., 2017)
- Secondary antibody (Alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody, Abcam, catalog number: ab97048)
- NBT-BCIP developing reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 11681451001)
- Non-aqueous mounting medium Eukitt (ORS, 6.00.01.0001.04.01.EN)
- Glacial acetic acid (Wako, catalog number: 516-33981)
- 37% Formaldehyde solution (Wako, catalog number: 063-04815)
- 10 mM Sodium Citrate buffer pH 6.0 (see Recipes, store at 4 °C)
- 10x PBS buffer (Phosphate buffered saline) (see Recipes, store at RT)
- TNM buffer (see Recipes, store at RT)
- TE buffer (see Recipes, store at RT)
- Blocking reagent (see Recipes)
- Washing buffer (see Recipes)
- Developing solution (see Recipes)
- FAA (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Forceps
- Copeland jar
- Slide rack (Non-metal)
- Shaker
- Microwavable container 1 (large enough to accommodate the slide rack, e.g., 10 cm x 10 cm x 5 cm)
- Microwavable container 2 (large enough to accommodate the container 1)
- Microwave
- Humid chamber–for incubation of slides with antibody
- Microscope equipped with camera
Procedure
Category
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > Protein
Molecular Biology > Protein > Detection
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link

